dt mock poooooooooo
1/56
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
57 Terms
the 6 rs
are the principles of reducing, reusing, recycling, recovering, remanufacturing, and redesigning waste materials to promote sustainability and minimize environmental impact.
what is a stock form?
Stock forms refer to raw materials that have been processed into standard sizes and shapes
why are stock forms so important?
Stock forms are essential as they standardize raw materials, streamline production processes, reduce waste, and facilitate easier storage and transportation, ultimately contributing to efficiency and sustainability in manufacturing.
examples of stock forms (metals)
-round rod
-round tube
-square
-hexagonal
-octagonal
-sheet
-channel
-square tube
-angle
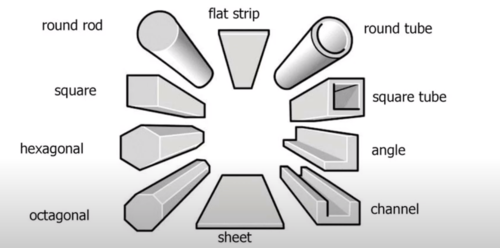
advantages of stock forms
-uniformity of material sizes across countries
-transported more easily compared to raw materials
-standard sizes are less expensive as theyre processed in large quantities
-less waiting time for a specialist size
-reduction in scrap material productions
mechanical properties of materials + examples
how a material reacts to an external force
-malleability
-ductility
-elasticity
-strength
-hardness
toughness
-durability
physical properties of a material + examples
actual structure of the material
-electrical properties
-thermal properties
-optical properties-density
malleability
withstand deformation by compression
ductility
deform under tensile strength
elasticity
bend and flex when force is applied (returning to its normal shape)
tensile strength
resist stretching/pulling forces
compressive strength
withstand pushing forces to resist deformation under compression
bending strength
withstand forces to bend material
shear strength
withstand forces acting against another
torsional strength
withstand twisting forces
hardness
how resistant a material is to indents/deformation
toughness
ability to absorb sudden impact before breaking
durability
resistance to wear and tear/corrosion
opaque
prevents light from passing through
translucent
allows light through but diffuses so objects look blurred
transparent
allows light to pass through easily so its clear
ferrous
contains iron, rusts, easily magnetic
non-ferrous
opposite of ferrous (copper/aluminium)
alloy
combination of a ferrous and non-ferrous material (bronze/brass)
hardwood
broad leaves
-ash
-maple
softwood
evergreen leaves, easier to cut
-pine
-cedar
manufactured board
sheet materials made through pressing/bonding
-mdf
-plywood
-flexiply
thermoplastics
becomes mouldable through heat and goes hard
-acrylic
-polyester
-tefilon
thermosetting polymers
resins with are set with heat
-epoxy
-silicone
elastomer
polymer with elasticity (weak)
-natural rubber
paper and boards
paper = recycled wood which has been rolled out
-wood
-pulp
composites
materials mixed with others to create better qualities
-reinforced concrete
smart materials
physical properties which can change in response to input
-titanium
-graphene
modern materials
materials engineered to increase the properties
-graphene
tensile strength test
-clamp materials in a vice
-add weights till material snaps
toughness test
-clamp in vice
-hit with a hammer
-if it withstands its tough, if not its brittle
hardness test
-centre punch on a material
-hit with a hammer
-the amount it dents shows how hard t is
malleability/ductility test
-clamp in vice
-if bends without creating a crack = ductile
corrosion test
-dropping material into salt water/acid
test for electrical conductivity
-use a volt meter
-amount of volts = conductivity
thermal conductivity
-use a thermometer when placing material above a bunsen burner
tensile test
-material placed in between grips
-weight applied to end
-materials tensile strength changes (measure till breaks)
die cutting
-cutting shape using a die
-die = sharp metal blades fixed to a block in the shape of the cut-
-rounded metal edges can also be in the block to create crease
-Can be used on paper, thin wood and polymer sheets
lathe
-turn a long length of material with specialist shaped tools
-Turning spins the material round whilst layers are shaved off
-is used for items like furniture and stair spindles
milling
-used for metal work
-a thin layer of metal is removed each turn at a carefully measured depth and speed
-can produce a really accurate finish
brazing, soldering and welding
-all use molten metal to join metal together
-Soldering uses solder melted at a relatively low temperature to join metal. It’s particularly used for electrical circuits and plumbing joints.
-Brazing heats joints to a higher temperature and uses brass to flood the joints.
-The strongest of all of the addition joints is welding which uses an electrical current to melt welding rod to flow together and cool between joints. Polymer can also be welded with plastic rod.
lamination
-sandwiches layers together to strengthen or protect
-plastic laminated paper, foam board, and plywood
Deforming and reforming
Vacuum forming heats sheet polymer until it is flexible and then sucks out the air between it and the mould to create a vacuum and an accurate copy.
blow moulding
-takes softened polymer and blows it into a mould with air like a balloon
-used to mould bottles and containers
casting
-pours molten material (pewter) into a mould (the die)
-used with metal, plastic, toilets and plastic soldier toys.
injection moulding
-injects liquid plastic into a mould under high pressure
-it creates accurate and quick products such as buckets and washing up bowls.
what is a nyloc nut?
-a kind of locknut with a nylon collar that increases friction on the screw thread so it is less likely to loosen
advantages and disadvantages of softwoods
Advantages of Softwoods:
Fast-growing and readily available
Generally less expensive than hardwoods
Easy to work with due to their softer nature
Good for general construction, framing, and paper production
Disadvantages of Softwoods:
Less dense and not as strong as hardwoods
Not as resistant to wear and decay
Limited aesthetic appeal compared to hardwoods
Not suitable for high-end furniture or flooring
advantages and disadvantages of hardwoods
Advantages of Hardwoods:
Higher density and more durable than softwoods
Greater strength, making them suitable for structural applications
More resistant to dents and scratches
Offer a wider range of aesthetic qualities with varied grains and colours
Disadvantages of Hardwoods:
Slower growth rates result in higher costs
Can be more challenging to work with due to their density
Some species are becoming less readily available due to deforestation
Generally heavier, which can complicate handling and installation
What is small scale production and what are its pros and cons?
-Small-scale production involves producing a limited quantity of items, often customized for niche markets, using less automation and more craftsmanship.
-This approach allows for greater customization, higher quality control, and stronger customer relationships.
-However, it generally results in higher per-unit costs and may not be suitable for mass markets.
What is medium scale production and what are its pros and cons?
-Medium-scale production involves producing goods in moderate quantities, balancing cost-effectiveness and customization.
Advantages include moderate per-unit costs, the ability to cater to a broader market than small-scale production, and some level of customization.
-However, it may lack the high level of customization seen in small-scale production and may not achieve the cost efficiencies of mass production.
What is large scale production and what are its pros and cons?
-Large-scale production refers to the manufacturing of goods in substantial quantities, utilizing highly automated processes and standardized procedures to achieve maximum efficiency.
-This approach is characterized by low per-unit costs, making products affordable and accessible to mass markets.
-However, large-scale production offers limited customization options and can be less adaptable to changing consumer preferences.
-It is well-suited for products with stable demand and uniform specifications.