Chapter 9 microbial genetics
1/147
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
148 Terms
What are genetics
The study of heredity
What does the science of genetics explore?
• Transmission of biological traits from parent to offspring
• Expression and variation of those traits
• Structure and function of genetic material
• How this material changes
levels of structure and function of the genome
-organism level
-cell level
-chromosome level
-molecular level
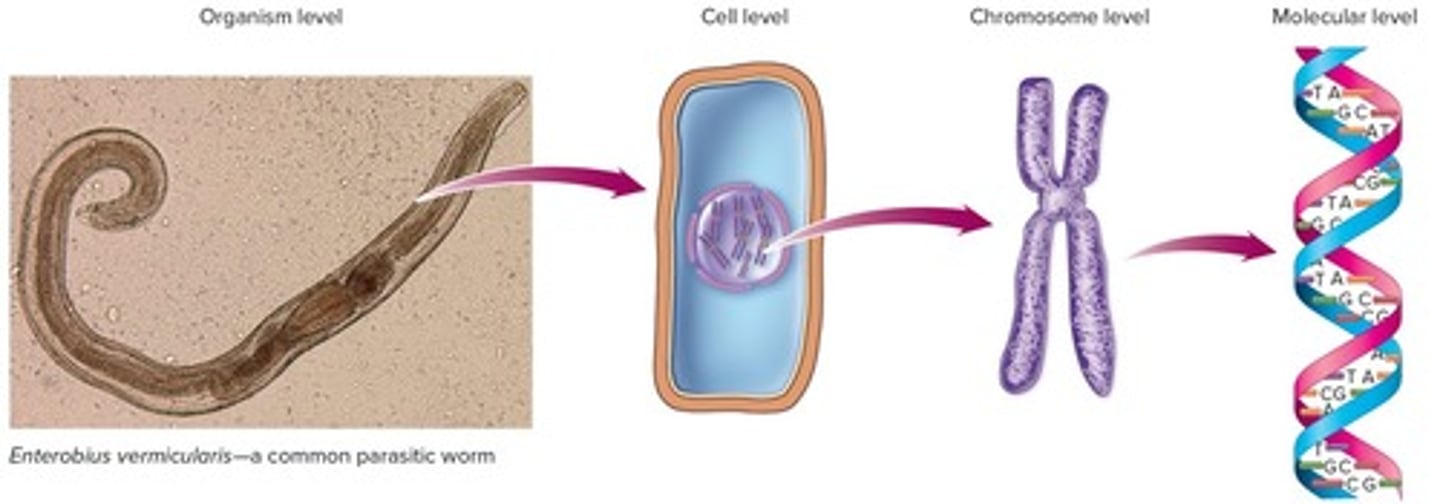
What is a genome?
sum total of genetic material of an organism
How many genes are there in a human
29,000 genes
Where do most genomes exist?
In chromosomes but can also appear in non chromosomal sites such as
-Mitochondria
-Chloroplast
-Plasmids
Genome of cells composed entirely of
DNA
genome of viruses are made of
DNA OR RNA
What is a gene?
sequence of DNA that codes for a protein
What is a chromosome?
discrete cellular structure composed of a neatly packaged DNA molecule
Where are chromosomes found it eukaryotic organisms?
Nucleus and are multiple and linear
How are bacterial chromosomes like?
Single circular loop
What are chromosomes subdivided into?
Genes, the fundamental unit of heredity responsible for a given trait
What is an allele?
an alternative version of a gene
What are genes?
-Site on the chromosome that provides information for a certain cell function
-Segment of DNA that contains the necessary code to make a protein or RNA molecule
What are the three basic categories of genes?
Genes that code for proteins - structural genes
Genes that code for RNA
Genes that control gene expression - regulatory genes
What is epistasis?
Where genes interact and stop one another
What is a genotype?
All types of genes constitute the genetic makeup
What is a phenotype?
The expression of the genotype creates observable traits
How many genes does the smallest virus have?
4-5 genes
How many genes does ecoli have?
4, 288 genes; total length = 1mm and 1 chromosome
How many genes does a human cell have?
