1.1 What is a business?
1/58
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
59 Terms
What is a Business
any organization that uses resources to meet the needs of customers by providing a product or service that they demand.
Nature of business
Businesses identify the needs of consumers or other firms
business activity exists to produce goods/services which can be classified in several ways:
consumer goods
consumer services
capital goods
Consumer goods
The physical-tangible goods sold to final users
ex: cars, food, clothes
Consumer services
Non-tangible products that are sold to final user
ex: hotel accomodation, insurance services, train journeys
Capital goods
Physical goods that are used by industry to aid in production of other goods/services
ex: machines, commercial vehicles, kitchen appliences
Business Inputs
Human, physical, and financial resources needed by a business to produce goods/services
Land
Labour
Capital
Enterprise
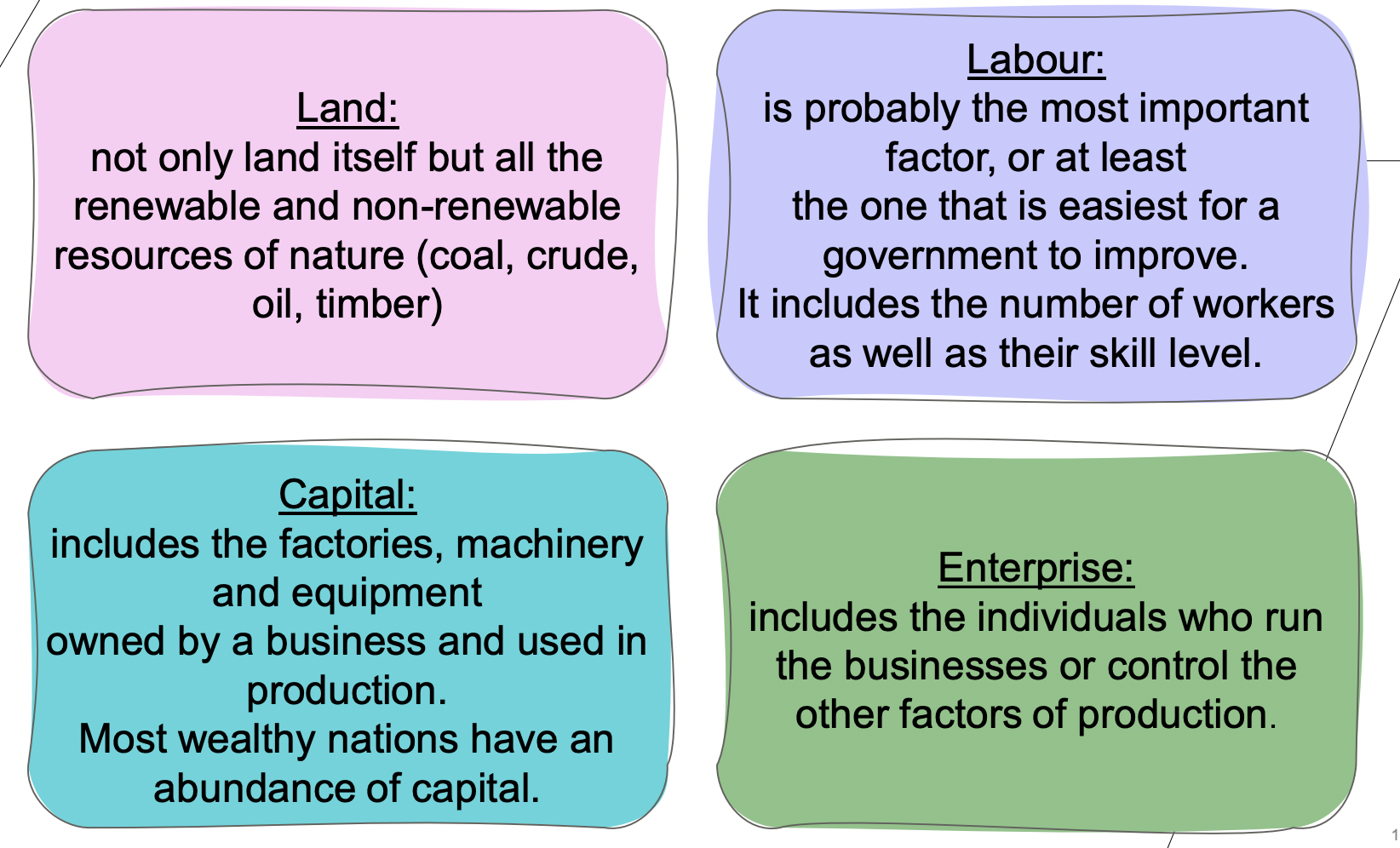
Land (business Input)
all renewable & non-renewable resources of nature
ex: crude oil, coal
Labour (business input)
Manual labour and skilled workers make up the workforce of the business
Capital (business input)
Finance needed to set up a business and pay for its continuing operations - including human made resources and machines, factories, and vehicles.
