APHG Unit 6 Practice Test (Study Guide)
1/78
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
79 Terms
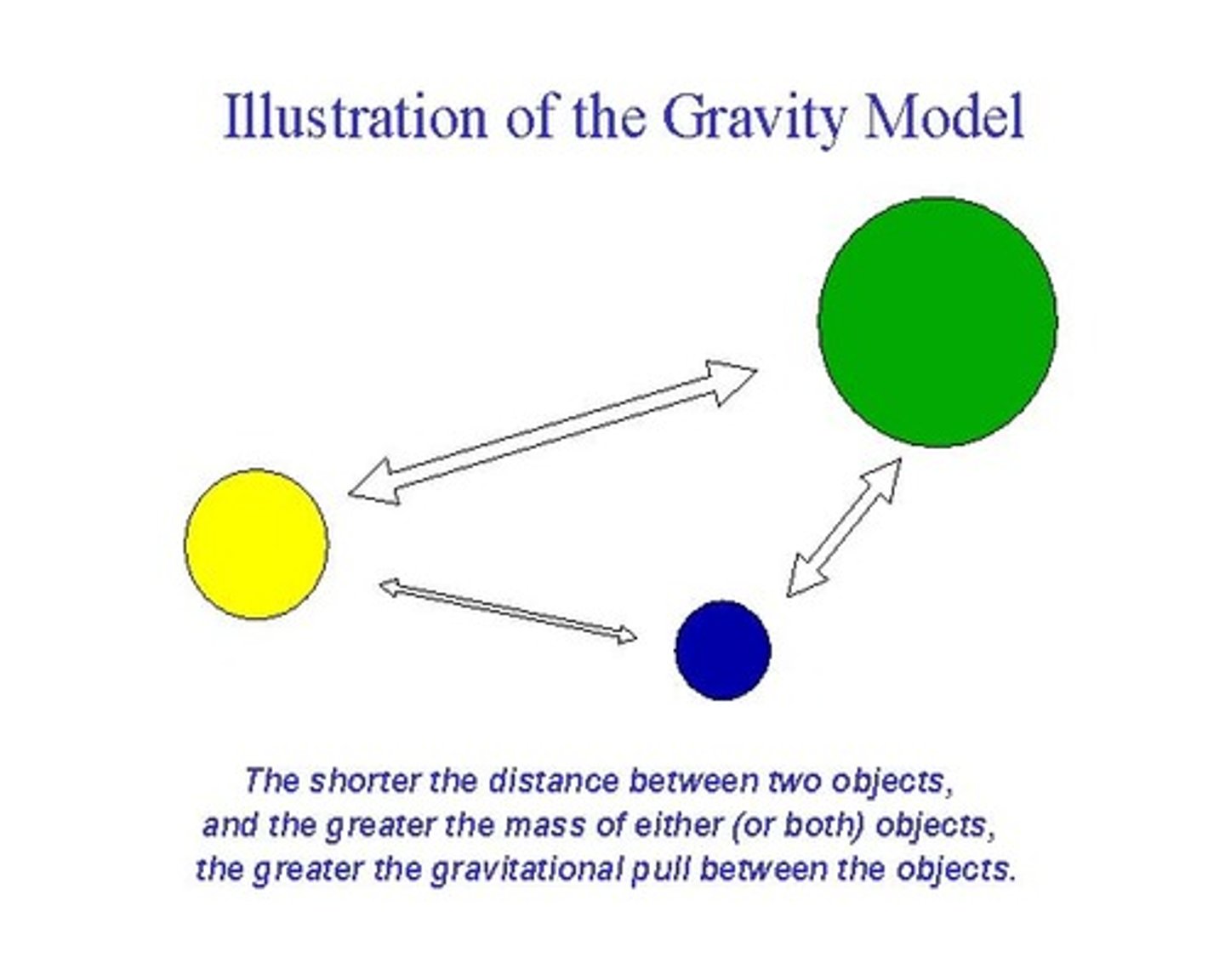
What model is shown?
