Histology Intro
1/62
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
63 Terms
Why are stains used
most tissue must be stained to visualise tissue components in the light microscope
Types of dyes
acidic
Basic
Basic dyes, name and what they stain
Basophilic dyes
RNA and DNA
Acidic dyes, name and what they stain
acidophilic
mitochondria
collagen
What are the most common dyes used
Haematoxylin→ basic→ preferential affinity for the acidici components of cells→ stained dark blue
nucleus and the cytoplasmic regions→ rich in ribosomes
Eosin→ acidc→ stained basic components pink/red
reacts with a variety of cytoplasmic proteins and extra-cellular strucutres
avid for RBC and eosinophils
(H&E)
Other types of stains

Making only smear of cheek cells
firmly wipe around inside of mouth with cotton bud
spread product onto slide
allow to dry
Stain with one or two drops of 1% methylene blue→ 2 mins
rinse with water
allow to dry
coverslip with DPX (weird kinda gluey thing)
Examine
4 Main primary tissue types→ based on types of cells and arrangement
Connective cells form connective tissue
Nerve cells form nervous tissue
Muscle cells form muscle tissue
Epithelial cells form epithelial tissue
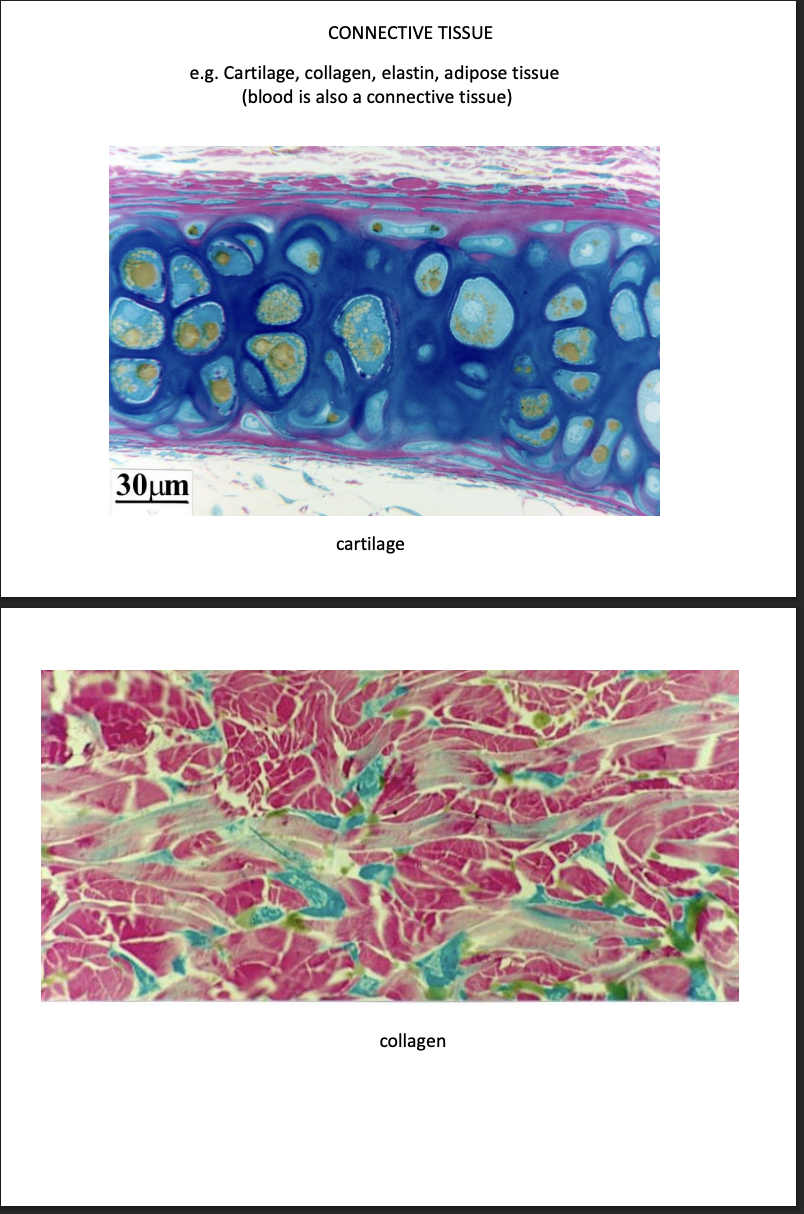
Connective tissue
comprise a variety of cells that differ in morphology and function
fribroblasts, adipocytes, chrondrocytes
What they do:
Secrete abundance extracellular matrix
provide support for other cells/tissues
Examples
collage
bone
elastin
adipose
White
unilocular, single large fat droplet per cell
Brown
multilocular, many small droplets per cell
blood
RBC
WBC
lymphocytes, neutrophils, monocytes, Eosinophils, Basophils
Plateletes
cartilage
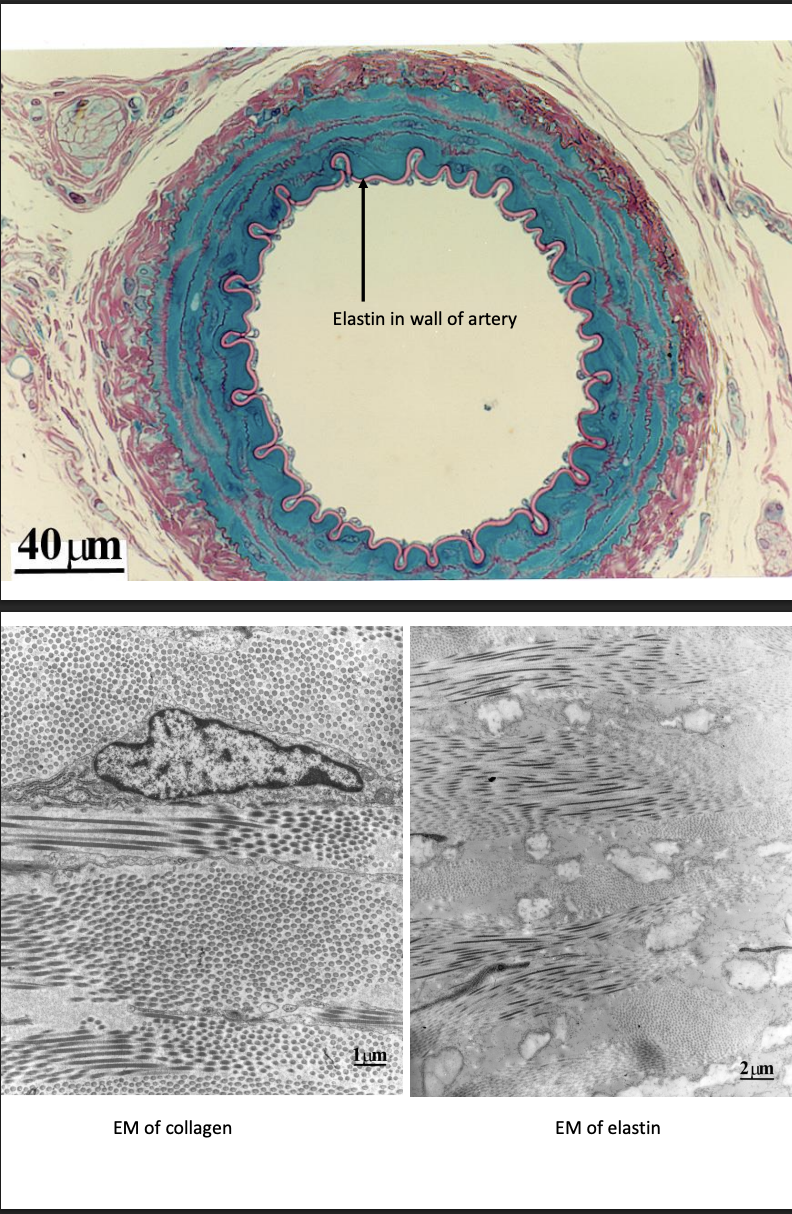
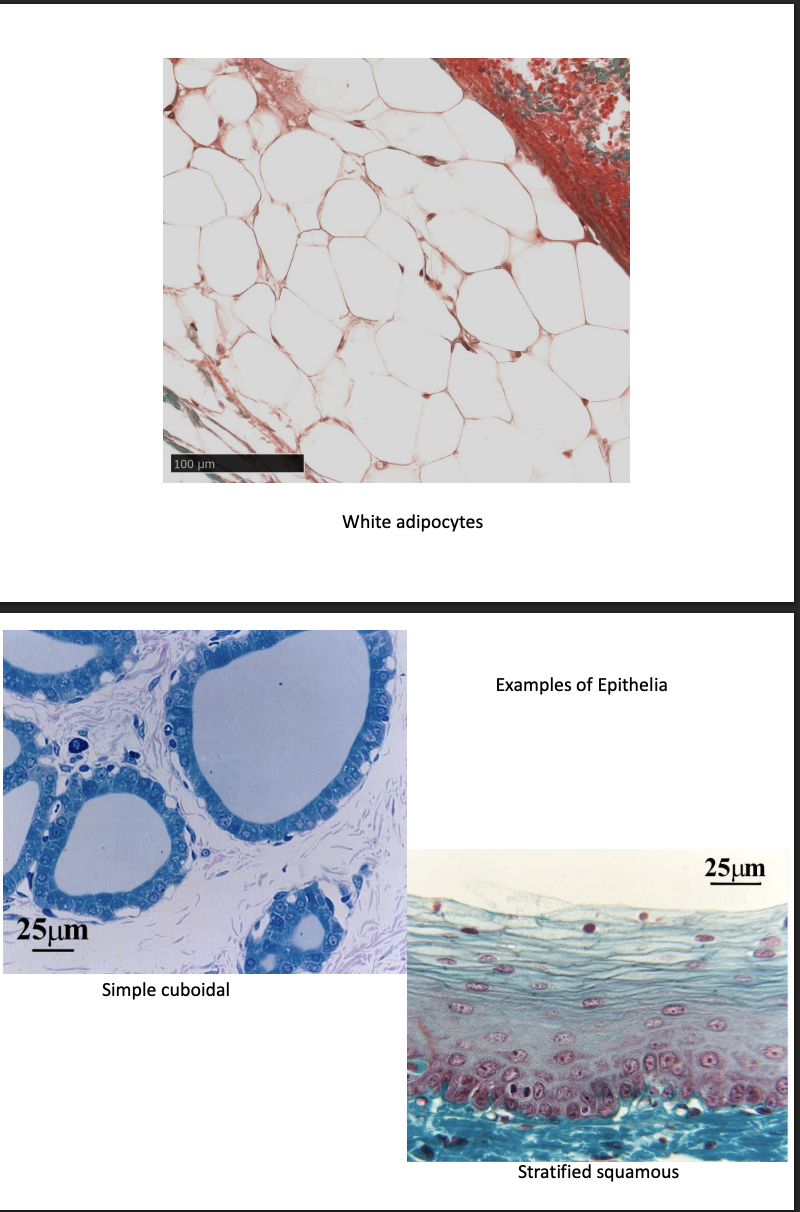
Connective tissue→ pics
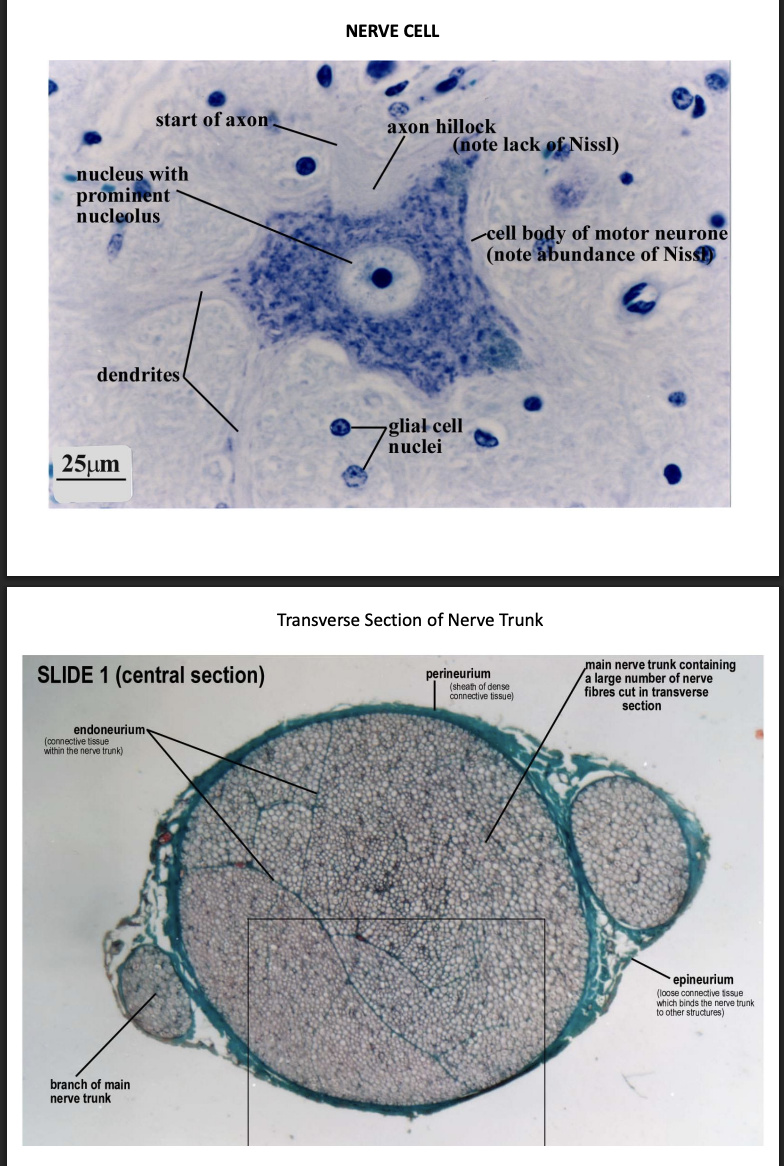
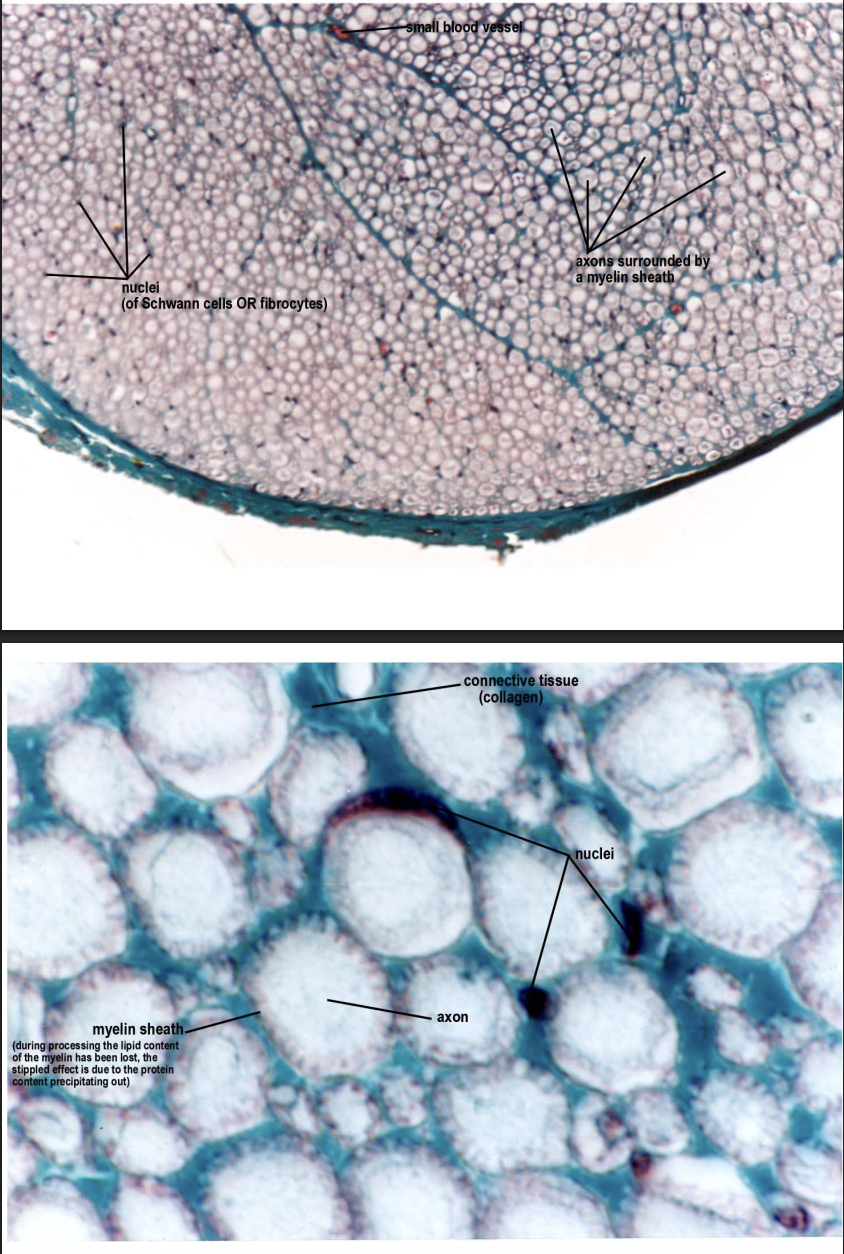
Nervous tissue
Function of nerve cells
receiving, generating and transmitting nerve impulses
Different types but will see
ganglia and nerve trunks
Support cells
different types
Schwann cells give rise to myelin
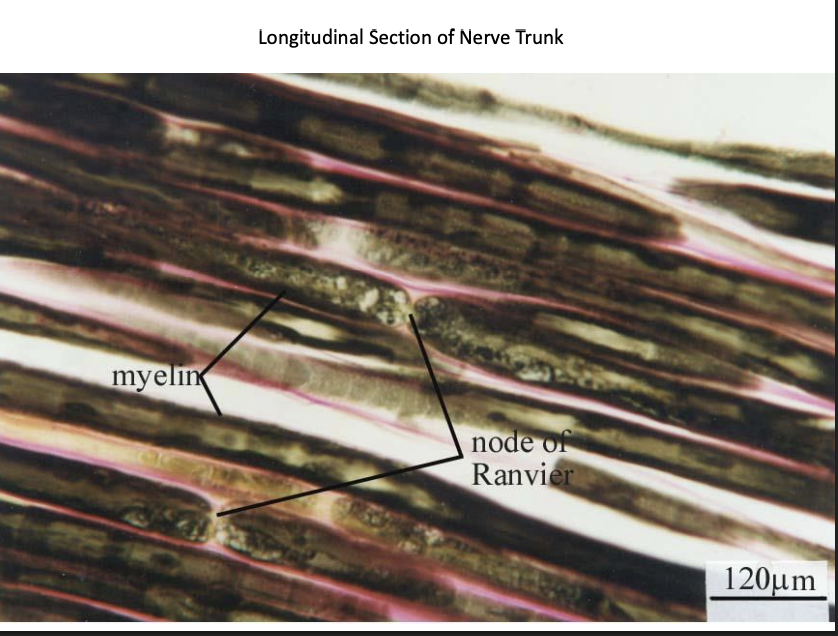
Nervous tissue→ longitudinal section of nerve trunk
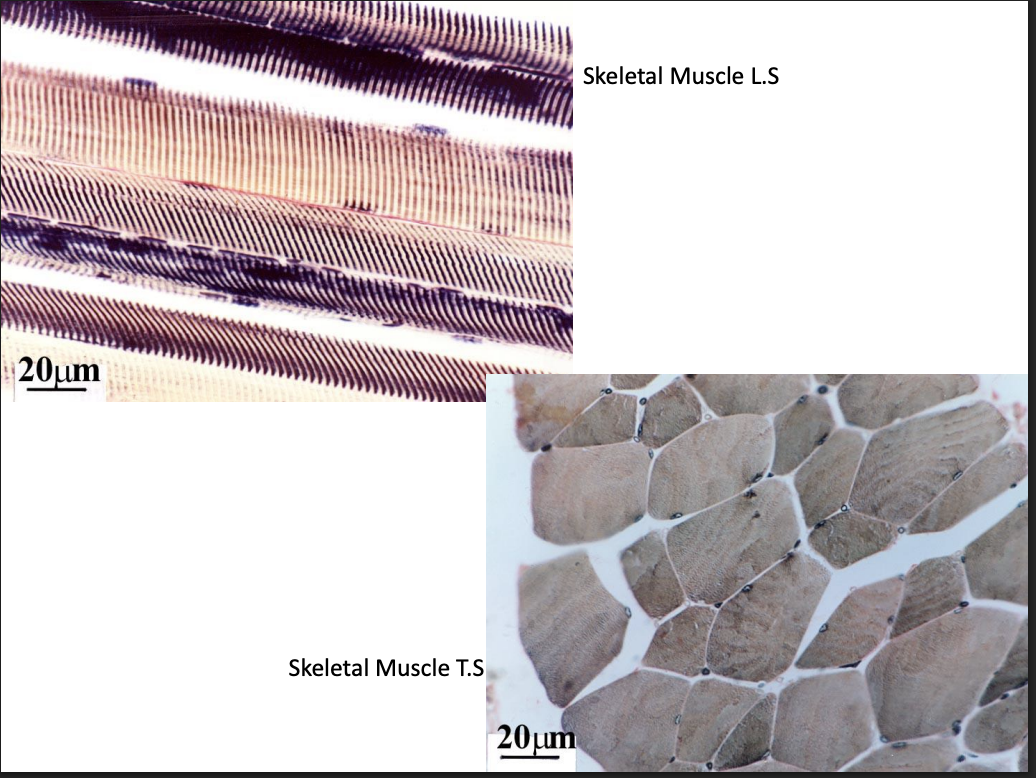
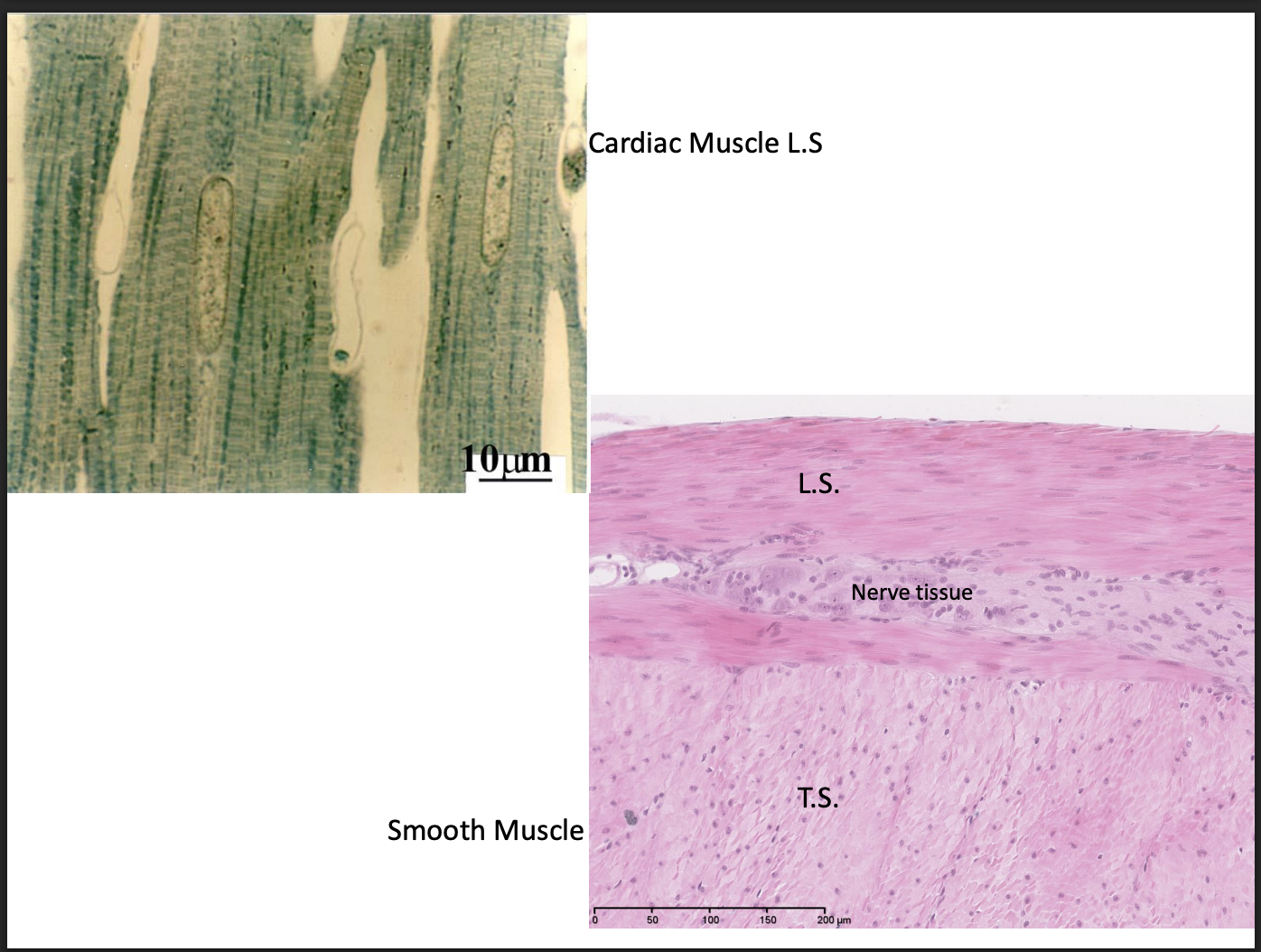
Muscle tissue
elongated
with contractile properties
Smooth:
tapered cells + central nuclei
Striated
cardiac
central nucleus
intercalated discs
Purkinje fibres
appear to branch
Skeletal
peripheral nuclei
motor end plates
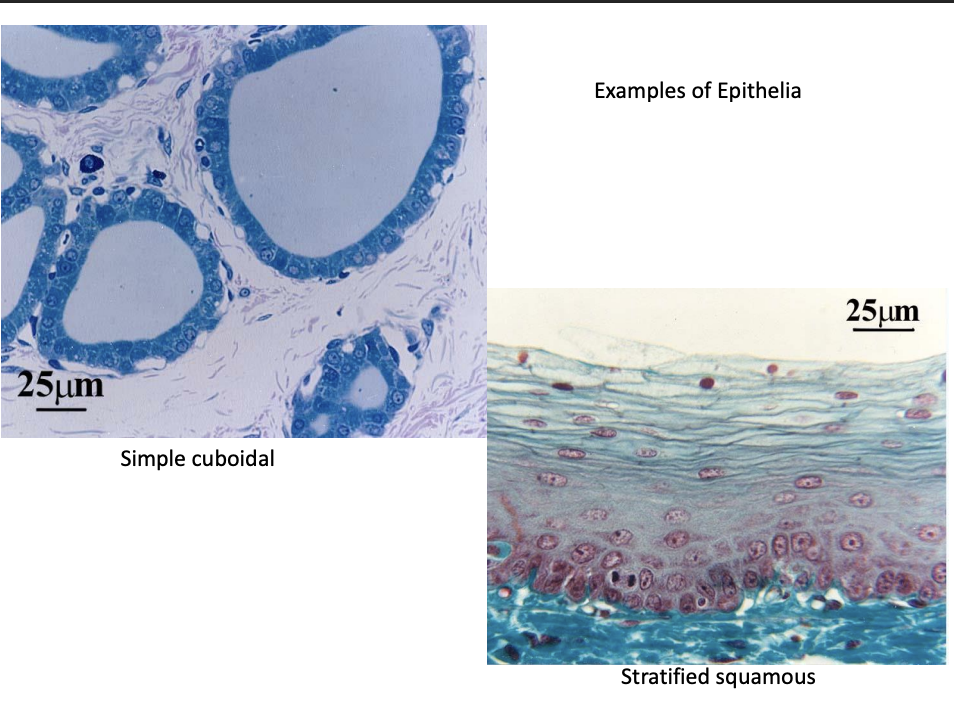
Epithelial tissue
cover body surfaces
line body cavities
form solid glands→ e.g salivary glands
Layers:
Simple
stratified
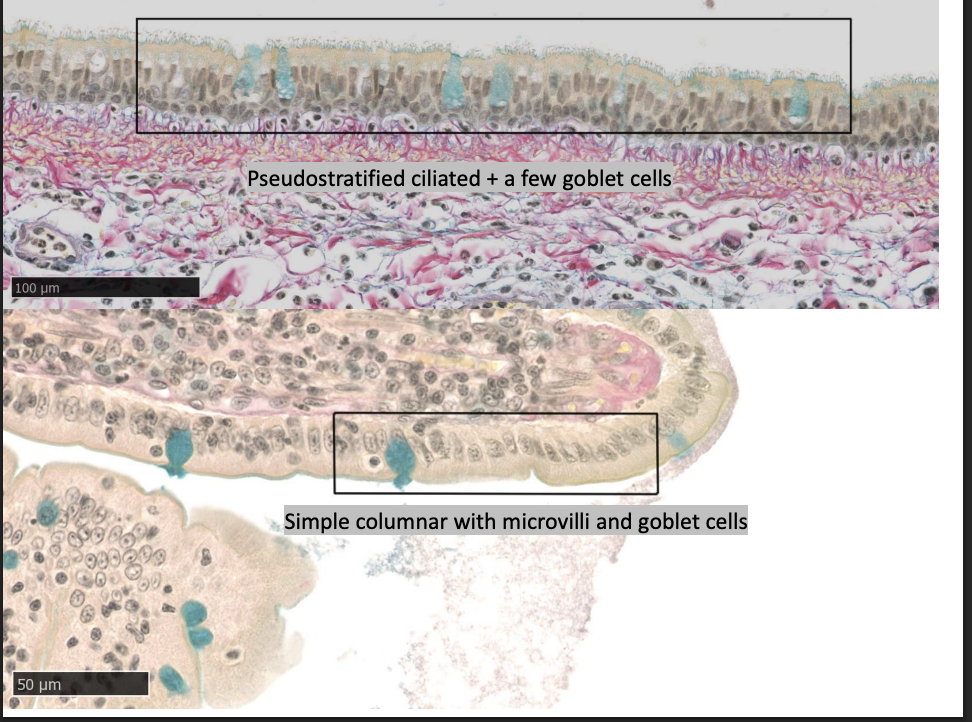
pseudostratified (simple but seems 2+ layers)
