Anatomy and Physiology Blood
1/86
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
87 Terms
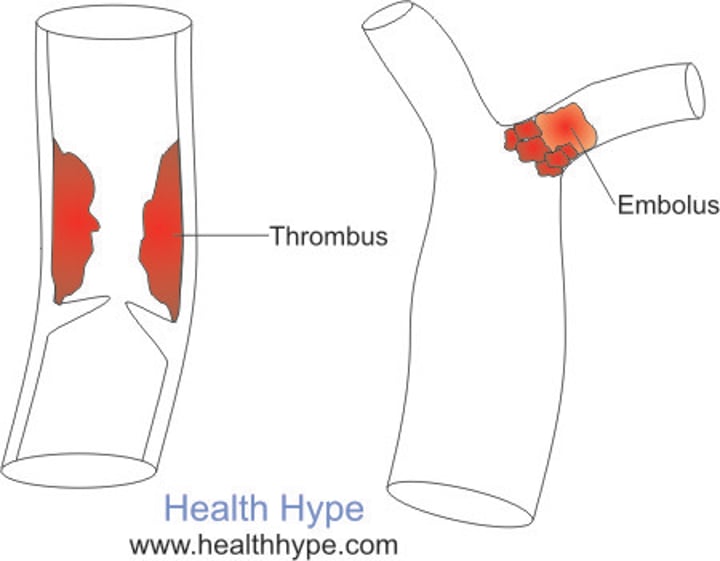
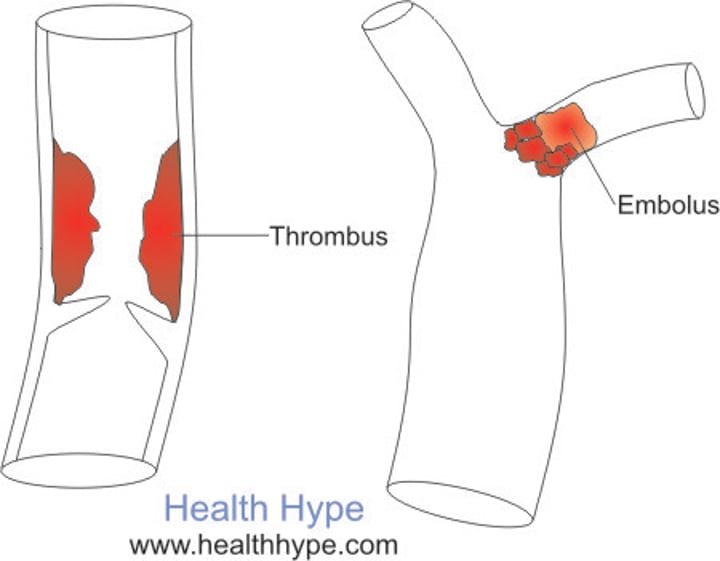
Thrombus
fixed clot that develops and persists in an unbroken blood vessel
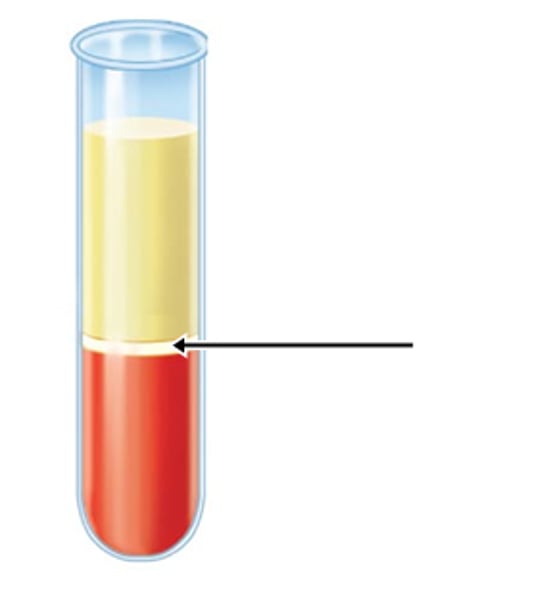
Buffy coat
whitish layer; contains leukocytes and platets
hemophilia
inherited clotting defect caused by absence of blood clotting factor
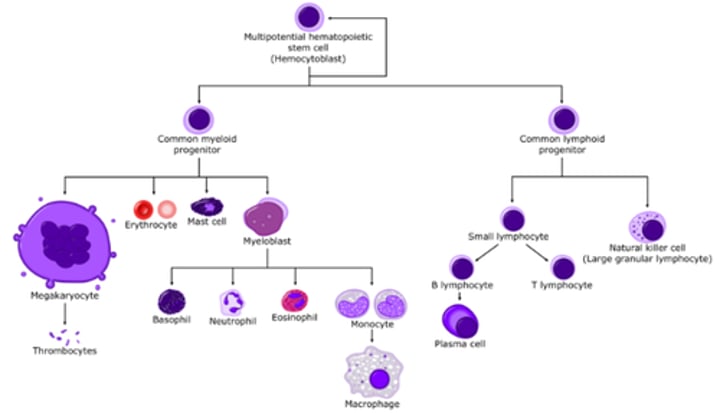
Hemocytoblast
stem cell that creates all formed element cells
Leukocytosis
increased leukocyte count; above 11000; generally indicates a bacterial or viral infection
what is the major constituent of blood
plasma
number of erythrocytes per mm^3
4-6 million
number of leukocytes per mm^3
4000-11000
number of platelets per mm^3
250,000-500,000
what salts are found in plasma
sodium, potassium, calcium, magnesium, chloride, bicarbonate
function of salts in blood plasma
Osmotic balance, pH buffering, regulation of membrane permeability
what is the function of plasma proteins in the blood plasma
osmotic balance, pH buffering, Clotting of blood, Defense, and lipid transport
what nutrients are transported by the blood
glucose, fatty acids, amino acids, vitamins
waht waste products of the metabolism are transported by the blood
urea, uric acid
Why don't erythrocytes have organelles
to provide more space for hemoglobin to transport more oxygen
function of neutrophils
active phagocytes; number increases rapidly during short-term or acute infections
function of eosinophils
Kill parasitic worms; increases during allergy attacks; might phagocytize antigen-antibody complexes and inactivate some inflammatory chemicals
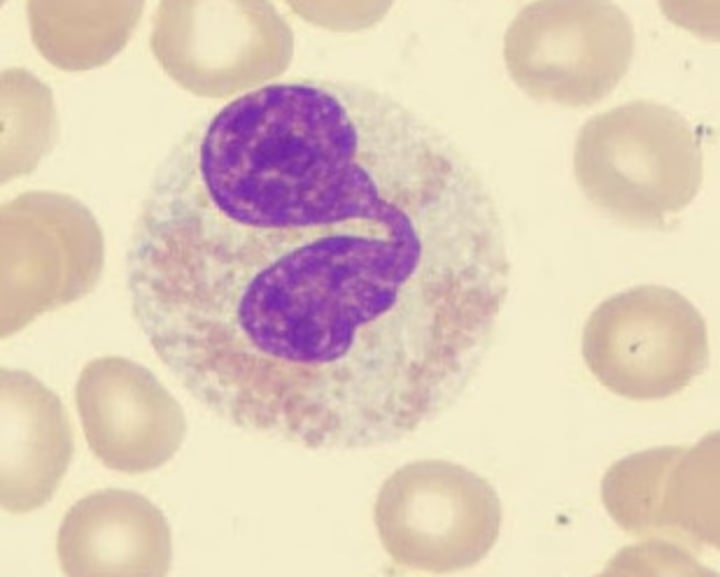
function of lymphocytes
part of immune system; B lymphocytes produce antibodies; T lymphocytes involved in graft rejection, fighting tumors and viruses and activating B lymphocytes
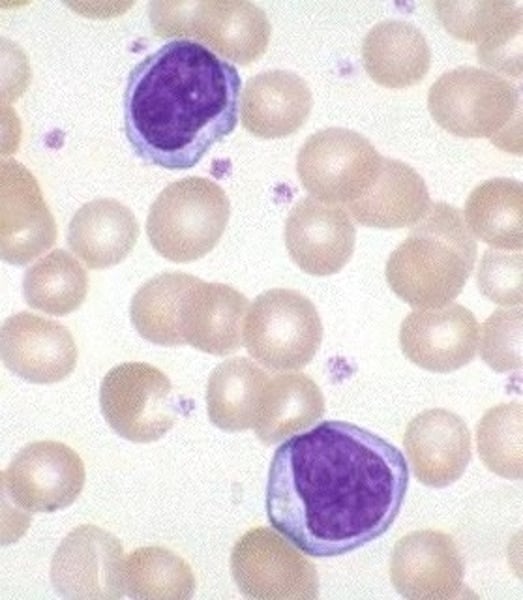
function of monocytes
active phagocytes that become macrophages in tissues; increased number during chronic infections such as tuberculosis; long-term cleanup team