gravity model
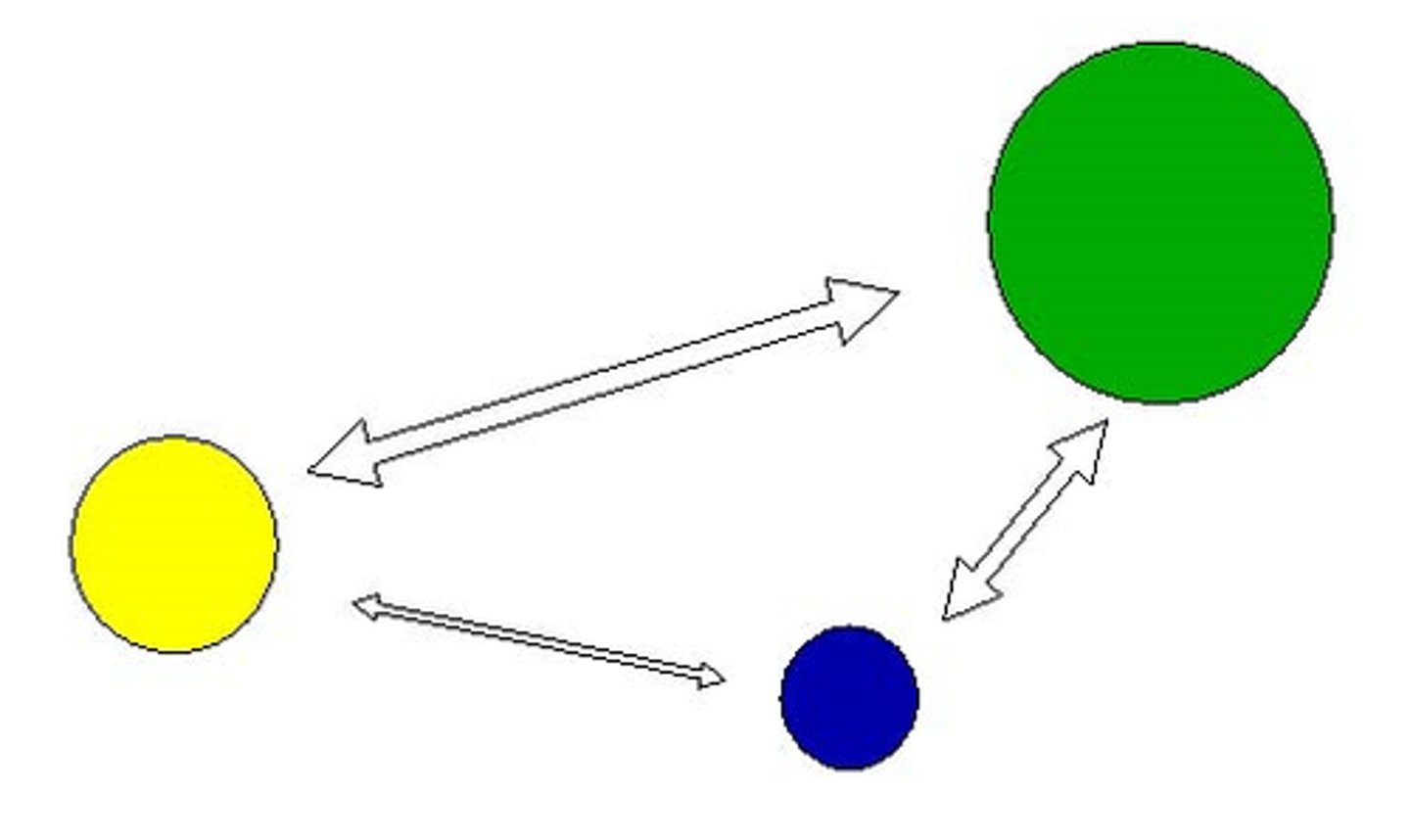
what premise is supported by the gravity model?
the interaction between two cities depends on their size
what best defines an urban area?
an urban area is any area defined by different countries using different criteria
The Global Power City Index ranks world cities. What factor is not part of its ranking?
Population size
what best applies to Australia's cities?
Australia does not have a primate city or follow the rank-size rule
what term describes a suburb that has grown rapidly into a large, sprawling city with more than 100,000 residents?
boomburb