31,000 genes; total length= 6FT and 46 chromosomes
What compacts DNA molecules?
Supercolis and or superhelices
What packages DNA in prokaryotes?
Action of enzyme DNA Gyrase
-Coils chromosomes into tight bundles by reversible series of twist into DNA molecule
What packages DNA in Eukaryotes?
More complex, and has three levels of coiling starting with a chain of nucleosomes
function of DNA gyrase
relaxes supercoiling ahead of the replication fork
What is the basic structure of DNA?
nucleotide
What is DNA consisted of?
Deoxyribose sugar
A phosphate group
Nitrogenous bases: Adenine, Guanine, Thymine and Cystosine
What are the nitrogenous bases in DNA?
Adenine, Thymine, Guanine, Cytosine
GCAT (GANGSTA' CAT)
What do the nucleotides form?
A sugar-phosphate backbone (Phosphodiester)
DNA nitrogen base pairs
A T
C G
What do nitrogenous bases bond to?
1' carbon of each base on the Osugar and span the center of the molecule to pair with a complementary there strand
How many hydrogen bonds does Adenine and Thymine form?
2 hydrogen bonds
How many hydrogen bonds does Guanine and Cytosine form?
3 hydrogen bonds
Structure of DNA double helix
Antiparallel arrangement: in one strand, the helix runs in a 5′ to 3′ direction and the other side is oriented from 3′ to 5′
(P much reversed)
Each strand provides a template for the exact copying of a new strand
Order of bases constitutes the DNA code
What is the significance of DNA structure?
1. Maintenance of code during reproduction
2. Providing variety
How does DNA maintain code during reproduction?
Constancy of base pairing guarantees codes will be retained
-When strands are separated, each strand serves as template for replication of the molecule into an exact copy
How does DNA provide variety?
Base pairs are responsible for RNA and protein synthesis, thus for the phenotype of each organism
Typically how does replication occur?
Simultaneously and semi conservatively
Semiconservative process
1. The parent DNA molecule is uncoiled
2. The two strands are separated exposing the nucleotide sequence to serve as templates
3. Two new complementary strands are synthesized by using each single-stranded template as pattern
What must all chromosomes have?
A specific origin of replication where replication will be initiated
