COGSCI 1 Lecture 4: Brain Mapping
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
25 Terms
Central Nervous System (CNS)
Brain + Spinal Cord
Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)
Sensory & Motor neurons connecting the CNS to the body
Sympathetic Nervous System
Division of autonomic nervous system
Controls arousal & energy expenditure functions
Parasympathetic Nervous System
Controls functions during relaxed state
Cerebral Cortex
Information storage, memory;
distinguishes humans from other animals
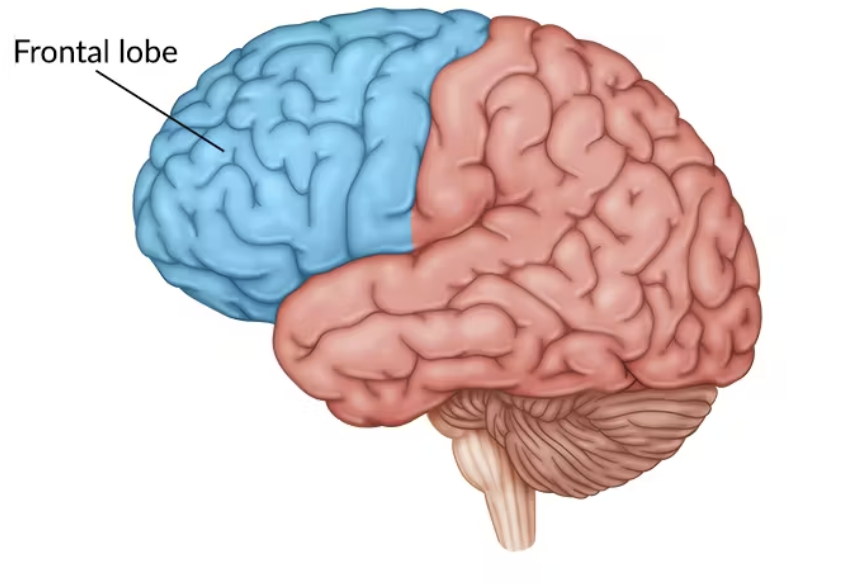
Frontal Lobe
Involved in Speaking, Muscle movements, Plans, Judgements, and Emotional Control
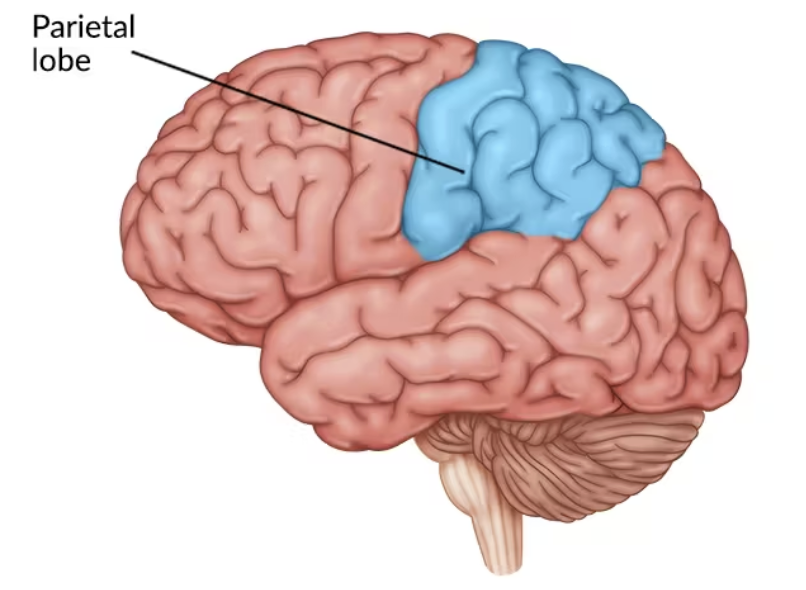
Parietal Lobe
processes sensory input from the body(touch, pain, temperature)