what is the major industry in San Jose, California, and Bengaluru, India?
Information technology
how does a metacity differ from a megacity?
a metacity has a larger population than a megacity
what contributed most to the fact that Africa has many primate cities, such as Dakar, Senegal?
Colonization
What infrastructure development contributed most to US suburbanization after WWII?
the automobile
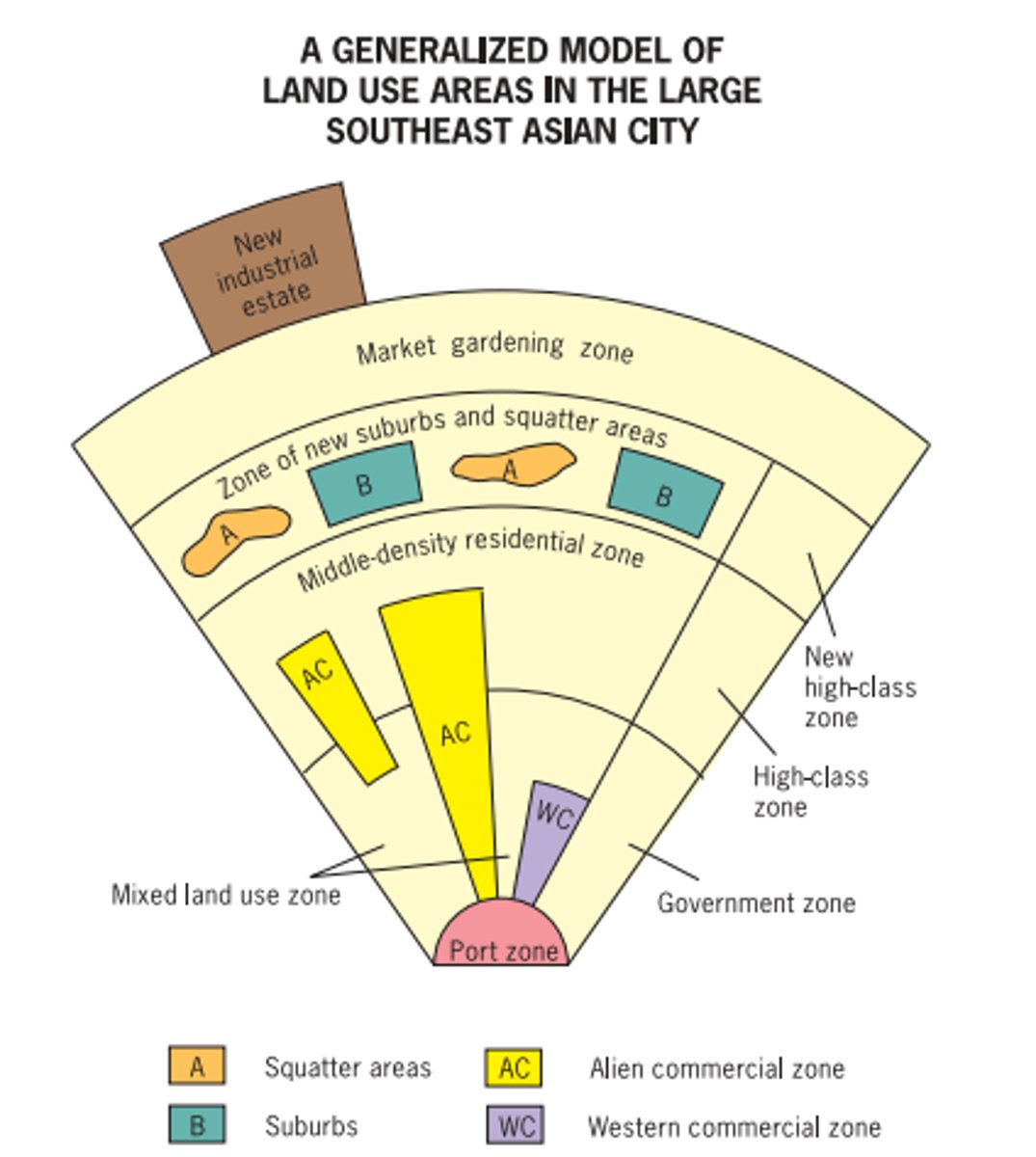
what premise framed the Southeast Asian city model?
Southeast Asian cities grew around ports and lack a clearly defined central business district
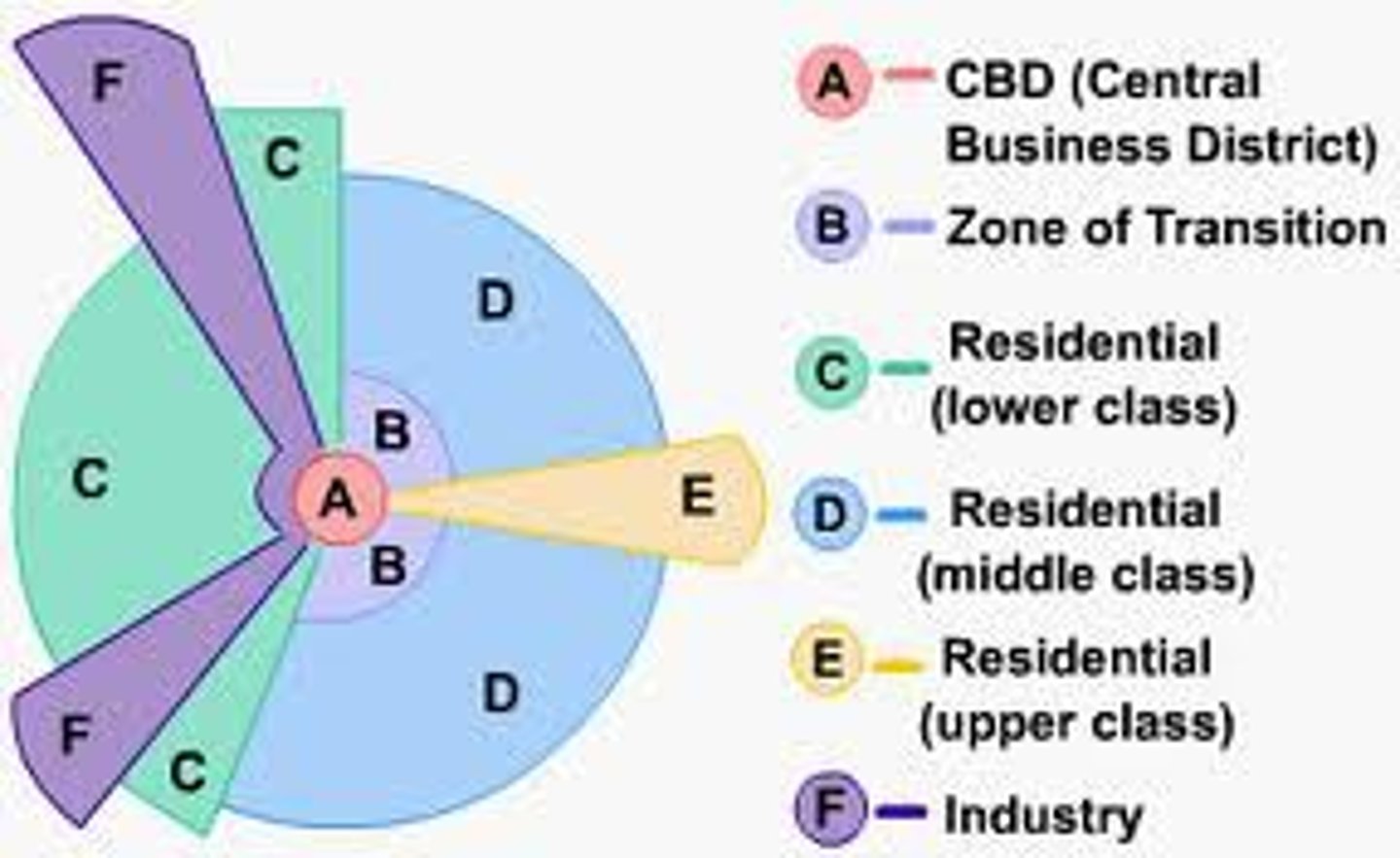
what model is shown?
