Antibodies
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
13 Terms
What are antibodies?
Y-shaped glycoproteins called immunoglobulins which bind to a specific antigen on the pathogen/toxin that has triggered the immune response.

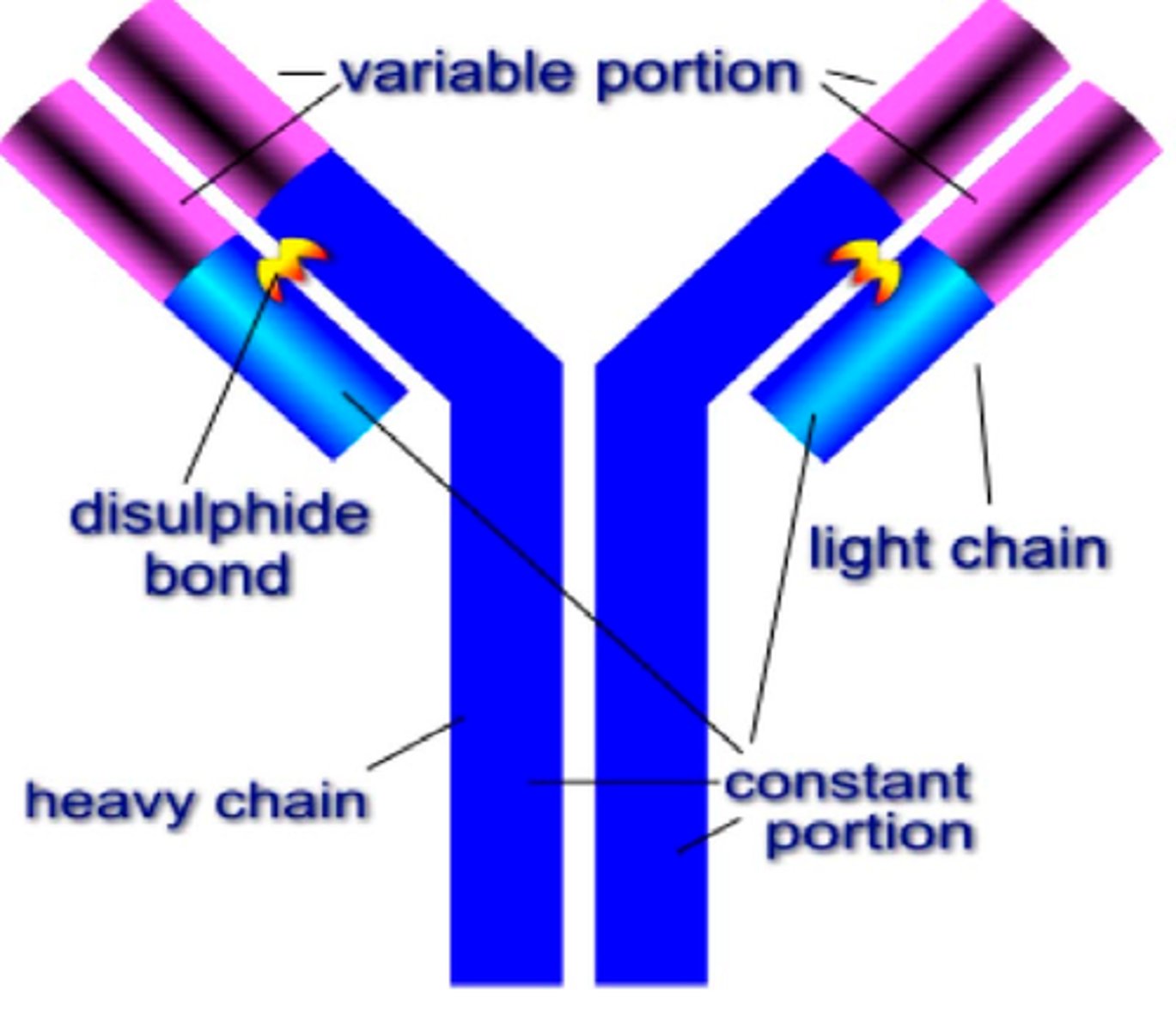
Describe the structure of an Antibody
Protein
Made of 4 polypeptide chains (2 light polypeptide chains, 2 heavy polypeptide chains)
More than 1 variable regions complementary and specific to an antigen
Hinge region allowing it to bind to more than one antigen (or pathogen)
Constant region allows it to find phagocytes, aiding phagocytosis
What is an antigen?