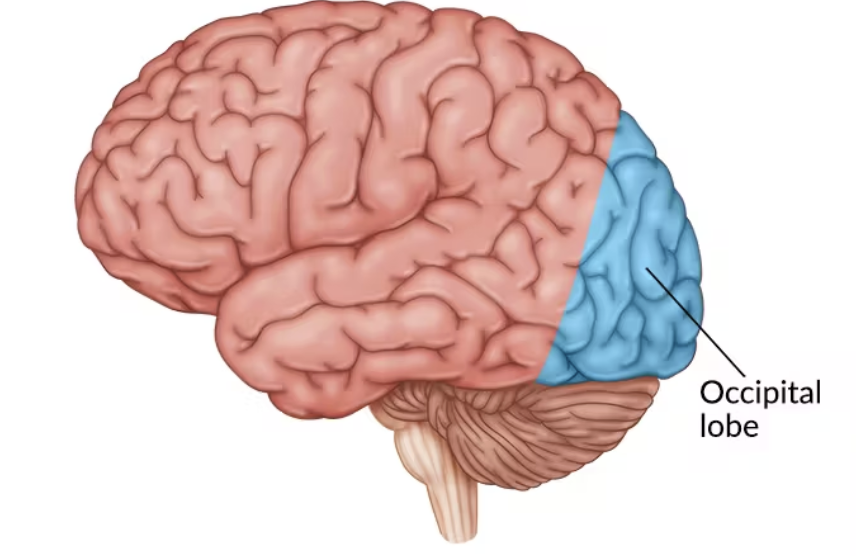
Occipital Lobe
Visual information from the opposite visual field;
includes the primary visual cortex
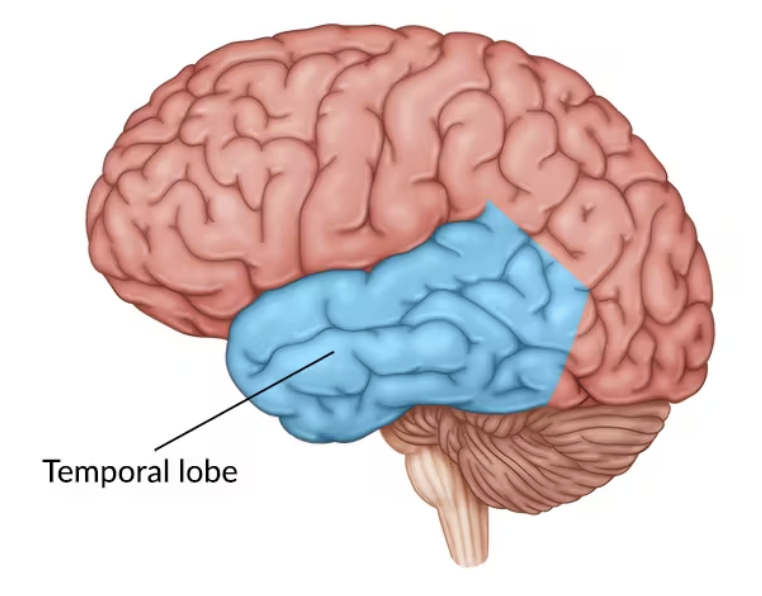
Temporal Lobe
Processes auditory information; includes primary auditory cortex
Aphasia
difficulty in producing or comprehending speech, caused by brain damage
Broca’s Aphasia (Expressive)
Meaningful speach but labored and ungramatical
