Ch 2: Enzymes (14%)
1/77
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
78 Terms
Oxidoreductases
Name the Enzyme Class
WORD BANK: Transferases, Lyases, Hydrolases, Oxidoreductases, Ligases, Isomerases
——
Catalyze oxidation-reduction reactions
Often have a cofactor that acts as an electron carrier, such as NAD+ or NADP+
Include dehydrogenases, reductases, and oxidases
Transferases
Name the Enzyme Class
WORD BANK: Transferases, Lyases, Hydrolases, Oxidoreductases, Ligases, Isomerases
——
Catalyze the movement of a functional group from one molecule to another
Includes kinases → catalyze the transfer of a phosphate group (generally from ATP) to another molecule
Hydrolases
Name the Enzyme Class
WORD BANK: Transferases, Lyases, Hydrolases, Oxidoreductases, Ligases, Isomerases
——
Catalyze the breaking of a compound into two molecules using the addition of water
Includes phosphatase, peptidases, nucleases, and lipases
Lyases
Name the Enzyme Class
WORD BANK: Transferases, Lyases, Hydrolases, Oxidoreductases, Ligases, Isomerases
——
Catalyze the cleavage of a single molecule into two products
Do not require water
Can also catalyze the synthesis of two molecules into a single molecule, but they are referred to as synthases in this case
Isomerases
Name the Enzyme Class
WORD BANK: Transferases, Lyases, Hydrolases, Oxidoreductases, Ligases, Isomerases
——
Catalyze the rearrangement of bonds within a molecule
Catalyze reactions between stereoisomers and constitutional isomers
Ligases
Name the Enzyme Class
WORD BANK: Transferases, Lyases, Hydrolases, Oxidoreductases, Ligases, Isomerases
——
Catalyze addition or synthesis reactions generally between large similar molecules
Often require ATP
Most likely to be encountered in nucleic acid synthesis and repair on Test Day
overall change in free energy, equilibrium
What 2 things in a reaction do enzymes NOT change?
lower the activation energy to increase reaction rate (make it easier for the substrate to reach the transition state)
What do enzymes do in reactions?
B complex vitamins, vitamin C (ascorbic acid)
WORD BANK: Vitamin K, Vitamin D, Vitamin C (ascorbic acid), Vitamin D, Vitamin A, Vitamin E, B Complex Vitamins
——
name the 2 types of water-soluble vitamins that can act as cofactors
vitamin A, vitamin D, vitamin E, vitamin K
WORD BANK: Vitamin K, Vitamin D, Vitamin C (ascorbic acid), Vitamin D, Vitamin A, Vitamin E, B Complex Vitamins
——
name the 4 types of fat-soluble vitamins that can act as cofactors
temperature, pH, salinity
name the 3 environmental factors that influence enzyme activity
Feedback Inhibition (Negative Feedback Regulation)
when the concentration of a product LATER in the metabolic pathway inhibits an enzyme EARLIER in the pathway
increase temperature, decrease activation energy
What are the 2 ways to increase the rate of a reaction?
activation energy
the minimum amount of energy it takes to pass over the transition state, meaning the reaction can proceed
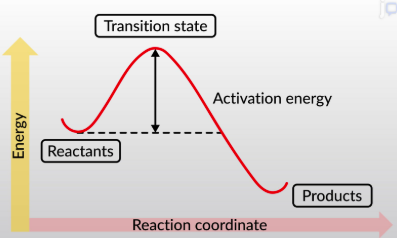
increase, lowering
Enzymes ________ reaction rates by _________ transition state energies
both directions
A catalyst lowers the activation energy in _____ __________
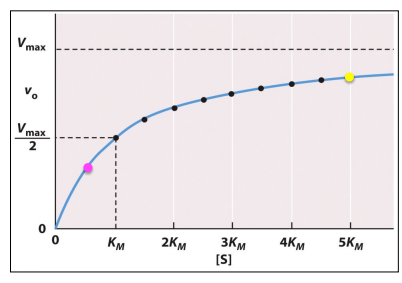
Vmax
Enzyme Kinetics
The maximum rate of the reaction achieved when all enzyme active sites are saturated with substrate
Appears as a horizontal asymptote on a Michaelis-Menten plot
total amount of enzyme
Enzyme Kinetics
What does Vmax depend on?
Km
Enzyme Kinetics
Michaelis constant
A measure of the affinity of an enzyme for its substrate
Measures how easily an enzyme-substrate complex forms
The substrate concentration required for the reaction rate to = ½ Vmax
lower/weaker, it requires a higher substrate concentration to be half-saturated
Enzyme Kinetics
Do enzymes with HIGH Km’s have a HIGHER/STRONGER or LOWER/WEAKER affinity for its substrate?
Why?
higher/stronger, it requires a lower substrate concentration to be half-saturated
Enzyme Kinetics
Do enzymes with LOW Km’s have a HIGHER/STRONGER or LOWER/WEAKER affinity for its substrate?