Why does it require little energy for replication at the origin of replication?
The origin of replication is rich with AT and so it takes less energy to seperate two strands
What is there when DNA is being synthesized, and what do they contain?
Two replication forks and each has its own set of replication enzymes
Where is RNA primer synthesized?
At the origin of replication by a primase
function of helicase
unwinds and unzips the DNA double helix
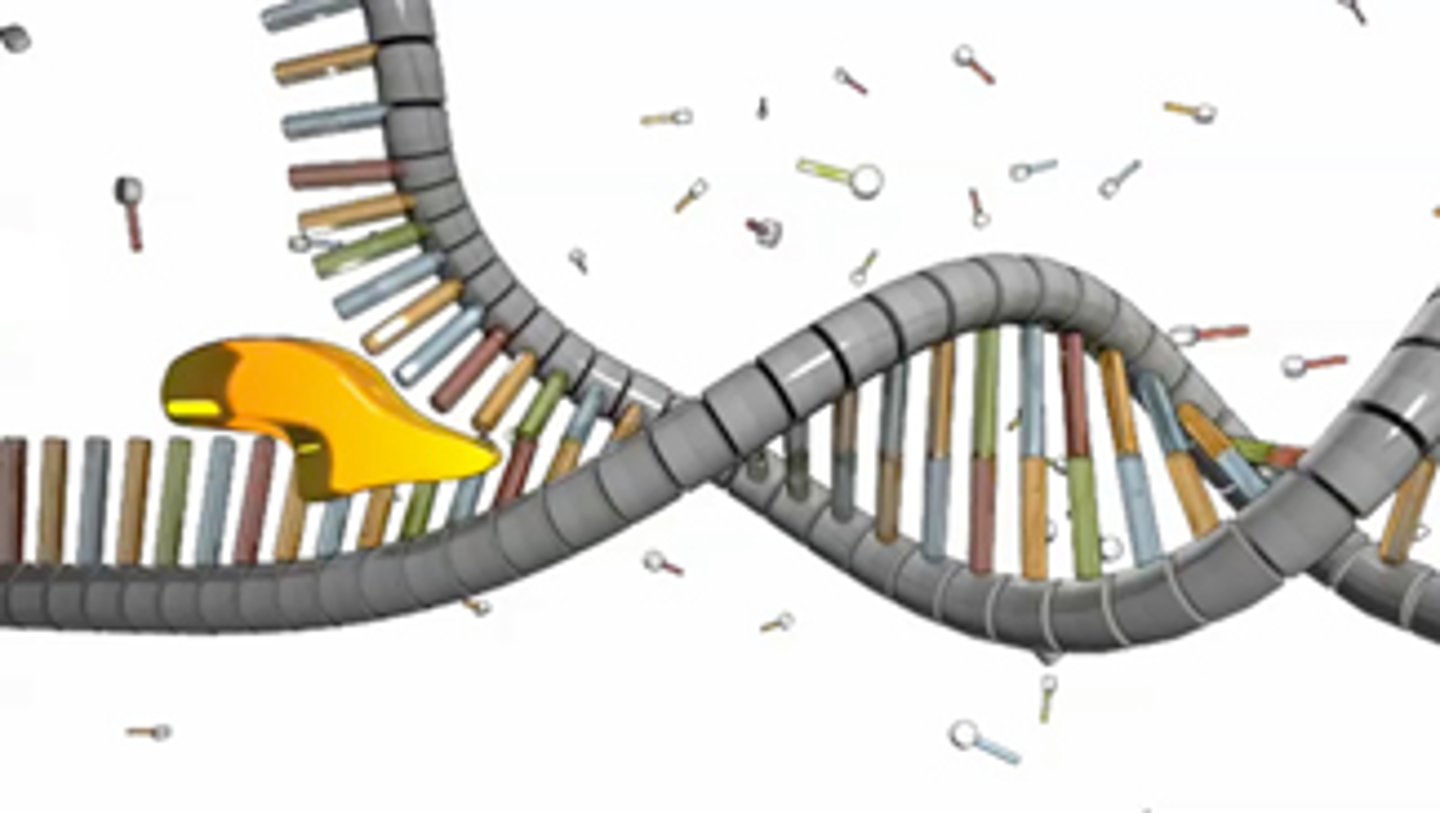
Function of DNA polymerase III
Replicates DNA
Function of DNA polymerase I
Removes RNA primers and adds DNA
Function of Ligase
final binding of nicks in DNA during synthesis and repair (Brings DNA TOGETHER)
What is ATP synthase?
Large protein that uses energy from H+ ions to bind ADP and a phosphate group together to produce ATP
lagging strand
The strand in replication that is copied 3' to 5' as Okazaki fragments and then joined up. (---------> Left to right and is more complicated)
leading strand
The new continuous complementary DNA strand synthesized along the template strand in the mandatory 5' to 3' direction. (Right to left <--------- Less complicated, contains only DNA polymerase 3)
DNA REPLICATION STEP 1
The chromosome to be replicated is unwounded by ahelicase, forming a replication fork with two templatestrands.
DNA REPLICATION STEP 2
The template for the leading strand (blue) is oriented 3' to5'. This allows the DNA polymerase III to add nucleotides in the 5' to 3' direction toward the replication fork, so it can be synthesized as a continuous strand. Note that direction of synthesis refers to the order of the new strand (red).
DNA REPLICATION STEP 3
The template for the lagging strand runs 5' to 3' (opposite o the leading strand), so to make the new strand in the 5'to 3' orientation, synthesis must proceed backward, away from the replication fork
DNA REPLICATION STEP 4
Before synthesis of the lagging strand can start, a primase adds an RNA primer to direct the DNA polymerase III. Synthesis produces unlinked segments of RNA primer and new DNA called Okazaki fragments.
DNA REPLICATION STEP 5
DNA polymerase I removes the RNA primers and fills in the correct complementary DNA nucleotides at the opensites
DNA REPLICATION STEP 6
Unjoined ends of the nucleotides (a nick) must beconnected by a ligase.