Wernicke’s Aphasia (Fluent)
Grammatical speech, but meaningless and low comprehension
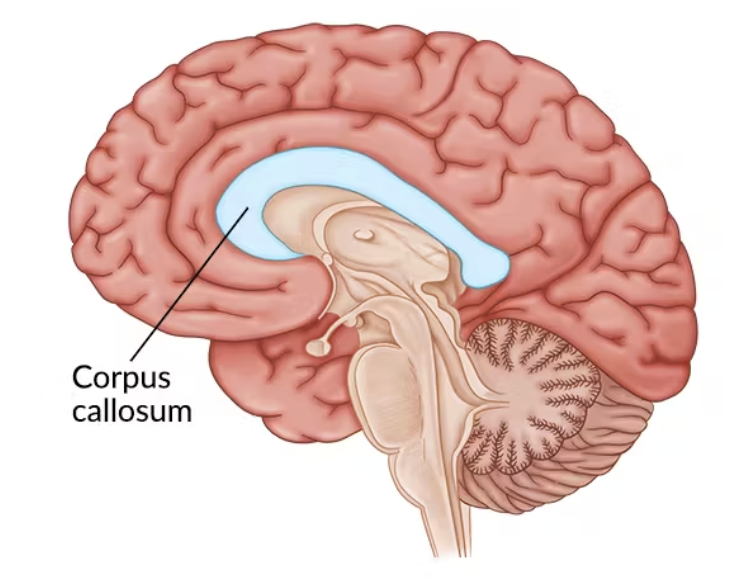
Corpus Callosum
Interconnects corresponding regions of the association cortex on each side of the brain
Left Cerebral Hemisphere
More analytical: Information analysis, event recognition, langauge, math & science
Right Cerebral Hemisphere