A toxin or foreign substance that induces an immune response in the body, especially the production of antibodies.
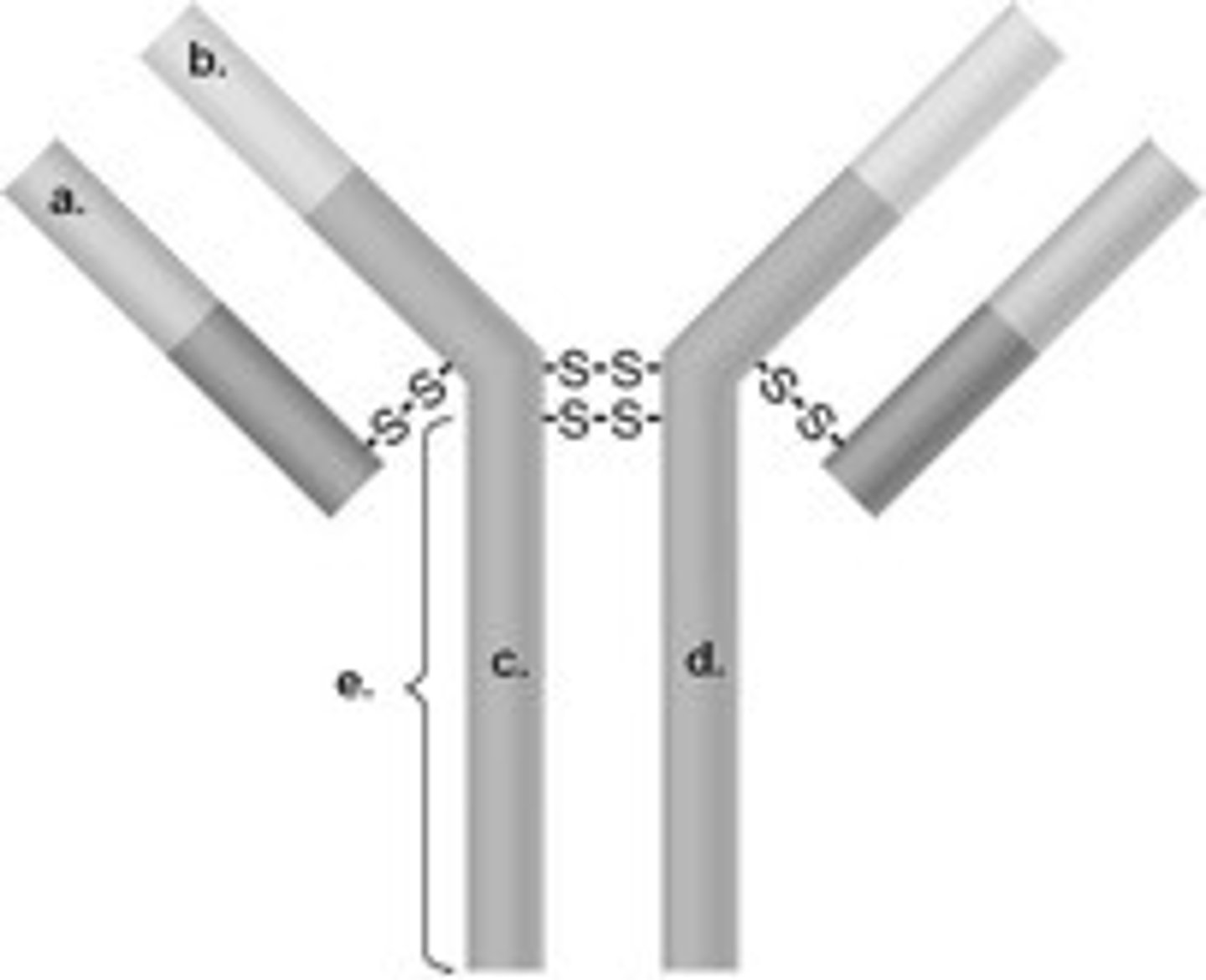
Antibody Structure
Antibody Chains
Antibodies are made up of 2 identical long polypeptide chains called the heavy chains, and 2 shorter identical chains called the light chains.
How are the chains held together in the antibodies?
Disulphide bridges hold and join the polypeptides, holding them in shape.