Why?
greater
(*** at low concentrations (< Km), the reaction rate is very sensitive to changes in [S])
Enzyme Kinetics
Will changes in substrate concentration have a GREATER or LESSER effect on reaction rate when the substrate concentration is less than Km ([S] < Km)?
lesser
(*** at high concentrations (> Km), the reaction rate is less responsive to changes in [S])
Enzyme Kinetics
Will changes in substrate concentration have a GREATER or LESSER effect on reaction rate when the substrate concentration is more than Km ([S] > Km)?

pic

Enzyme Kinetics
What is the general enzyme-substrate complex formula? (answer in pic)
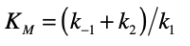
(rate of substrate/enzyme complex dissociation + rate of product formation) / rate of enzyme/substrate complex formation
Enzyme Kinetics
write out the formula for Km using the rate constants

high, saturated, [S]»Km
Enzyme Kinetics
Does Vmax occur at low or high substrate concentration?
In this state, is the enzyme saturated or unsaturated?
In this state, what is the relationship between [S] and Km?
![<p><u>Enzyme Kinetics</u></p><p>Does <em>V<sub>max</sub> </em>occur at low or high substrate concentration?</p><p>In this state, is the enzyme saturated or unsaturated?</p><p>In this state, what is the relationship between <em>[S] </em>and <em>K<sub>m</sub></em>?</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/86d4b53d-5734-4c1f-b5e0-2c5d09177db1.png)