More expressive and Creative: Synthesis of Information, Pattern Recognition, Perception, Emotional expression, Arts/Music
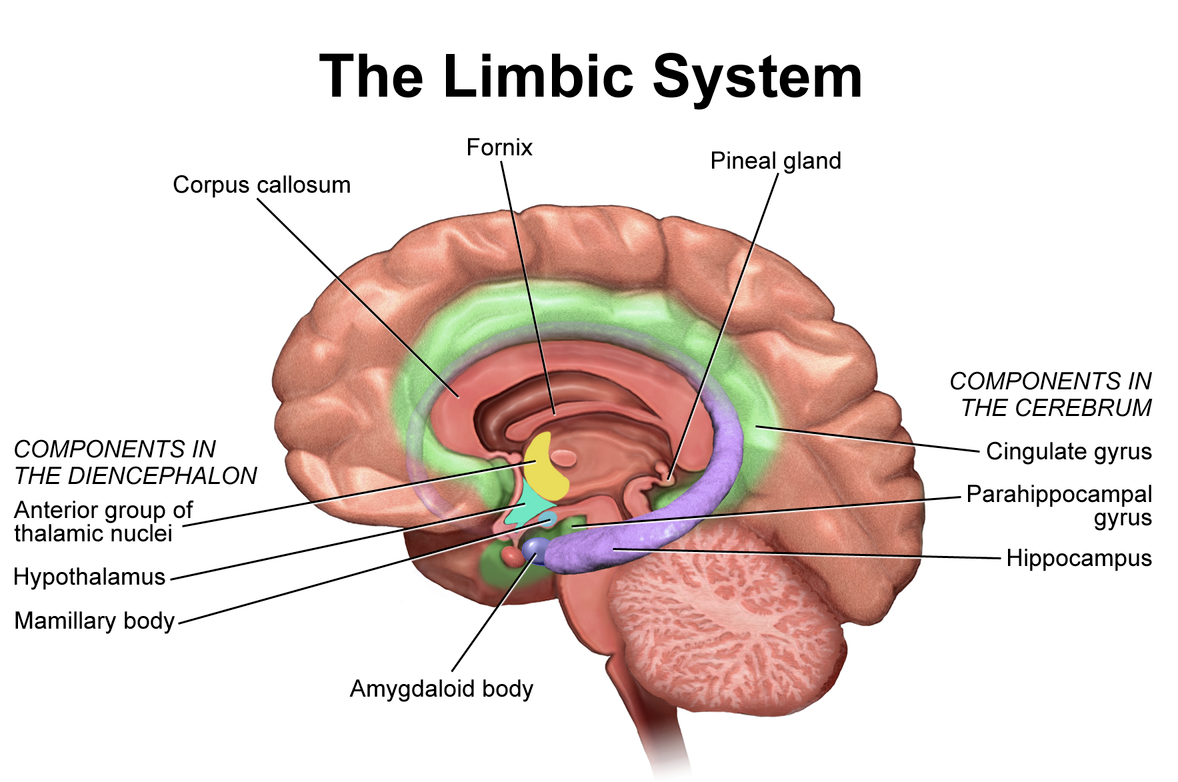
Limbic system
Associatied with emotions and memory; donut shaped
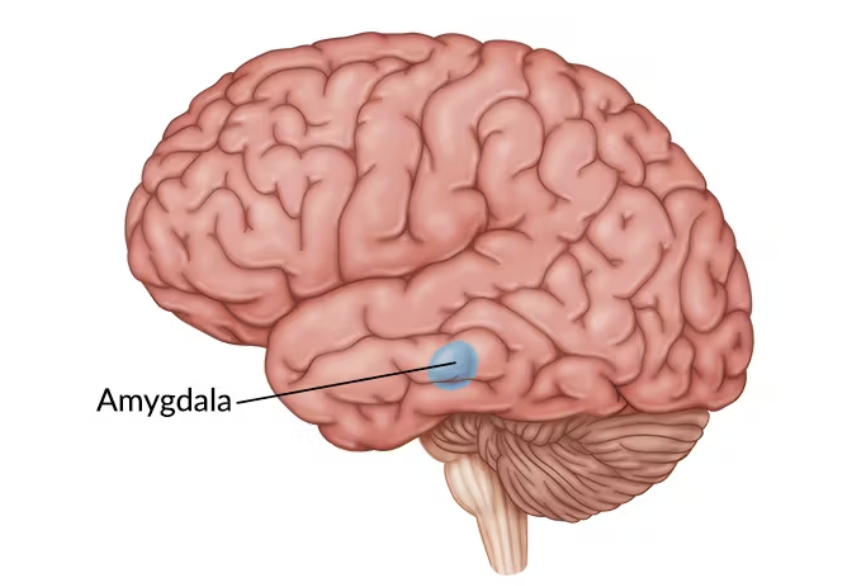
Amygdala
Linked to emotion (fear and aggression specifically)
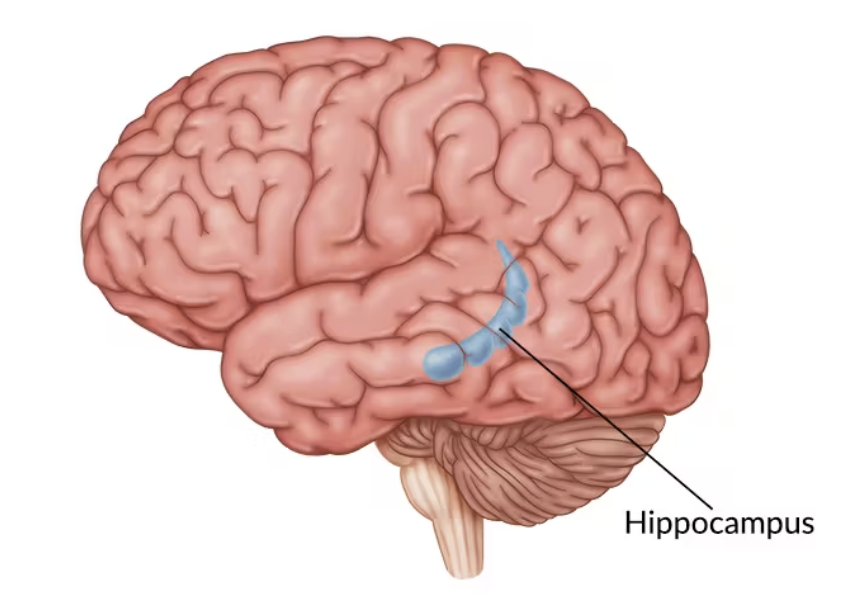
Hippocampus
Important in memory