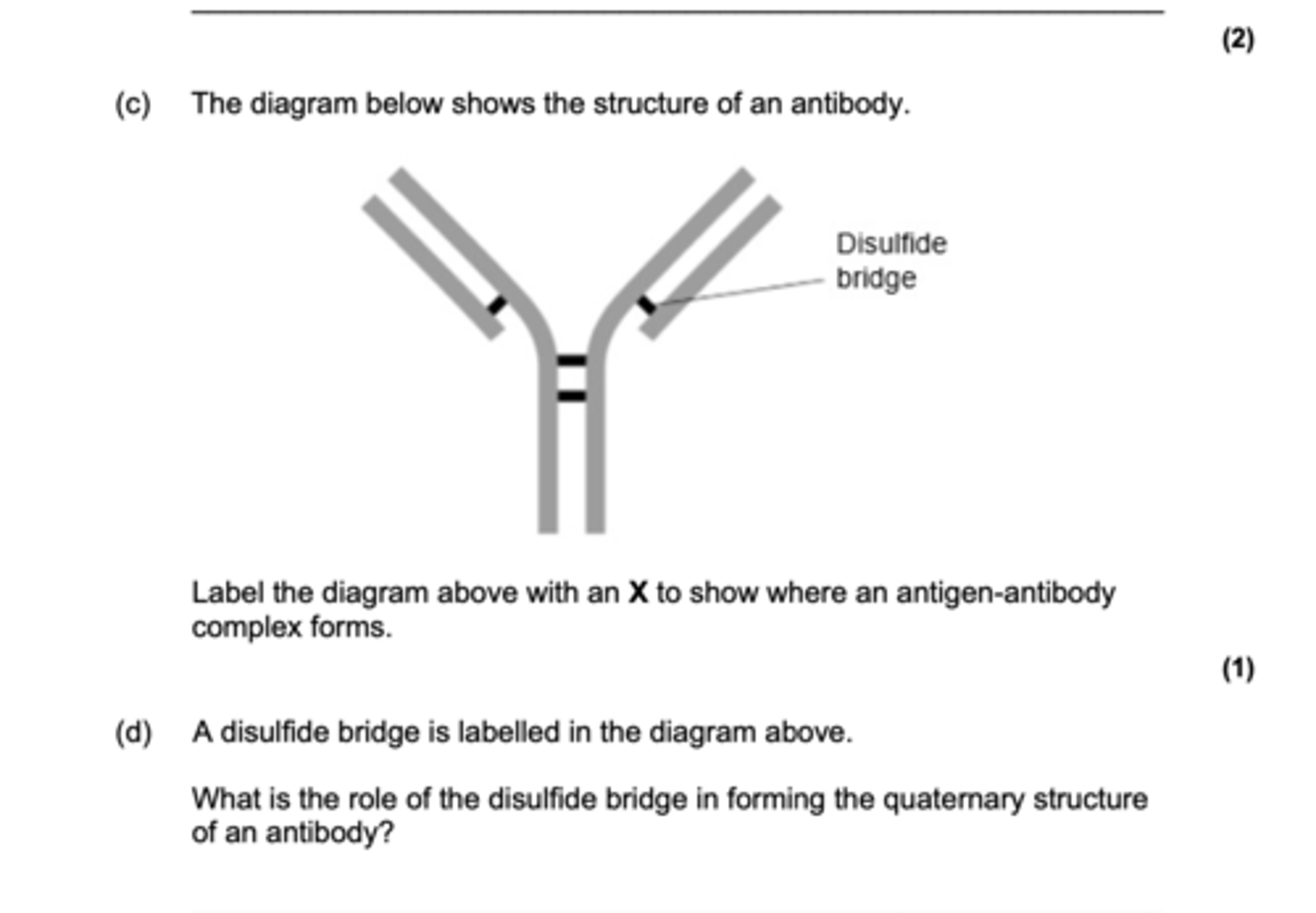
Binding Sites
Antibodies bind to antigens in a lock and key mechanism
It is a different shape on each antibody and gives the antibody its specificity
Hinge Region
Provides the molecule with flexibility, allowing it to bind to 2 separate antigens, one at each of its binding sites.