![<p>(Vmax x [S]) / (Km + [S])</p><img src="https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/69b5bb21-1a60-4020-9dfd-83fde41fca69.png" data-width="100%" data-align="center" alt="knowt flashcard image"><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/69b5bb21-1a60-4020-9dfd-83fde41fca69.png)
(Vmax x [S]) / (Km + [S])
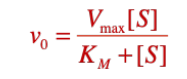
Enzyme Kinetics
write out the Michaelis-Menten equation
properties, enzyme
Enzyme Kinetics
The unknowns Vmax and Km are ____________ of the particular __________
Km = [S]
Enzyme Kinetics
write out the relationship between Km and [S] when the reaction velocity = ½ Vmax
![<p><u>Enzyme Kinetics</u></p><p>write out the relationship between <em>K<sub>m</sub></em> and <em>[S]</em> when the reaction velocity = ½ <em>V<sub>max</sub></em></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/3865dcfb-7c56-407a-94e6-ff58ec32b663.png)
higher, lower
Enzyme Kinetics
More efficient enzymes have ________ Vmax’s and _______ Km’s which gives you a faster reaction rate for a given level of substrate
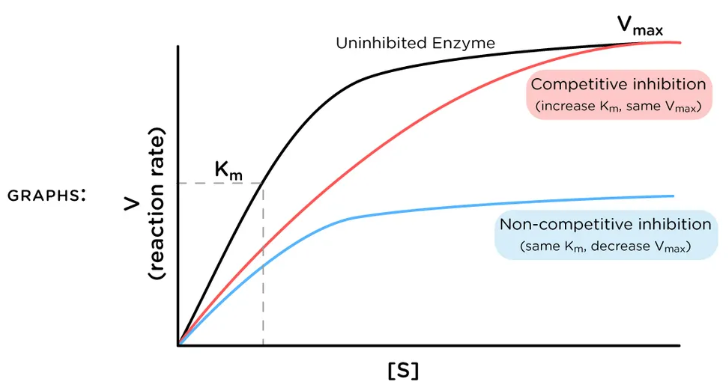
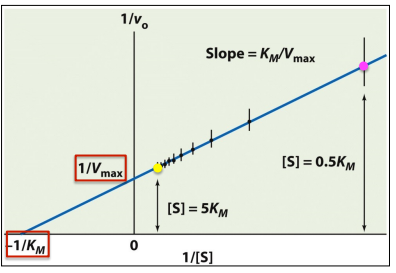
Michaelis-Menten
Enzyme Kinetics
Michaelis-Menten vs. Lineweaver-Burk Plot
displays a hyperbolic curve
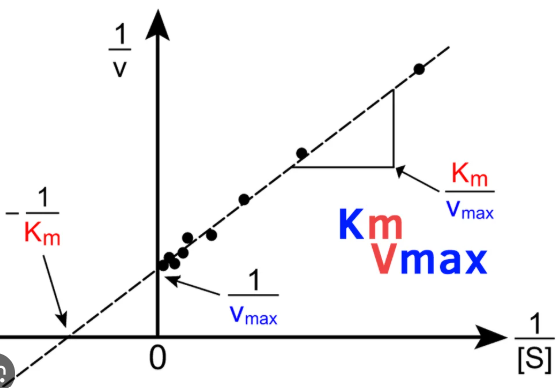
Lineweaver-Burk
Enzyme Kinetics
Michaelis-Menten vs. Lineweaver-Burk Plot
displays a linear function
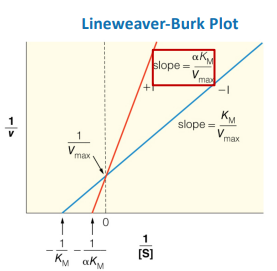
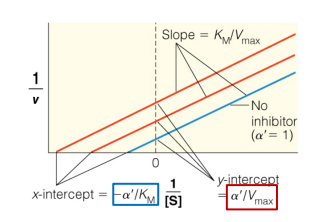
Km/Vmax
Enzyme Kinetics
