Economics, Microeconomics, 2.7 Government Intervention
1/32
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
33 Terms
Productive efficiency
A society is not wasting resources and producing with the lowest possible cost/fewest resources
Allocative efficiency
producing the perfect combination of goods wanted by society
Indirect tax =
Tax imposed on expenditure (e.g., an excise tax; sales taxes such as a “goods and services tax” [GST] or “value added tax” [VAT])
indirect taxes cause two things:
Allows government to gain extra revenue
Discourages consumption of a certain good or service
There are two types of indirect taxes:
Specific tax: fixed amount of tax imposed on a product (e.g., $1 per unit)
Ad valorem (percentage) tax: tax is a percentage of the selling price (increases as price of product rises)
Taxes will raise firms’
cost of production which will affect the supply curve on graphs
Tax incidence refers to
who pays what share of a tax
Who pays what share of a tax depends on the elasticity of the product
If PED is greater than PES
producers bear the majority of the tax burden
If PES is greater than PED
consumers bear the majority of the tax burden
The more price inelastic a product is
the more consumers pay the tax burden
The more price elastic a product is
the more producers pay the tax burden
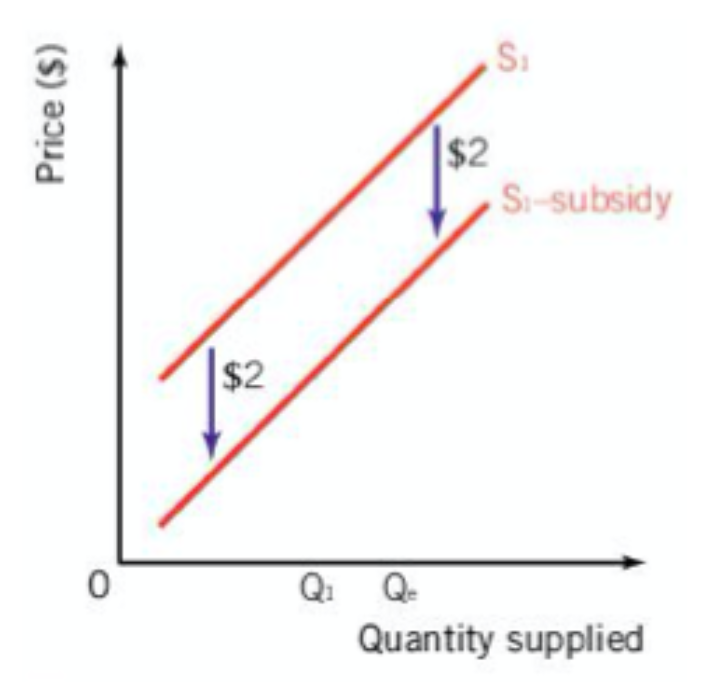
A Subsidy is
money paid by the government to a firm
subsidies are given to firms so that:
Lower prices for consumers
Guarantee supply of products the government thinks are necessary for the economy
Enable domestic producers to compete with international producers
A subsidy reduces production costs for firms
causing a rightward (or outward) shift of the supply curve
subsidies for producers result in
lower prices and increased output
subsidies for consumers result in
consumers paying lower prices but there may be an increase in expenditure that may offset it
subsidies for the government result in
consumers paying lower prices for goods
from subsidies, both consumers and producers gain
