Surgery E.O.R. Trauma and Acute Care
1/86
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
87 Terms
Acute Abdomen
sudden onset of severe abdominal pain that requires urgent evaluation and often surgical intervention
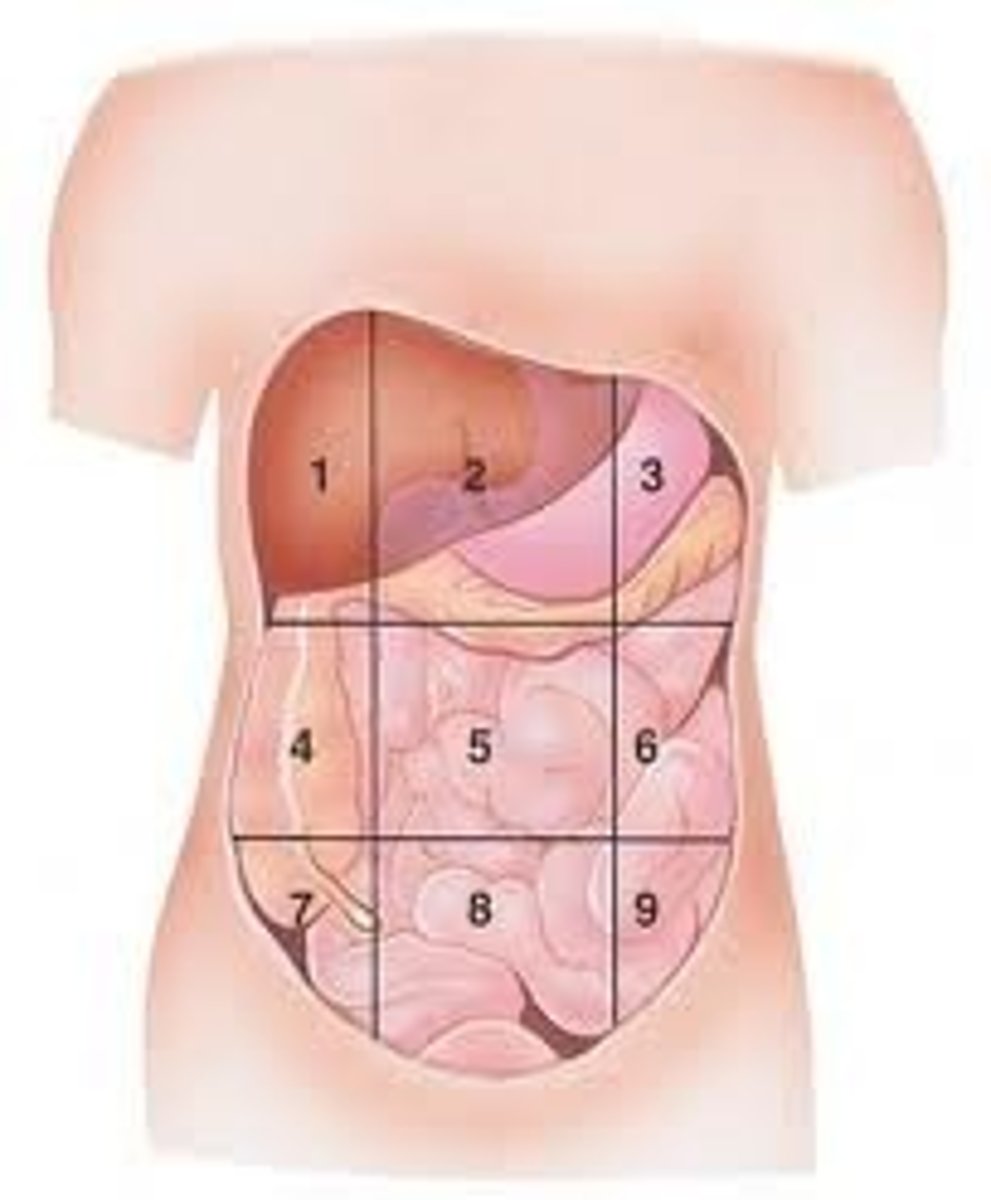
Right Hypochondraic
(1)
gallstones
cholangistis
hepatitis
live abscess
cardiac abscess
lung causes
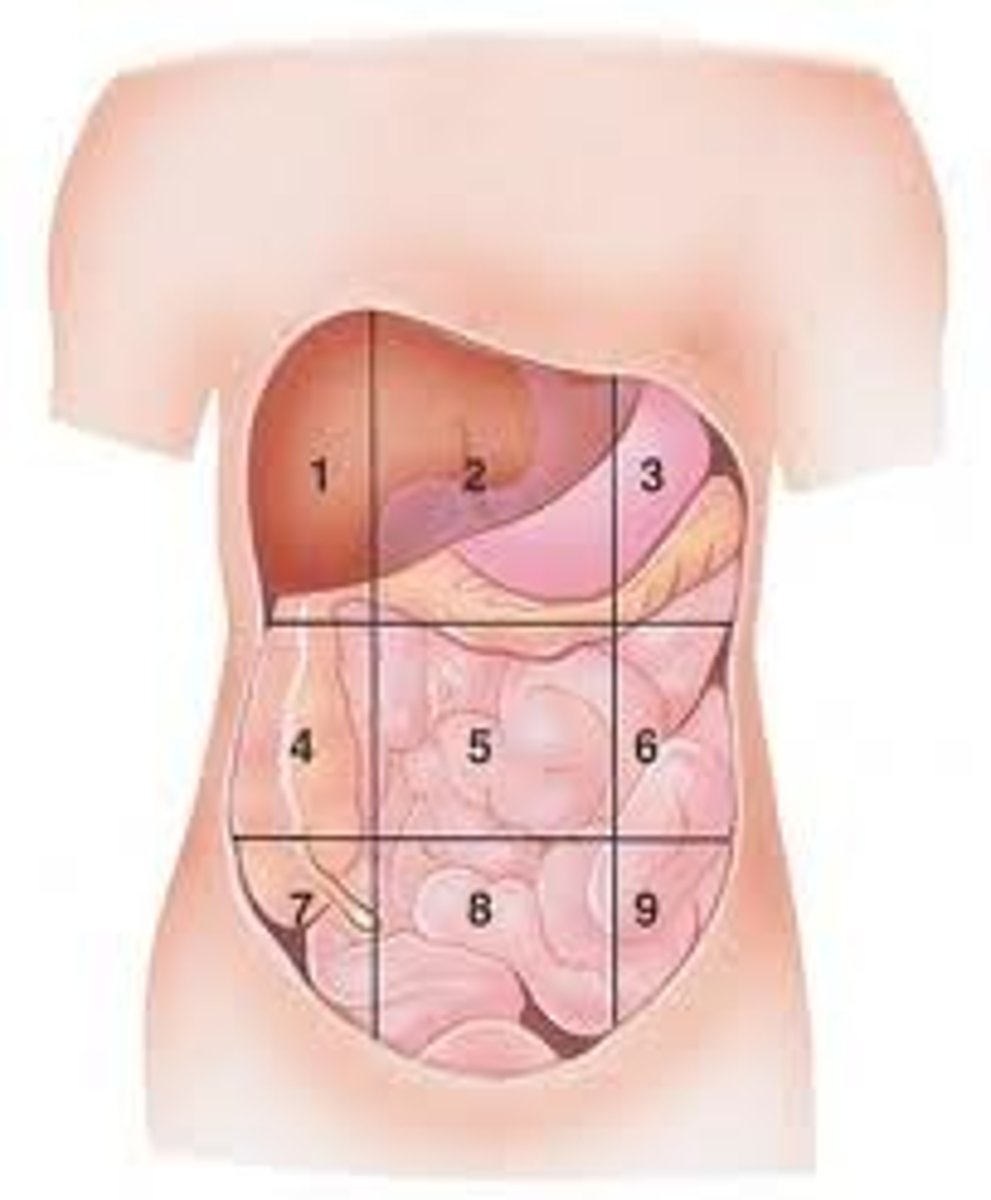
Epigastric
(2)
esophagitis
peptic ulcer
perforated ulcer
pancreatitis
GERD
Left Hypochondraic
(3)
spleen abscess
acute splenomegaly
spleen rupture
Right Lumbar
(4)
ureteric colic
pyelonephritis
Umbilical
(5)
appendicitis
mesenteric lymphadenitis
meckel diverticulitis
lymphomas
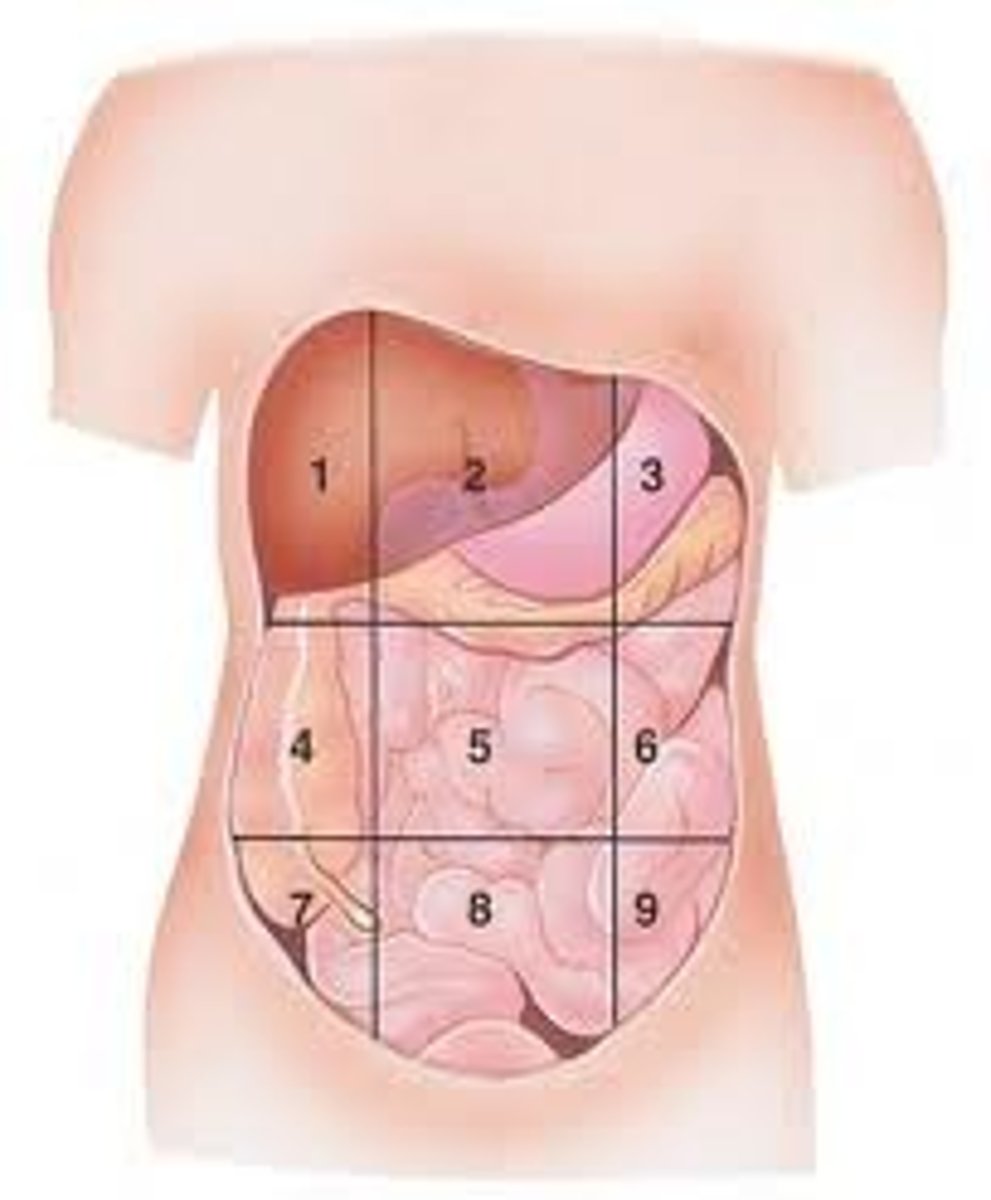
Left Lumbar
(6)
ureteric colic
pyelonephritis
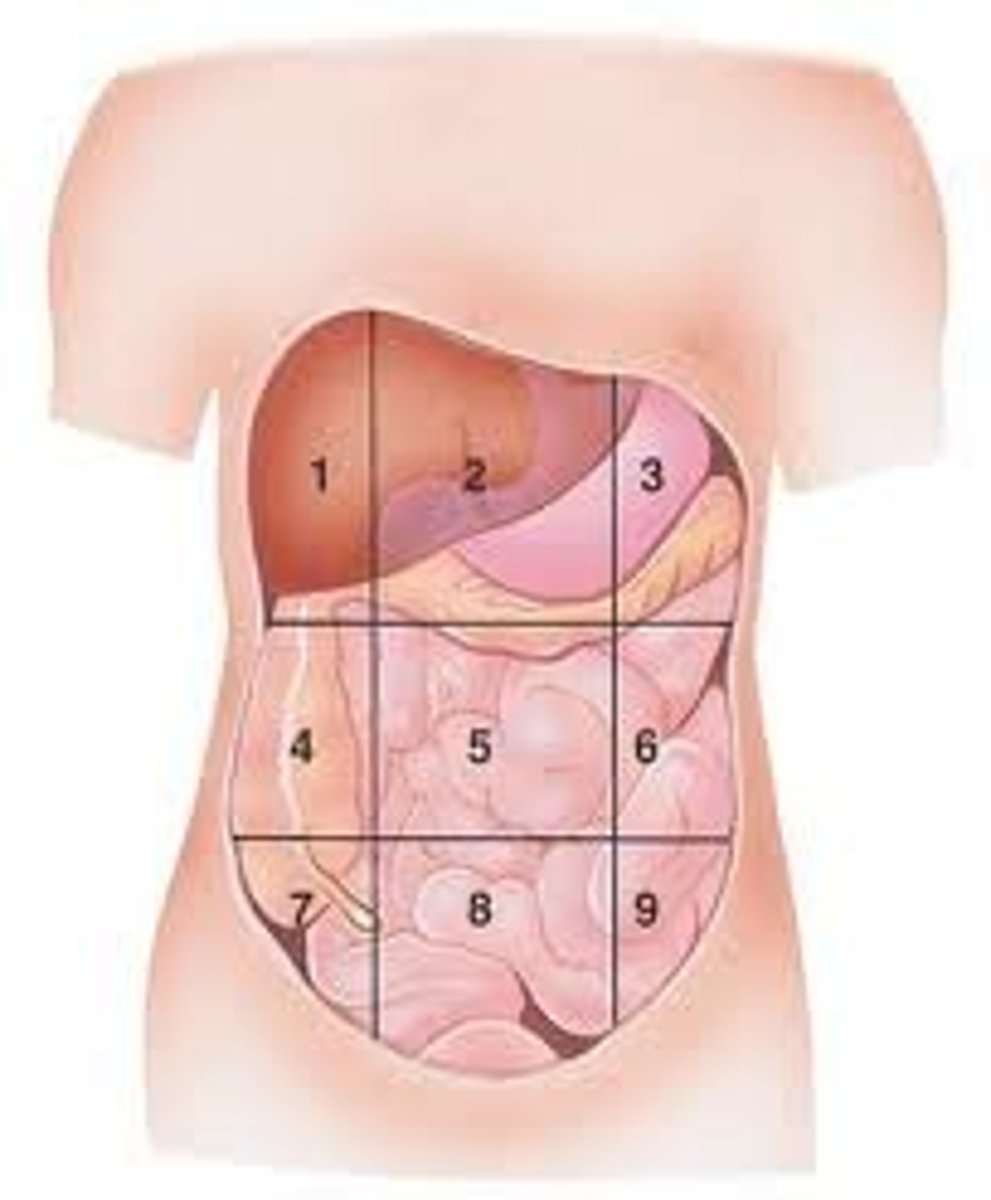
Right Iliac
(7)
appendicitis
Crohn disease
cecum obstruction
ovarian cyst
ectopic pregnancy
hernias
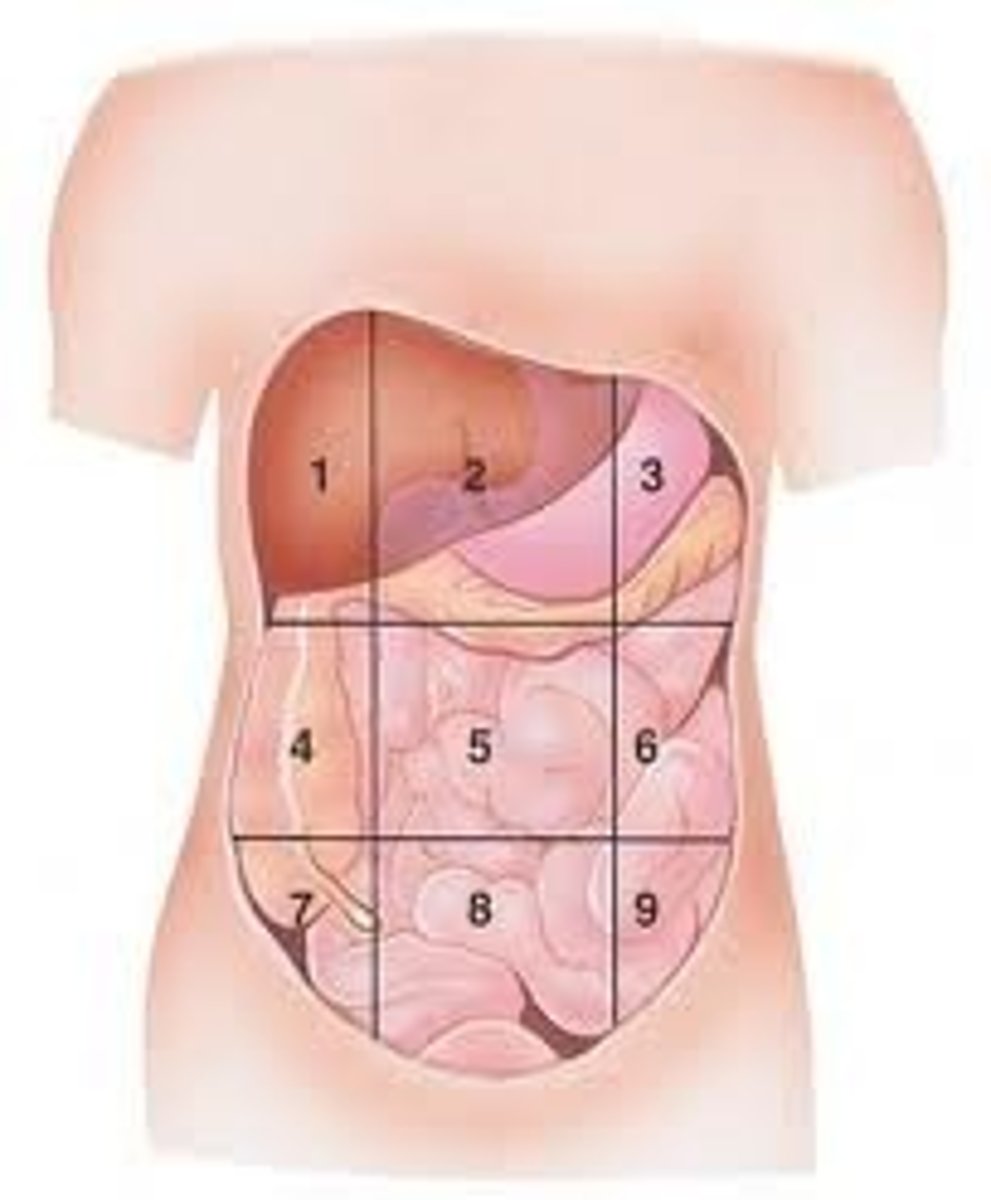
Hypogastric
(8)
testicular torsion
urinary retention
cystitis
placental abruption
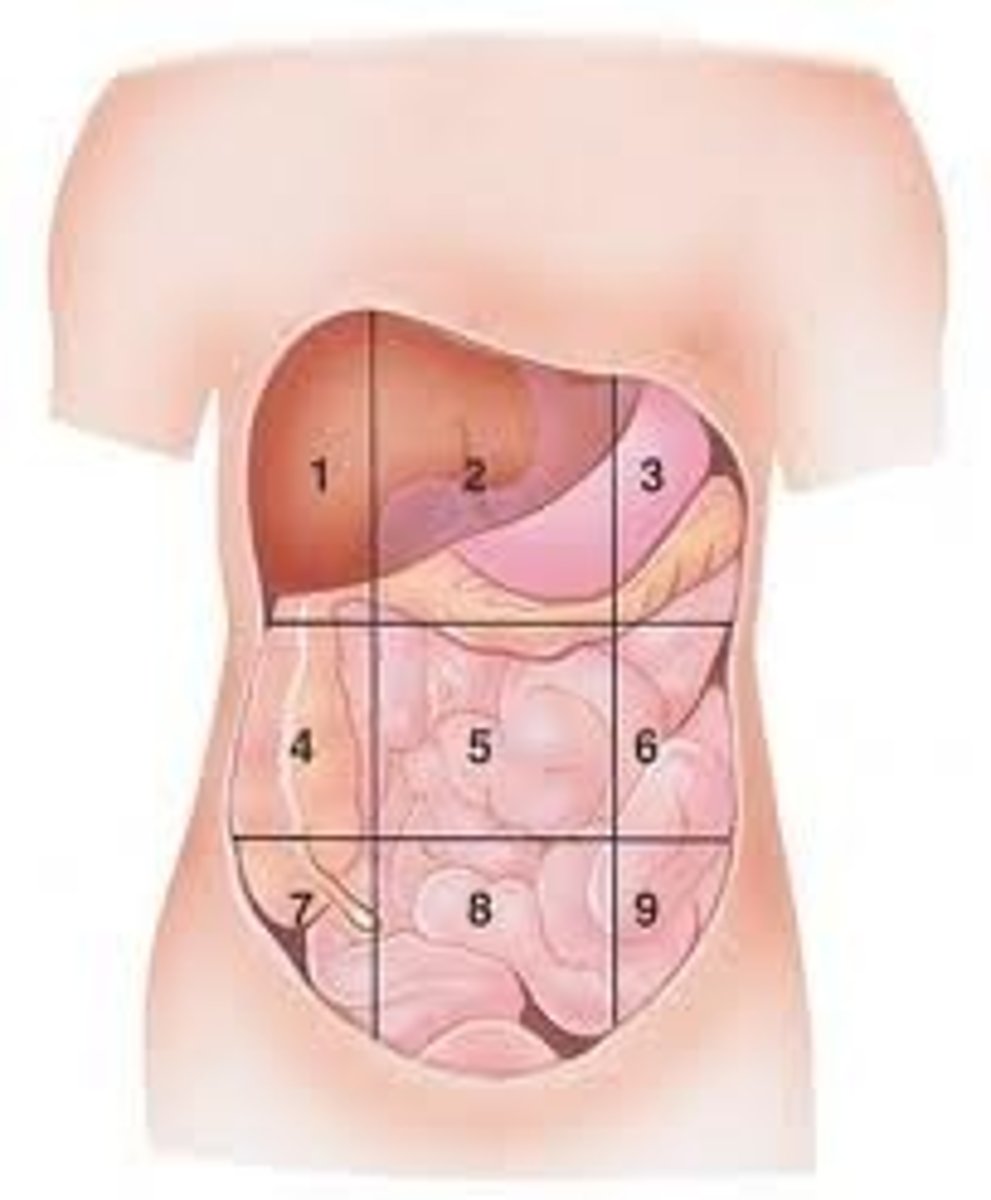
Left Iliac
(9)