How many enzymes is required to create an exact duplicate of DNA?
30
Replication forks
the areas where the double helix separates
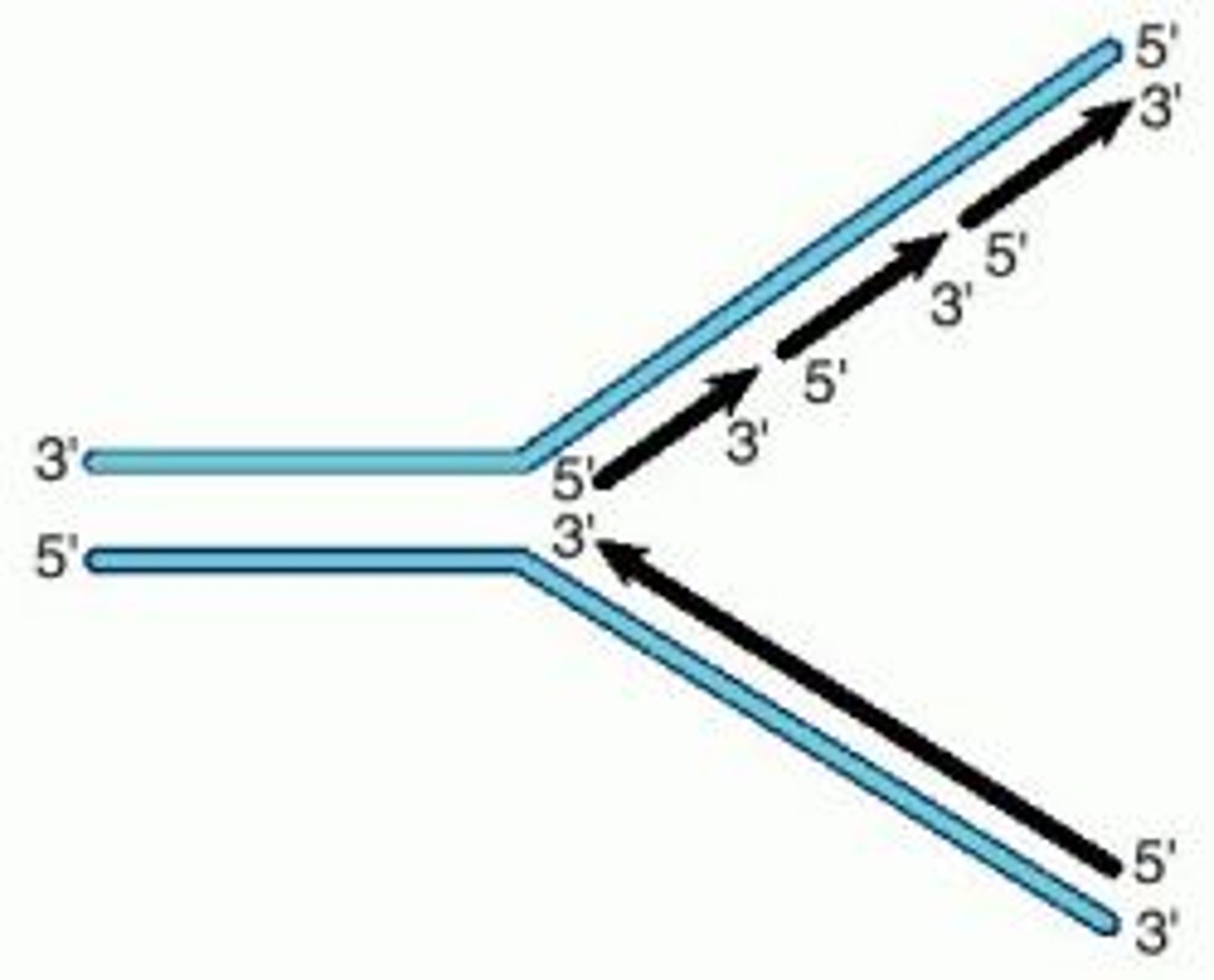
What occurs when replication forks meet?
Ligase links the DNA fragments along the lagging strand
What happens when the forks have gone in full circle?