Transitional (found in urinary system→ appearance changes if stretched/unstretched)
Shape
Squamous
Cuboidal
Columnar
Modifications
cilia
microvilli
secretory bodies (mucus droplets, secretory granules)
Light microscopy overview
most widley used form of microscopy
optical and mechnaical pats
Visual light passes through specimen
collected by image-forming optices
reveal strucutre of living cells and tissues (and non-living)
Optical components
Condenser lens
collects and focuses light from light source
onto specimen
Objective len
collect light from specimen
enlarge and project illuminated image to eyepeice
Eyepiece (ocular) lens
further magnified image
projects it onto viewer’s eye
Mechanical parts
stage
platform slides mounted
Illumination system
tungsten lamp for transmitted light
with varibale control
diaphragm
alters amount of light reaching condenser and passes to specimen
Control knobs
focus image→ moving stage up and down
stage control→ movement of speciment along x and y
regulation of light intensity
Nosepiece
holds objective lenses
The types of microscope we used
upright→ illumination system below stage and lens system above the stage
binocular→ 2 eye pieces
3 objective lenses (x4,x10,x40
two x10 eyepieces
mechanical stage with x an y vernier scales
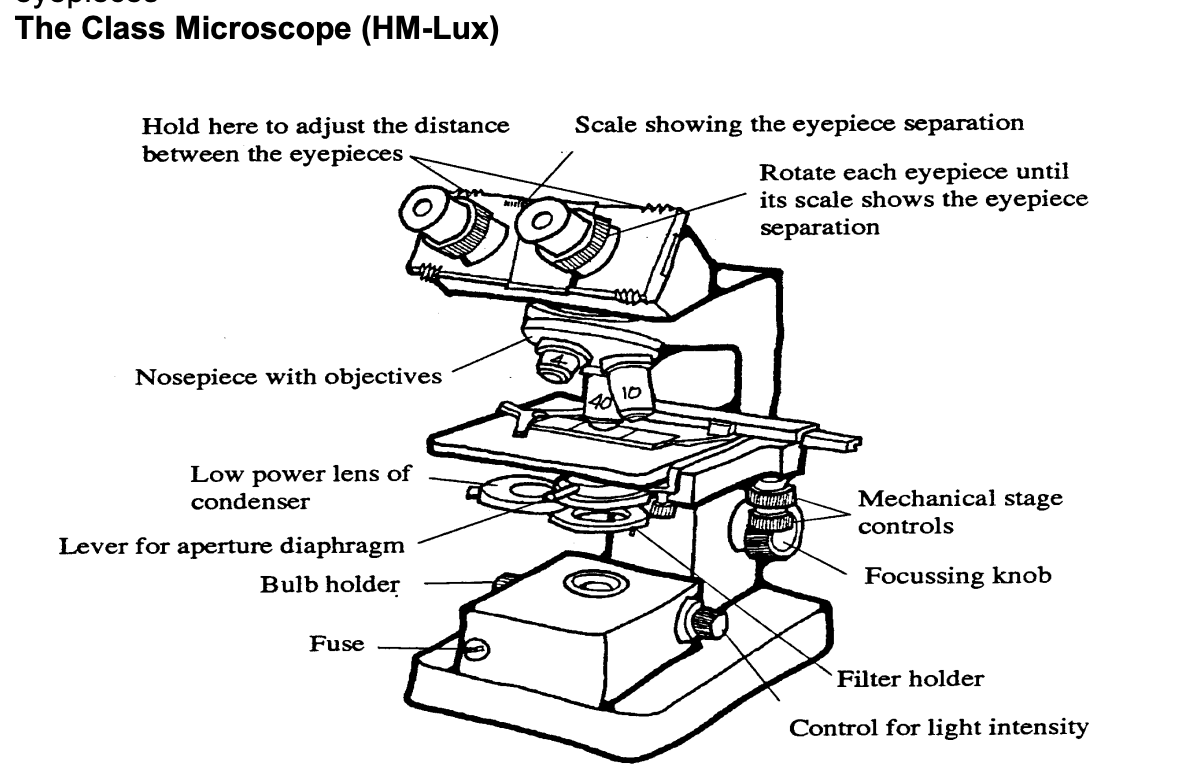
Total magnification oof light microscope
magnifying power of objective x magnifying power of the eyepieces