write out the formula for calculating the slope of a Lineweaver-Burk plot
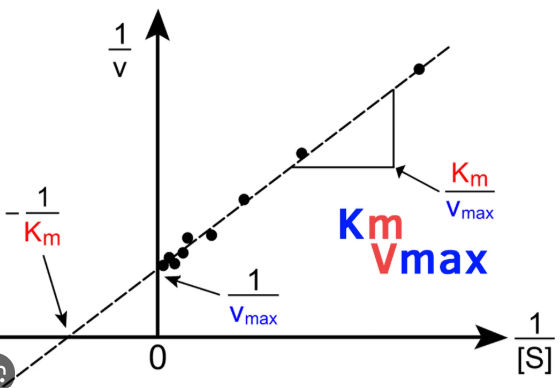
1/Vmax
Enzyme Kinetics
write out the formula for calculating the y-intercept of a Lineweaver-Burk plot
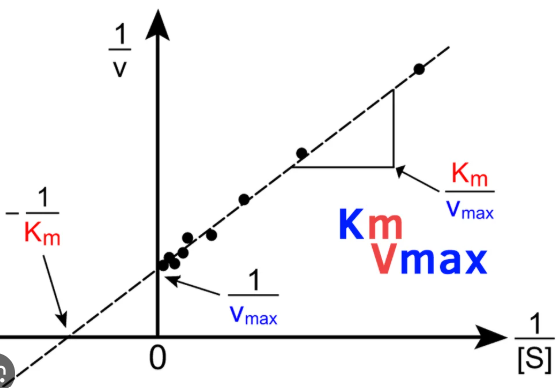
-1/Km
Enzyme Kinetics
write out the formula for calculating the x-intercept of a Lineweaver-Burk plot
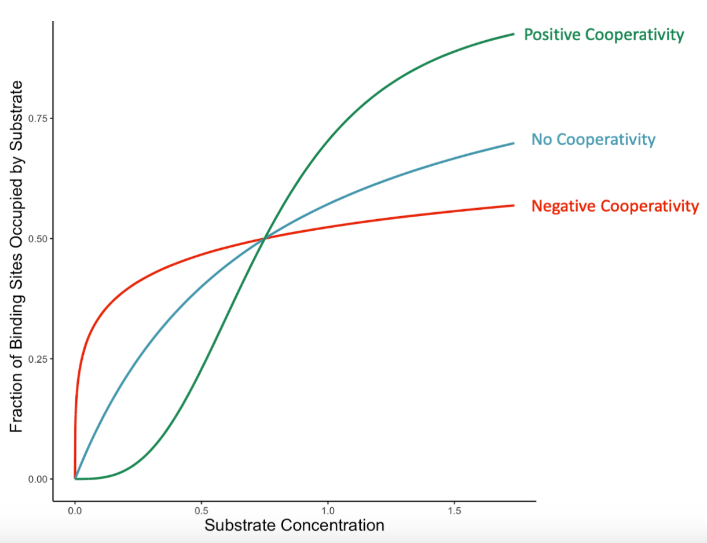
cooperativity
Enzyme Kinetics
enzymes that display THIS characteristic (ex: hemoglobin) have a sigmoidal (S-shaped) Michaelis-Menten graph
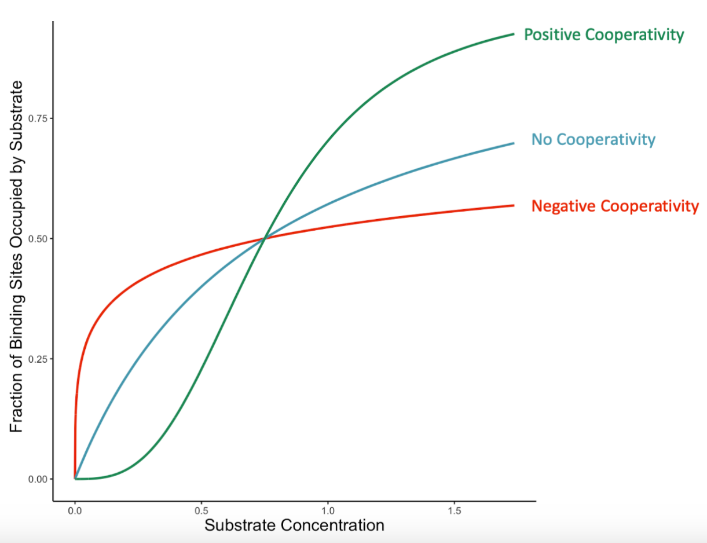
cooperativity

Enzyme Kinetics
the phenomenon where the binding of a substrate molecule to one subunit of a multi-subunit enzyme influences the enzyme's affinity for additional substrates
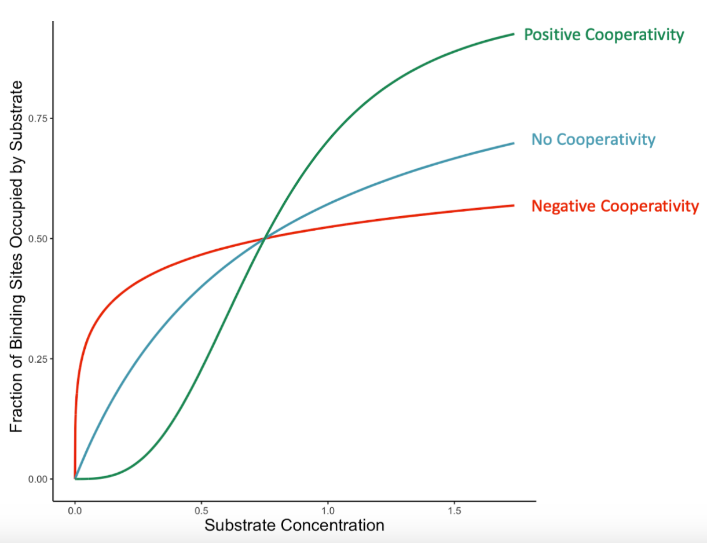
>1
Enzyme Kinetics: <1 vs. =1 vs. >1
Hill’s coefficient when POSITIVE cooperative binding is occurring → After one ligand is bound the affinity of the enzyme for further ligands increases
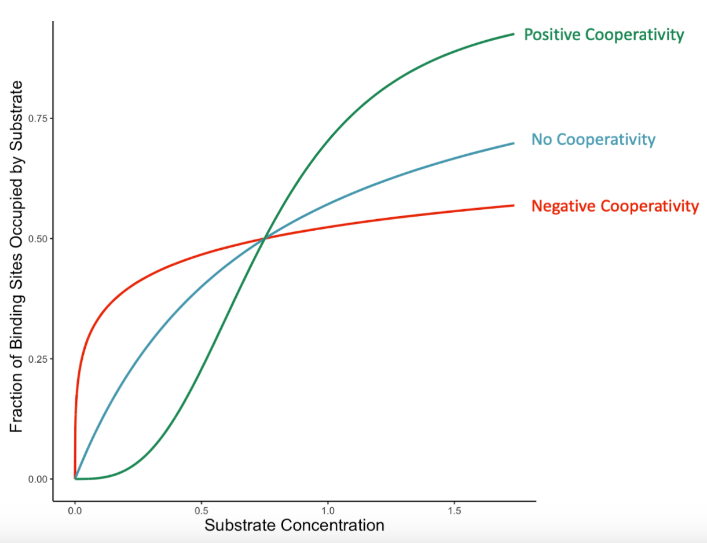
<1
Enzyme Kinetics: <1 vs. =1 vs. >1
Hill’s coefficient when NEGATIVE cooperative binding is occurring → After one ligand is bound the affinity of the enzyme for further ligands decreases
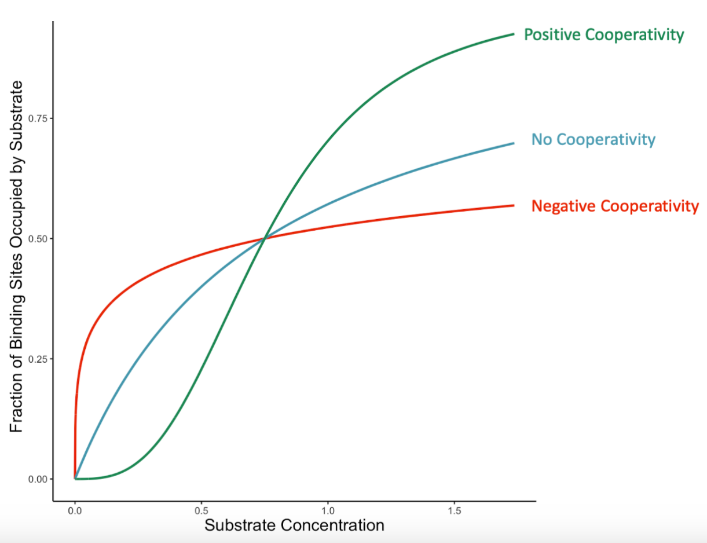
= 1
Enzyme Kinetics: <1 vs. =1 vs. >1
Hill’s coefficient when the enzyme does NOT exhibit cooperative binding
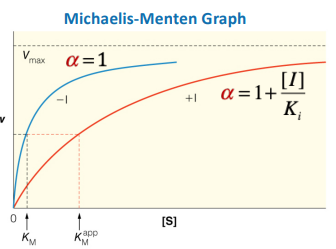
Michaelis-Menten graph
Michaelis-Menten Graph vs. Lineweaver-Burk Plot
What is this a picture of?
