hematology
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
Hematology
the study of blood
bone marrow
red blood cells
white blood cells
platelets
identification of cells
correlation abnormalities with disease
study of coagulation and hemostasis
intro to hematology
average person has 5 L of blood (5-6 qt)
separated into 3 L of plasma and 2 L of cells
plasma is liquid derived from the intestines and organs
the cells are formed mainly by the bone marrow
the blood can be thought of as a tissue
without plasma, cells cannot circulate
without cells, vascular fluid alone cannot maintain life
cells found in the blood
erythrocytes (red blood cells)
leukocytes (white blood cells)
granulocytes (polymorphonuclear leukocytes)
neutrophils
eosinophils
basophils
no granulocytes 9agranulocytes)
lymphocytes
monocytes
platelets or thrombocytes
why do we study blood?
red blood cell disorders
disorders of RBCs are grouped into
anemias - reduction in circulating red blood cells or decreased hemoglobin concentration
may be due to
blood loss
impaired heme production
impaired DNA synthesis
increased destruction (hemolytic disorders)
polycythemias
abnormal increases in circulating red cells
leading to hyper viscosity
leukocyte disorders
disorders of the leukocytes are termed either
leukocytosis (an increased number of cells)
infections - viral, bacterial, fungal, tubercular
leukemia
leukopenia (a decreased number of cells)
agranulocytosis
granulocytopenia
ionizing radiation
chemotherapy
platelet disorders
thrombocytopenia
a decreased number of platelets
manifests itself in hemorrhage
thrombocytosis
an increased number of platelets
platelet dysfunction
disorders of platelet aggregation
disorders of platelet adhesion
disorders of platelet secretion
collection procedures - skin puncture
capillary blood obtained from:
the tip of a finger or earlobe in adults
lateral heel in infants
tip of the finger in infants over 1 year
properly identify the patient using 3 forms of ID
name, DOB, medical record number, ask them to identify themselves
puncture site is wash with disinfectant (70% isopropyl alcohol)
allowed to air dry
punctured no deeper than 2 mm
using a sterile disposable lancet
dispose in sharps container
skin puncture continued
if povidone-iodine (betadine) is used
must be allowed to dry thoroughly to be effective
first drop of blood is wiped away with sterile gauze
subsequent drops are collected
clinical alert:
avoid squeezing the extremity to obtain blood
doing this will alter composition of blood
hemodilution
venipuncture
venipuncture
necessary for most tests
anti-coagulation
larger quantities of blood
site
median cubital vein
median antebrachial
cephalic
no variation in blood values if specimens are obtained from different veins
procedure for venipuncture
properly identify the patient suing 3 forms of ID
name, DOB, medical record number, ask them to identify themselves
a tourniquet is placed to cause venous congestion
puncture site is cleansed with 70% iso-propyl alcohol and allowed to air dry
the vein is cleanly punctured with a sterile needle
syringe or a vacutainer system
release the tourniquet pressure
remove needle and apply sterile gauze with pressure
make sure patient stops bleeding
cover puncture site with an adhesive bandage
clinical alert
do not allow the tourniquet to remain in place for prolonged periods of time >1 minute
causes hemoconcentration of bloof cells
falsely elevates cell counts
do not collect blood from arm with IV fluids
causes hemodilution
may collect blood from below the IV site or use other arm
blood for legal alcohol testing
do not use alcohol disinfectant
falsely elevates test results
specimens
whole blood
anti-coagulant
plasma
fluid fraction
separated from anti-coagulated blood
serum
fluid fraction
separated from clotted blood
basic blood tests
complete blood count (CBC)
basic screening test in all patients
one of the most frequently ordered lab procedures
CBC consists of
White blood count (WBC)
Red blood count (RBC)
Hematocrit (HCT)
Hemoglobin (Hgb)
Red blood cell indices
Mean corpuscular volume (MCV)
Mean corpuscular hemoglobin (MCH)
Mean corpuscular hemoglobin concentration (MCHC)
Red cell distribution width, (RDW)
Platelet count (often included in CBC)
White cell Differential count (Diff)
White cell Differential count (Diff)
Ethylene-diamine tetra acetic acid (K2EDTA)
Purple top tube
Calcium chelator
preventing coagulation to occur.
Used in cell counts and morphologic examination
Blood smears should be made & examined within 2
hours of collection.
Alert:
EDTA-induced pseudothrombocytopenia
Platelet clumping may occur
“EDTA phenomenon”
Platelet Satelitism
Collect blood in Citrate tube, repeat PLT count
sodium citrate
Blue top tube
Calcium chelator
Used in coagulation studies
Blood to anticoagulant ration must be 9:1
Low specimen ratio, elevates coag results
Used in Platelet Satellitism
Platelet count has to be multipled by 1.1 in order to correct for
anticoagulant volume
heparin
Green top tube
Lithium Heparin
Mechanism of action:
inhibits the action of thrombin.