what is the general temperature of blood
arund 100 degrees(98.6 degrees); slightly higher than normal body temperature
physical characteristics of blood
Sticky, opaque, fluid with metallic taste
what stem cell only produces lymphocytes
lymphoid stem cells
what feedback mechanism is responsible for controlling blood production
negative feedback mechanism
what stimulates the production of erythrocytes in Red bone marrow
erythropoietin
what are the Vascular spasms
2nd phase of blood clotting; anchored platelets release serotonin which causes the vessels to go into spasms to narrow the blood vessel and prevent blood vessel
what is coagulation
final step in blood clotting; injured tissues release tissue factor (TF); PF3 (a phospholipid on platelet surfaces) interacts with TF, vitamin K, and other blood protein clotting factors and calcium to form an activator that triggers the clotting cascade; this prothrombin activator converts prothrombin to thrombin enzyme; thrombin joins fibrinogen proteins into long insoluble fibrin and after an hour the slot squeezes serum that seals the gap
what is the role of serotonin in blood clotting
causes blood vessel to go into spasms
what ion is essential for blood clotting
calcium; combines with other substances to form prothrombin activator
how long does blood clotting take
3-6 minutes
what makes up prothrombin activator
PF3, TF, vitamin K, calcium, and other blood protein clotting factors
what makes up fibrin
thrombin and fibrinogen
what are platelets formed from
megakaryocytes; formed in bone marrow
what is hemophilia
hereditary beleeding disorder in which blood fails to clot
how much blood can you lose before there is a danger of shock
30%
what happens in a transfusion reaction
the erythrocytes that were given to the patient are attacked by the immune system; dizzy, kidney shutdown
what determines someones blood type
the antigens on the surface of the Erythrocytes and the antibodies that it produces
what is aggulation
the binding to antibodies which causes erythrocytes to clump
what antigens does type A blood make
A antigens
what antibodies to type A blood make