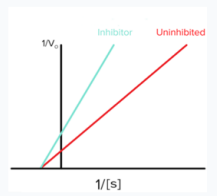
Lineweaver-Burk plot
Michaelis-Menten Graph vs. Lineweaver-Burk Plot
What is this a picture of?
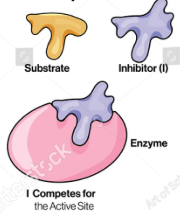
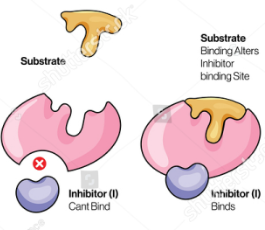
inhibitor
Enzyme Kinetics
Molecules that reduce the activity of an enzyme by combining it with a way that either affects substrate binding or affects conversion of substrate to product (can be a small molecule or a protein)
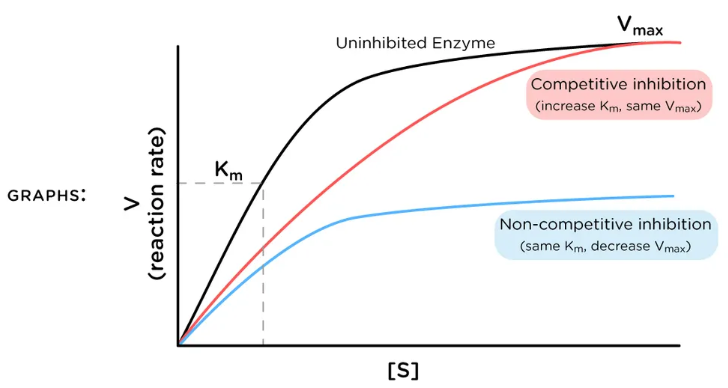
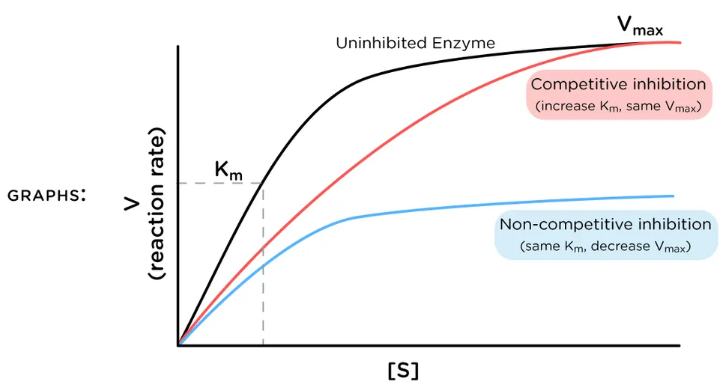
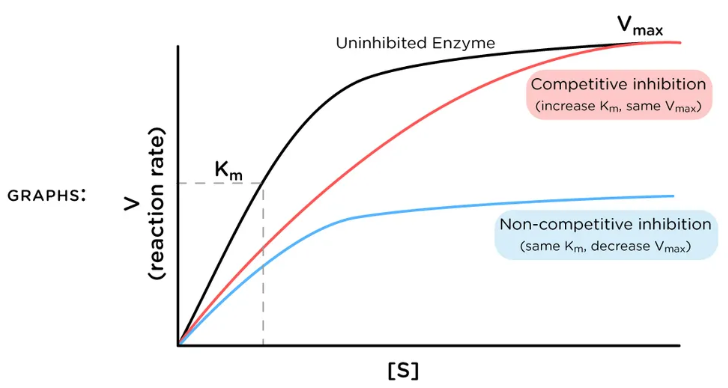
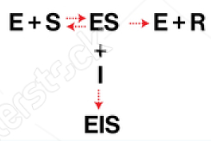
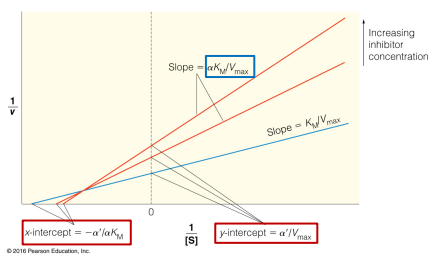
competitive inhibition
Enzyme Kinetics
Competitive vs. Uncompetitive vs. Noncompetitive vs. Mixed Inhibition
When inhibitor and substrate compete for the same active site
Can be overcome by adding more substrate
no
Enzyme Kinetics - Competitive Inhibition
Does competitive inhibition affect Vmax?
If so, does it INCREASE or DECREASE it?
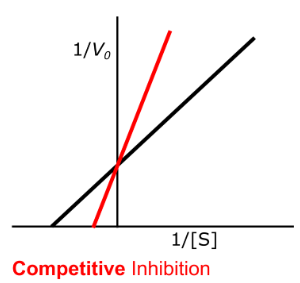
no, yes
Enzyme Kinetics - Competitive Inhibition
Does competitive inhibition change the y-intercept?