A termination site shuts down replication
At the end of replication, what happens to the two daughter molecules that remain?
They remain connected for a bit, then they are nicked and seperated by a helicase
What is the central dogma of bio?
DNA -> RNA -> Protein
DNA-> MRNA
transcription caused by RNA polymerase
mRNA-> Protein
translation caused by a ribosomes
How is genetic information in DNA molecules conveyed to RNA?
Through transcription
How is the information within the RNA molecule used to produce proteins?
Through translation
What are different types of RNA?
mRNA (Messenger)
tRNA (Transfer AKA Thug RNA)
rRNA (Ribosomal)
smRNA (small nuclear RNA)
mRNA (messenger RNA)
a single-stranded RNA molecule that encodes the information to make a protein (Carries the DNA master code to the ribosomes)
tRNA (transfer RNA) THUG RNA
type of RNA molecule that transfers amino acids to ribosomes during protein synthesis/ translation
rRNA (ribosomal RNA)
Forms the major partof ribosomes andparticipates in proteinsynthesis
smRNA (short nuclear RNA)
Makes spliceosomes; splicing of introns from primary genomic transcripts.
What are codons?
a sequence of three nucleotides that together form a unit of genetic code in a DNA or RNA molecule.

What determines the shape and function
A proteins primary structure (Chain of amino acids)
How is RNA different from DNA?
1. RNA is single stranded and can assume secondary and tertiary levels of complexity allowing for different forms of RNA such as tRNA, mRNA etc.
2. RNA contains URACIL rather than THYMINE
3. RNA's sugar is RIBOSE rather than deoxyribose
What does mRNA contain codes for?
Sequences of amino acids in proteins
What does tRNA contain codes for
Specifying a given amino acid
What does rRNA contain codes for
Several large structural rRNA molecules
What type of RNA is translated
mRNA (messenger)
What types of RNA are not translated?
tRNA and rRNA
What does Primer contain codes for?
An RNA that can begin DNA replication
Function of Primer
primes DNA
Can Primer be translated
no
Function of RNASE
degrades RNA (think pacman eating RNA in the untranslated phase)
untranslated region (UTR)
The region of mRNA before the start codon AUG, it allows the ribosome to bind to mRNA

