Neuro Week 3 - Specialized Support Systems of the Brain
1/70
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
71 Terms
what are the three meninges?
dura mater
arachnoid mater
pia mater
what are the three fossa’s of the brain and what parts do they hold?
anterior fossa: ventral aspects of the frontal lobe
middle fossa: much of the temporal lobe
posterior fossa: brainstem and cerebellum
falx cerebri
the fold of the dura matter than descends vertically in the longitudinal fissure separating the two hemispheres
surrounds the corpus collosum
what is the tunnel that connects the lateral ventricles to the third ventricle?
the interventricular foramens
describe where the third ventricle is
in between the two thalami, a narrow midline space between the right and left diencephalon (thalamus + hypothalamus)
what connects the two thalami together?
axonal tract
where is the fourth ventricle?
between the dorsal brainstem and cerebellum
what connects the third and fourth ventricle?
the cerebral aqueduct
what does the choroid plexus do?
modifies vascular structure lining the ventricles that produces CSF by filtering blood
create a flow chart of the circulation of the CSF
lateral ventricles → interventricle foramen → 3rd ventricle → cerebral aqueduct → fourth ventricle → subarachnoid space → arachnoid granulations
Foramen of Magendie
a small midline opening that drains CSF from 4th vent. to the subarachnoid space
Foramina of Luschka
two lateral openings that drains CSF from the 4th vent. to subarachnoid space
arachnoid granulations
specialized portions of the arachnoid that protrude
through the inner layer of dura matter and into the superior sagittal sinus
what region of the ventricular system would be prone to blockage
cerebral aqueduct
what is hydrocephalus?
occurs when there is an abnormal buildup of CSF in the ventricles due to an obstruction
common in children
blockage of the cerebral aqueduct
caused by congenital or aquired due to cerebral disease (ex. meningitis, hemorrhage, traumatic brain injury, brain injury, brain tumors)
what happens with patients Alzheimer’s (brain size and ventricles)
brain can shrink up to 1/3 of normal size
ventricles become larger
provides more space for the ventricles to expand
how long does it take to loose consciousness when you have no blood supply going to the brain?
10 sec
what is a stroke?
the sudden loss of brain function caused by a sudden blockage or rupture of a blood brain vessel
symptoms of a stroke
loss of balance
blurred vision
one side face drooping
one side arm or leg weakness
speech difficulty
FAST
difference between a ischemic stroke vs. a hemorrhagic stroke
blocked blood vessel vs. ruptured blood vessel (caused by high BP)
two types of ischemic strokes
thrombotic stroke: fatty plaque blockage on cerebral vessels
embolic stroke: blood clot somewhere else that then travels the brain
the entire blood supply of the brain and spinal cord depends on which 2 sets of branches of the aorta?
internal carotid arteries
extend from the carotid artery and extends up the neck
vertebral arteries
extends against the side of the cervical vertebrae later fusing together to form the basilar artery
what arteries are part of the circle of willis
Posterior Cerebral Artery
Posterior Communicating Artery
Internal Carotid Artery
Anterior Cerebral Artery
travel anterior from the internal carotid artery,
towards the medial longitudinal fissure
• Supplies regions in the medial aspect and dorsal margins of the frontal lobe
Anterior communicating artery
middle cerebral arteries
travel out laterally from the internal carotid artery, towards the lateral (sylvian) fissure
Supplies an extensive region of the central and lateral cerebral hemispheres (sensorimotor, language)
Lenticulostriate arteries
the deep-penetrating branches of the MCA that supplies most of the basal ganglia
aka the end arteries
prone to blockage and rupture (stroke)