Burgess concentric-zone model
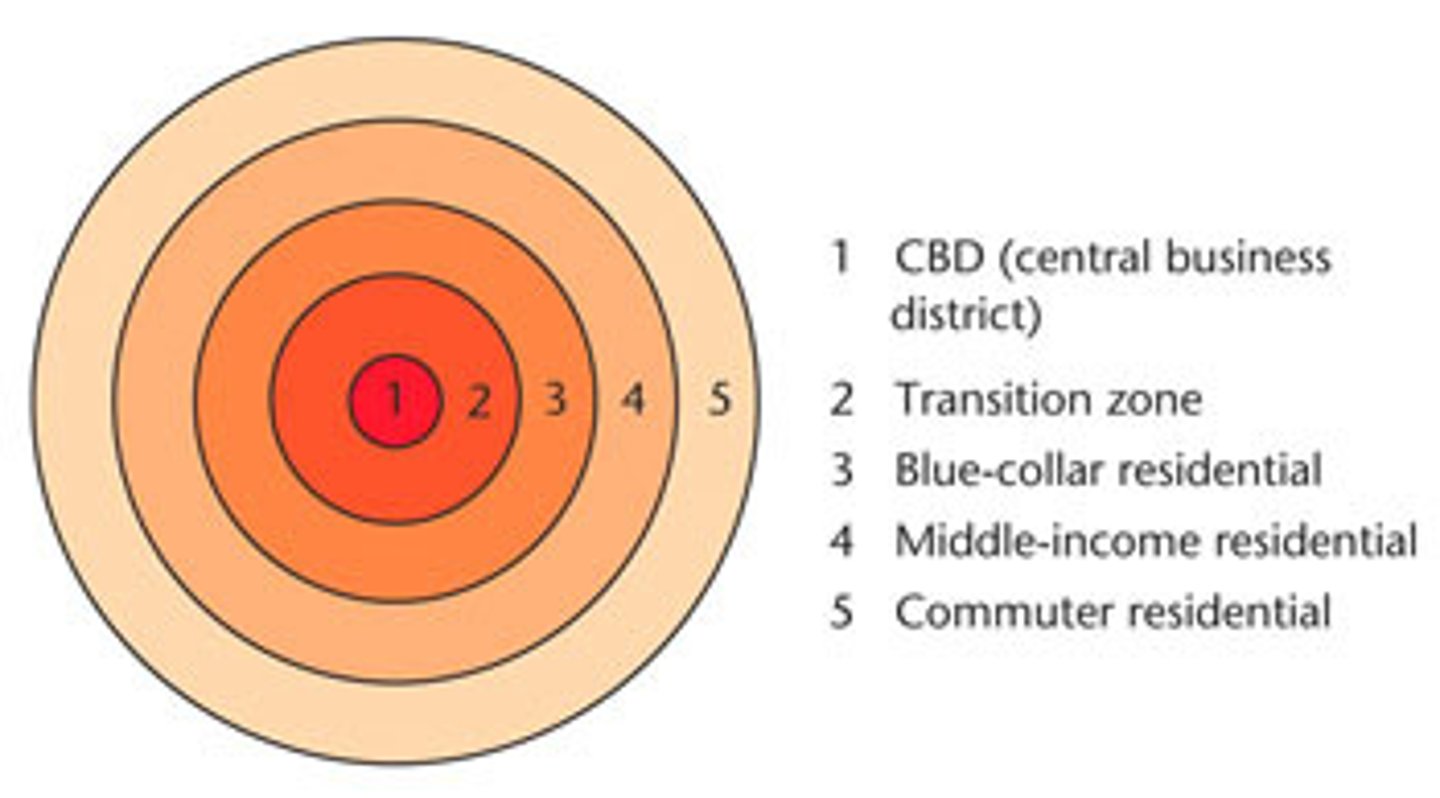
what conclusion about cities is fundamental to the burgess concentric-zone model?
a city grows outward from the central business district in a series of rings
how does the urban population density of US cities compare with other parts of the world?