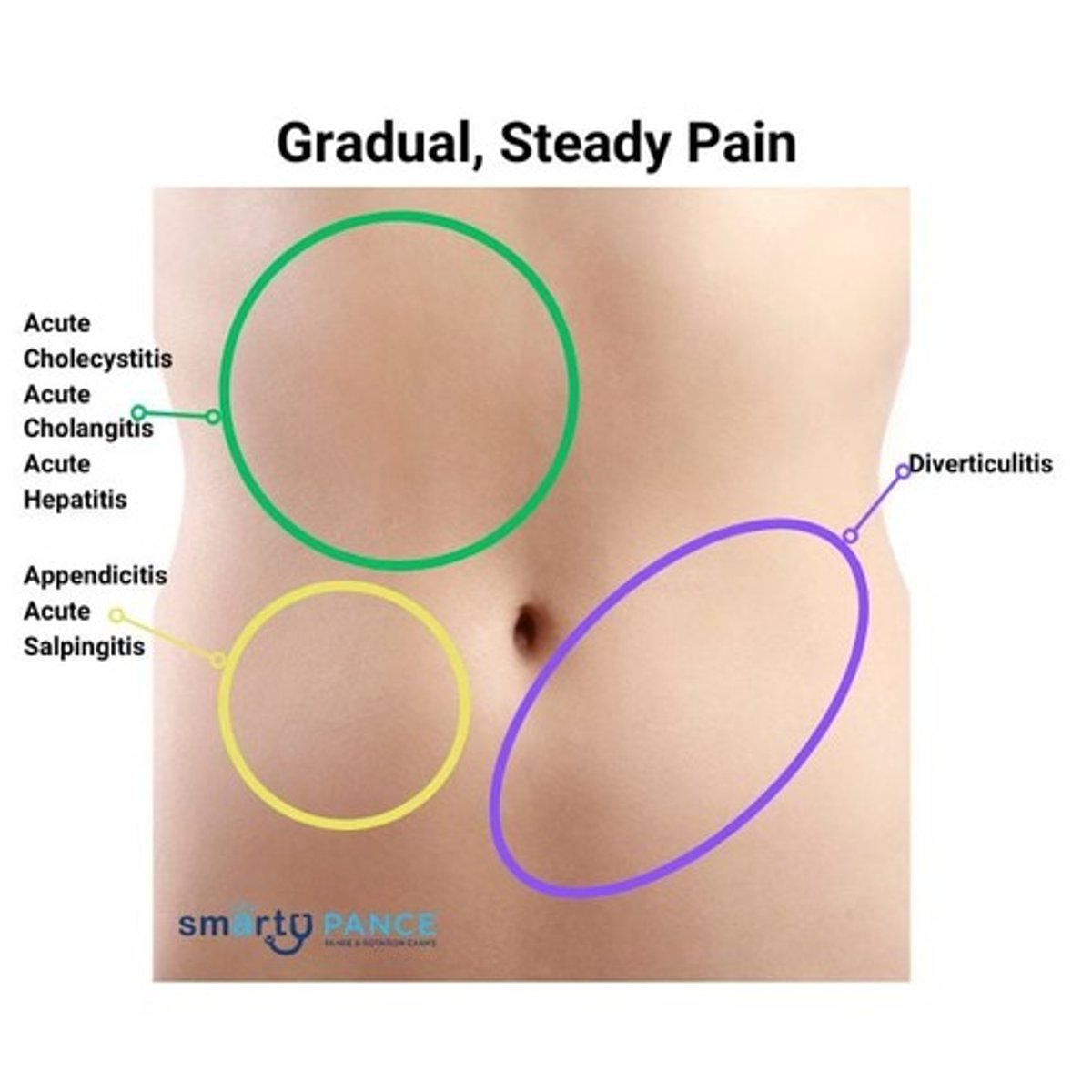
diverticulitis
ulcerative colitis
constipation
ovarian cysts
hernias
MCC of Acute Abdomen Requiring Surgical Intervention
appendicitis -- most frequent
cholecystitis
perforated peptic ulcer
intestinal obstruction
diverticulitis
ectopic pregnancy
acute mesenteric ischemia
trauma
perforated diverticulum
Cholecystitis
inflammation of gallbladder, due to gallstones
Perforated PUD
results in peritonitis from gastric or duodenal perforation
Intestinal Obstruction
adhesions, hernias, or tumors
Diverticulitis
complicated by abscesses, perforation, or obstruction
Ectopic Pregnancy
emergency surgery
signs: gradually worsening pelvic pain +/- vaginal bleeding/spotting; often >6 weeks pregnant
PE findings: adnexal tenderness/mass, rebound/guarding in pelvic regions
diagnostics: serum hCG, TVUS, +/- Rhogam
management: laparoscopic salpingostomy (ruptured) or methotrexate (unruptured)
Acute Mesenteric Ischemia
arterial or venous occlusion
signs: sudden severe abdominal pain, pain out of proportion to the exam, usually in older adults (W>M)
