PE - Applied Anatomy and Physiology
1/56
Earn XP
Description and Tags
skeleton, muscular system, cardio-respiratory system, aerobic + anaerobic exercise, the effects of exercise
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
57 Terms
Function of Skeleton: Structure and Support
bones offer the framework to support the body and house vital organs
Function of Skeleton: Protection of Vital Organs
different types of bones protect vital organs such as the heart, brain and lungs
Function of Skeleton: Mineral Storage
bones store minerals such as calcium and phosphate
Function of Skeleton: Movement
bones act as levers for muscles to allow the body to move
Function of Skeleton: Blood Cell Production
bone marrow creates blood cells
The four types of bones
Long, Short, Flat, Irregular
Long Bones
used in most of our movements e.g. running, throwing
Short Bones
used to help you to grip things and enable you to balance and perform fine movements
Flat Bones
used for protection
Irregular Bones
unique functions
examples of long bones
humerus, radius, ulna, femur, tibia, fibula, metacarpals, phalanges, metatarsals
examples of short bones
carpals, tarsals
examples of irregular bones
vertebrae, patella, jawbones, cheekbone
examples of flat bones
cranium, clavicle, scapula, sternum, ribs, pelvis
the main head/neck bones and functions
cranium (flat bone, offers protection for the brain), vertebrae (irregular bone, protect the spinal cord and offers support for the weight of the body and head.)
the main shoulder bones and functions
scapula (flat bone, attaches the upper arm to the trunk of the body, allowing for movement of the arm to occur), humerus (long bone, between elbow and shoulder joint, also known as the ‘funny bone’)
allow us to perform sporting actions such as rotation of the arm in swimming
the main chest bones and functions
sternum (flat bone, forms in front of the rib cage, offers protection to the lungs and heart), ribs (flat bone, protection to the lungs and heart, supports chest and upper body structure, also allows respiration)
allow us to perform sporting actions safely, like when receiving body shots in boxing
the main elbow bones and functions
ulna (long bone, allows for rotation of the forearm), radius (long bone, connects with the wrist joint, and also located in the forearm), humerus
allow us to perform sporting actions such as throwing a ball effectively
the main hip bones and functions
pelvis (flat bone, offers the location for many muscles to join, allows us to move, sit, and kneel.) femur (long bone, longest and strongest bone in the body, transmits force from the tibia to the hip joint.)
allow us to perform sporting actions such as jogging and running effectively.
the main knee bones and functions
femur (long bone, connects to the tibia at the knee joint), tibia (long bone, bears most of the body’s weight and absorbs shock as we walk or run. plays an essential role in movement of the body)
allow us to perform sporting actions such as kicking a football efficiently.
the main ankle bones and functions
