Kreb Cycle and Glycolysis
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
23 Terms
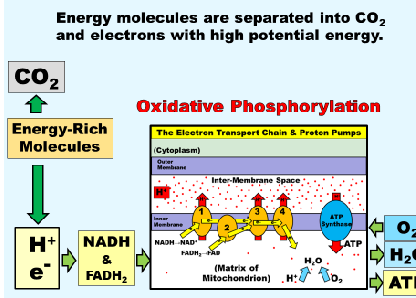
Where does Co2 and eletrons come from before starting oxidative phosphorylation
Enegry-rich moleulces with high potential energy, meaning it goes from C-c to H-C
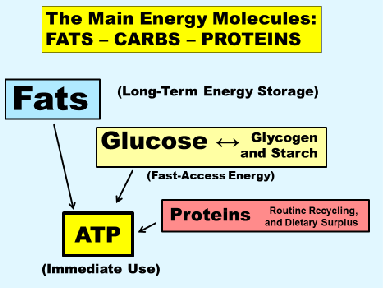
What are the main energy molecules for kreb cycle and glycolysis ?
Fats (long term energy storage), glucose (glucogen and statch, fast-access energy)and proteins (routine recycling and dietary)
What do fats glucose and proteins use for energy
ATp
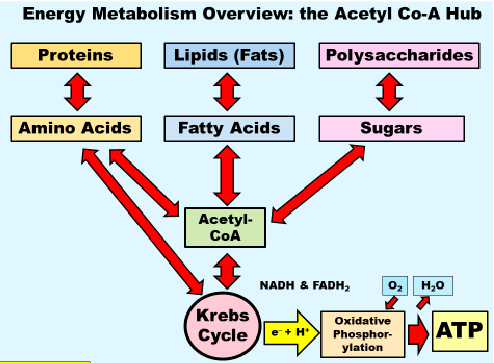
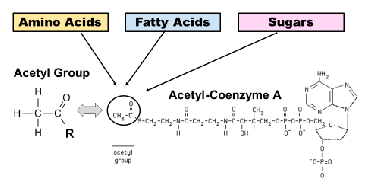
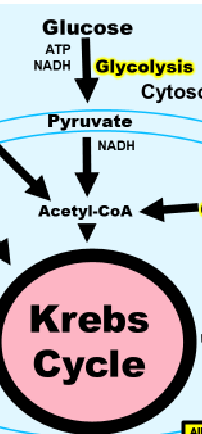
How do amino acids (from proteins), fatty acids (from lipids) and sugars (form polysaccarids) get into the the kreb cycle
through the Acetyl-CoA hub or amino acids can get straight to the krebs cycle
How does the Kreb cycle make H+ and e- for ETC?
Acetic Acid turns into Acetate by deattaching a H
a Acetyl group is attached to coA
There is a sulfate group (SH) at the end of Acetyl-coA and the H goes away
the sulfer attaches to a carbon and it allows the coenzyme to carry anything
All of these thing can donate high energy electrons
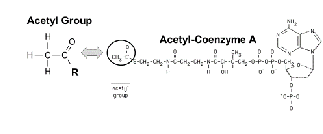

What are these two compounds
Acetic acid becoming acetate by deattaching a H
How can acetyl be yelid for the kreb cycle
sugars, fats and some amino acids all can be broken down to yeild acetyl forn the krab cycle in the Acetyl Co A
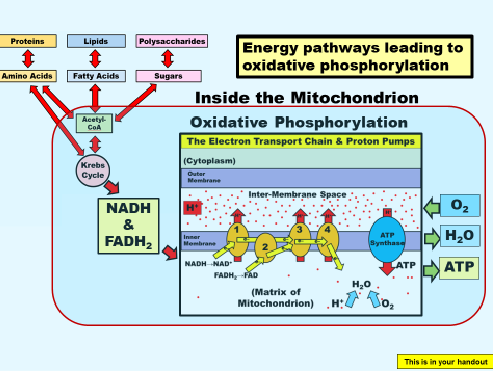
Where does the kreb cycle take place
inside the matrix in the mitochondria
Kreb Cycle
is a series of chemical reactions to release stored energy through the oxidation of acetyl-CoA derived from carbohydrates, fats, and proteins
-circular metabolic pathway.