Using light microscope
examine slide with naked eye on white background
place on stage
make sure right way up→ coverslip on top
focus x4 with focus knob
increase magnification
x40 objective→ constantly adjust the fine focus control
high power→ depth of field is less than the thickness of section→ so it is possible to scan and assemble a picture of all available details
depth of field→ thickness of the layer which is brought to sharp focus
note: easier to search for structure in low power→ look for it in lower power first then increase power
How condenser is set up
set up with top lens almost touching the under surface of the slide
should not be needed to vary its position unless frosted surface of the light source is exactly in focus and interfers with observations
Use only lower-power lens of the condenser for→ lower-power x4 objective lens
Aperture diaphragm of condenser
should be reset whenever objective is changed:
open then gradually close until contrast of object is adequate
not too dark as to produce distortions
Resolution
ability of the objective lens to distinguish detail
When is the resolution optimum
when the aperture of the diaphragm is set just to fill the back focal plane
What happens when the diaphragm aperture closes
contrast increases
contrast→ relative difference in light intensity coming from different parts of the specimen
usually low in most sections
Therefore, the aperture of the diaphragm comprimisers between
structure being clearly and comfortably visible
ability to see as much fine detail as possible
Other features of mechanical stage
has vernier scale
used to record exact position of an object on the slide
read like map references with east-west given first
Objectives are par-focal
→ have the same focal length
Meaning:
if one is corrently focused→ the others will also be approximately in focus when switched
But→ working distances are very different (i.e the x40 is much closer than the x10)
working distance of the x40 is less than the thickness of a slide
so spaciment cannot be focused on x40 if slide upside down
Cleaning
slides→ ordinary tissues
lenses→ special lens tissue→ rub gently using moisture from breath
Estimating size of a structure
imagine how many of the structures can fit into the diamter of a field
or
compare object of known size
e.g RBC→ 7 um
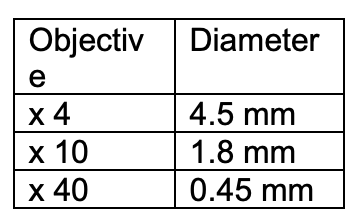
Electron microscopy
must higher resolution and magnification than light
enables to exam cells and sub-cellular strucutures
Resolution
minimum distance between two points on a specimen
than can still be distinguished as two separate entities
Electron vs light resolution and magnitudes
resolution
E→ 2.5-7.5nm
L→250nm
Magnification
E→x 100,000
L→ x1000
Cell structure: cell membranes