what part of the brain layers is called real space
subaracnoid space
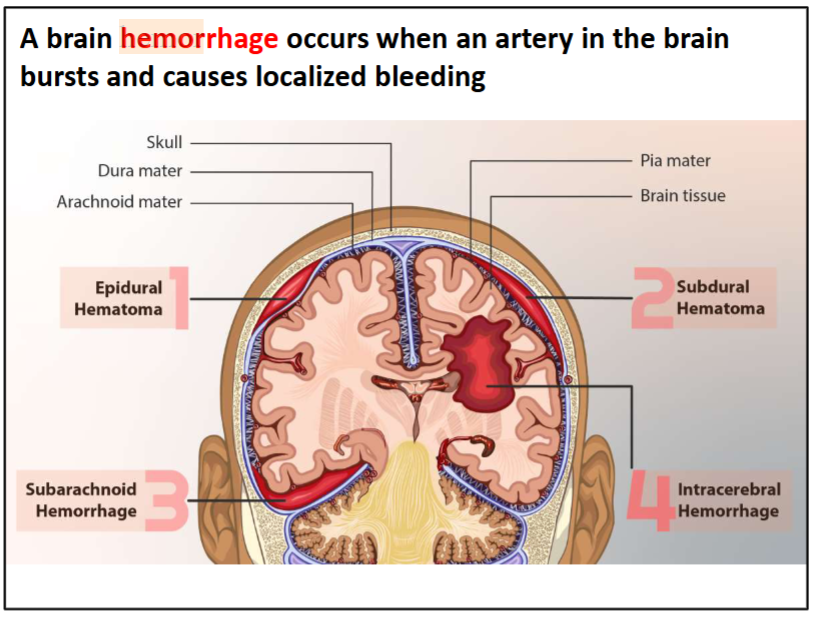
what are the 4 areas that cause localized bleeding (hemorrage/hematomas)
epidural hematoma
a collection of blood between the skull and dura mater
- Usually happens due to injury (e.g., skull fracture causes tear to underlying
blood vessels)
subdural
a collection of blood between the dura mater and
arachnoid mater
• Symptoms can occur suddenly or take days to weeks to develop
subarachnoid
a collection of blood within the subarachnoid space
surrounding the brain (the area between the arachnoid and pia mater)
• Usually happens due to brain aneurysm
intracerebral
bleeding within the brain tissue itself
Medullary arteries
a collection of 6-10 arteries that arise from various branches of the aorta and supply the anterior and posterior spinal arteries along the spinal column
what is the purpose of the BBB
makes the movement of substances from blood vessels into brain cells difficult
what/ how can cross the blood brain barrier
soluble in lipids
special transporters
glymphatic system
a lymphatic system in the brain to remove wastes and aid movement of nutrients
when is the glyphatic flow the fastest
during sleep because the extracellular spaces expand (by about 50%) and the CSF flows faster
immune factors go into the glymphatic system supporting damaged tissue to roles in learning and social behaviour
what does the dura matter consist of?
the outer layer and the inner layer
tentorium cerebelli
U-shaped infolding of dura matter that runs under the occipital lobe dividing the occipital lobe and the cerebellum
what does the tentorial notch provide space for?
the brainstem
falx cerebelli vs. falx cerebri
falx cerebelli is the dura matter that divides the cerebellum (smaller one)
falx cerebri is the dura matter that divides the cerebrum (larger one)
follow the same orientation
tentorium cerebelli
U-shaped fold that runs between the occipital lobe and the cerebellum
tentorial notch
space created by the tentorium cerebelli providing a space for the brainstem to pass
Falx cerebelli
small midline fold that runs in the space between the two cerebellar hemispheres
subarachnoid space
space under the arachnoid layer filled with cerebral fluid
falx cerebri
a crescent shape fold that descends vertically in the longitudinal fissure, separating the two hemispheres
meningiomas
are typically benign tumors arising from the dura mater
meningitis
is an infection and inflammation (swelling) of the two inner meningeal layers
what is the common cause of meningitis?
viral or bacterial infection
what are the major functions of the ventricular system
protects brain (shock absorber for brain)
provides buoyancy (reduces weight of brain from 1400gm to only 50gm)
provides a medium for the exchange of materials between blood vessels and brain
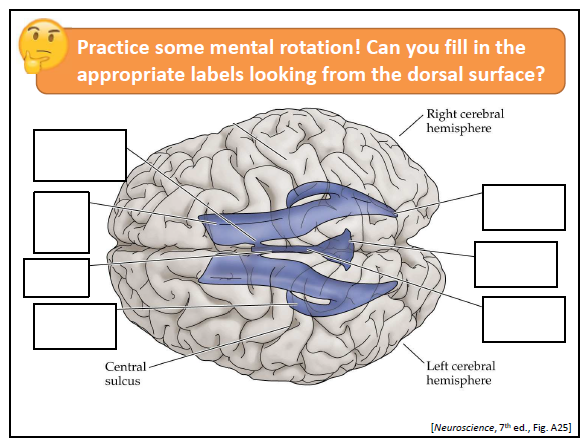
label the diagram
left side top to bottom:
interventricular foraman
frontal horn of lateral ventricle
third ventricle
temporal horn of lateral ventricle
right side top to bottom:
occipital horn of lateral ventricle
fourth ventricle
cerebral aqueduct
what is the cauliflower-like fronds in the lateral and fourth ventricle that produce the CSF by filtering blood
choroid plexus
what is CTE?
chronic traumatic encephlopathy
cause and result of CTE
cause: smaller, repeated, subconcussive hits to the head causing a natural occurring protein known as tau to build up over time in certain patters
diagnosed: diagnosed post-mortem
result: clumps of tau strangle brain cells often causing affect to the dorsolateral frontal cortex, an area critical for cognition and executive function, working memory, planning and abstract reasoning.
how do you measure the amount of deformation of the brain when shaking your head/brain injury
MRI with grid overlap to measure deformation
what protects our brain and spinal cord?