Enterprise (business input)
The driving force of business, provided by risk-taking individuals, who combine other factors of production into a unit that is capable of prducing goods&services. (Managing and decision making)
(individuals who run the business or contol other factors)
Business functions
Human resource management
finance and accounts
marketing
operations management
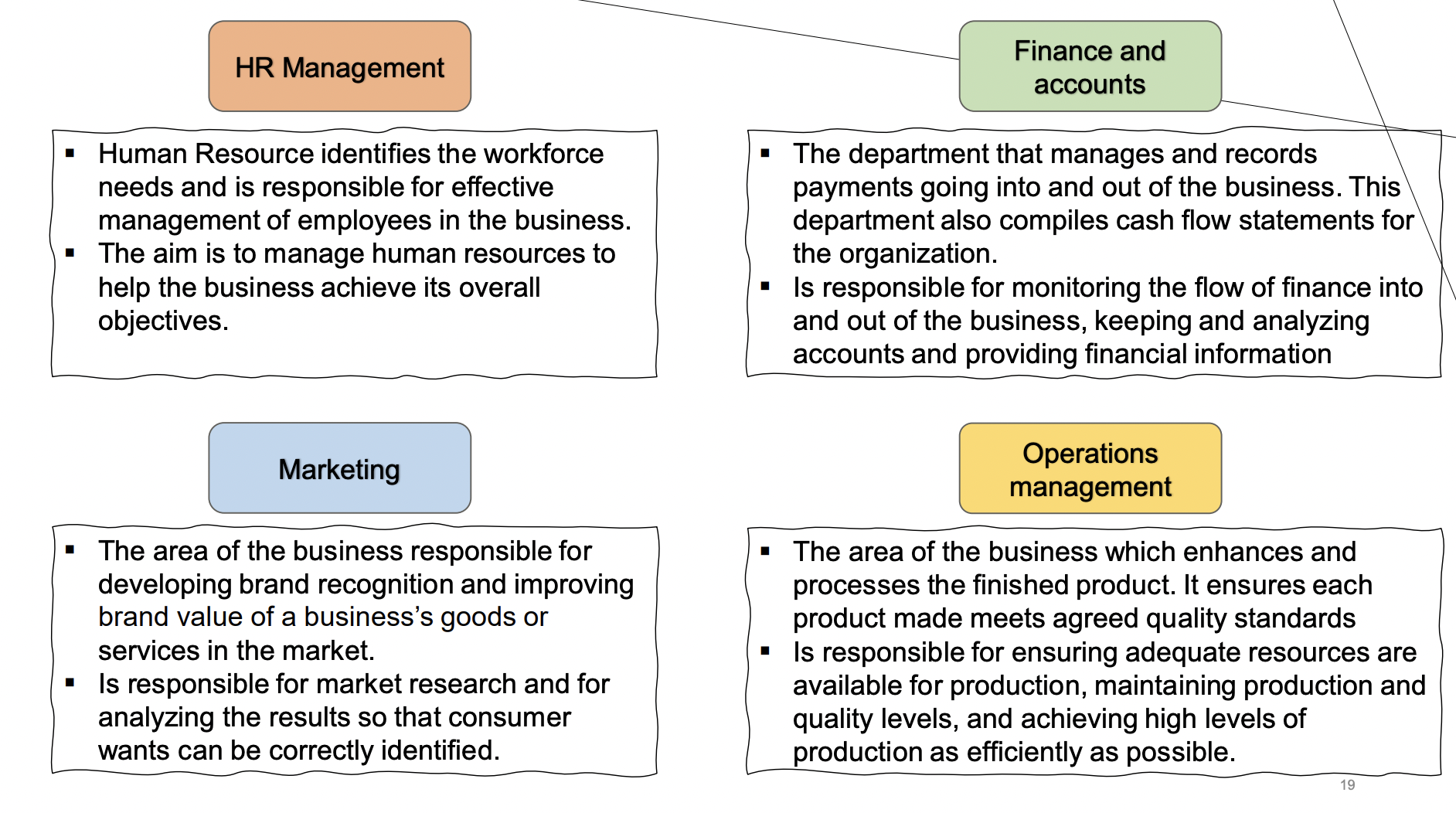
HR managements (business function)
identifies workforce needs and responsible for effective management of employees (recruits and trains individuals and encourages them to work productively), aim to help business achieve its overall objectives.