PE findings: abdomen soft, non-distended, extreme pain
diagnostics: laparotomy for necrosis
management: anticoagulation (if no active bleeding), antibiotics
Trauma
blunt or penetrating leading to organ damage
Perforated Diverticulum
generalized peritonitis
Clinical Presentation of Acute Abdomen
sudden, severe, sharp/stabbing abdominal pain (location and nature dependent on underlying condition)
N/V, fever, anorexia, D/C (dependent of etiology)
peritoneal signs (rebound tenderness, guarding, rigidity)
distention and absent bowel sounds (obstruction)
hemodynamic instability (hemorrhage or sepsis)
Life-Threatening Acute Abdomen Etiologies
AAA dissection
bowel obstruction/volvulus
ectopic pregnancy
mesenteric ischemia
myocardial infarction
perforation of GI tract
splenic rupture
AAA Dissection
signs: severe abdominal or flank pain described as "ripping" or "tearing" sensation radiating to back, common in elderly
PE findings: hypotension, tachycardia, guarding/rebound, pulsatile mass
diagnostics: CT angiography
management: endovascular repair if stable
Bowel Obstruction/Volvulus
signs: vomiting, generalized abdominal pain and distention, constipation, hx of abdominal surgery
PE findings: vomiting + feculent material, tinking or absent bowel sounds
diagnostics: abdominal X-ray, CT AP w/contrast
management: bowel rest or surgical intervention
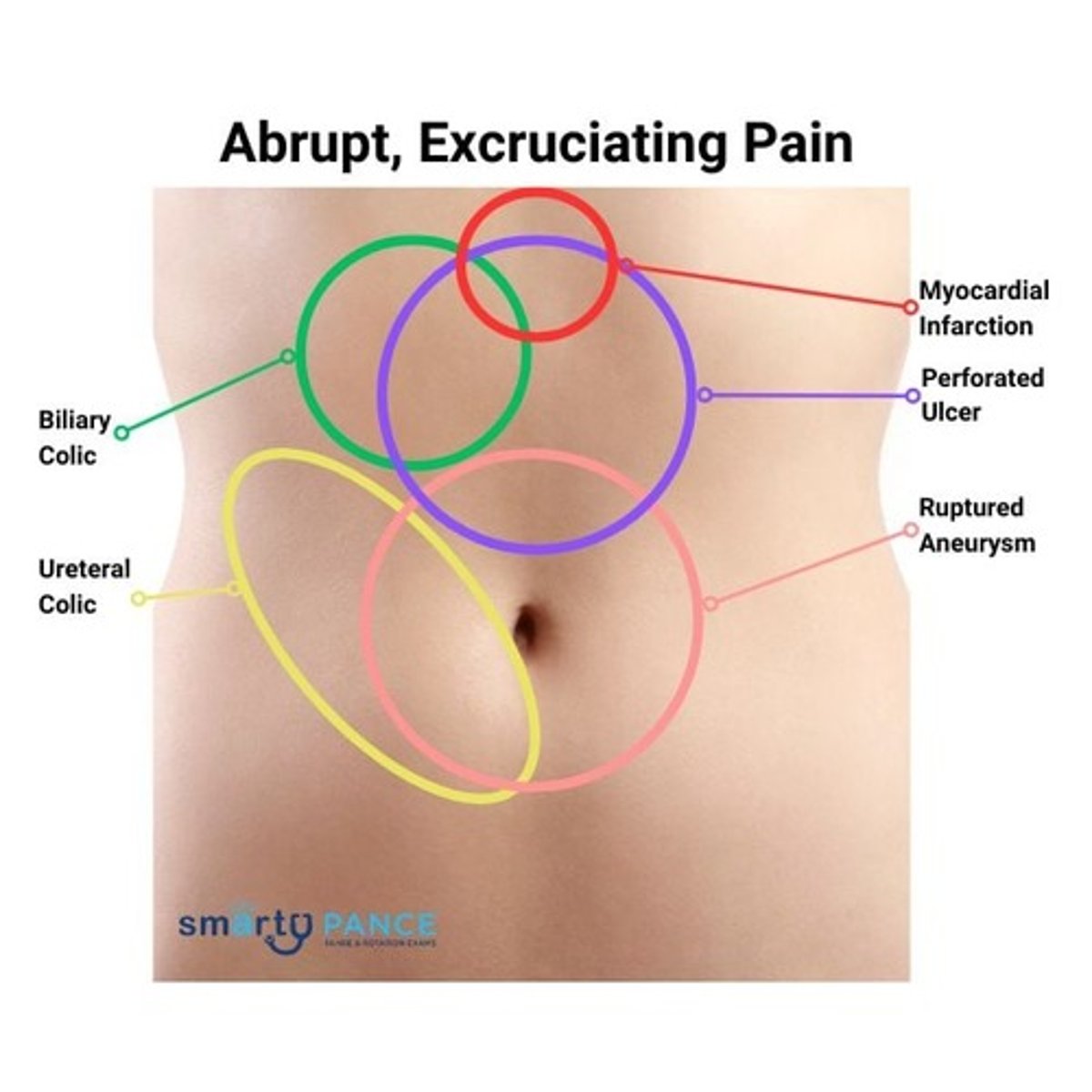
Myocardial Infarction
epigastric pain
signs: crushing, pressure-like chest pain worsened by exertion, radiating to jaw or left arm, N/V, dyspnea
PE findings: diaphoretic, clutching chest or upper abdomen (Levine sign)
diagnostics: EKG, troponin
management: MONA (morphine, oxygen, NTG, ASA), PCI or fibrinolysis
Perforation of GI Tract
signs: severe generalized abdominal pain +/- fever, signs of hematochezia, melena, or hematemesis
PE findings: firm abdomen with generalized tenderness, rebound, guarding
diagnostics: erect CXR (free air), CT AP w/contrast
management: surgical repair of cause
Splenic Rupture
signs: LUQ pain +/- rebound or guarding; hx of blunt trauma or splenomegaly
PE findings: LUQ tenderness, Kehr sign (left shoulder pain from blood)