-It has no beginning and no end.
what feeds the ETC
oxygen, ATP leaves the mitochondria in all directions
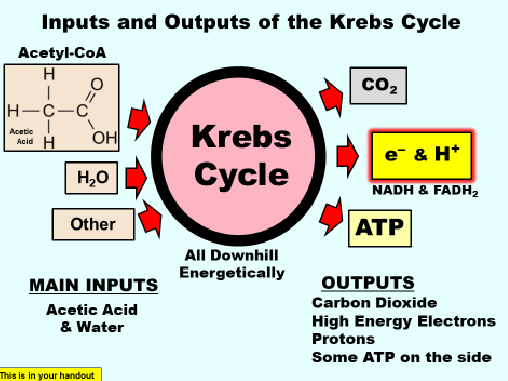
what are the inputs and outputs of the kreb cycle
Main inputs are acetic acid and water
outputs are carbon dioxide. high energy electrons, protons and some atp on the side
Why is the kreb cycle also called the citric acid cycle
because it contains Citrate molecule
what are the molecular outputs during the kreb cycle
3 NADH, 2 CO2, ATP, FADH2
-ATP comes out of step 5 cus its more effient that way
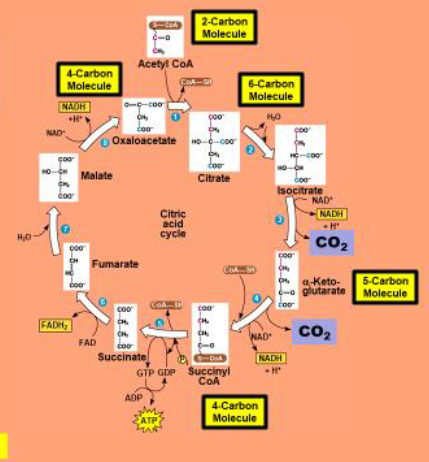
why is the krebs cycle also called tricarboxylic acid cycle (TCA cycle).
because there are tricarboxylics within the process
Singifigant events for Glycolysis
Goes from 6 carbons to 3 carbons
1.glucose gets phosporlated
become furcose with 2 phosphates while using ATP
eventually becomes pyruvate
will get a NADH out of it
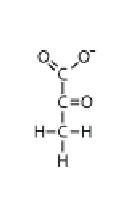
what is this compound
pyruvate
what role does pyruvate play in for the kreb cycle
pyruvate contains 2 ATP for the mitochandria and enters kreb by generating a NADH anf go into the Acety-coA hub
mitochondrial pyruvate carriers protein funtion
pulls pyruvate in and where CO2 comes out
Beta oxidation
breaking up fatty acuds and how fatty acids got into kreb through Acetyl CoA
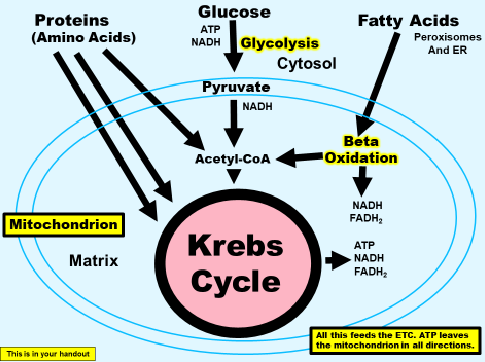
How does Beta oxidative work
all kinds of fatty acids are different in length
if not to long, it can go through the membrane
then it takes acdric acids to the matrix
where do long carbons go
to prysomes, to break down the fatty acid and send them to the mitochondria
how mostly everything is metabolised
what are two ways ATP are made
oxidative phoralation
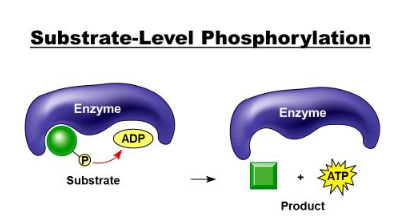
substarte level phorylation
substarte level phorylation
where a phosphate bonds to an ADP from the reactant and the product becomes a new molecule and ATP