Bone, Meninges, CSF
foramen magnum (area)
a large, oval-shaped opening in the occipital bone of the skull that the spinal cord passes through when exiting the cranial cavity.
explain how the meninges form on the spinal cord
dura is on the outside (not on the actual spine) then the arachnoid part is on the dorsal side (still not on the spine) and then the pia mater will grip on the spine
what happens to the meninges when forming the sinuses?
the dural matter is made up of two parts (the inner and outer layer) that are usually fused together, but when it needs to make the venous sinus, the inner layer creates a dural folding that creates deep fissures to house dural venous sinuses
what space is a frequent site of bleeding following trauma or during rupture of an aneurysm on a cerebral artery
subarachnoid space
where is CSF found?
subarachnoid space under normal conditons, but can be filtered into the venous sinus to remove it
meningiomas
are typically benign tumors arising from the dura mater
• Grows slowly, usually without symptoms for many years
• Symptoms due to compression of the brain and depend on
where tumor is located
meningitis
is an infection and inflammation (swelling) of the two inner meningeal layers (in between the arachnoid pia layers)
cause and result of meningitis
cause: viral or bacterial infection, non-infections conditions like cancer or head injuries
result: swelling in the two inner meningeal layers can interfere with blood flow, resulting in stroke, brain damage, or death
infects the CSF
symptoms: cold symptoms + double vision, stiffness of neck, rash
major functions of the ventricular system
1. Protects brain – acts as a shock absorber for brain
2. Provides buoyancy – reduces weight of brain from 1400gm
to only 50gm
3. Provides a medium for the exchange of materials between blood vessels and brain tissue
what can enter the CSF and what does the CSF do?
Nutrients and hormones can enter the brain via ventricles. Likewise, excretion of waste can be carried in CFS and then removed by being reabsorbed into the blood stream
Septum pellucidum
(“translucent wall”): a very thin membrane separating the frontal
horns and body of the left and right ventricles
choroid plexus
is a modified vascular structure lining the ventricles that produces CSF by filtering blood
found in the lateral and fourth ventricles
internal jugular vein
Drainage of venous blood is through sinuses that finally
supply the internal jugular vein and back to the heart
track the branching of the internal carotid artery into the brain
carotid → internal carotid → anterior cerebral and the middle cerebral arteries (supplies middle and dorsal margins of frontal lobe as well as the central and lateral cerebral hemishperes)
why is the circle of willis important
alternative route → if a main artery is damaged or blocked
→ Reduces damage!
Lenticulostriate arteries
the deep-penetrating branches of the MCA that supplies most of the basal ganglia
end arteries
Small diameter and sharp right angles make them highly susceptible to rupture/occlusion
→ Leads to classic stroke symptoms
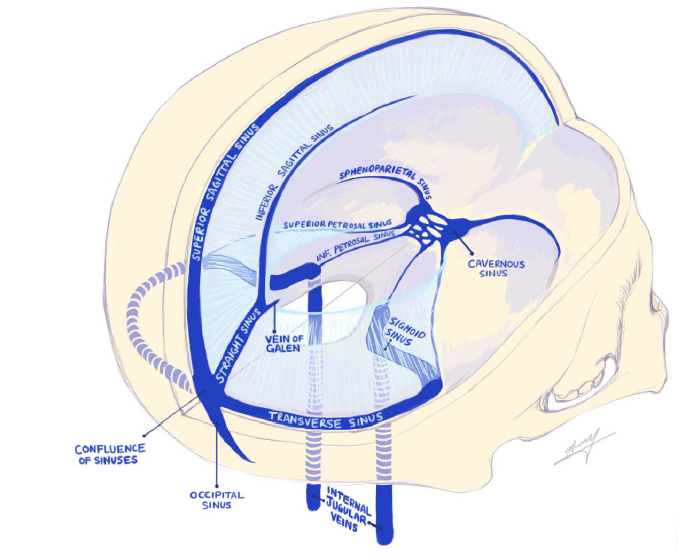
explain the path of the sinuses
superior sagittal (most) → inferior sagittal (on the bottom of the falx cerebri/ on top of the corpus collosum) → straight sinus → confluence and cavernous → left and right transverse → sigmoid → internal jugular venus
(just look at image tbh)
posterior spinal arteries
supply much of the dorsal horn and the dorsal columns (carries sensory information from the body
endothelial cells
form much tighter junctions than in the rest of the body in the BBB
ways to bypass the BBB
Mimic chemical structure of something that cross naturally
ex. L-DOPA treatment lets dopamine in the brain by mimicking the amino structure of a specific transporter that is already being let into the cell natural
Temporarily disrupt BBB to allow delivery of larger molecules (e.g., hyperosmotic agents, focused ultrasound)
risk of letting anything into the brain, weaking the endothelial cells, not specific weaking to the type of drug you wanna let in
Intranasal administration to bypass BBB
go through olfactory or trigeminal nerves
Use of nanoparticles to transport drugs
what is the tie between B-amyloid proteins, sleep and AD?
B-amyloid is found in the in fluids of glymphatic system because trying to remove toxic substances
B-amyloid proteins are harmful substances implicated in AD
therefore less sleep = more susceptible to AD