diagnostics: FAST exam, CT AP w/contrast
management: laparotomy with splenectomy or embolization
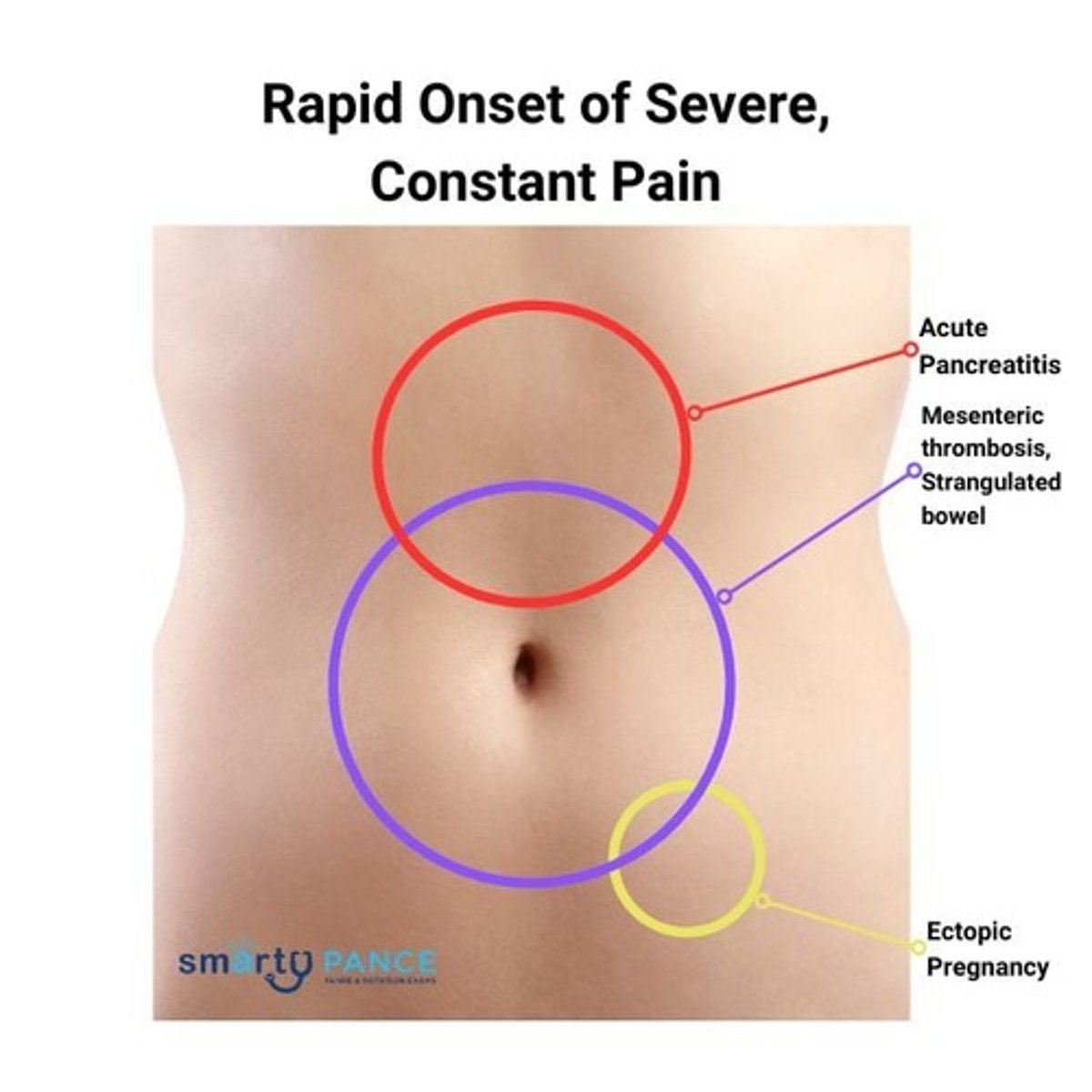
Rapid Onset Severe, Constant Pain
Gradual, Steady Pain
Abrupt, Excruciating Pain
Intermittent, Colicky Pain, Crescendo + Pain-Free Intervals
Acute Pancreatitis
epigastric pain
acute-onset, persistent upper abdominal pain radiating to the back, accompanied by nausea, vomiting, abdominal tenderness, fever, and rapid heartbeat
Chronic Pancreatitis
epigastric pain radiating to the back, often with a history of chronic alcohol use or gallstones
Peptic Ulcer Disease (PUD)
epigastric pain
burning or gnawing epigastric pain related to meals (worse with eating in gastric ulcers, relieved by eating in duodenal ulcers), bloating, early satiety, nausea, and epigastric discomfort
Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD)
epigastric pain
associated with heartburn, regurgitation, dysphagia, and epigastric discomfort
Gastritis/Gastropathy
epigastric pain
epigastric discomfort or pain, nausea, vomiting, bloating, feeling of fullness after eating, and possible gastrointestinal bleeding such as hematemesis
