Pe - things i dont know
1/24
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
Process of inhalation
Diaphragm contracts and flattens
Intercostal muscles contract to pull the ribs up and out
The volume of chest cavity increases, so a decrease in blood pressure
Air moves inwards from area of high pressure to an area of low pressure
Process of exhalation
diaphragm relaxes and moves upwards back into a dome shape
Intercostal muscles relax and ribs drop DOWN and IN
The volume of the chest cavity decrease leading to an increase in air pressure inside the lugs
Air moved outwards of an area of high pressure to low pressure
Inhalation in EXERCISE
Volume of chest cavity is increased by pectorals and sternocleidomastoid - (allows more air to be drawn in)
Exhalation during exercise
rib cage is pulled DOWN and in more rapidly by contraction of - ABDOMINALS, this forces more air out the lungs
What is plyometric training?
Training involving bounding, jumping and hopping. -
Develops power, speed and explosive strength
Equipment is needed
What is interval training?
period of high intensity followed by period of restr or low intensity training
Good for netball as meet demands of black - as sprint and stop
Training both anaerobic and aerobic
No equipment
Pathway of air
Moth nouse
Trachea
Bronchi
Bronchioles
Lungs
Alveoli
Heart rate of an individual in exercise diagram
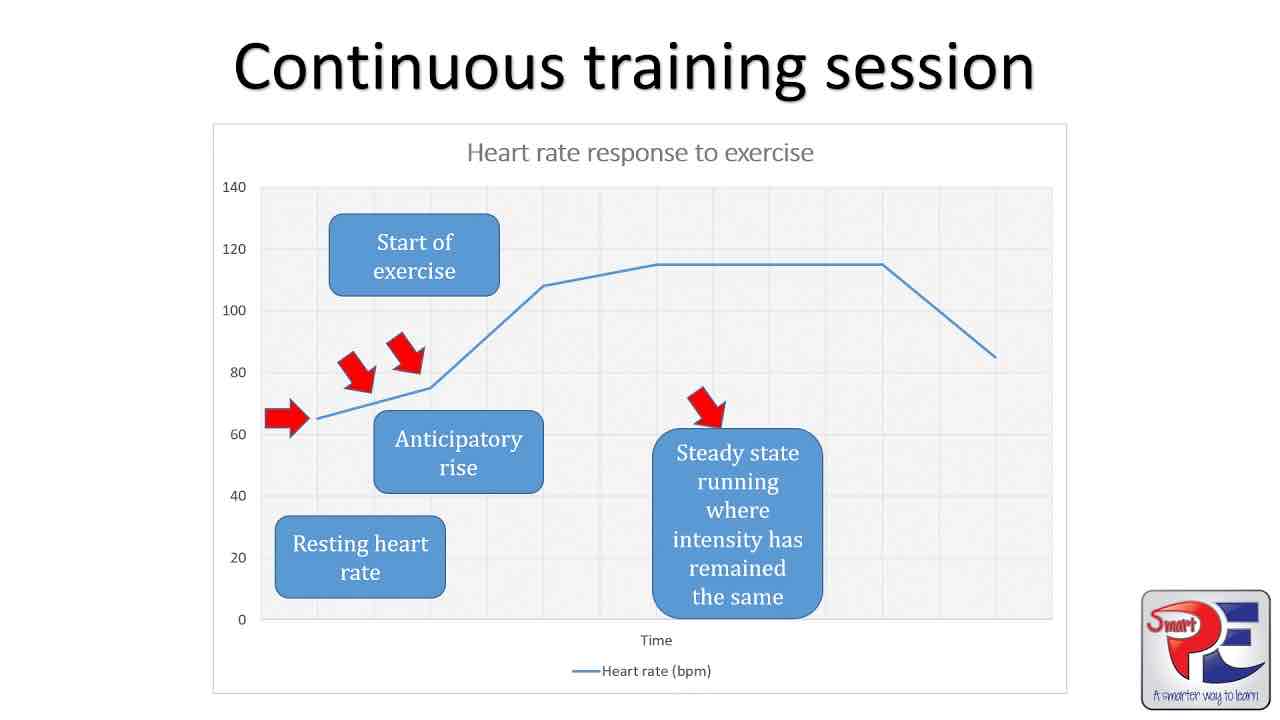
What happens to heart rate before exercise
The anticipatory rise
Heart rate increases
Caused by a realise of the hormone, adrenaline.
What is the insanity called in the middle of one of the heart rate diagrams, during exercise
The submaximul
What is vasodilation?
Vasoldilation - when your blood vessels widen to let in more blood. Face gets red.
enhances blood flow to areas your body needs it
Allows more heat to be lost from blood
What is vasoconstriction
The narrowing of blood vessels, when body temperature gets cold.
Takes blood away from the surface to prevent it from loosing heat
What is systolic value and diastolic value? - blood pressure
Systolic - heart contracts - blood pressure when heart is squeezing. So when exercising your pressure of blood will increase as your heart beat does.