US cities are less densely populated than cities in most other parts of the world
triple-deckers in boston and row houses in new orleans are example of which type of housing?
medium-density housing
what explains the effect of a strong infrastructure on a community?
strong infrastructure enables the effective transportation of goods to market and people to access goods
what would be the best use of the data shown in the bike ridership in seattle graph?
whether recent biking-related ordinances are effective
what accurately compares urban population density?
newer cities tend to have less population density than older cities
what is the best example of how infrastructure can be used to create a more equitable living environment?
dedicated bus lanes in Bogota, Columbia
what is the purpose of zoning?
to allow only specific land uses in various areas of a city
what is an example of housing discrimination?
redlining
what concept is illustrated in the photograph of the bridge?
gentrification
what is the goal of an urban growth boundary?
to define where new development can take place
What are brownfields?
abandoned and polluted industrial sites
what is a major challenge for cities with urban growth boundaries?
lack of affordable housing
what was the cause of contaminated drinking water in Newark, New Jersey, and Flint, Michigan?
Lead from water pipes (might not be right answer)
What is the main benefit of diverse housing?
diverse housing promotes mixed-income neighborhoods
what do greenbelt towns such as Greenbelt, Maryland, and Greenhills, Ohio, have in common?
they were built during the Great Depression to provide affordable housing
what is shown in the photograph of the neighborhood?
a favela
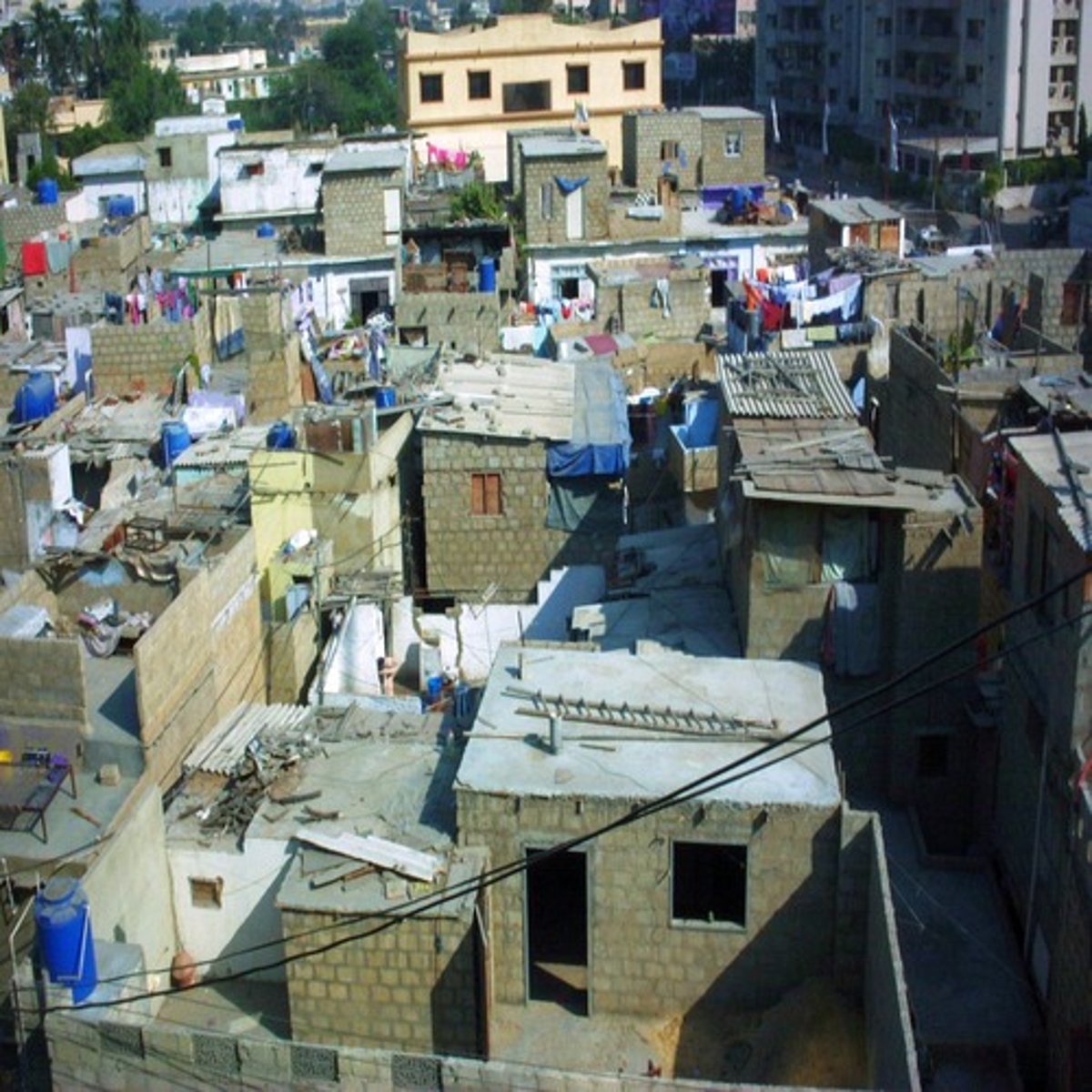

what is most closely associated with the type of settlement shown in a favela?
