Infectious Diseases Flashcards: Antibiotics & Key Terms (copy)
1/316
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
317 Terms
What do you call a disease that is spread from person to person?
communicable or contagious
What are the 3 primary factors that impact tx decisions in ID?
the bug/pathogen
the drug
the patient/host
Describe infection characteristics
infection site, severity, community/hospital acquired
The presence of infection is determined by..?
signs/symptoms
Antibiotic characteristics include..?
spectrum of activity and ability to penetrate the site of infection
What pt characteristics impact ID tx choices?
age, body weight, renal and hepatic function, allergies, comorbidities
Describe empiric tx
broad-spectrum antibiotics started before the pathogen is identified, targeting likely organisms
What kind of information does a gram stain provide?
categorizes shape/morphology of organisms present, provides quick preliminary results, does NOT identify the exact orgamism
What does a positive gram stain tell us?
organisms have a thick cell wall
What does a negative gram stain tell us?
organisms have a thin cell wall
What does it mean when organisms do not stain well with a gram stain?
atypical
What color is a positive gram stain?
purple or bluish (from the crystal violet stain)
What color is a negative gram stain?
pink/red (from taking up the safranin stain)
What are the gram positive rods?
Listeria monocytogenes
What are the gram positive cocci (GPC)?
Staphylococcus (including MRSA & MSSA) (clusters)
Streptococcus (pairs/chains)
Enterococcus (pairs/chains)
What are the anaerobes?
(+)
- clostridium
- peptostreptococcus (mouth flora)
(-)
- bacteroides
- prevotella (mouth flora)
What are the atypicals?
Mycoplasma pneumonia
Chlamydia
Legionella
Mycobacterium terboculosis
What are some enteric gram negative rods (enteric GNR)?
P. mirabalis
E. coli
Klebsiella
Enterobacter
What are some gram negative rods that do not colonize the gut?
Psudomonas
H. Influenzae
Providencia
h. pyrlori
What organisms can infect the CNS/Cause meningitis?
streptococcus (+)
N. meningitis (-)
H. influenzae (-)
Listeria (+)
What are some organisms that can infect the mouth?
peptostreptococcus (+ anaerobe)
prevotella (- anaerobe)
What are some organisms that can infect the URT?
GPC: streptococcus pyogenes (+), streptococcus pneumoniae (+)
GNR: H. influenzae (-)
What are some organisms that can infect the LRT (community)?
GPC: streptococcus pneumoniae (+)
GNR: H. influenzae (-)
Atypicals: Legionella, Mycoplasma, Chlamydophilia
Enteric GNR: P. mirabalis, E. coli, Klebsiella, Enterobacter
What are some organisms that can infect the LRT (hospital)?
MSSA, MRSA (+)
psudomonas (-)
acinetobacter (-)
Enteric GNR: P. mirabalis, E. coli, Klebsiella, Enterobacter (incl. ESBL & MDR)
What is ESBL?
extended spectrum beta-lactamase - resistance to cephalosporins and penicillins - generally treated with carbapenems or newer cephlasporins +beta lactase inhibitor combos
What is MDR?
multidrug resistance
What are some organisms that can infect the heart/cause endocarditis?
GPC: MSSA, MRSA, staph epidermis, streptococcus, enterococcus
What are some organisms that can cause SSTI?
GPC: MSSA (+), streptococcus pyrogenes, staph epidermidis
GNR: pseudomonas, H. influenzae, providencia, H. pylori (esp in pt w/ DM)
What organisms can infect the bones/joints?
GPC: MSSA (+), staph epidermidis, streptococcus
N. gonorrhoeae (-)
GNR: pseudomonas, h. influenzae, providencia, h. pylori
What organisms can cause IAI?
Enteric GNR: P. mirabalis, E. coli, Klebsiella, Enterobacter
Enterococcus (+)
Streptococcus (+)
Bacterioides (anaerobic)
What organisms can cause UTI?
GNR: E. coli, Klebsiella, P. mirabalis
Staph saprophyticus (GPC)
Enterococcus (GPC)
What is CFU?
colony forming units that grow on the agar plate in the lab. Represents # bacterial cells present in the culture
What is MIC?
Minimum inhibitory concentration: smallest concentration of drug that visibly inhibits growth.
(specific to each antibiotic and organism)
When an angiogram has a lot of susceptible antibiotics, how do you decide which to choose?