functions involved with employee hiring, retention and development
Finance and accounts (business function)
Manages and records payments going in and out of business, complies cash flow statements for the organization.
responsible for monitoring flow of finance in/out business, keeping and analysing accounts & providing financial info.
basically money department
Marketing (business function)
Responsible for developing brand recognition and improving brand value of a business’s goods/services in the market
responsible for market research and analysing the results so consumer wants can be correctly identified.
Operations management (business function)
Enhances and processes the finished product, ensures each product made meets the agreed quality standards
responsible for ensuring adequate resources are available for production, maintaining production and quality levels, achieving high levels of production efficiency as possible.
Economic sectors
Primary sector
Secondary sector
tertiary sector
quaternary sector
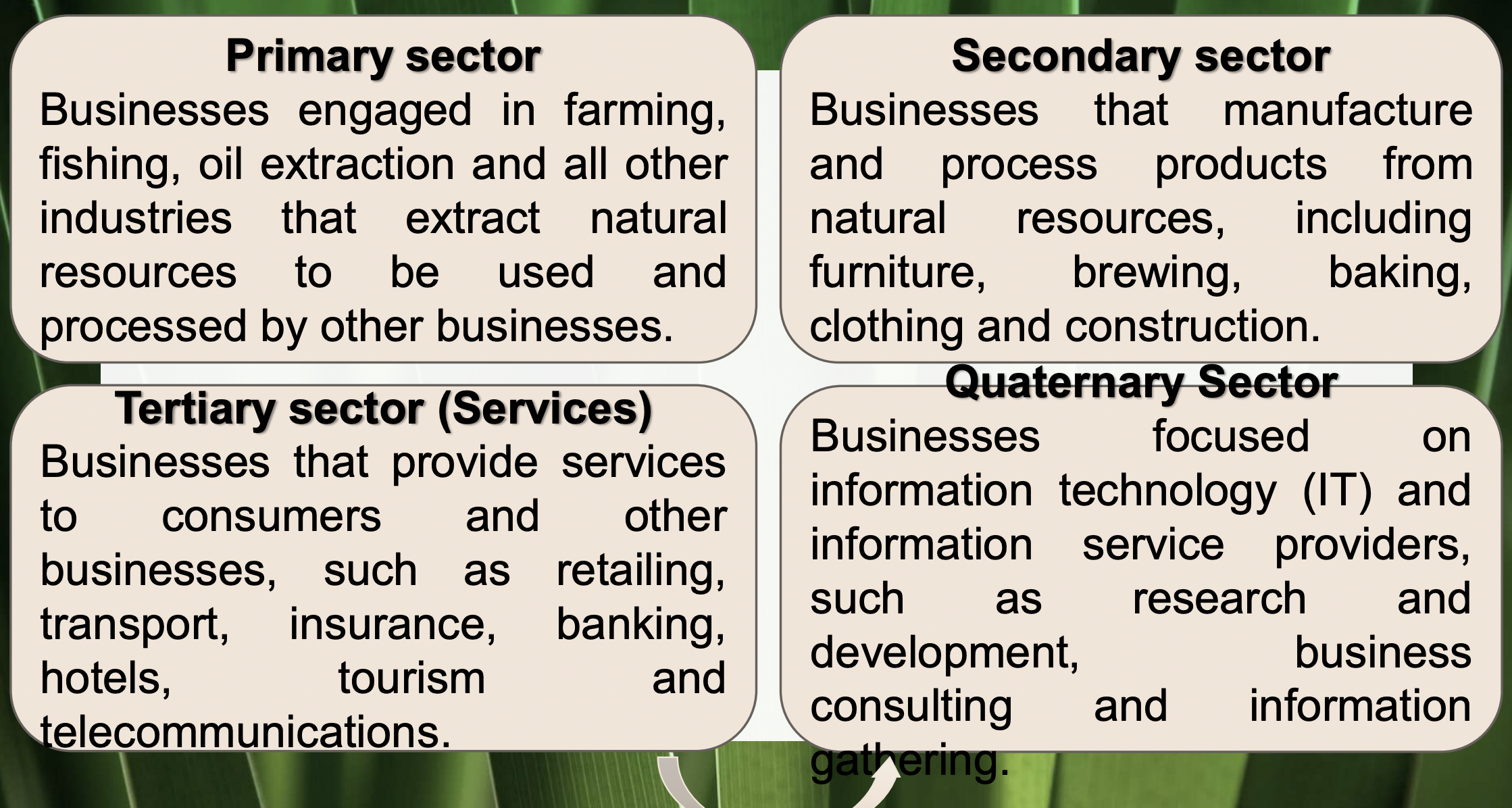
primary sector
industries that extract natural resources to be used and processed by other firms
ex: farming, fishing, oil, etc
Secondary sector
businesses that manufacture and process products from natural resources
ex: furniture, brewing, baking, clothing, construction
Tertiary sector
Businesses that provide services to consumers and other businesses
ex: retailing, transport, insurance, banking, hotels, tourism and telecommunications.
