Visual Fields III
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms
What does the superior retina relate to ?
inferior visual field
How do macular fibres sit?
centrally → Papilomacular Bundle
what is the structure of the fibres at the optic chiasm?
macula fibres move to centre
What happens at the Optic chiasm?
NASAL fibres CROSS OVER
inferior Nasal fibres → anterior chiasm
Superior nasal fibres → posterior chiasm
temporal fibres stay at same side
What happens at the optic tract?
Macular fibres → crossed (nasal retina) + uncrossed (temporal)
Superior Peripheral → fibres from superior retina = inferior visual field
Medial
Ipsilateral Sup-Temp
Controlateral Sup-Nasal
Inferior Peripheral
Lateral
Ipsilateral Inf-temp
Controlateral Inf-Nasal
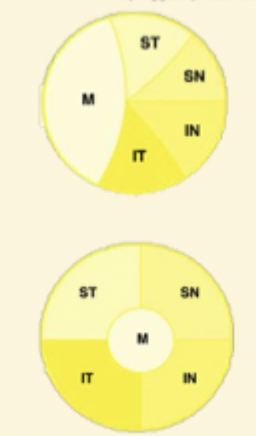
What happens at the LGN?
More organisation here
6 layers
layers 1,4 + 6
→ crossed nasal fibres
→ Controlateral retina
layers 2,3 and 5
→ uncrossed (temporal)
Ipsilateral retina → same side
Where are the Magnocellular layers?
Layers 1+2
Magno cells:
Retinal rods
magno ganglion cells
which layers are the parvocellular layers?
layers 3-6
Retinal Cones
Parvo Ganglion cells
where are the Koniocellular layers?
in between layers 1-6
ganglion cells → process colour
what is the path of optic radiations that represent inferior retina?
Fibres leaving lateral LGN
Inferior radiations
Head to OCCIPITAL LOBE via temporal lobe
form Meyer loops along the way
What is the path involving superior radiations?
Fibres leave medial LGN
represent superior retina
superior radiations → Parietal lobe
where are the macular fibres situated?
between superior + inferior fibres
Primary Visual Cortex - superior radiations
Occipital Lobe
Cuneus gyrus → above calcarine fissure
superior radiation terminated at cuneus gyrus
PVC→ Inferior radiations
Occipital lobe
Lingual gyrus → below calcarine fissure
lingual → inferior radiation terminated
where are the macula fibres in the primary visual cortex?
more posterior the cortex , relates more to central vision
Superior Macular fibres → Cuneus gyrus
Inferior Macular fibres → Lingual Gyrus
What is a Haeminopia?
respects vertical midline
affects ½ of VF → nasally or temporally
what is heterotonyomus ?
affects opposite sides of space
what conditions relate to horizontal midline being obeyed?
Retinal
Glaucoma , MD, Retinal detachment
what conditions associated with vertical midline?
Post retinal
emergency if vertical midline until proven otherwise
optic nerve , optic chiasm , LGN
What is a Junctional Scotoma?
affects both eyes
meningioma compressing on optic nerve just as its beginning to enter optic chiasm
affects superior field , LVF completely affected
Pituiatry Tumour?
= more noticeable when one eye closed → notice ½ vision of one eye missing
Bitemporal Haeminopia
what is Amsler grid used for?
quick assessment of Mucular fucntion
AMD
alternative to 10-2, can be used to self monitor at home
used to look for scotomas+ metamorphopsia
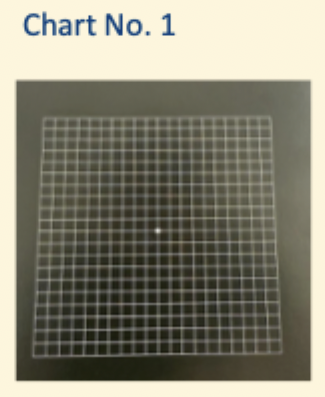
what is Amsler chart No 1?
Standard chart
5mm squares
Central white fixation target
Each square subtends 1 degree when held at 30cm
white on black more sensitive than black on white
What is Chart NO. 2?
Diagonal lines assist with fixation → guidelines to look in centre

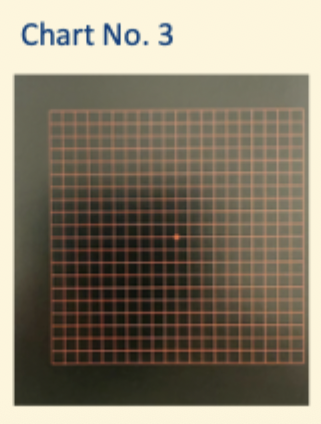
What is Chart No.3?
RED GRID
useful for
- Toxic amblyopia
- optic neuritis
What is Chart Number 4?
Scattered white dots
similar to chart 1 for relative scotoma detection
Can NOT detect metamorphopsia
what is Chart 5 used for?
can be rotated to change orientation of lines
Investigates metamorphopsia at dif meridians

chart 6
similar to 5
black lines on white
additional lines that subtend 0.5 degrees → greater sensitivity
chart 7
0.5 degrees for central 8 degrees
used for more subtle macular disease → could be missed by 1 degree square