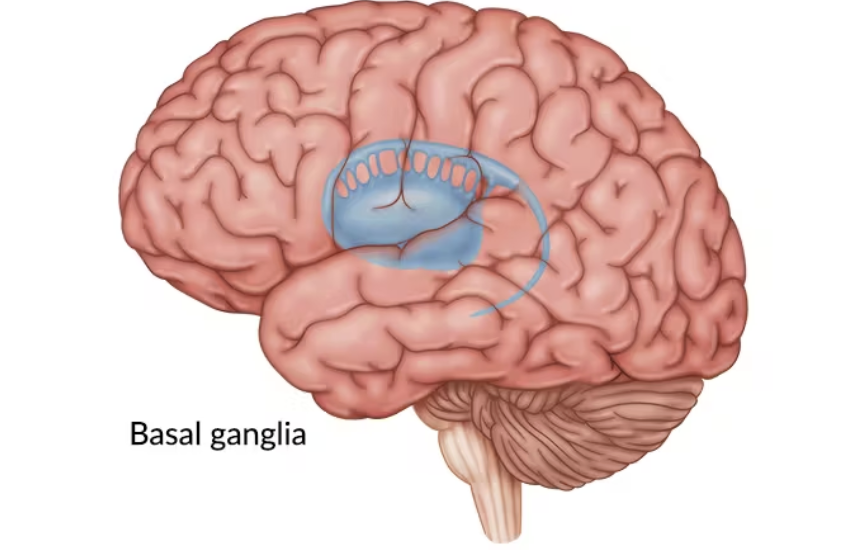
Basal Ganglia
Function: Control of movements
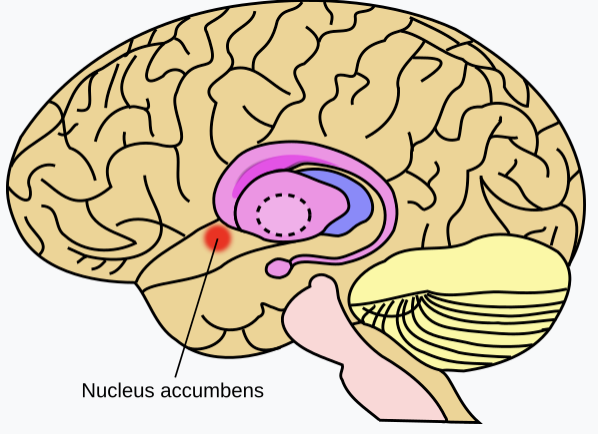
Nucleus Accumbens
Reward Center; Releases Dopamine
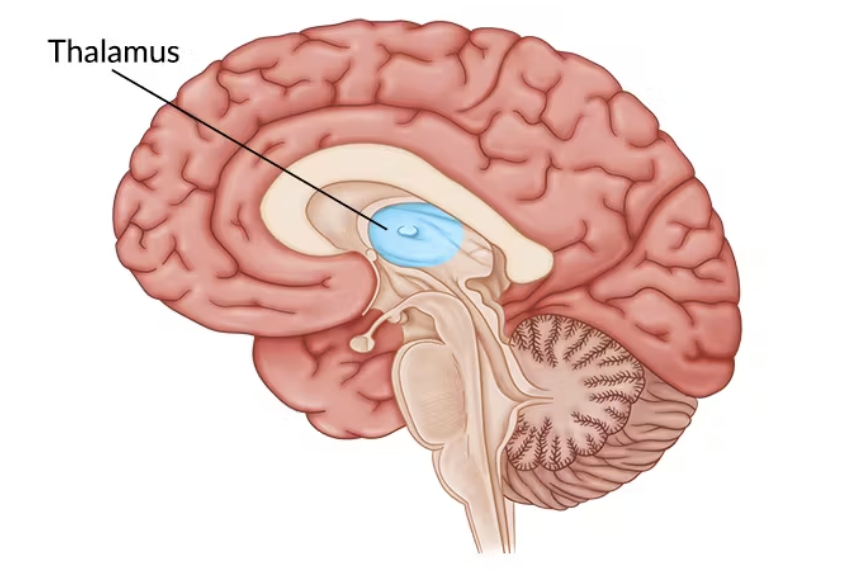
Thalamus
Directs incoming and outgoing information
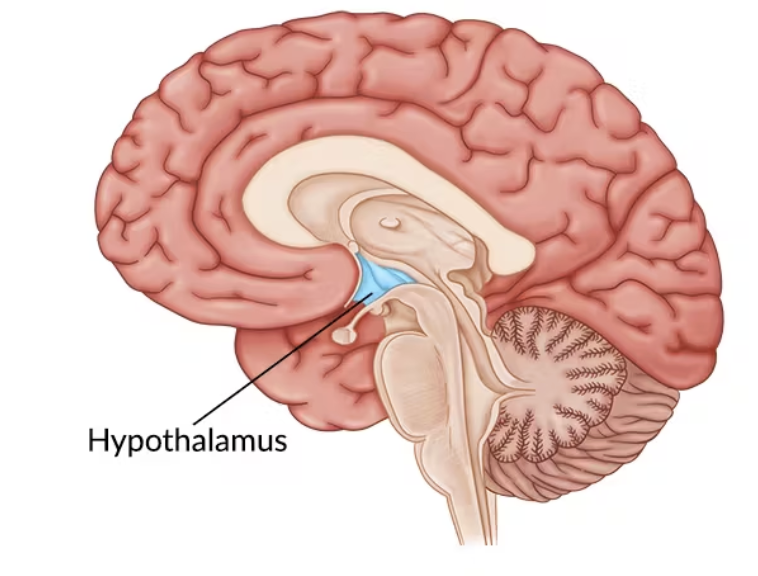
Hypothalamus
Survival Behavior (Four Fs: Fight, Feed, Flee, Fornication); beneath the thalamus