- most narrow spectrum
- pt factors (guidelines, need of IV, allergy, renal/hepatic function, etc)
What does it mean when an antibiotic is showing as intermediate in an angiogram?
it may be effected under certain circumstances (ex: higher doses, extended infusions, etc)
They are generally not accepted over a susceptible antibiotic
Describe the synergistic relationship between beta lactase and aminoglycosides
Used to treat invasive gram + infections like endocarditis
the beta lactic allows the aminoglycloside to reach its intracellular target (ribosome) where if can then cause lethal damage to the bacteria. w/out the beta lactic the amino glycoside cannot penetrate the cell wall at safe doses --> allows for reduced doses of the aminoglycoside and faster clearing of the infection.
Describe tx assessment after starting an antibiotic
1. fever trend
2. WBC trend
3. s/sx
Describe the different types of resistance
- Intrinsic: resistance is natural to the organism
- Selection Pressure: antibiotics kill off susceptible and leaves the resistant ones left to multiply, becoming more prominent
- Acquired: resistant gene transfer
- Enzyme Inactivation: enzymes produced by the bacteria break down the antibiotic (ex: ESBL, CRE)
What is CRE?
Carbapenem-resistant Enterobacteriaceae: MDR enteric GNR like Klebsiella & E. coli produce enzymes that can break down penicillins, most cephalosporins, and carbapenems.
They typically require multi drug regimen like polymyxins (that have high risk toxicity)
What are common resistant pathogens?
Kill Each And Every Strong Pathogen
Klebsiella pneumoniae (ESBL, CRE)
E. coli (ESBL, CRE)
Acinetobacter baumannii
Enterococcus faecalis, E. faecium (VRE)
Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA)
Pseudomonas Aeruginosa
What is VRE?
vancomycin resistant enterococcus
What is an antibiotic with a high risk for c. diff?
clindamycin
What are the DNA/RNA inhibitors?
Quinolones (DNA gyrase, topoisomerase IV)
Metronidazole, tinidazole
Rifampin
What are the Cell Membrane Inhibitors?
Polymyxin
Daptomycin
Telavancin
Oritavancin
What are the Protein Synthesis Inhibitors?
aminoglycosides
macrolides
tetracyclines
clindamycin
linezolid, tedizolid
quinupristin/dalfopristin
What are the Cell Wall Inhibitors?
beta-lactams (penicillins, cephalosporins, carbapenems)
monobactams (aztreonam)
Vancomycin ( & dalbavancin, telavancin, oritavancin)
What are the Folic Acid Synthesis Inhibitors?
Sulfonamides
Trimethoprim
Dapsone
What are the hydrophilic antibiotics?
BAD VP
Beta-lactams
Aminoglycosides
Daptomycin
Vancomycin
Polymyxins
What are the lipophilic antibiotics?
quinolones
macrolides
rifampin
linezolid
tetracyclines
chloramphenicol
What are the PK parameters of hydrophilic antibiotics?
- small Vd --> poor tissue penetration
- renal elimination --> drug accumulation if poor renal function
- low intracellular concentration --> not active against atypicals
- increased clearance/distribution in sepsis --> consider loading doses & aggressive dosing w/ sepsis
- lower bioavailability --> Not used PO or IV to PO generally not 1:1
What are the PK parameters of lipophilic antibiotics?
- large Vd --> good tissue penetration (inc. bone, lung, brain)
- hepatic metabolism --> risk hepatotoxicity & drug-drug interactions
- good intracellular concentration --> active against atypicals
- no changes to clearance/distribution in sepsis --> dose adj not needed in sepsis
- excellent bioavailability --> given PO OR IV to PO generally 1:1
Which antibiotics are concentration-dependent?
aminoglycosides, quinolones, daptomycin
Which antibiotics are exposure-dependent?
vancomycin, macrolides, tetracyclines, polymyxins
Which antibiotics are time-dependent?
Beta-lactams (penicillins, cephalosporins, carbapenems)
How do you maximize MIC in concentration-dependent antibiotics?
have higher peaks (increase efficacy) and have lower troughs (decreased toxicity) by giving larger doses and decreased frequency
How do you maximize MIC in exposure-dependent antibiotics?
increase exposure over time
How do you maximize MIC in time-dependent antibiotics?
maintain the drug level to increase MIC over the dosing interval by having shorter dosing intervals & extended/continuous infusions
What are the beta-lactams and how do they work?
penicillins, cephalosporins, carbapenems
Beta-lactams MOA
They are characterized by a beta-lactam ring. They bind to penicillin binding proteins which prevents peptidoglycan synthesis --> inhibiting bacterial wall synthesis
What are all penicillins NOT active against?