Quaternary sector
focuses on Information technology (IT) and information service providers
ex: research development, business consulting, info gathering
Gross domestic product (GDP)
key economic indicator that measures the total monetary value of all goods and services produced within a country's borders over a specific period, typically annually or quarterly.
It provides a snapshot of a country's economic performance.
Entrerpreneur
a person who takes a financial risk of starting and managing a new venture
skills needed: innovation, commitment/self motivation, leadership skills, self belief, risk taking
Challenges when starting business
do you have appropriate qualities?
is there market for product?
do you have sufficient capital?
Location of business?
how to build customer base?
how to compete effectively?
how to keep accurate business records?
do have necessary management skills?
how deal with change?
Business Plan
a written document that describes a business, its objectives and strategies, the market its in, and its financial forecasts
content: executive summary- overview of new business & strategies, description of business opp-details of who what when blabla
Importance: for new business-to obtain finance for startup. Helps entrepreneurs to stay on track
share
a certificate confirming part ownership of a company.
shareholders
individuals or institutions that buy/own shares in a limited company
Privately held company
a business that is owned by shareholders who are often members of the same family — cannot sell shares to general public
publicly held company
a limited company with a legal right to sell shares to financial institutions and general public - share price quoted on general stock exchange
Initial public offering (IPO)
the process of offering for sale the shares of a privately held company to financial institutions and the general public
Private sector
comprises businesses owned and controlled by individuals - groups of individuals
(not govt)
Public sector
comprises organizations accountable to and controlled by central or local government (state)
(yes govt)
Mixed economy
Economic resources are owned and controlled by both private and public sectors
Free-market economy
economic resources are owned largely by Private sector, little state intervention
Command economy
economic resources are owned, planned, and controlled by the state (only)
Privatisation
the scale of the public sector organizations to the private sector
Sole trader
business that is exclusively owned by one person who has full control of it and is entitled to all the profit
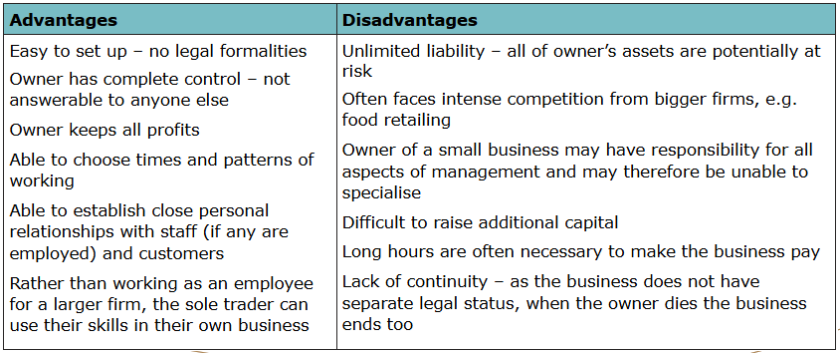
Partnership
business formed by 2 or more ppl to carry on a business together, with shared capital investment and usually shared responsibilities.