Diastolic - your blood pressure when heart is relaxed. Doesn’t change much during exercise
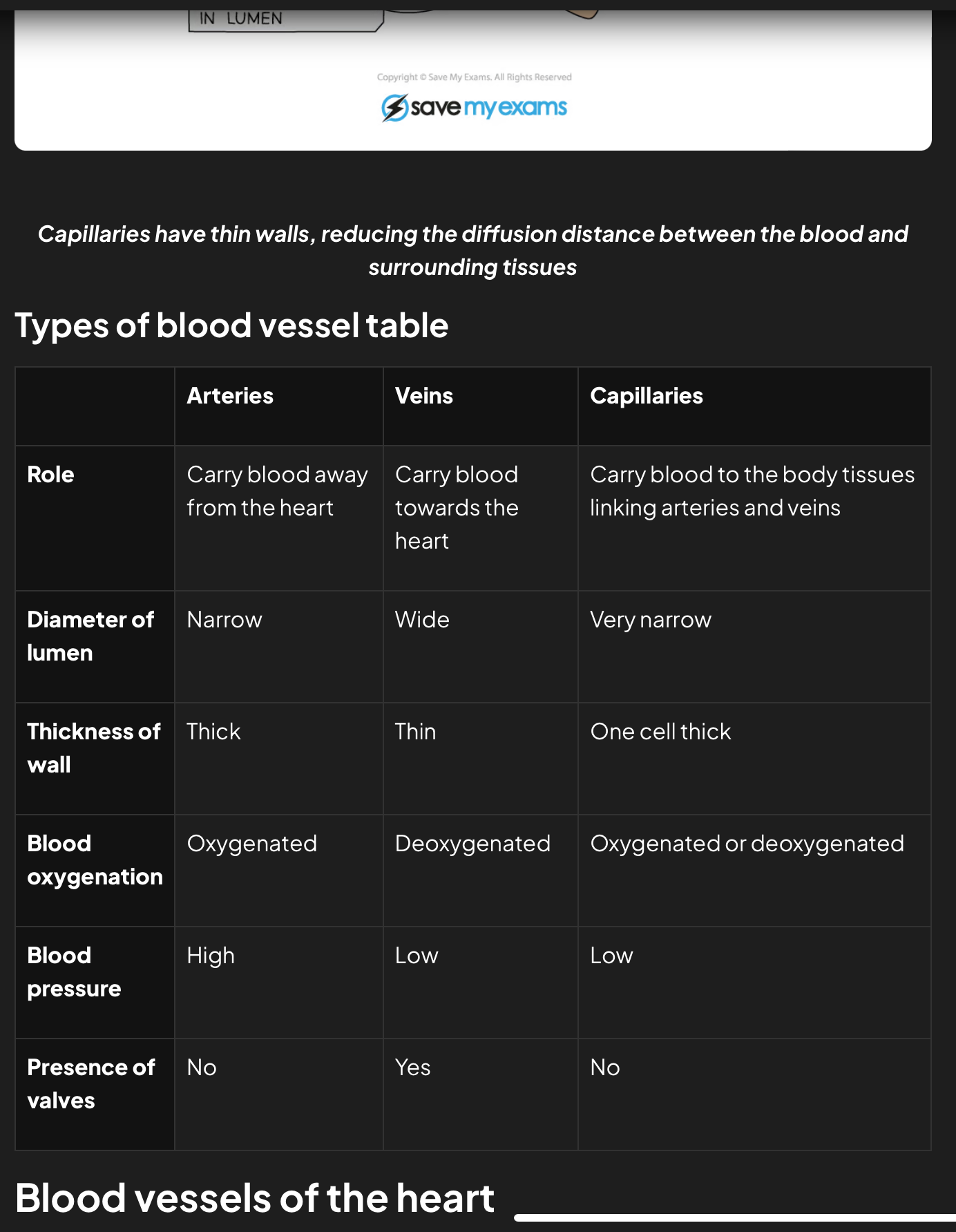
Types of blood vessel table
What is health
State of completed social, mental and physical well being without merely the absence of disease or infirmity
What is fitness??
The ability to meet/cope with the demands of the environment
What is cardio vascular endurance and how do you carry out the test?
Cardiovascular endurance - the ability for heart and lungs to work together to supply oxygen to the working muscles.
Multistage fitness test
20m shuttles
If you miss a bleep you are allowed 2 to catch up. If you miss a third the level and number you are on is your final score
Gets progressively harder as faster
What is agility
Agility is the ability to change body position or direction quickly with control
Illinois test
Cones 3.3m apart
Start on front
5m wide 10m long - 60m in total
Measure in seconds
What is speed and test
Rate of which an individual is able to move or cover a distance in a given amount of time
30m sprint test -
Run 30m between cones as wuick as you can
The shorter the time faster you are
Measure in seconds
What is reaction time and test
Time taken to respond to a stimulus
Ruler drop test
Friend holds up a ruler in between you index finger and thumb
Friend will drop ruler and you have to catch it
Read off the distance on the ruler where you caught it
The lower you get the faster your reaction time
Power test
Speed x strength
Vertical jump test
Put chalk on your finger and stand side on to the wall
Raise arm that is nearest to the wall and mark highest point you can reach
Jump high as you can still side on
Measure distance from original chalk and end of chalk in cm
Larger distance more powerful legs are
What is strength and the test
Strength is the maximum amount of force that a muscle or muscle group can apply against a resistance
Handgrip dynamometer test
Need a dynamometer = shows strength in hard and forearm
Grip as hard as you can for 5 seconds record your score in kg
Do this three times and choose your best score
What is balance and the test
Ability to keep body’s centre of mass over its base of support
Stork stand test
stand on your best leg with your other foot touching your knee and your hands on your hips
stand on toes and time how long you can hold the position
Test ends when heel touches ground
Take best of three
Longer better balance
Test for muscular endurance
Sit up bleep test
Lie on mat in sit up position
Partner holds ankles
Sit up on bleep and lie back down by next bleep
Have to do as many in time with the bleeps
Fail when fail to do two in a row