MRSA or atypical organisms
What are the natural penicillins and what do they cover?
penicillin V, penicillin G
cover streptococcus, enterococcus, gram + anaerobe (mouth flora peptostreptococcus)
(Little gram - , NO STAPH)
What are the antistaphylococcal penicillins and what do they cover?
Nafcillin
Oxacillin
Dicloxacillin
cover streptococcus and MSSA
(NO gram -, enterococcus, or anaerobes)
What are the amino penicillins and what do they cover?
amoxicillin, ampicillin
(+)
strep, enterococcus, gram + anaerobe (mouth flora peptostreptococcus)
(-)
h. influenzae, p. mirabalis, E, coli
Why are aminopenicillins combined with beta-lactimase inhibitors and how does this change coverage?
allows coverage MSSA
More gram (-): Klebsiella + h influenzae, neisseria, p. mirabalis, e. coli (HNPEK)
Added gram (-) anaerobes like bacterioides fragilis
What is the extended spectrum penicillin and what is its coverage?
piperacillin/tazobactam
Same as amibopenicillin + beta lactase inhibitors:
MSSA
(-): HNPEK
gram (-) anaerobes like bacterioides fragilis
PLUS expanded gram - coverage CAPES + pseudomonas
What is HNPEK?
Haemophilus (GNR), Neisseria (GNC), Proteus (enteric GNR), E. coli (enteric GNR), Klebsiella (enteric GNR)
What is CAPES?
Citrobacter (enteric GNR), Acinetobacter (-), Providencia (GNR), Enterobacter (enteric GNR), Serratia (enteric GNR)
Which penicillins come as INJ?
penicillin G aq, nafcillin, ampicillin, Unasyn, Zosyn
What is the brand name for amoxicillin/clavulanate?
Augmentin

What is the brand name for ampicillin/sulbactam?
Unasyn
What is the brand name for piperacillin/tazobactam?
Zosyn

What penicillins come a chewable?
amoxicillin and Augmentin
Which penicillin has a BBW for IV use?
penicillin G benzathine
only penicillin G aqueous can be used IV
What antibiotics require renal adjustments?
beta lactams (CI in penicillins if CrCl < 30, beside antistaphyloccocus penicillins)
aminoglycosides
Vancomycin
Polymyxins
What adjustments should be made if a pt CrCl <30 and they are on augmentin?
do not give ER , max dose 875 mg
Penicillins: SEs
seizures with accumulation, GI upset, diarrhea, rash (incl anaphylaxis, SJS), hemolytic anemia
Which penicillins are preferred for MSSA?
antystaphylococcus: dicloxacillin, nafcillin, oxacillin
How is ampicillin given and why?
IV due to poor bioavailability
How is Zosyn given?
prolonged or extended IV infusions over 4h