increased crime rates
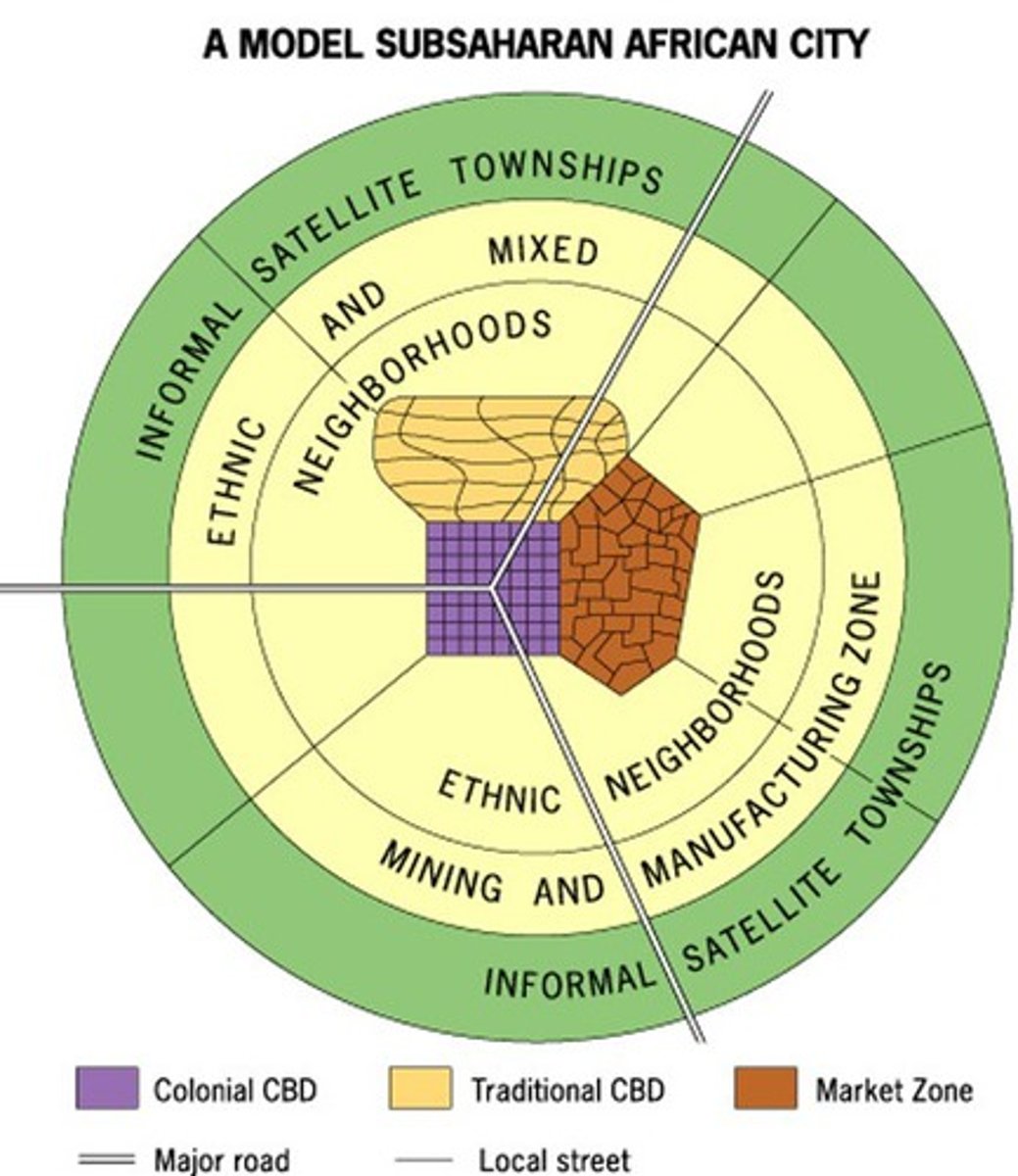
african city model
a model of urban development depicting a city with three central business districts, growing outward in a series of concentric rings
annexation
Legally adding land area to a city in the United States
bid-rent theory
a theory that describes the relationships between land value, commercial location, and transportation (primarily in urban areas) using a bid-rent gradient, or slope; used to describe how land costs are determined
Blockbusting
when real estate agents would stir up concern that "undesirable" families would soon move into a neighborhood to convince white property owners to sell their houses at below-market prices
boomburbs
a suburb that has grown rapidly into a large and sprawling city with more than 100,000
Central Business District (CBD)
the central location where the majority of consumers services are located in a city or town because the accessibility of the location attracts these services
magacity
a great city that has more than 5 million people but number changes between countries
Megalopolis
a very large, heavily populated city or urban complex.