tibia (long bone), fibula (long bone, calf bone, located laterally to the tibia, stabilises the ankle and supports the muscles in the lower leg), talus (short bone, allows lower body movement from the ankle joint)
allow us to perform sporting actions such as lunging to reach a badminton shot effectively.
joint
the place where 2 or more bones meet
synovial joints
the most common form of joint in the human body, joints filled with fluid that surrounds cartilage attached at the end of each of the bones that meet at the joint
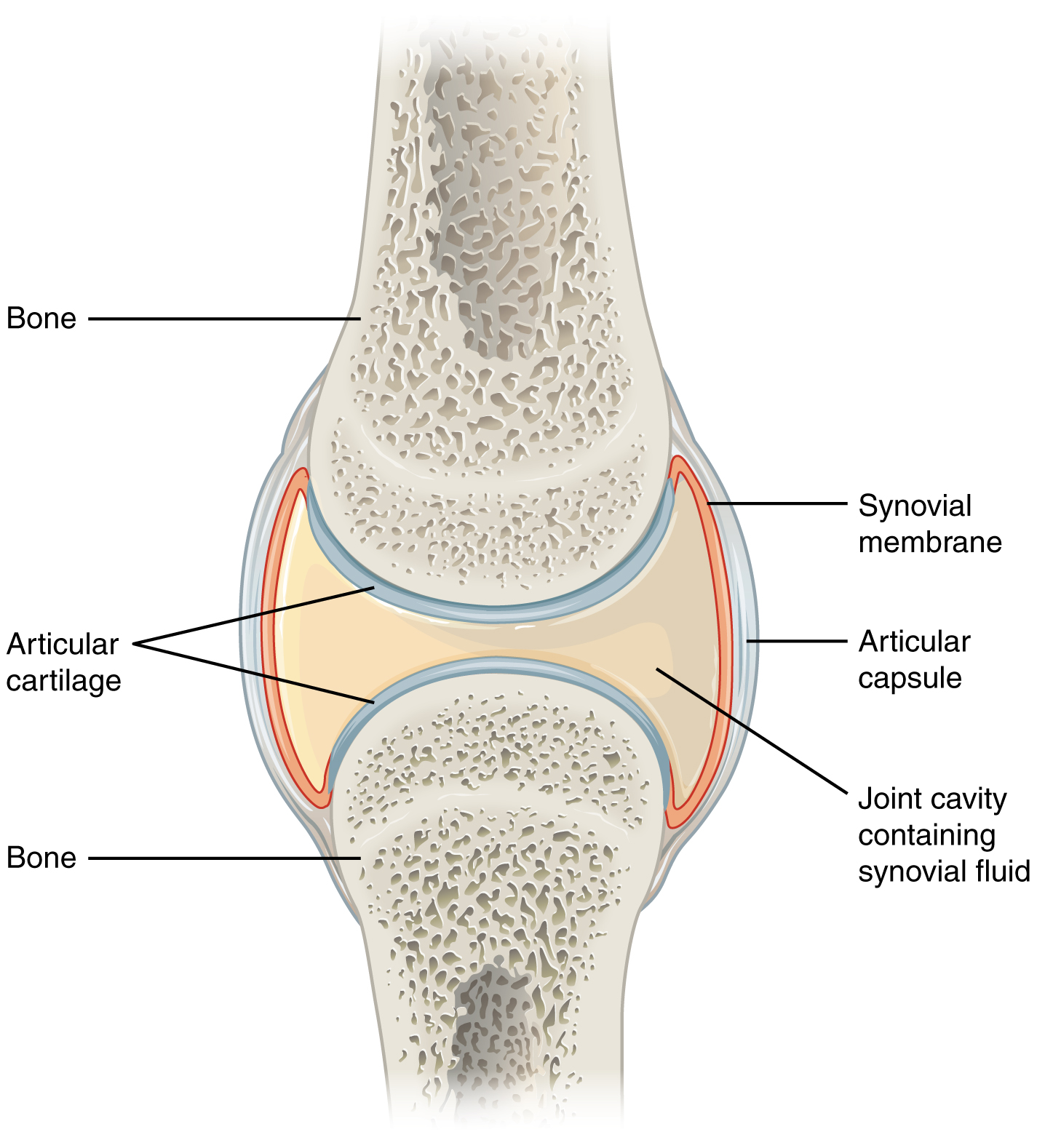
Synovial Joints: Capsule
surrounds the joint, lined by a synovial membrane
Synovial Joints: Ligaments
join bones to bones, preventing unnecessary movements and dislocations
Synovial Joints: Synovial Fluid
lubricates the joints and is created in the capsule, which reduces friction and wear of the joint
Synovial Joints: Bursae
further small bags of synovial fluid, surround the joint to prevent fiction from the movement of tendons across the surface of the joint
Ligaments
join bone to bone
Tendons
join muscle to bone
6 types of synovial joints
ball and socket, hinge, pivot, condyloid, saddle, gliding
Ball and Socket joints
most moveable joint, turns in many directions (hip and shoulder)
Hinge joints
bone can swing back and forward, like a door (knee and elbow)
Pivot joints
only allows rotation (neck (atlas and acid) and joint between radius and ulna - below elbow)
Saddle joints
allows movement back and forward and from side to side, with a greater range of motion than the condyloid joints (joint at the base of the thumb.)
Condyloid joints
allows movement back and forward and from side to side (at the wrist between radius and carpals)
Gliding joints
allows movement over each other, smallest movement of all synovial joints (between carpals and between tarsals)
hinge joints examples
located at the knee and the elbow
flexion and extension
preparing for (F) and kicking a ball (E)
ball and socket joints examples
located at the shoulder and the hip
flexion, extension, abduction, adduction, and rotation
rowing pulling (F), rowing recovery (E), sidesteps (Ab), breaststroke arms (Ad), front crawl arms (R)
condyloid joints examples
located at the wrist
flexion, extension, rotation
badminton smash pre (F), badminton smash exe (E), badminton drop shot (R)
pivot joints examples
located at the neck
rotation
front crawl breathing
flexion
bending the joint, so that the angle of the joint decreases
extension
straightening the joint, so that the angle of the joint increases
rotation
the movement of the joint at 360 degrees
abduction
movement away from the midline of the body
adduction
movement towards the midline of the body
three types of muscle contraction
isotonic (concentric and eccentric) and isometric
concentric muscle contraction
when the muscle shortens (bicep shortens when the elbow bends)
eccentric muscle contraction
when the muscle gradually lengthens and returns to its normal length and shape (bicep lengthens when the arm straightens back up after it has been bent)
isometric muscle contraction
no actual movement of a limb or a joint so the length of the muscle is not affected. muscles are still working although they are stationary (gymnast holding a handstand)