Intro to Proofs
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
15 Terms
Addition Property
If a = b and c = d then a + c = b + d
Subtraction Property
If a = b and c = d then a - c = b - d
Multiplication Property
If a = b then a × c = b × c
Division Property
If a = b and c ≠ 0 then a ÷ c = b ÷ c
Substitution Property
If a = b, then anywhere I have a, I can replace it with b (and vice versa)
Reflexive Property (Equality)
a = a, AB = AB, and m∠C = m∠C
Symmetric Property (Equality)
If a = b, then b = a
Transitive Property (Equality)
If a = b and b = c, then a = c
Reflexive Property (Congruence)
Line AB ≅ Line AB, and ∠C ≅ ∠C
Symmetric Property (Congruence)
If Line AB ≅ Line EF, then Line EF ≅ Line AB; If ∠C ≅ ∠H, then ∠H ≅ ∠C
Transitive Property (Congruence)
If Line AB ≅ Line CD and CD ≅ Line EF, then AB ≅ EF
If ∠A ≅ ∠B and ∠B ≅ ∠C, then ∠A ≅ ∠C
Midpoint Definition
If M is the midpoint of segment AB, then AM ≅ MB
(midpoint → congruent segments)

Midpoint Theorem
If M is the midpoint of segment AB, then AM = 1/2 AB and MB = 1/2 AB
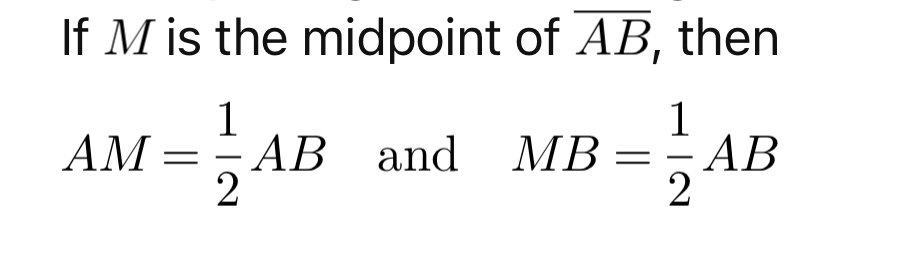
Angle Bisector Definition
If ray BX bisects angle ABC, then ∠1 ≅ ∠2
(angle bisector → congruent angles)

Angle Bisector Theorem
If ray BX bisects angle ABC, then m∠1 = 1/2 m∠ABC and m∠2 = 1/2 m∠ABC