Metacity
A city with a population over 20 million
mixed-use neighborhoods
Zoning that has a mix of homes and businesses with a variety of sizes and price ranges.
multiple nuclei model
a model of urban development depicting a city where growth occurs around the progressive integration of multiple nodes, not around one central business district
new urbanism
a school of thought that promotes designing growth to limit the amount of urban sprawl and preserve nature and usable farmland
place character
A sense of uniqueness that can also be erased as a result of new urban designs
planned community
a city, town, or community that was designed from scratch, and grew up more or less following the plan
primate city
the largest city in a country which far exceeds the next city in population size and importance
rank-size rule
second largest city is 1/2 size of the largest; third largest will be 1/3 of largest
relining
when lending institution refuses to offer home loans on the basis of a neighborhood's racial or ethnic makeup
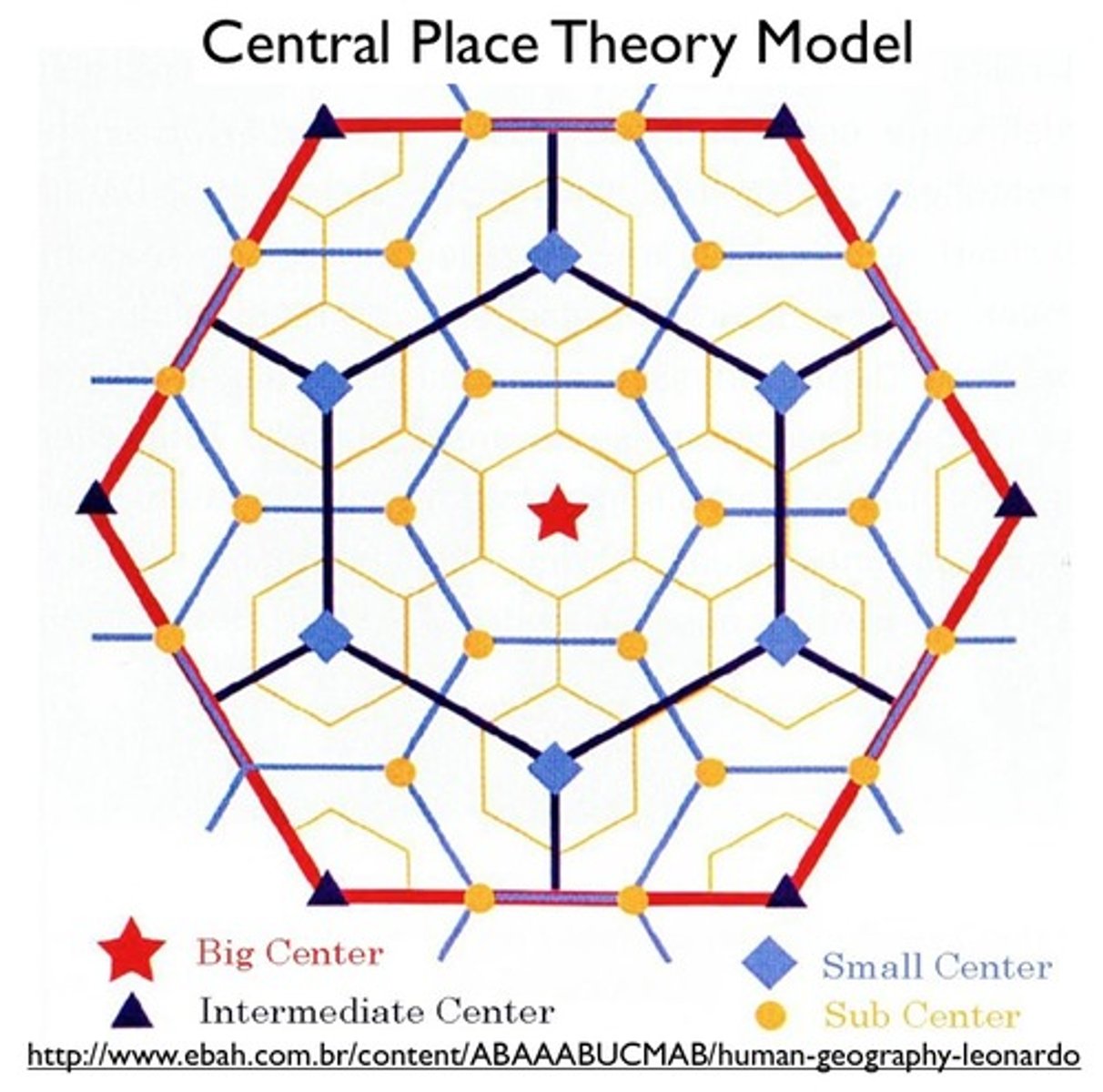
Central Place Theory
theory used to describe the spatial relationship between cities and their surrounding communities
Census Tract
An area delineated by the U.S. Bureau of the Census for which statistics are published; in urbanized areas, census tracts correspond roughly to neighborhoods.
Concentric Zone Model
a model of urban development depicting a city growing outward from a CBD in a series of rings
Disamenity Zones
high-poverty urban areas in disadvantaged locations containing steep slopes, flood-prone ground, rail lines, landfills, or industry
Edge City
type of community located on the outskirts of a larger city with commercial centers with office space, retail complexes, and other amenities typical of an urban center
Exurbanization
typically fast-growing community outside of or on the edge of a metropolitan area where the residents and community are closely connected to the central city and suburbs
food desert
area where residents lack access to healthy, nutritious foods because stores selling these foods are too far away
Galactic/Peripheral Model
a model of urban development depicting a city where economic activity has moved from the CBD toward loose coalitions of other urban areas and suburbs
Gentrification
the renovations and improvements conforming to middle-class preferences
Reurbanization
growth of population in metropolitan central cores, following a period of absolute or relative decline in population
Sector Model
a model of urban development depicting a city with wedge-shaped sectors and divisions emanating from the CBD
segregation
Separation of people based on racial, ethnic, or other differences
site
absolute location, as well as its physical characteristics, such as the landforms, climate, and resources
situation
the location of a place relative to other places
Favela
a poor neighborhood where many people live in a state of poverty
smart growth
placing development in convenient locations and designing it to be more efficient and environmentally responsible
Southeast Asia city model
model of urban development depicting a city oriented around a port and lacking a formal CBD; growing outward in concentric rings and along multiple nodes
Squatter Settlement
An area within a city in a less developed country in which people illegally establish residences on land they do not own or rent and erect homemade structures.