Does competitive inhibition change the x-intercept?
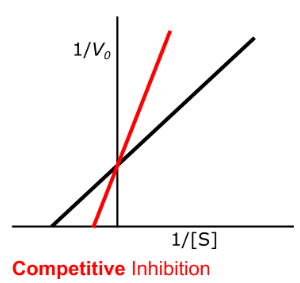
low
Enzyme Kinetics - Competitive Inhibition
High vs. Low
Competitive inhibition has more of an effect at _____ levels of substrate concentration
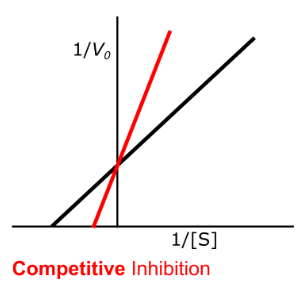
yes, increase, decrease
Enzyme Kinetics - Competitive Inhibition
Does competitive inhibition affect Km?
If so, does it INCREASE or DECREASE it?
Does this mean an INCREASE or DECREASE in binding affinity for the substrate?
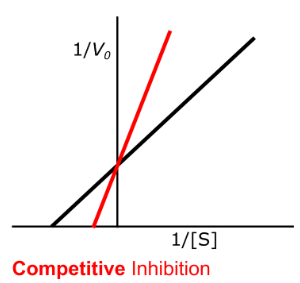
competitive
Enzyme Kinetics
Competitive vs. Uncompetitive vs. Noncompetitive vs. Mixed Inhibition
competitive
Enzyme Kinetics
Competitive vs. Uncompetitive vs. Noncompetitive vs. Mixed Inhibition
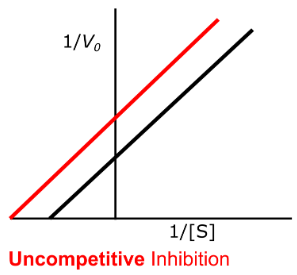
uncompetitive
Enzyme Kinetics
Competitive vs. Uncompetitive vs. Noncompetitive vs. Mixed Inhibition
When inhibitor binds to the enzyme-substrate complex (not the free enzyme) and prevents the conversion of substrate to product
Can be interpreted as an increase in binding affinity between the enzyme and substrate
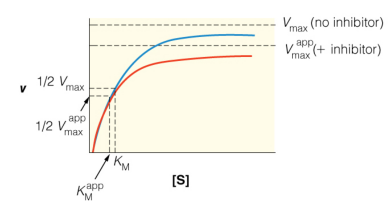
yes, decrease
Enzyme Kinetics - Uncompetitive Inhibition
Does uncompetitive inhibition affect Vmax?
If so, does it INCREASE or DECREASE it?
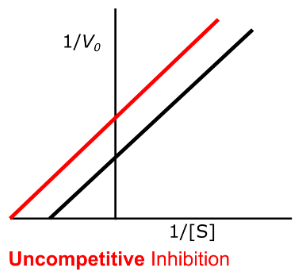
yes, decrease, increase
Enzyme Kinetics - Uncompetitive Inhibition
Does uncompetitive inhibition affect Km?
If so, does it INCREASE or DECREASE it?
Does this mean an INCREASE or DECREASE in binding affinity for the substrate?
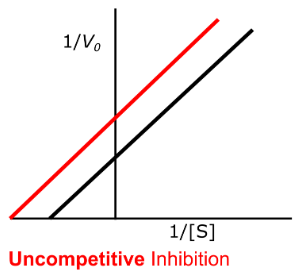
high
Enzyme Kinetics - Uncompetitive Inhibition
High vs. Low
Uncompetitive inhibition has more of an effect at _____ substrate concentration
yes, yes
Enzyme Kinetics - Uncompetitive Inhibition
Does uncompetitive inhibition change the y-intercept?
Does uncompetitive inhibition change the x-intercept?