surplus
when subsidies are implemented there is an opportunity cost on the
government
due to over-allocating resources because of the subsidy
allocative inefficiency occures
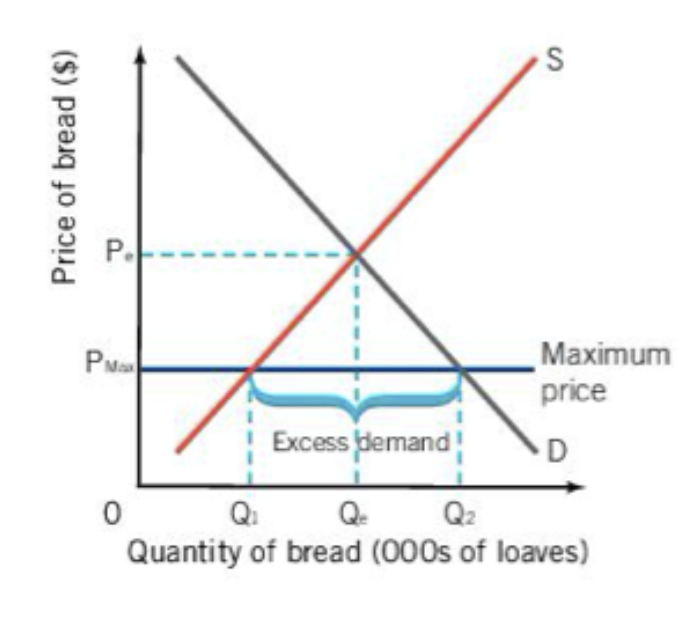
when governments set a maximum price on a product it is a called a
price ceiling
price celings are usually placed on
necessities (merit goods)
A price ceiling usually creates a
shortage--demand is much higher than supply
price ceilings will also lead to
parallel markets
long lines/waitlists for certain products
a government can reduce a price ceiling induced shortage by
Offer subsidies to firms to encourage production
Government production of the product (direct provision)
Release stored goods on the market (only for non-perishable goods, and given they had previously stored some of the product)
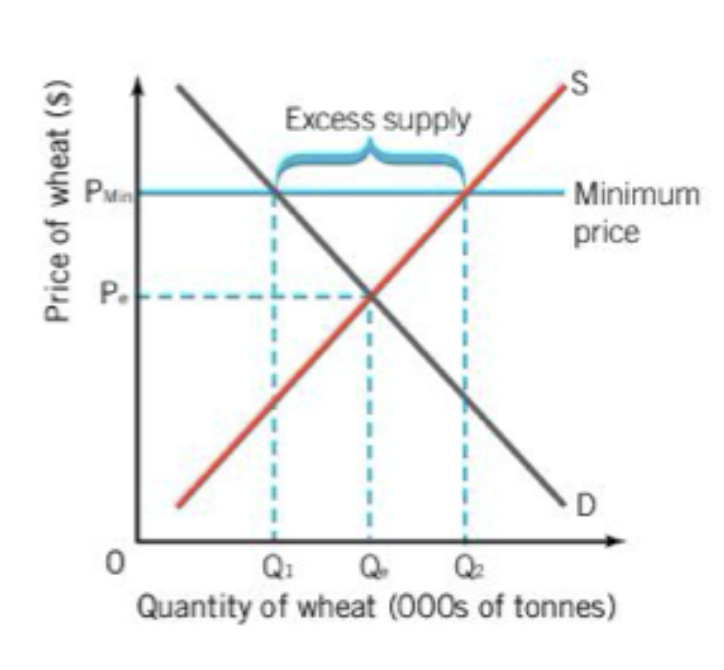
when governments set a minimum price on a product it is called a
price floor
price floors are done to benefit
producers and workers
producers see the benefit from price floors by
Raising income for producers and can be a protection against supply shocks, especially producers of commodities
workers see the benefit from price floors by
Having a minimum wage to ensure a higher standard of living
Governments will also impose minimum prices to
discourage consumption of demerit goods (products that can have harmful effects to society and are overprovided by the free market)
Price floors usually lead to
excess supply, or a surplus, that will lead to reduced consumption (demand)
there are problems with a surplus such as
Reduced demand leads to less revenue for companies
Surplus will eventually cause firms to try to get around the price controls to get rid of the surplus
Inefficiency/waste of resources
governments can solve the surpluses with actions such as
Government can buy the surplus and store it (if it is non-perishable, but storage is expensive)
Impose a quota
Attempt to increase demand for the product
“Dump” the surplus by selling on the international market