plasma membrane- >highly selective barrier between cytoplasm and environment
EM→ thin line 10nm thick enclosing cell
EM provides evidence for the fluid mosaic model
Eukaryotic membrane around organelles
Organelles
most organelles can be resolved under EM
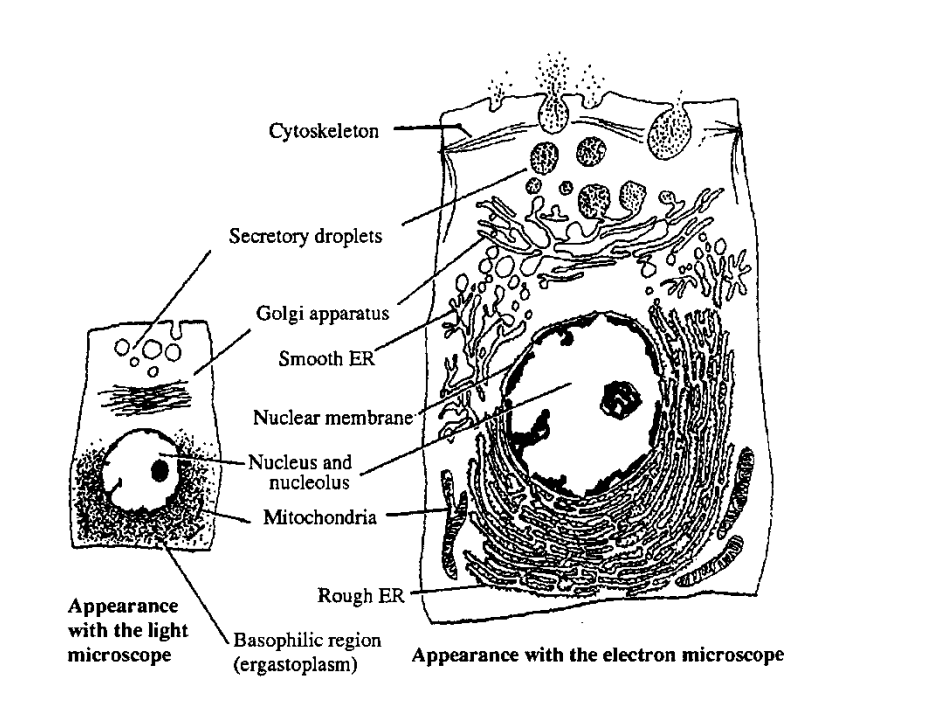
Mitochondria
inner membrane→ cristae
contains enzymes for ox phos
Endoplasmic reticulum
tubular membrane strucutres
faltterned sheets and sacs
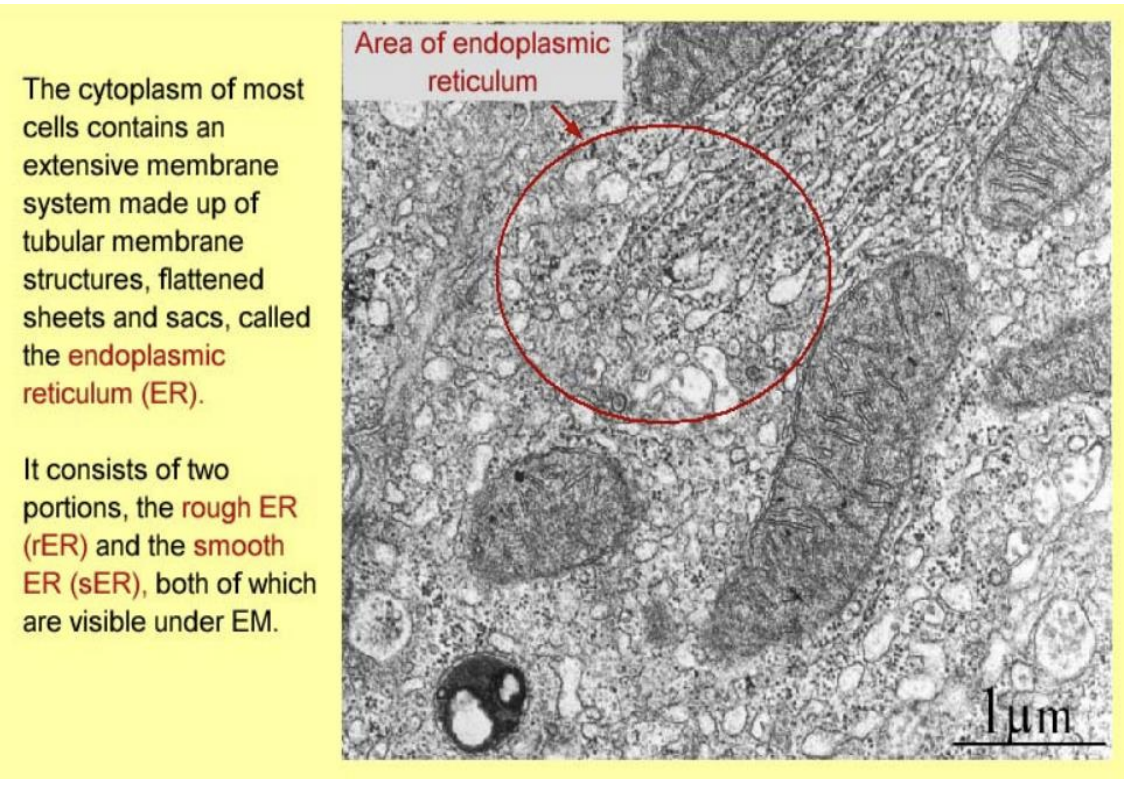
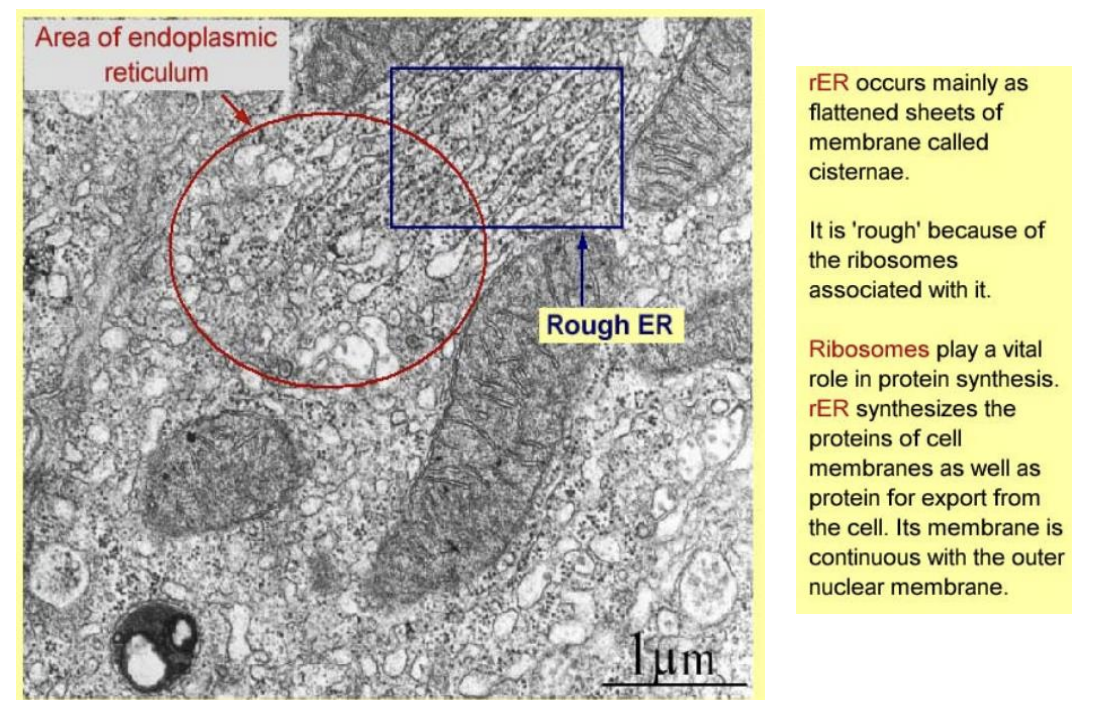
Rough ER
flattened sheets→ cisternae
rough→ ribosomes
protein synthesis and export
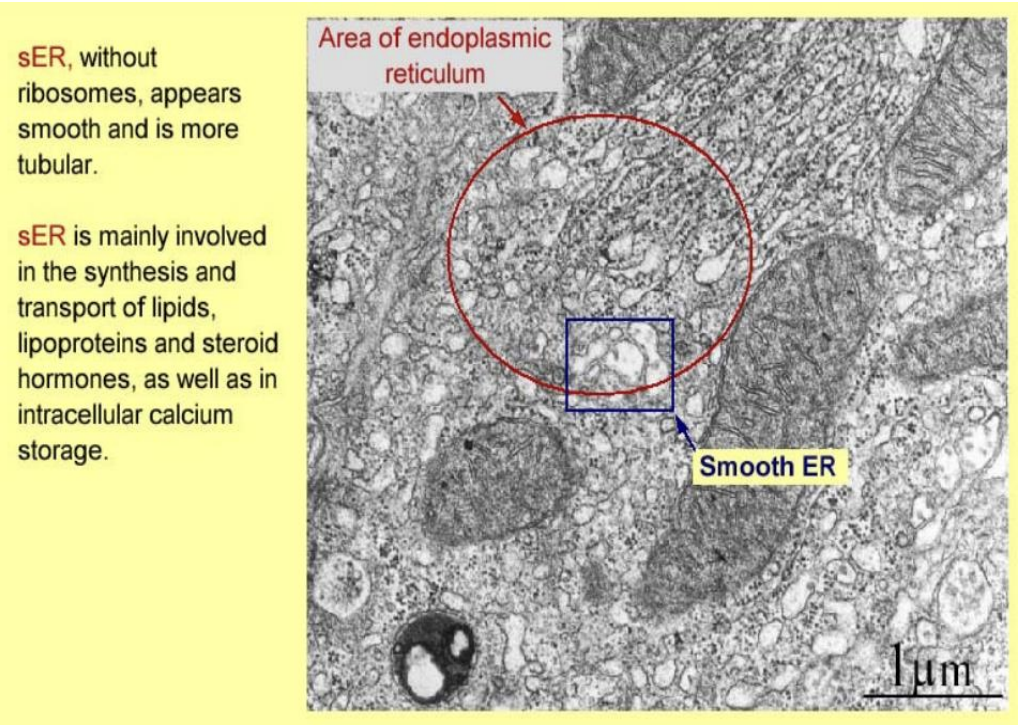
Smooth ER
no ribosomes
smooth
tubular
lipid synthesis and transport
intracellular C2+ storage
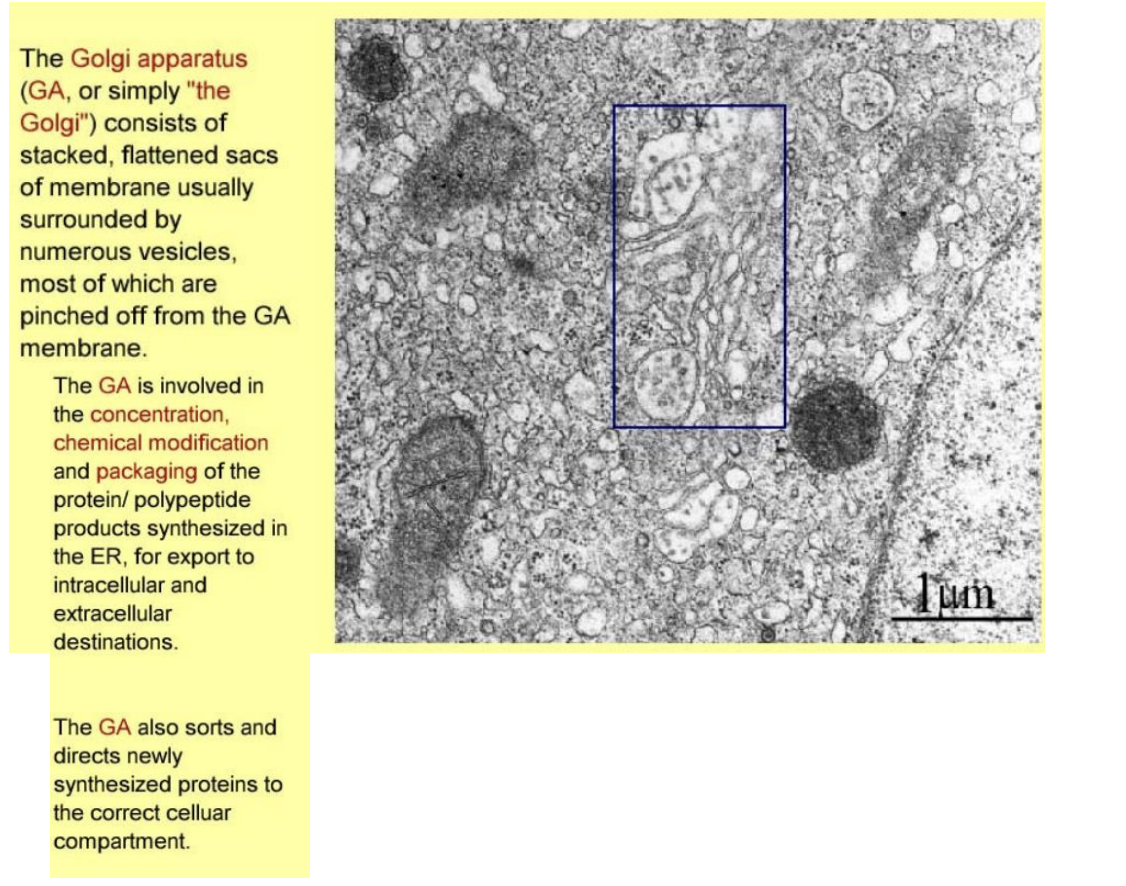
Golgi apparatus
stacked, faltterend sacs of membrane
surrounded by numerous vesicles→ pinched off from golgi
concentration, chemical mod and packaging of proteins from ER
sorts and directs protesin to correct cellular compartment
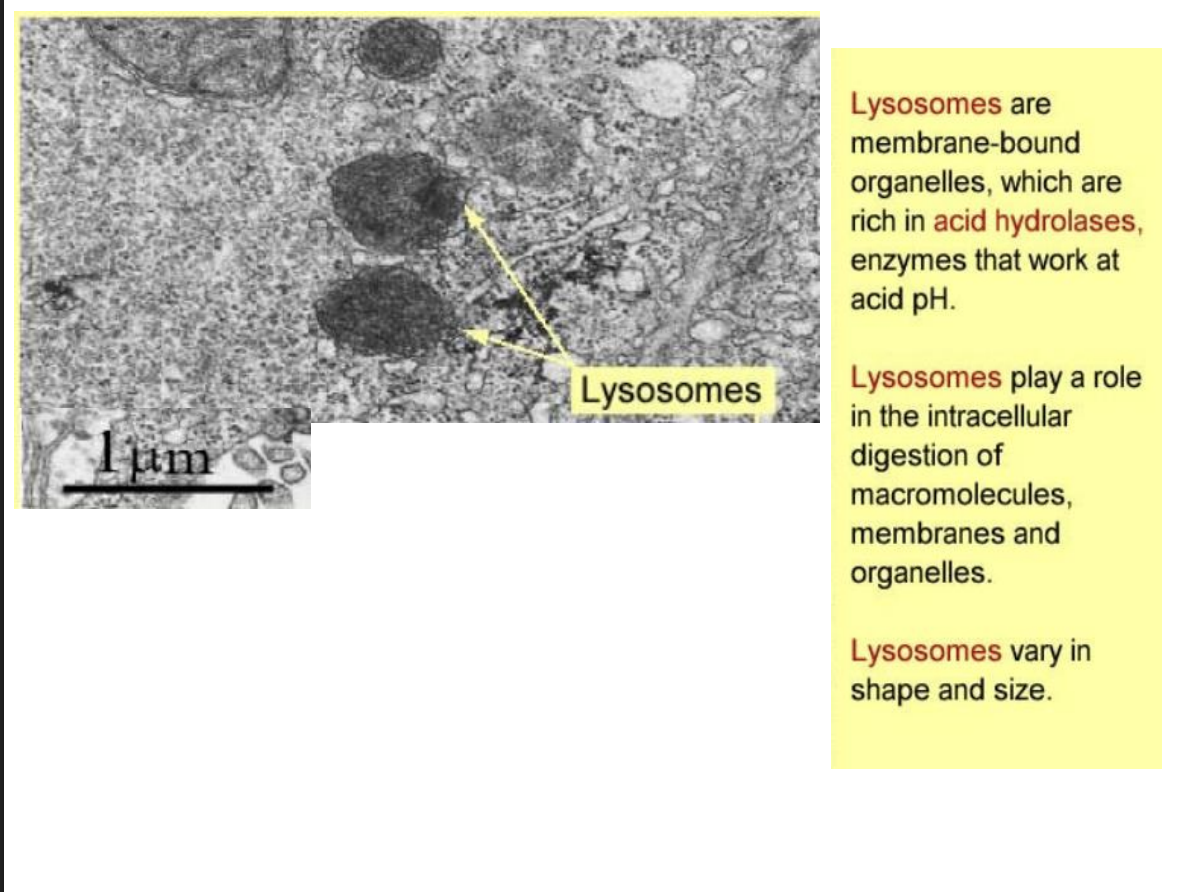
Lysosomes
membrane bound
acid hydrolases
intracellular digestion of macromolecules
vary in size and shape
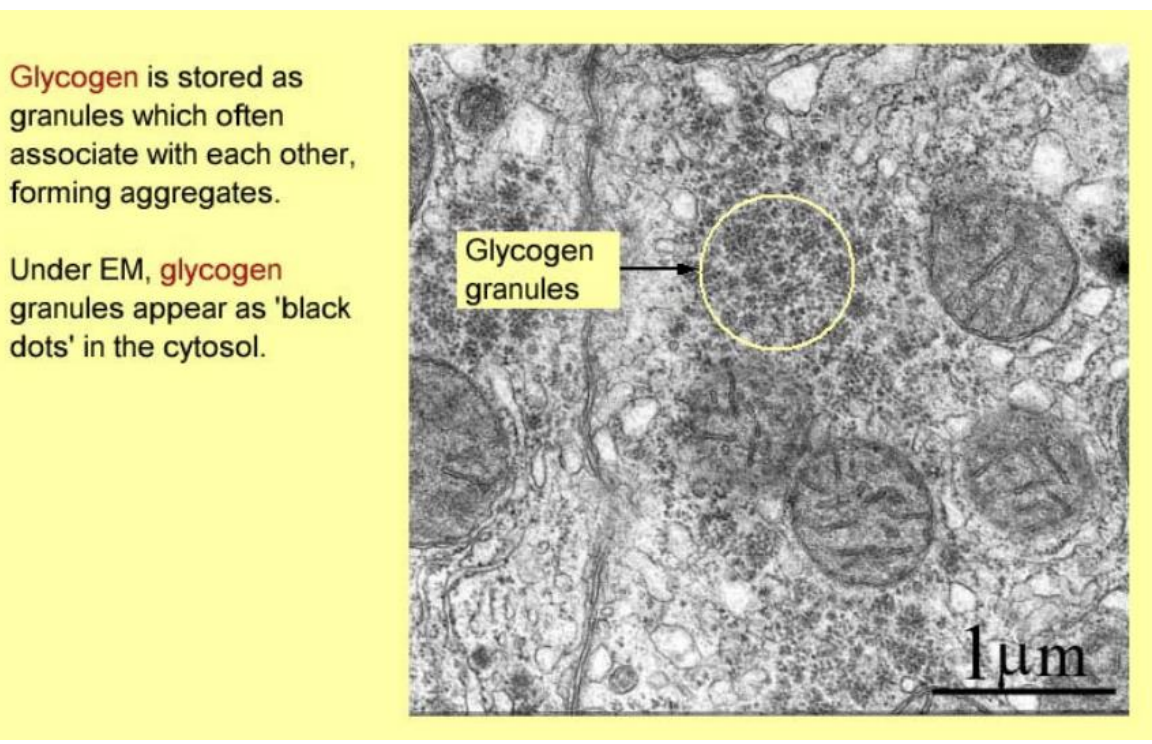
Glycogen granules
form aggregates
appear as black dots in cytosol
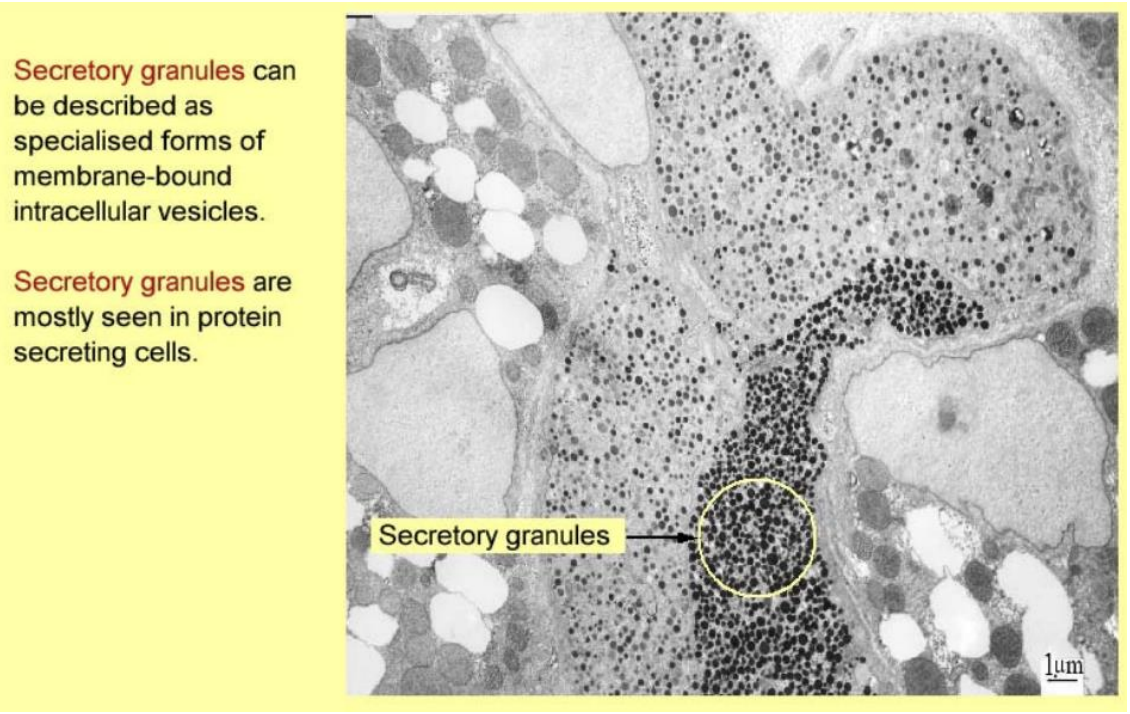
Secretory granules
intracellular vesicles
seen in protein secreting cells
Immunocytochemistry
technique used to detect presence of specific moelcules in cells and tissues→ especilaly protein
How does it work
antibodies (immunoglobulins, Igs) bind to targets with high specificty and affinity
can be generated by immune reactions and isolated and purifed
tagged with→
radioactive isotopes
gold colloid
fluoresent compounds
enzymes that catalyse formation of coloured reaction
electron sense protducts
Antibody binding sites viewed on LW or EM→ to find protein location
ALSO→ can be used as rough estimate for amount of protein
→ when calibrated→ e.g brightness of fluorescent light
In situ hybridisation
short nucleic acid segments of particular sequence synthesized chemically→ ‘probes’
tagged in similar way to antibodes
bind to
complementary uncoiled DNA in nucleus or
mRNA in cytosol
Shows gene expression→ cox uncoiled DNA (only in transciption and replication) and mRNA only in transciption
Therefore the use of in situ hybridisation
map location of genes in chromosome
localize the site of production of peptide hormones
detect presence of viruses
How is the probe localised
Use
immunocytochemistry
or
autoradiography
Preparing a tissue microscopic examination: aim
preserve the normal tissue structure
how
cut with microtome→ very thin sections to allow light pass through
mount to glass slide
stain coz most tissue is colourless
Observed without sectioning?