Anti-thrombin activity
Used for most chemical testing and
Not recommended for hematology testing
Heparin distorts cellular morphology
Interferes with coagulation studies.
Not recommended for Lithium assays.
Falsely elevates Li values
Used in treatment of Bi-polar disorders
quality management system
QMS in the laboratory includes all processes,
procedures and resources to ensure quality
results
Quality Assurance focuses on the processes
Provide the best services to maintaining
excellence in patient care
It is the sum of three components:
Pre-analytical
Analytical
Post analytical
Pre-analytical
Test Utilization
Correct ordering of tests
Patient Preparation
Patient Identification
Proper Collection of Specimen
Timely Specimen Transport
Proper Specimen Handling
Specimen Separation
Proper Personnel Education & training
Analytical
Proper storage, labeling and use of reagents
Calibration of pipetting devices
Preventative maintenance of instruments
Checking temperatures of refrigerators/incubators
Periodic checking of centrifuge speeds
Analytical Methodology verification
Use of Standards and Calibration
Procedures Manuals are up to date
Verification of Reference intervals
Technical Staff Competencies
Inventory Control of Materials
Monitoring Method Problems and Remedies
post analytical
Verification of Final Reports
Review of test results for possible errors
Reports that are easy to read and interpret
Procedures for informing the physician of results
that require immediate attention (critical values)
Timeliness of reporting values to patient charts
Constant interaction with the institution to ensure
quality in direct patient care as a result of lab
testing
types of quality control
internal
continuous evaluation of reliability of the daily works of the lab with validation of tests
primary tool required is called a control - a specimen with a predetermined range of result values, processed in the same manner as patient sample
if the result of a test on a control sample is different from its known value, this indicates a problem in the equipment or the methods being used
external
evaluation by an outside agency of the comparability a laboratory’s testing to a source outside the laboratory
this comparison can be made to the performance of a peer group of laboratories or to the performance of a reference laboratory
the analysis of performance is retrospective
internal quality control
physical measurement of assayed controls
every 8 hours, run 2 levels of controls
one level within the normal range, one level outside the normal range
application of statistical analysis of quality assurance
moving average of RBC indices
delta check
control material
needs to have same matrix as patient specimen
acceptable limits predetermined by manufacturer
within 2 SD or two standard deviations of given mean
plotted on LEvy-Jenning’s Chart
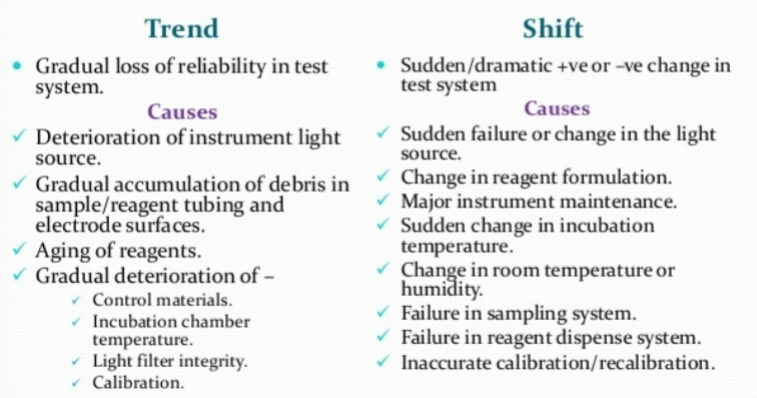
westgard rules
accuracy
describes how close a test result is to the true value
implies freedom of error
precision
describes how close the test results are to one another when repeat analysis of specimens is performed
precision refers to the reproducibility of test methods and results
precision is freedom from variation
accuracy and precision
accuracy is a measure of rightness
refers to closeness to the true value
precision is measure of exactness
refers to reproducibility of the test
basic statistical concepts
mean - arithmetic average value of a group of data
mean = Ex/n
standard deviation
expression of variation of data around the mean
measure of variability or precision of a test method
SD = √variance
coefficient of variation
Expression of the standard deviation
as a percentage of the mean
Useful for comparison of data sets
with different units
Levy Jennings Control Charts
QC charts graphically display data values versus time.
Confidence limits or control limits are calculated from the
mean and SD:
Mean ± 2 SD = 95% confidence limits
Control values are plotted on the y axis; time is plotted on
the x axis.
The mean is plotted as a center line with the + 2SD above
and the - 2SD below the mean.
Within the confidence limits, control results are assumed to
be accurate.
If control results are outside the Confidence limits, it said
to be “out of control”
- Patient results cannot be reported
Errors