What are anticodons?
A set of three nucleotides bases found on the tRNA. It is complementary to the codons on the mRNA.
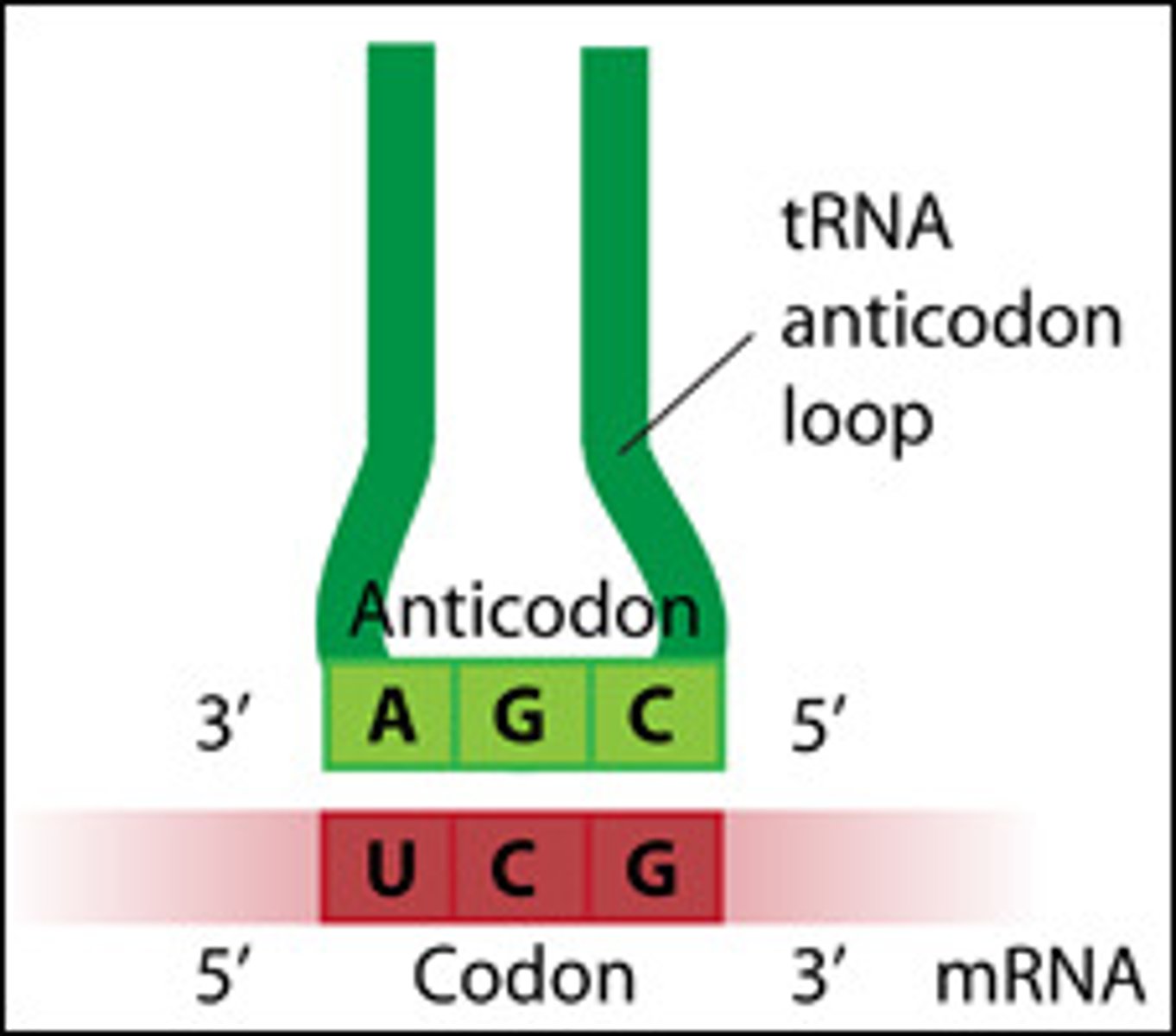
What is specific for each anticodon?
Binding sites for amino acids
RNA codons
AUCG Pairs with
UAGC
Uracil, Adenine, Cytosine, Guanine
DNA Codons.
ATCG Pairs with
TAGC
Adenine, Thymine, Cytosine, Guanine
What happens during transcription?
RNA molecule is synthesized using the codes on DNA as a guide or template
What are the three stages of transcription
1. Initiation
2. Elongation
3. Termination
initiation of transcription
RNA polymerase binds to promoter region upstreamof the gene
elongation of transcription
RNA polymerase adds nucleotides complementaryto the DNA template strand in the 5′ to 3′ direction (Uracil (U) isplaced complementary to adenine (A)
Termination of transcription
RNA polymerase recognizes a "STOP" sign in the DNA and releases the transcript (LONG ASF 😲 ACCORDING TO HIM ITS LONGER THAN 1,200 BASES )
What is the start codon
AUG (methionine)
What are the stop codons?
UAA, UAG, UGA
major events of transcription
1. Each gene contains a specific promoter region and a leader sequence for guiding the beginning of transcription. Next is the region of the gene that codes for a polypeptide and ends with a series of terminal sequences that stop translation.
2. DNA is unwound at the promoter by RNA polymerase. Only one strand of DNA, called the template strand, supplies the codes to be transcribed by RNA polymerase. This strand runs in the 3' to 5' direction.
3. The RNA polymerase moves along the DNA strand, adding complementary nucleotides as dictated by the DNA template. The mRNA strands reads in the 5' to 3' direction.
4. The polymerase continues transcribing until it reaches a termination site, and the mRNA transcript is released to be translated. Note that the section of the transcribed DNA is rewound into its original configuration.
(NEEDS TO BE SIMPLIFIED)
In translation where are all the elements needed to be synthetized go?
To the ribosome
What is translation?
the decoding of an mRNA message into a protein
What are the stages of translation?
1. Initiation
2. Elongation
3. Termination
4. Protein folding
5. Processing