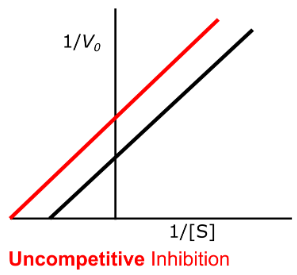
uncompetitive
Enzyme Kinetics
Competitive vs. Uncompetitive vs. Noncompetitive vs. Mixed Inhibition
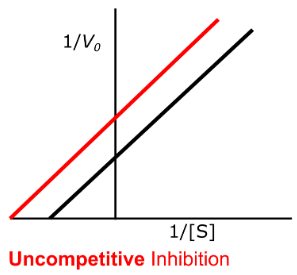
uncompetitive
Enzyme Kinetics
Competitive vs. Uncompetitive vs. Noncompetitive vs. Mixed Inhibition
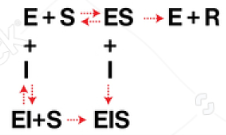
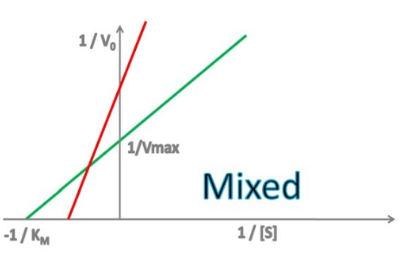
mixed
Enzyme Kinetics
Competitive vs. Uncompetitive vs. Noncompetitive vs. Mixed Inhibition
When the inhibitor binds to both the enzyme/substrate complex and the free enzyme, but has different affinities for each
competitive
Enzyme Kinetics
Competitive vs. Uncompetitive vs. Noncompetitive vs. Mixed Inhibition
prevents substrate binding to the enzyme

uncompetitive
Enzyme Kinetics
Competitive vs. Uncompetitive vs. Noncompetitive vs. Mixed Inhibition
prevents conversion of substrate to product
mixed
Enzyme Kinetics
Competitive vs. Uncompetitive vs. Noncompetitive vs. Mixed Inhibition
prevents both substrate binding & conversion of substrate to product
yes, decrease
Enzyme Kinetics - Uncompetitive Inhibition
Does uncompetitive inhibition affect Vmax?
If so, does it INCREASE or DECREASE it?
yes (the change depends on whether or not affinity for the substrate is increased or decreased)
Enzyme Kinetics - Mixed Inhibition
Does mixed inhibition affect Km?
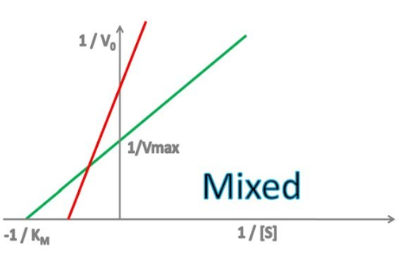
yes, yes
Enzyme Kinetics - Mixed Inhibition
Does mixed inhibition change the y-intercept?
Does mixed inhibition change the x-intercept?
mixed
Enzyme Kinetics
Competitive vs. Uncompetitive vs. Noncompetitive vs. Mixed Inhibition
noncompetitive
Enzyme Kinetics
Competitive vs. Uncompetitive vs. Noncompetitive vs. Mixed Inhibition
When the inhibitors bind to an allosteric site instead of the active site, which leads to a change in enzyme conformation
When the inhibitor binds to the enzyme and the enzyme-substrate complex with equal affinity
A specific type of mixed inhibition
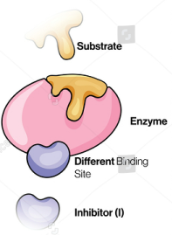
yes, decrease
Enzyme Kinetics - Noncompetitive Inhibition
Does noncompetitive inhibition affect Vmax?
If so, does it INCREASE or DECREASE it?
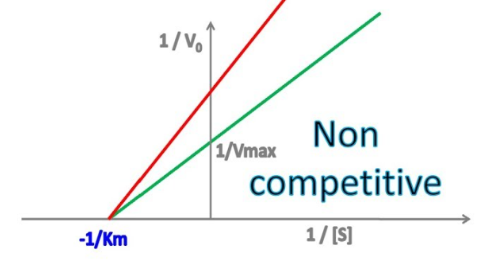
no
Enzyme Kinetics - Noncompetitive Inhibition
Does noncompetitive inhibition affect Km?
If so, does it INCREASE or DECREASE it?
Does this mean an INCREASE or DECREASE in binding affinity for the substrate?
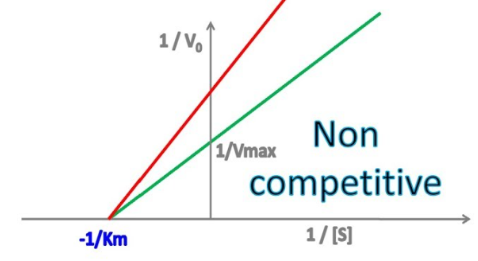
yes, no
Enzyme Kinetics - Noncompetitive Inhibition
Does noncompetitive inhibition change the y-intercept?
Does noncompetitive inhibition change the x-intercept?
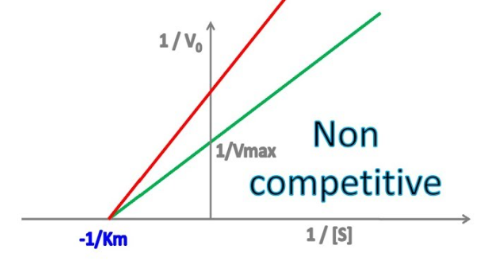
noncompetitive
Enzyme Kinetics
Competitive vs. Uncompetitive vs. Noncompetitive vs. Mixed Inhibition
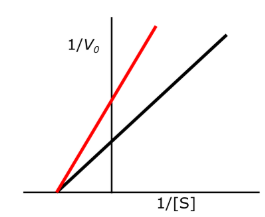
C, F
Select all of the following that would INCREASE the rate of a reaction:
A. decreasing the free energy (G) of the substrate
B. decreasing the free energy (G) of the product
C. increasing the temperature
D. decreasing the temperature
E. increasing the free energy of activation (delta G naught cross)
F. decreasing the free energy of activation (delta G naught cross)
D
A reaction proceeds at a rate ≈ Vmax. What is the substrate concentration [S]?
