Nutrition and Disease Final
1/76
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
77 Terms
Name the correct acid/base issue
hyperventilation
tachycardia (fast HB)
decreased or normal BP
hypokalemia (low potassium)
numbness/tingling/cramping
seizures
causes hyperventilation
respiratory alkalosis
Name the correct acid/base issue
restlessness/lethargy
dysrhythmias (tachycardia = fast HB)
causes hypoventilation
confusion, dizziness
vomiting
metabolic alkalosis
Name the correct acid/base issue
rapid/shallow respiration
cyanotic (blue)
hyper kalemia
caused by COPD, pneumonia, or ARDS
respiratory acidosis
Name the correct acid/base issue
headache
decreased BP
warm flushed skin
nausea/ vomiting/ diarrhea
metabolic acidosis
This is catastrophic failure that ruptures a damaged cell and it doesn’t require any energy
necrosis
This is a controlled death of a cell that requires energy
apoptosis
What occurs after a cell ruptures from necrosis
the immune system (macrophages and neutrophils) attack the stuff that came out and clean it up
how does apoptosis occur
signal binds death receptor or leaking initiates response
Pro C-8 reacts with FADD to form C-8
Pro C-3 reacts with C-8 to form C-3
C-3 destroys organelles
placed into garbage bags for macrophages so it doesn’t cause immune response
who is the final electron acceptor
oxygen gas
normal concentrations for the following
glucose
sodium
potassium
glucose: 70-100mg/dL
sodium: 135-145 mEq/L
potassium: 3.5-5.5 mmol/L
concentration ranges for the following
hypertonic
isotonic
hypotonic
hyper: >350mOsmol/L
Iso: 270-300mOsmol/L
hypo: <200mOsmol/L
What elements make up the following compartments
vascular
interstitial
intracellular/cellular
vascular: Na and Cl
Interstitial: Na and Cl
cellular: k and PO4
Name the type of movement for the following signaling pathways
autocrine
paracrine
juxtacrine
endocrine
Auto: to itself
Para: to a neighbor
Jux: Through a channel (intestines)
endo: to another organ
This condition causes a deficiency in saliva secretion that is caused by fear, anxiety, dehydration, fever, or drugs
xerostomia
this condition causes the secretion of too much saliva which is brought on by pregnancy, tumors, diseases
sialorhoea
This causes tiny calcium stones on salivary gland
sialolithiasis
what can inhibit saliva secretion
medicine, diabetes, blocked nose, radiotherapy
this is inflammation of the mouth/lips
stomatitis
this is inflammation from a B12 deficiency
glossitis
this causes heart burn (ulcers in esophagus) that is brought on by stomach acid leaking into lower esophagus
pyrosis
this is when the pyloric sphincter doesn’t close (bottom sphincter on stomach)
dumping syndrome
this is when the pyloric sphincter doesn’t open because there isn’t enough nitric oxide to tell muscles to relax. Causes vomiting and is usually found in premies.
pyloric stenosis
This occurs when the stomach isn’t able to squeeze which leads to a liquid diet
gastroparesis
This is caused by H. pylori and it embeds itself into the mucous barrier and eats away
gastric and duodenal ulcers
how do you treat H. Pylori
triple therapy - 2 antibiotics and 1 antacid
This occurs when muscles split and the intestines pop through
hernia
this type of hernia occurs from someone eating too much food and it pops above the diaphragm - needs surgery and is very painful