living cells
thin, transparent membrane→ e.g mesentery
→ observed directly
Preparation of a tissue for miscroscopic examination consists of
Fixation
Embedding
Sectioning
Distortion
Mounting
Staining
Fixation
in vivo cellular strucuture preserved
Chemical fixation with fixatives
solutions of stabilising or cross-linking agents
e.g Formaldehyde and glutaraldehyde most common
protein cross-linker
produce less distortion than fixative that coagulate protein (alcohlic fixers)
Other fixative effects→ induce chemical changes to tissue
e.g alcohol or organic solvents→ extract fat→ fat droplets look empty
Fixation→ must be fixed in a way that it can survive
embedding→ in semi-rigid medium (wax/plastic)
Slicing→ into 5-10um sections)
staining→ with selective dyes
1.1 Embedding
infiltrate tissue with small molecules
which can then be cross-linked to form matrix hard enough to withstand thin sectioning with microtome
Most common→ paraffin wax and acrylic resins
Because embedding media is water insoluble…
Must be dehydrated
How:
pass tissue through series of graded alcohol to 100% alcohol
then immersed in monomer plastic at room temp
or
melted paraffin wax in oven at 60 degrees
Cooled to room temp→ suitably hard for sectioning
1.2 Sectioning
slice with microtome
thin enough to transmit light
wax sections→ 7um thin
resin section→ 1-2 um thick
1.3 Distortion
Can be introduced to tissue during embedding and sectioning. How?
alcohol for dehydrating→
extracts fats
coagulates poorly fixed proteins
Paraffin wax and other embedding agents
shrink and sistort tissues
produces artefacts o nsections
Mounting
stuck onto glass slide
Staining
Variety of histologic stains commonly used to show up particular biochemical components of the tissue
Alcain blue →mucopolysaccharides
Eosin (neg charged, stains acidic)→ mitochondria, collagen, some secretory granules
Haematoxylin (pos charge, stain basophilic)→ nuclei, ribosomes, DNA
Ponceau S→ elastin
Osmium tetroxide→ lipid
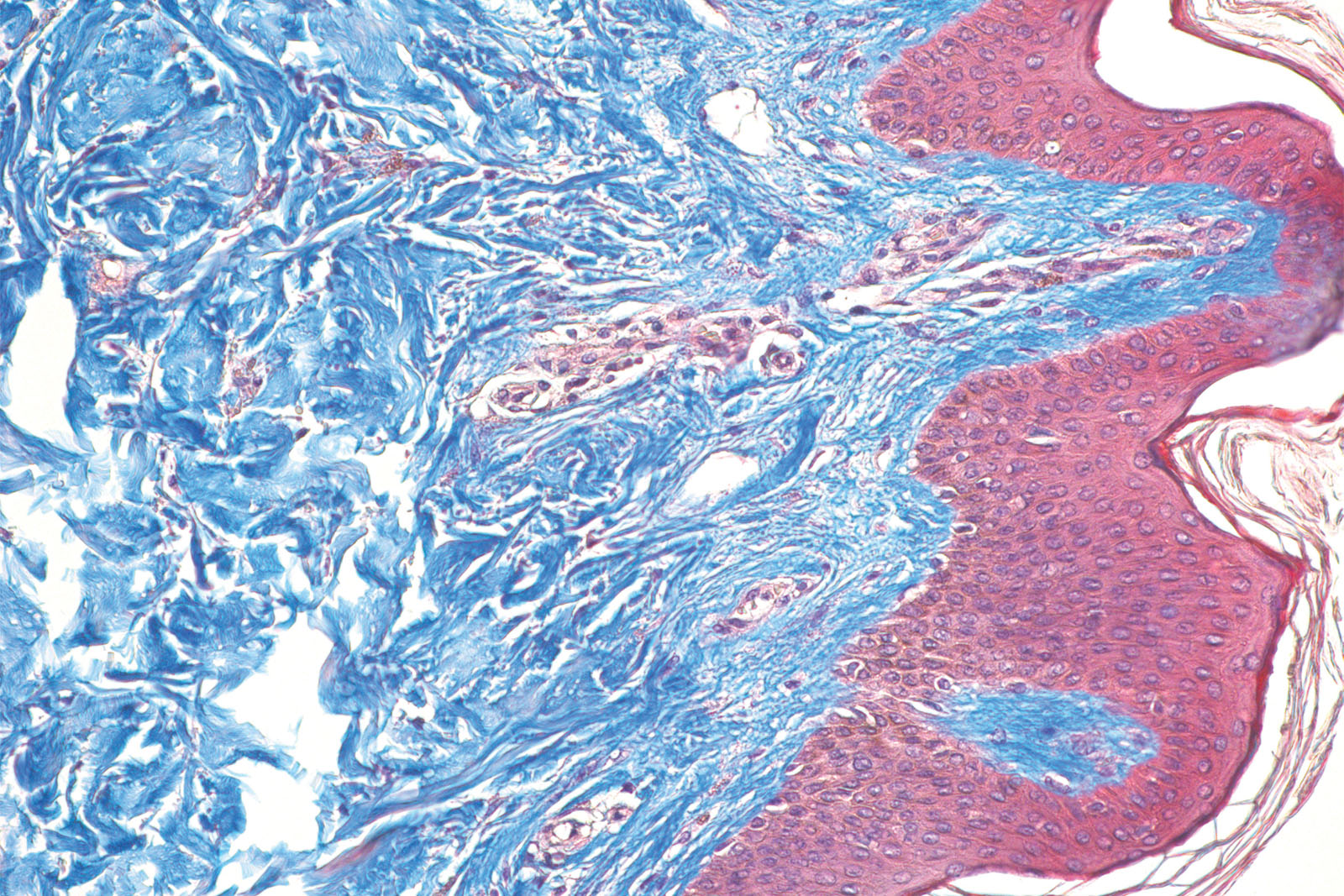
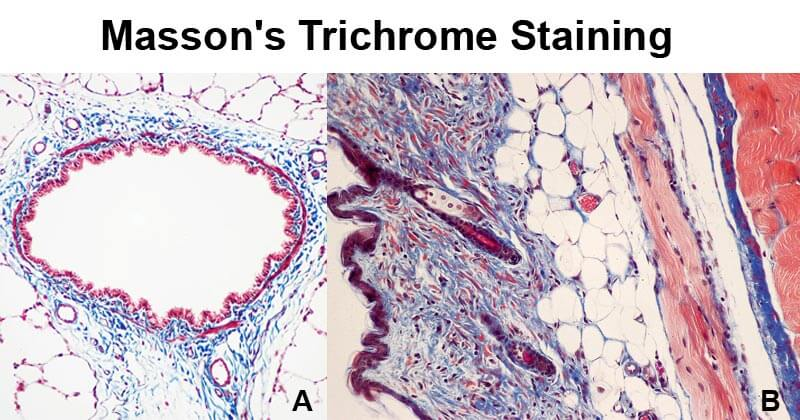
Trichome stain
comprise three different dyes
to stain different components in different colours