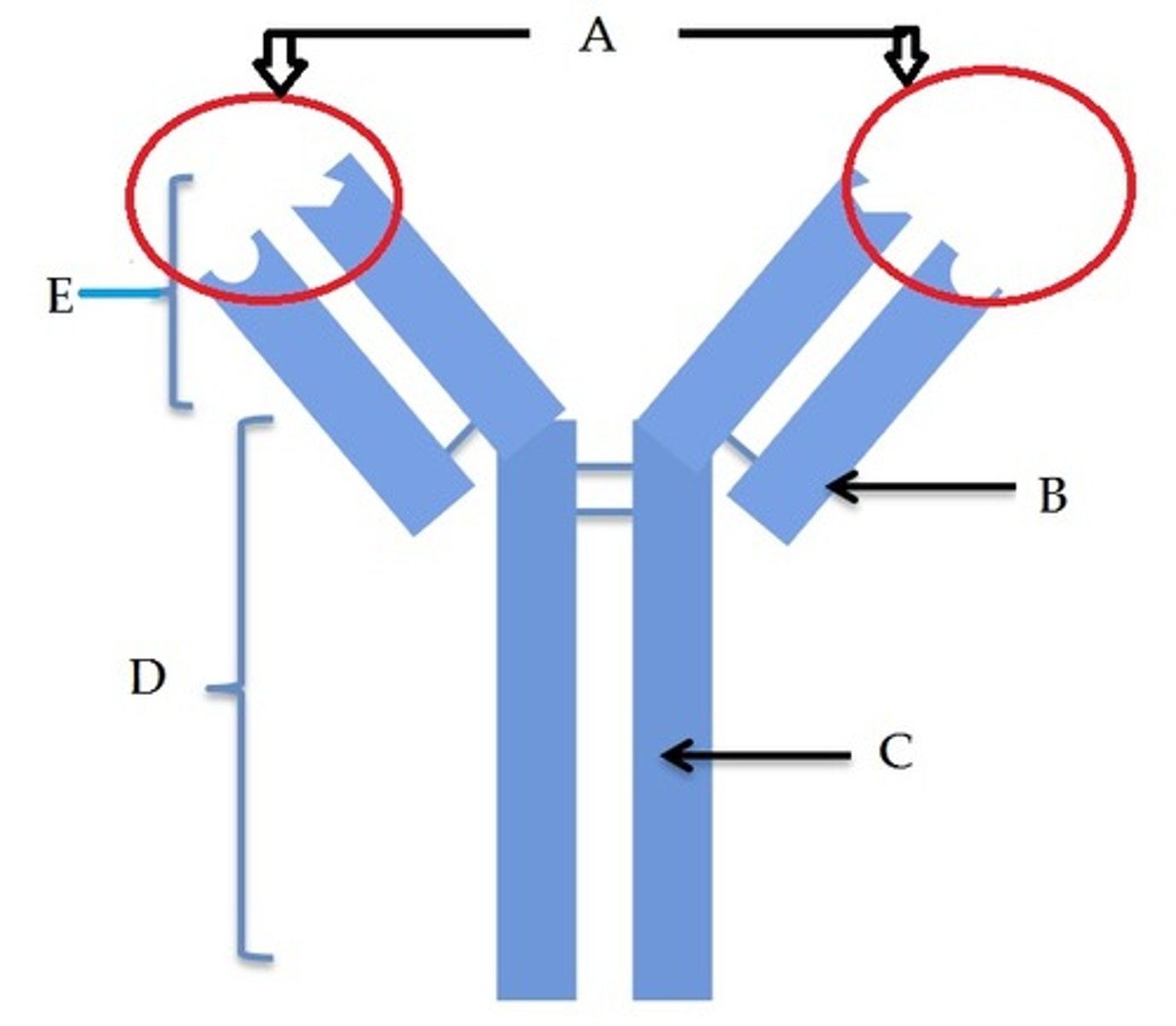
Variable Region
Region of an antibody which is particular to a specific antigen and is responsible for binding
What are opsonins?
Molecules that bind to antigens on the surface of pathogens, making them easier for phagocytes to recognize and engulf, thereby increasing the rate of phagocytosis
What is agglutination?
The process of clumping/binding together many pathogens, making them too large to enter the host cell and increase the likelihood of phagocytosis.
What is neutralisation?
Antibodies cover binding sites on the pathogen or bind to toxins. This prevents binding or entry into the host cell.
How do antibodies defend the body?
The antibody of the antigen-antibody complex acts as an opsonin so the complex is easily engulfed and digested by phagocytes
Most pathogens can no longer effectively invade the host cells once they are part of an antigen-antibody complex
Antibodies acts as agglutinins, causing pathogens that are carrying antigen-antibody complexes to clump together.
This helps prevent the spreading through the body, and makes it easier for phagocytes to engulf a number of pathogens at the same time