hiatel hernia
This can happen after TPN and the intestines atrophy
refeeding syndrome
what is it called when there is bacteria growth in the small intestines
C. diff
This is driven by bacteria slipping through the intestinal cells and into the blood - driver for IBD
leaky gut
What is DAMP and PAMP
DAMP: damage response
PAMP: pathogen response
how is the immune response stopped from leaky gut
T-cells release TGFB
is celiacs disease an allergy or autoimmune response
allergy (goes away if gluten is removed)
how does the liver detox blood
liver cells gobble things up as it passes by
this liver cell destroys things that leak from leaky gut
Kupffer cell
This liver cell stores vitamin A
stellate cell
how is fibrosis caused in the liver
stellate cell gets pissed off when there is damage to the cells so it makes collagen to repair the damaged cells resulting in scars
where do xenobiotics go when they make it into the liver
they can bind with bile and then get secreted out with bile
this disease causes thickening of mucous which attracts bacteria that eats through
cystic fibrosis
Explain the harm of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease
fat accumulates on the liver which confuses the cells and stresses it out
what is a hallmark sign that your body isn’t creating enough bile
you poop fat
how can gallstones cause pancreatitis
the stones can clog the pancreas from secreting enzymes - leads to the enzymes breaking down the pancreas
What parts of the pancreas secrete/produce what
Endocrine and Exocrine
endocrine - pancreatic inslet: hormones (insulin and glucagon)
exocrine - lobule: enzymes
how can you measure pancreas damage
there are markers on the liver ALT and AST
bilirubin - jaundice
distended abdomen - fluid buildup
Explain the RAA pathway
angiotensin is released by liver
angiotensin is turned into angiotensin 1 by renin (from kidneys)
angiotensin 1 is turned into angiotensin 2 by ACE (from the lungs)
angiotensin 2 causes constriction of vessels and increases Na and H2O retention
what hormone causes fluid retention
aldosterone
what is RAA supposed to be used for
dehydration
what hormone affects epinephrine and mimics aldosterone
cortisol
what increases the pre-load which results in heart failure
B vitamin deficiency - chronic alcoholics
massive vasodilation from more fluid makes heart work harder
How do we treat heart failure
myocardial infarction - antiplatelet drug (aspirin makes blood less sticky)
massive vasodilators - nitric oxide donor
Name the ABCDE for treatment of heart failure or hypertension
A: angiotensin inhibitor - decrease fxn of angiotensin 2
B: beta adenergic receptors - decreases speed of heart and force of contraction
C: calcium channel blockers - reduces force of contraction and repolarization
D: diuretics/diet/digitalis - decreases blood volume and sodium reabsorption
E: exercise - dilates blood vessels to decrease BP
what does the top and bottom number for blood pressure mean and what is the normal BP
top: systolic - reflex
bottom: diastolic - volume
120/80
How does hardening of the arteries occur?
increased glucose
glycosylation triggers cells to make adhesion molecules
immune cells are recruited
collagen synthesis increases