Functional Dyspepsia
epigastric pain
one or more of the following: postprandial fullness, early satiation, epigastric pain, or burning
Gastroparesis
epigastric pain
N/V, abdominal pain, early satiety, postprandial fullness, and bloating; associated with diabetes mellitus, post-surgical vagal nerve injury, hypothyroidism, scleroderma, and medications (e.g. opioids, anticholinergics)
Biliary Colic
epigastric pain
sudden, intense epigastric or right upper quadrant pain after fatty meals; may radiate to the right shoulder or back, with nausea and vomiting
Gastric Volvulus
epigastric pain
severe epigastric pain, unproductive retching, inability to pass a nasogastric tube, and abdominal distension
Mallory-Weiss Tear
epigastric pain
vomiting followed by bright red blood (hematemesis), epigastric or back pain, and possible signs of shock
Biliary Colic
right upper quadrant pain
occurs when a gallstone temporarily obstructs the cystic duct, leading to episodic pain
intense, dull discomfort in the RUQ or epigastrium; associated with nausea, vomiting, diaphoresis; generally lasts at least 30 minutes and plateaus within an hour; benign abdominal examination
Acute Cholecystitis
right upper quadrant pain
prolonged (>4-6 hours) RUQ or epigastric pain, fever, nausea, vomiting, abdominal guarding, and positive Murphy's sign
Acute Cholangitis
right upper quadrant pain
fever, jaundice, RUQ pain (Charcot's triad); may progress to hypotension and AMS (Reynold's pentad)
Sphincter of Oddi Dysfunction
right upper quadrant pain
occurs when the sphincter fails to relax properly or has increased tone, leading to obstruction and buildup of pressure in bile duct, pancreatic duct, or both
Acute Hepatitis
RUQ pain with fatigue, malaise, nausea, vomiting, anorexia, jaundice, dark urine, and light-colored stools
Perihepatitis (Fitz-Hugh-Curtis)
right upper quadrant pain
inflammation of the liver capsule associated with pelvic inflammatory disease
RUQ pain with pleuritic component; may radiate to right shoulder; associated with PID
Liver Abscess
RUQ pain, fever, chills, weight loss, malaise, and abdominal pain.