anti-B antibodies
what antigens does type B blood make
B antigens
what antibodies does type B blood make
anti-A antibodies
what antigens does type AB blood make
anti-A and anti-B antigens
what antibodies does type AB blood make
no antibodies
what antibodies does type O blood make
Anti-A and Anti-B antibodies
what is the most common blood type
O positive
what blood type is the universal recipient; why
Type AB; it does not make antibodies so it will not attack any blood that it recieves
what is Rh
the presence of Rh antigens on erythrocytes
what is the potential problem with a Rh-negative mother and a Rh-positive baby
the mother will make antibodies against the Rh-positive Erythrocytes (Rh is foreign to the mother) and will attack any Rh-positive babies that the mother carries after this one.
How do you treat a Rh-negative mother with a Rh-positive baby
she is given a RhoGAM serum after giving birth to prevent sensitization and a subsequent immune response
Embolus
when a thrombus breaks away from the vessel wall and float freely in the bloodstream
Hemoglobin
and iron-bearing protein that transports oxygen through the blood; found in erythrocytes
coagulation
3rd step of clotting blood
agglutination
binding of antibodies that causes RBC's to clump; found when blood typing (artifical)
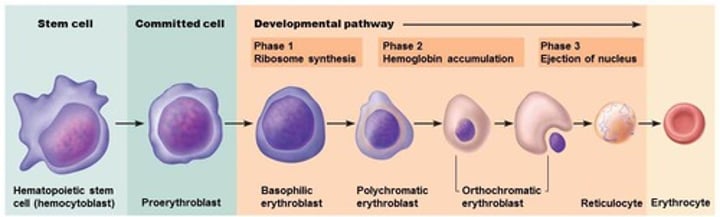
Erythropoiesis
process of making red blood cells
Hemostasis
stoppage of blood flow; platelet plug formation, vascular spasms, coagulation
Diapedesis
ability of Leukocytes to slip into and out of blood vessels
Chemotaxis
Leukocytes ability to locate tissue damage and infection by responding to certain chemicals that diffuse from damaged cells
Hemolysis
rupture of erythrocytes (sickle cell anemia)
Hematocrit
percentage of erythrocytes to total blood volume; 45%
Leukopenia
abnormally low leukocyte count; commonly caused by certain drugs (corticosteroids and anticancer agents)
Plasma (composition)
made of water, salts, plasma proteins, nutrients, waste products, hormones, and respiratory gasses
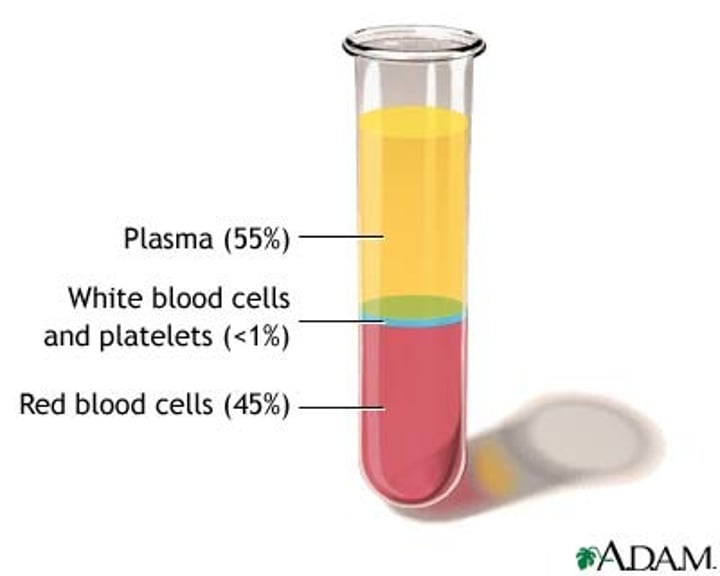
Formed elements (composition)