collagen causes fibrosis of the vessels
what can increase the risk for atherosclerosis
hypertension-vessels dilate so macrophages don’t get ripped off
inactivity
type 2 diabetes
smoking
sleep
why does atrial fibrillation occur
nodes are firing out of rhythm which causes an irregular heart beat
what is commonly associated with atrial fibrillation
stroke - heart can’t fill all the way so it can throw a clot
what are some treatments for atrial fibrillation
pacemaker or ablation - burning the fibers in the atrium
which steals electrons and which donates electrons
steals - oxidant
donates - antioxidant
what is the pathway for oxidation protection in the body
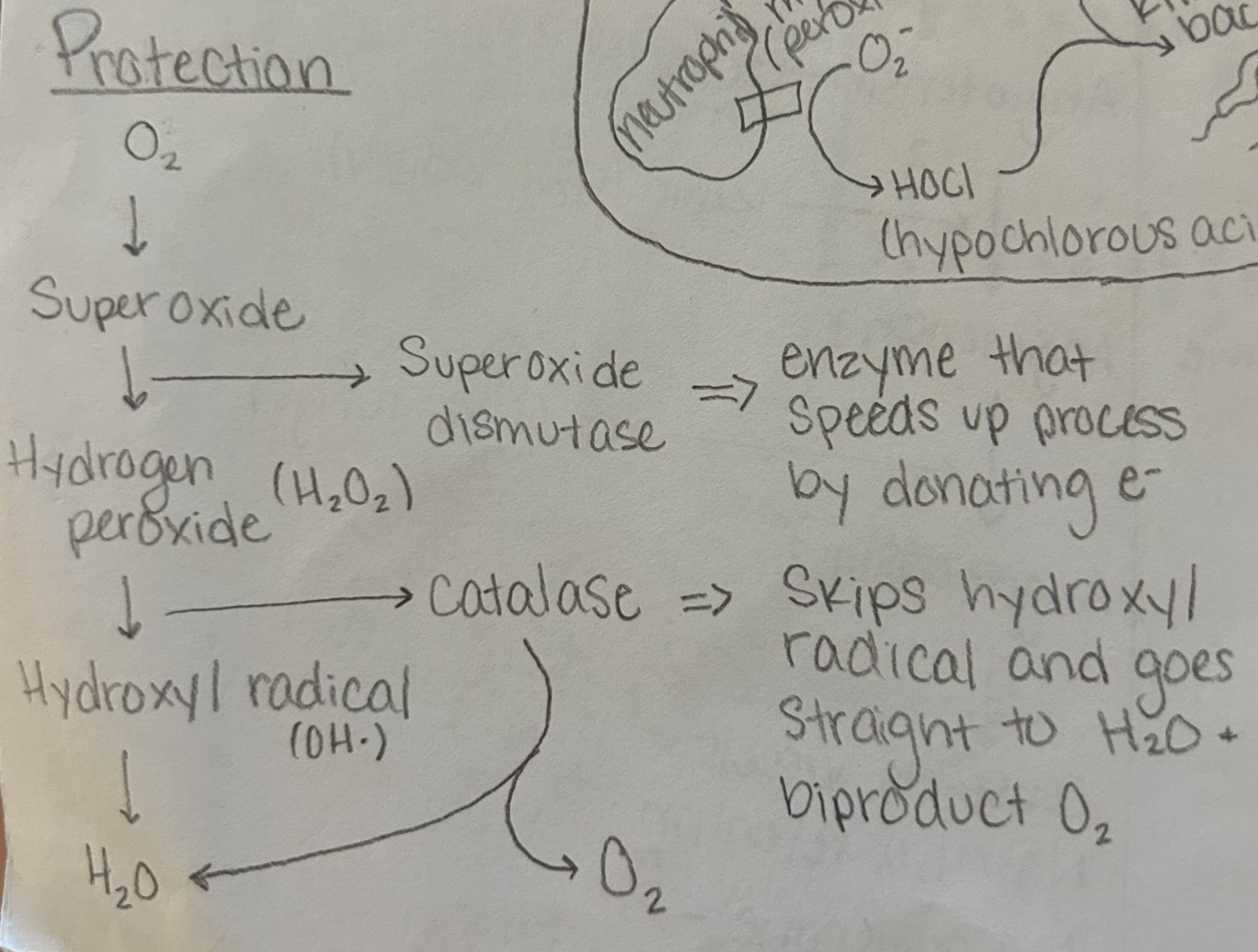
How do oxidants cause damage to proteins
oxidants steal electrons from the little posts on proteins therefore changing it function and structure
how do oxidants cause damage to lipids
oxidants steal electrons from the double bonds on lipids which make them free redicals and it creates a chain event
how can we prevent oxidation in the body
vitamin E - in membrane and it stops the cascade from the lipid radical
benzene ring - electron bounces around within the ring
endegenous antioxidants - antioxidants made by the body such as albumin or glutathione
how do macrophages and neutrophils use oxidation to destroy bacteria
macrophages - NADPH oxidase oxygen into superoxide which kills bacteria
neutrophils - myelo peroxidase turns superoxide into hypochlorous acid which kills bacteria
what is systolic and diastolic mean
systolic - contraction
diastolic - filling in between beats
which artery provides blood to the heart
coronary
how is artery walls different than arteriole walls
there is a layer of smooth muscle that surrounds the muscle of arteriole wall
what is the equation for pressure
pressure = flow x resistance
what is laminar flow
blood drag caused by the walls of the vessel
what is the steps of the heart pumping
atrial filling
atrial squeeze
ventricular filling
ejection
what is the formula for cardiac output
CO = HR x SV
what happens to muscles during strenuous exercise
muscles go anaerobic which overrides epi and causes a release of adenosine. Adenosine causes the blood vessels surrounding that muscle to dilate increasing blood flow.
How does atheroscleosis occur
LDL is oxidized and taken up by macrophage
macrophage then gets sleep and mad so it adheres to the wall of the artery
it then migrates up forming a foam cell
macrophage sends out chemotaxi to call more macrophages to join it
macrophages then pile up causing the artery to close up = plaque
what is myocardial infarction
part of the heart dies because blood flow was cut of from a portion of the heart
what is an angina
heart hurts because it is getting worn out from working so hard
what is the downfall of a stent
the mesh can get sticky which can cause macrophages to attach leading to a heart attack
what is a double bi-pass
veins from other parts of the body are inserted into the coronary artery and past the point of blockage to provide blood flow to the heart
explain congestive heart failure
pressure increases causing the lungs to get leaky. fluid leaks into lungs and causes the person to have a congested sounding cough and swelling in the ankles and feet.