Computer Networking Chapter 5 Quiz
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
What is the role of the Gateway/next hop parameter in a routing table?
It determines the speed at which the packet is forwarded.
It specifies the final destination of the packet.
It identifies the router's physical location.
It indicates the next router or gateway along the path to the destination.
It indicates the next router or gateway along the path to the destination
Considering the example below of three routers connected in a series, which static routes is Router A configured with? (Select two.)
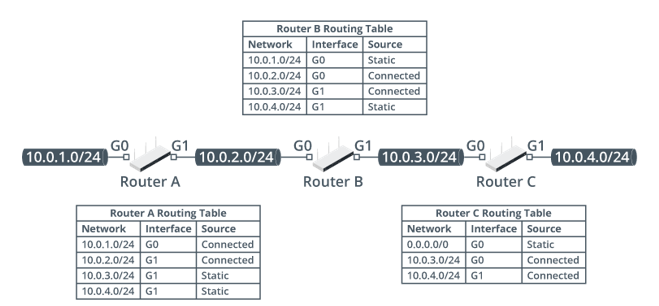
10.0.2.0/24
10.0.4.0/24
10.0.1.0/24
0.0.0.0/0
10.0.3.0/24
10.0.4.0/24 & 10.0.3.0/24
What is the default probe message type used by the tracert command on Windows systems?
TCP SYN
UDP
ARP Request
ICMP Echo Request
ICMP Echo Request
How does IPv6 handle packet fragmentation differently from IPv4?
IPv6 uses a different header field for fragmentation management.
IPv6 increases the MTU to avoid fragmentation.
IPv6 allows routers to perform fragmentation.
IPv6 requires the host to perform path MTU discovery.
IPv6 requires the host to perform path MTU discovery.
What is the purpose of inspecting the ARP cache table?
To increase the router's memory
To view the device's routing table
To modify the device's IP address
To discover duplicate IP addresses and misconfigurations
To discover duplicate IP addresses and misconfigurations
What is the purpose of applying an IP configuration to each interface on a router?
To enhance the processing power of the router
To increase the storage capacity of the router
To enable the router to serve its function in routing data
To secure the router from external threats
To enable the router to serve its function in routing data
Which of the following best describes a directly connected route in a routing table?
A route that is manually added and requires manual updates
A route for subnets and IP networks that are not directly attached to the router
A route that is automatically added for each active router interface, representing subnets for which the router has a local interface
A special type of static route that serves as the gateway of last resort
A route that is automatically added for each active router interface, representing subnets for which the router has a local interface
A network technician is using traceroute on a corporate network to make use of ICMP "Time Exceeded" in order to identify routers along a delivery path.
What is the TCP/IP feature that traceroute uses to accomplish this.?
Static route
Time To Live (TTL) header field
Default route
Fragmentation
Time To Live (TTL) header field
Which command outputs the active routing table and includes details such as destination, gateway, and the source of the route?
show arp
show route
ip route show
route print
show route
What does the Time to Live (TTL) header field represent in a packet?
The maximum distance the packet can travel
The maximum time the packet can exist on the network
The maximum number of routers the packet can pass through
The priority assigned to the packet for data transmission
The maximum number of routers the packet can pass through
If a router has two routes to the same destination with identical prefix lengths from the same routing protocol, how does it choose which route to use?
By using the Administrative Distance (AD) value
By preferring the route with the shortest prefix
By choosing the route with the lowest metric
By selecting the route with the largest packet size
By choosing the route with the lowest metric
What happens when a routing protocol's database contains more than one route to the same destination prefix?
The router randomly selects one of the routes for use.
The router selects the route with the highest cost metric.
The path with the lowest cost metric is used.
All routes are used simultaneously to balance the load.
The path with the lowest cost metric is used
What can cause convergence problems in a dynamic routing network?
Consistent routing information across all routers
A stable network with no changes
The use of static routing protocols
A flapping interface
A flapping interface
What is the purpose of the hello messaging in EIGRP?
To transmit routing updates
To encrypt data packets
To confirm connectivity with its neighbors
To assign IP addresses to routers
To confirm connectivity with its neighbors
What is the principal difference between link state and distance vector protocols?
Link state protocols rely on directly connected neighbors for information about remote networks.
Distance vector protocols allow each node to hold a copy of the complete network topology.
Distance vector protocols use a shortest path first algorithm.
Link state protocols allow each node to hold a copy of the complete network topology.
Link state protocols allow each node to hold a copy of the complete network topology
What type of routing system is OSPF considered to be?
Circular
Hierarchical
Flat
Linear
Hierarchical
What protocol does BGP use for its operation?
ARP
UDP
TCP
ICMP
TCP
In RIP, what happens when a router receives an update that includes a route to a network it already knows about?
It increments the hop count of its existing route by 1.
It replaces its existing route with the new one only if the hop count is lower.
It ignores the update.
It always replaces its existing route with the new one.
It replaces its existing route with the new one only if the hop count is lower
What was the primary reason for the development of Enhanced IGRP (EIGRP)?
To replace the TCP/IP protocol
To address limitations in IGRP, such as lack of support for classless addressing
To provide a routing protocol for inter-domain routing
To improve the security features of routing protocols
To address limitations in IGRP, such as lack of support for classless addressing
Under which of the following circumstances might you implement BGP on your company network and share routes with internet routers?
If the network has over 15 hops
If the network is connected to the Internet using multiple ISPs
If the network has over 15 areas and uses IPv6
If the network is connected to the Internet using public addressing
If the network is connected to the Internet using multiple ISPs