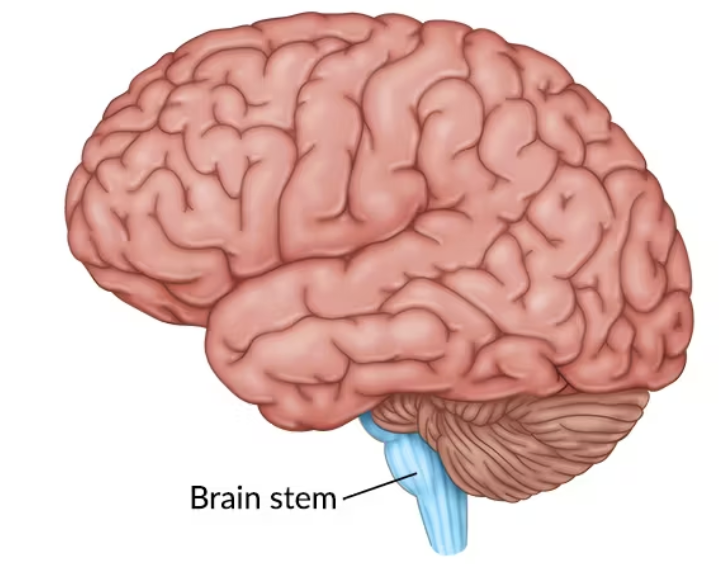
Brain Stem
Responsible for automatic survival functions
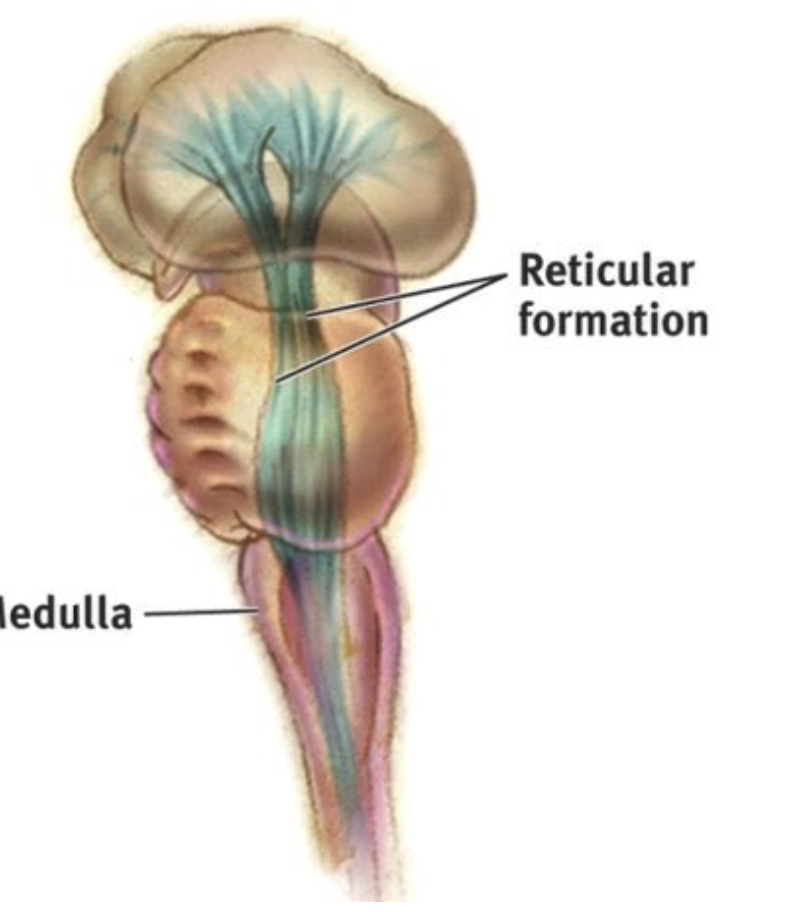
Reticular Formation
Involved in Sleep, Arousal, Attention, Vital Reflexes;
Central part of the brain stem
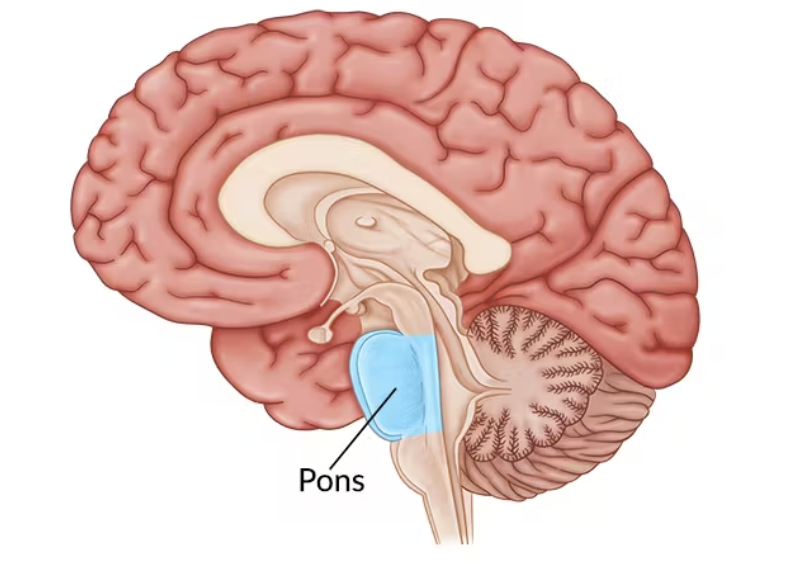
Pons
Part of Reticular Formation;
Important in sleep, arousal, sensory analysis, and movement