Limited companies (private and publicly held)
shareholders have limited liability (sole traders/partnerships dont)
companies have a legal personality (sole traders/partnerships dont)
companies can continue after death of an owner (sole traders/partnerships cant)
Limited liability
only liability (loss) is what the shareholder invested
social enterprise
a business with a social/environmental objective that reinvests most of its profits into benefiting society rather than maximising returns to owners
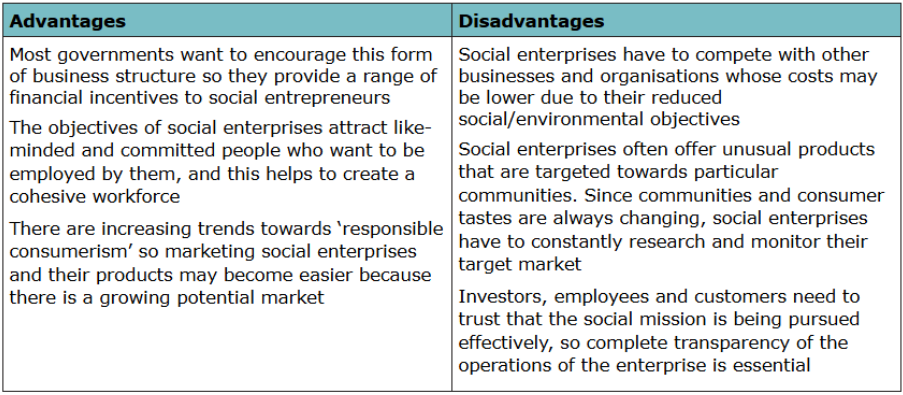
social entrepreneur
a person who establishes an enterprise with the aim of solving social problems or achieving social change
Charity
an organization set up to raise money to help people in need or support causes that require funding
Triple bottom line
the 3 objectives of social enterprises

public corporations
business enterprise owned and controlled by the state Not in private sector
cooperative
a group of ppl acting together to meet the common needs-aspirations of the members, sharing ownership and making decisions democtatically
Non-profit organization
Any organization that has aims other than making and distributing profit and which is usually governed by a voluntary board
(aim isnt profit)
non governmental organization
Functions independently of any government and that has a specific social aim/purpose
ex: red cross
vision vs mission statement
vision = someday
mission = everyday
business objectives
short term goals-targets -specific - must be achieved for an organization to attain its corporate aim
Tactical objectives - easier to change- specific targets with definitive timelines.
Strategic objectives- targets that the whole organization is striving to achieve. -greater investment in human/financial resources than tactical & operational objective.
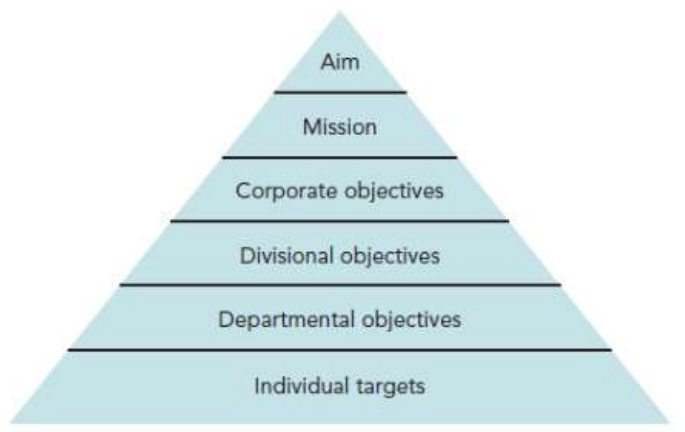
corporate aim
long-term goals which a business hopes to achieve
Profit objective
Profit Maximisation: producing at the level of output where the greatest positive difference between total revenue and total costs is achieved (make big profit)
Growth Objective
to grow company…
benefits: higher profit/revenue, economies of scale, reduced risks
protecting shareholder value (objective)
investors buy shares to benefit from shareholder value: the financial gains recieved by owners of company’s shares.
ethical objective
-company’s philosophy, set to meet regulations, build reputation & trust, consumer expectations, long term profit
benefits: enhanced brand image, customer loyalty, operational efficiency, regulatory compliance
Corporate-social responsibility (CSR)
concept applies to businesses that consider the interests of society by taking responsibility for impact of their decisions on customers/employees/communities/environment
csr report—explains company’s ethics and how they effect society and what they’ve done
when business fully accepts its legal+moral objectives, its accepting corporate social responsibility
SWOT analysis

ANSOFF matrix

Stakeholders
poeople/groups who can be effected by, therefore have interest in, any action taken by an organization
stakeholder concept: view that business&managers have responsibilities to a wide range of groups not just shareholders:
Internal: employees, managers, shareholders
External: customers, suppliers, government, banks, special interest groups, competitors