made of Erythrocytes, Leukocytes, and platelets
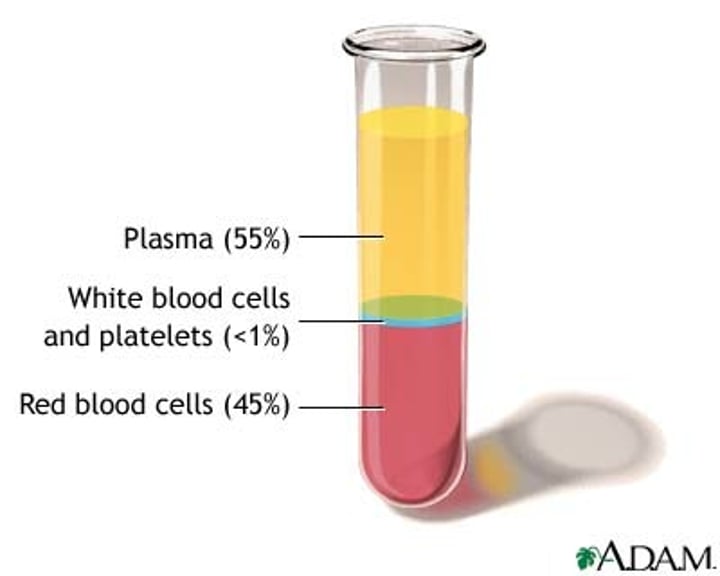
what percentage of blood is plasma?
55%
what percentage of blood is formed elements
45%
function of erythrocytes
transport oxygen and help transport carbon dioxide
function of leukocytes
defense and immunity
function of platelets
blood clotting
function of water in blood plasma
solvent for carrying other substance; absorbs heat
What plasma proteins are found in the blood
Albumin, Fibrinogen, Globulins
what is the Buffy coat composed of
leukocytes and platelets
what type of tissue is blood classified as
Connective tissue
what is thelifespan of a red blood cell
100-120 days
what is the function of hemoglobin
to carry oxygen; one hemoglobin molecule can carry 4 oxygens
function of Basophils
granules contain histamine (vasodilator chemical), which is discharges at sites of inflammation
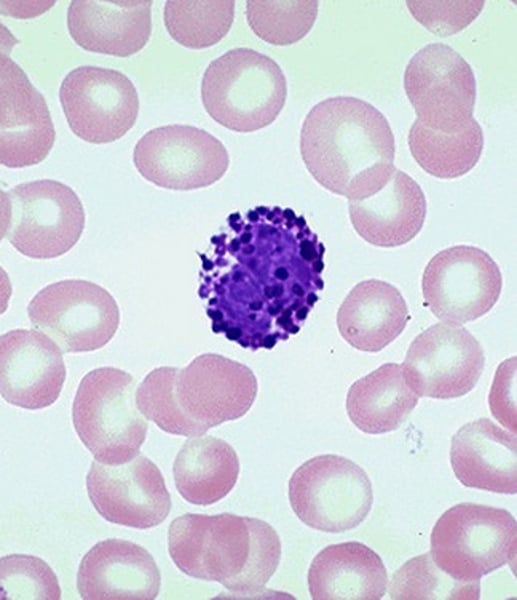
characteristics of granulocytes
lobed nuclei and stained cytoplasm with cytoplasmic granules
characteristics of agranulocytes
no visible granules and more normal nuclei
what is general pH of blood
between 7.35 and 7.45
What stem cell produces all formed elements
hemocytoblast stem cell
what stem cell produces all formed elements except for lymphocytes
myeloid stem cells
what causes the kidneys to release erythropoietin
reduced oxygen levels in the blood
what causes the kidneys to stop the release of erythopoiein
increased oxygen levels in the blood
where is erythropoietin produced
the kidneys
What is platelet plug (white thrombus) formation
1st step in blood clotting; platelets become sticky and cling to damaged site' anchored platelets release chemical to attract more platelets
what is thrombocytopenia
a bleeding disorder that results from an insufficient number of circulating platelets
how is blood typed
mix the blood samples with two different types of immune serum (anti-A and anti-B) and look for clumping in each serum
what antigens does type O blood make
no antigens
what blood type is the universal donor; why
Type O; it does not have any antigens so other blood types' antibodies will not attack it