Budd-Chiari Syndrome
fever, RUQ pain, abdominal distention (from ascites), jaundice, lower extremity edema, gastrointestinal bleeding, and/or hepatic encephalopathy
Portal Vein Thrombosis
RUQ pain
abdominal pain, gastrointestinal bleeding, dyspepsia, and signs of portal hypertension (e.g., ascites, splenomegaly)
Liver Tumors
RUQ pain
dull pain, weight loss, anorexia, jaundice, abdominal swelling, and hepatomegaly
Choledocholithiasis
RUQ pain
presence of gallstones in common bile duct
jaundice, dark urine, pale stools, pruritus, elevated liver enzymes
Confusion
Reduced mental clarity and reasoning
Drowsiness
Difficulty being aroused; cannot sustain alertness
Lethargy
Depressed awareness of self and surroundings
Stupor
Aroused only with vigorous stimuli; some avoidance of discomfort
Coma
Unarousable, no purposeful response to stimuli
Delirium
Acute, fluctuating cognition with impaired attention/consciousness
Hypovolemic Shock
loss of intravascular volume, leading to decreased perfusion and oxygen delivery
tachycardia, hypotension, cool, calmmy skin
hemorrhage, dehydration, burns
Cardiogenic Shock
heart's inability to pump effectively, resulting in decreased cardiac output and perfusion
hypotension, pulmonary edema, elevated JVP
MI, heart failure, arrhythmias
Distributive Shock
systemic vasodilation, leading to relative hypovolemia and poor perfusion
warm, flushed skin, tachycardia, hypotension
spetic shock
Septic Shock
overwhelming infection, causing systemic vasodilation and increased capillary permability
severe bacterial infection
Anaphylactic Shock
severe allergic reaction leading to widespread vasodilation, bronchospasm, and increased capillary leakage
Neurogenic Shock
spinal cord injury, causing unopposed parasympathetic activity and vasodilation
high spinal cord injury
Obstructive Shock
impaired blood flow due to a mechanical obstruction, reducing cardiac output and perfusion
symptoms based on underlying cause
tension PTX, caridac tamponade, massive PE
Key Components of Risk Assessment
hypotension, tachycardia, signs of hypovolemia
need for intubation, chest tube placement, respiratory interventions
optimize comorbidities (CV disease, coagulopathy, DM)
Injury Severity Score (guide triage)
correct malnutrition
Common Perioperative Complications
hemorrhage
infection
DVT/PE
AKI, MI, resp. failure
surgical-specific complications
Hemorrhage
treat with hemostasis, transfusion, or reoperation
Manage Infection with...
perioperative antibiotics (cefazolin)
Prevent DVT/PE with...
early mobilization, mechanical compression, anticoagulation in at-risk patients
Preoperative Optimization
restore euvolemia w/crystalloids or blood products
reverse coagulopathy with FFP, vitamin K or specific agents
Spinal Procedures, Internal Fixation, Joint Replacement
common pathogens: S. aureus, S. epidermidis
antibiotics: Cefazolin, Vancomycin, Clindamycin
Antibiotic Use after Prosthetic Join Replacement
only use antibiotic prophylaxis for joint patients undergoing invasive dental procedures if patient has risk factors:
-- severely immunocompromised
-- prior prosthetic joint infection
-- poor BGL control
-- <1 year since joint replacement
Postoperative Monitoring
-- hypotension, tachycardia, hypo perfusion
-- hemoglobin, renal function, organ injuyr
-- escalate care for signs of infection, bleeding, or organ dysfunction
Anticoagulant Use
total hip or total knee = aspirin or anticoagulants
prefer DOACs over LMWH; LMWH over Warfarin
hip fracture repair = pharmacological prophylaxis (LMWH) over nonpharmacological options
Trauma/Acute Care Procedures
remember ABCDEs
resuscitative efforts begin by obtaining peripheral IV access and administering 1L IV fluids for adults and 20 mL/kg bolus for kids
Responses to Fluid Resuscitation: Vital Signs
rapid response: return to normal
tranisent response: transient improvement; recurrence of decreased BP and increased HR
minimal or no response: remain abnormal
Responses to Fluid Resuscitation: Estimated Blood Loss
rapid response: minimal (<15%)
transient response: moderate-ongoing (15%-40%)
minimal or no response: severe (>40%)
Responses to Fluid Resuscitation: Need for Blood
rapid response: low
transient response: moderate-high
minimal or no response: immediate
Responses to Fluid Resuscitation: Blood Preparation
rapid response: type and crossmatch
transient response: type-specific
minimal or no resposne: emergency blood release
Responses to Fluid Resuscitation: Need for Operative Intervention
rapid response: possibly
transient response: likely
minimal or no response: highly likely
Responses to Fluid Resuscitation: Early Presence of Surgeon
rapid response: yes
transient response: yes
minimal or no response: yes
Transfusion Indication
acute blood loss and symptomaic anemia
whole blood ideal, rarely used today; blood product selected depends on patient needs
Transfusioni Rate in Absence of Acute Hemorrhage
transfuse 1 unit of PRBCs (packed red blood cells) at a time preferred
PRBCs
raises hemoglobin by 1 g/dl
Fresh Frozen Plasma (FFP)
best used when coagulation factors are needed (i.e. cardiopulmonary bypass, massive transfusion, DIC, advanced liver disease)
Platelet Transfusion
indicated when there is a a platelet deficiency or other dysfunction
Cryopercipitate