What medication can increase the concentration of penicillins?
probenecid
What is the brand name for penicillin G benzathine?
Bicillin L-A
Which penicillin has pseudomonas coverage?
Zosyn
Which penicillin is used for h. pylori infection?
Amoxicillin
What are all cephalosporins NOT active against?
enterococcus and atypicals
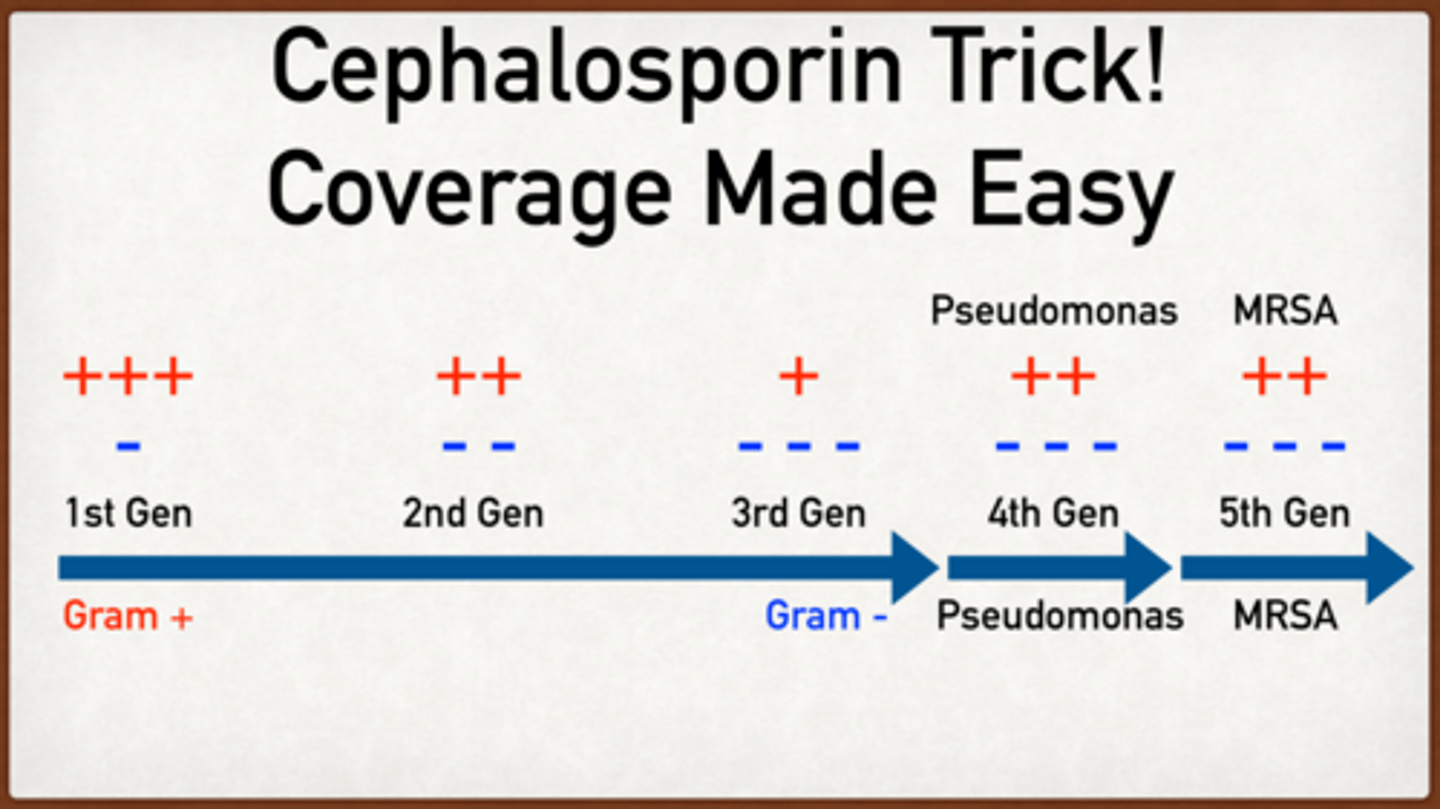
How does coverage change among the cephalosporin generations?
1st: strep, staph The least gram (-)
2nd:
cefuroxime: more resistant strep, more gram (-) incl anaerobe
3rd:
Group 1 - : resistant strep, MSSA, gram + anaerobes, resistent gram -
Group 2 - ceftazidine pseudomonas
4th: Pseudomonas (broad gram -)
5th: like resistent gram -, broad gram + incl MRSA
Describe coverage of beta-lactamase inhibitor + cephalosporin
MDR pseudomonas, MDR GNR (PEK/CAPES)
What are the first generation cephalosporins and what do they cover?
cefazolin, cephalexin
cover strep, staph (preferred for MSSA), PEK
What is the brand name for cephalexin?
Keflex
What are the second generation cephalosporins and what do they cover?
cefuroxime: staph, more resistant strep, HPNEK
cefetetan & cefoxitin: same + gram (-) anaerobe bacterioides fragilis
What are the 3rd generation cephalosporins and what do they cover?
Group 1 - : ceftriaxone, cefotaxime, cefdinir: resistant strep, MSSA, gram + anaerobes (mouth flora peptosptrep, c.diff), resistant HNPEK
Group 2 - ceftazidine: pseudomonas
What are the 4th generation cephalosporins and what do they cover?
cefepime
broad gram (-): HPNEK, CAPES, pseudomonas
resistent strep, MSSA, gram + anaerobe
What are the 5th generation cephalosporins and what do they cover?
ceftaroline
resistant HPNEK, broad gram + (MSSA, strep), MRSA
How is Keflex PO dosed?
250-500 mg q6-12h
What is the brand name for cefotetan?
Cefotan
What is the brand name for ceftazidime?
Fortaz
What is the brand name for cefuroxime?
Ceftin

Ceftriaxone: CIs
Can cause high bilirubin in neonates --> biliary slugging and kernicterus (brain damage). Do not use concurrently with Ca-containing IV products in neonates <28 days old
What antibiotics have cross-sensitivity with penicillin allergy?
cephalosporins
carbapenems
What are warnings specific to cefotetan?
increased risk bleeding due to side chain
increased risk disulfiram-like rxn (hangover sx) with alcohol
Cephalosporin: SEs
seizures with accumulation, GI upset, diarrhea, rash/allergy, hemolytic anemia, severe skin rxns like SJS/TEN