urban sprawl
areas of poorly planned, low-density development surrounding a city
Globalization
the expansion of economic, political, and cultural processes on a worldwide scale
Gravity Model
model that predicts the interaction of two or more places
greenbelts
a ring of parkland, agricultural land, or another type of open space maintained around an urban area to limit sprawl
infilling
redevelopment that identifies and develops vacant parcels of land within previously built areas
infrastructure
the many systems and facilities that a country needs in order to function properly
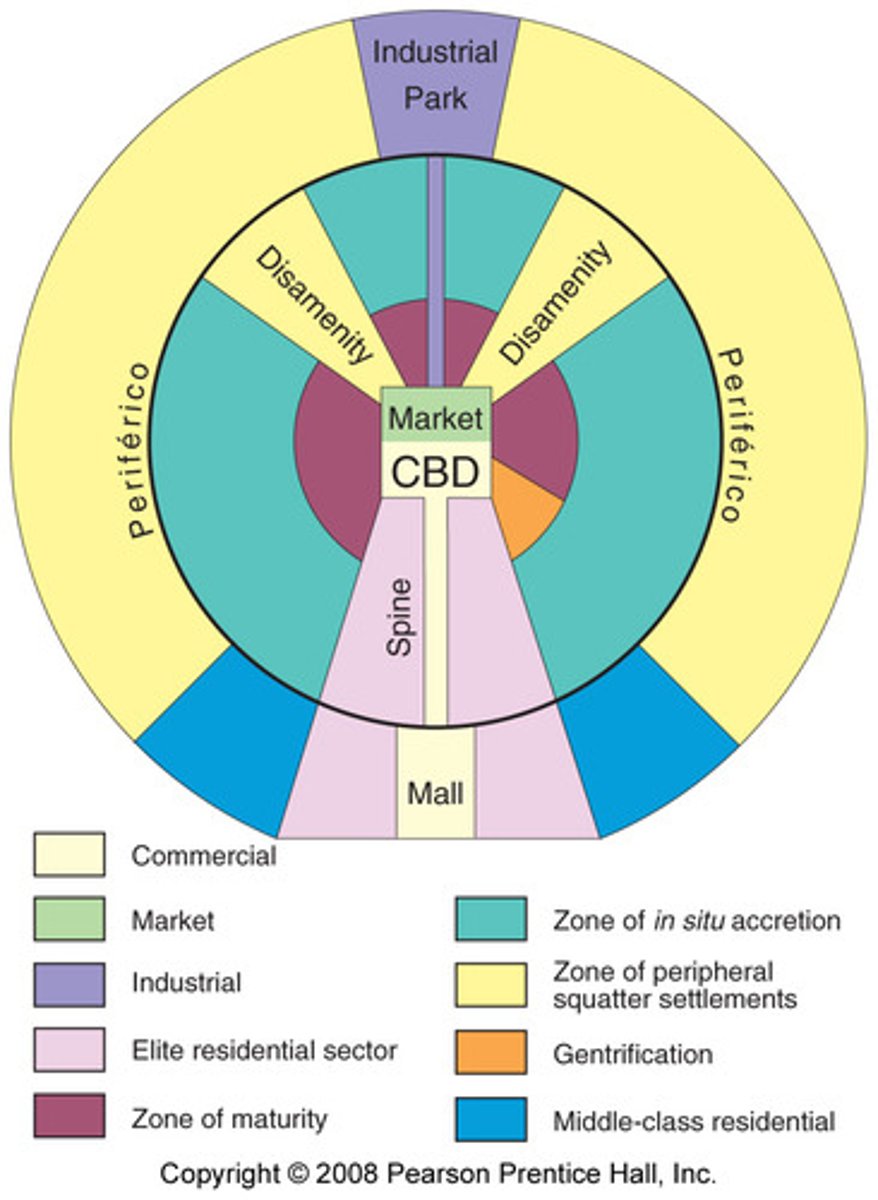
Latin American City Model
model of urban development depicting a city with a CBD, concentric rings, and sections stricken by poverty
metropolitan area
city and the surrounding areas that are influenced economically and culturally by the city
Suburbanization
shifting of population away from cities into surrounding suburbs
urban renewal
nationwide movement that developed in the 1950s and 1960s when US cities were given massive federal grants to tear down and clear out crumbling neighborhoods and former industrial zones as means of rebuilding their downtowns
urban area
a city and its surrounding suburbs
world city
city that wields political, cultural, and economic influence on a global scale
zone of abandonment
areas that have been deserted to lack of jobs, declines in land value, and falling demand
Zoning
the process of dividing a city or urban areas into zones within which only certain land uses are permitted