A. [S] = [E]T
B. [S] = Km
C. [S] = 2 x Km
D. [S] » Km
B
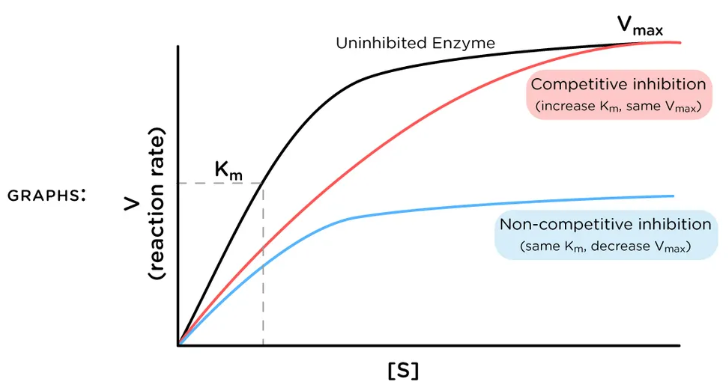
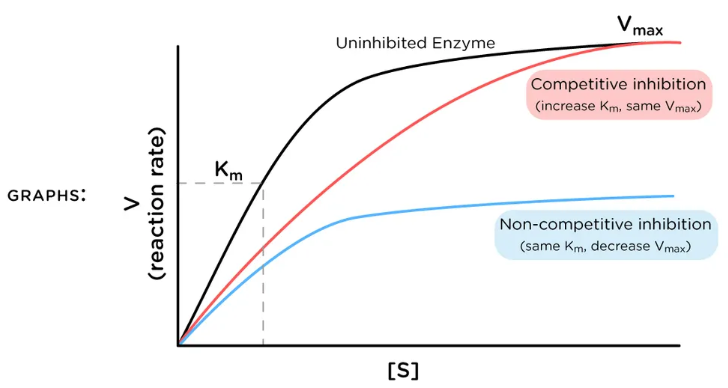
For the type of inhibition shown, what does the inhibitor bind to?
A. the enzyme only (E)
B. the enzyme:substrate complex only (ES)
C. Both the enzyme (E) and the enzyme:substrate complex (ES)
D. none of the choices are correct
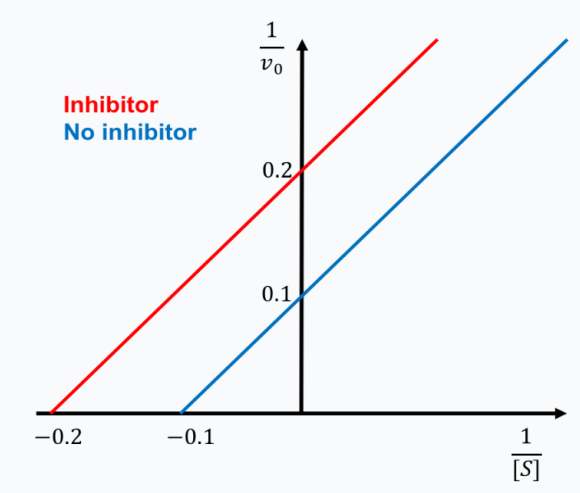
B
The graph shows a special type of mixed inhibition where the inhibitor binds both E and ES with equal affinity. How does the presence of this inhibitor change the EFFECTIVENESS of both Vmax and Km?
A. decreases Km; decreases Vmax
B. no change to Km; decreases Vmax
C. increases Km; decreases Vmax
D. no change to Km; increases Vmax
E. increases Km; no change to Vmax
C
Catalysts primarily work by:
A. providing additional kinetic energy for a substrate to overcome free energy barriers
B. increasing the free energy of the substrate
C. stabilizing the transition state of a reaction
D. decreasing the free energy of the product
C
In the case of competitive inhibition, which of the following statements about the Lineweaver-Burk plot is TRUE?
A. The slope does not change as inhibitor is added
B. The intersection point as inhibitor is added is given by [-1/α, 1/α]
C. The y intercept does not change as inhibitor is added
D. The x intercept does not change as inhibitor is added
A
In the case of uncompetitive inhibition, which of the following statements about the Lineweaver-Burk plot is TRUE?
A. The slope does not change as inhibitor is added
B. The x intercept does not change as inhibitor is added
C. The y intercept does not change as inhibitor is added
D. The intersection point as inhibitor is added is given by [-1/α', 1/α']
D
If a Lineweaver-Burk plot of a reaction is not linear, which of the following is TRUE?
A. The reaction is performed with a competitive inhibitor
B. The reaction is performed with an uncompetitive inhibitor
C. The reaction is performed with a mixed inhibitor
D. The reaction does not obey Michaelis-Menten kinetics