Carbonyl compounds
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
Draw the functional group of alcohol
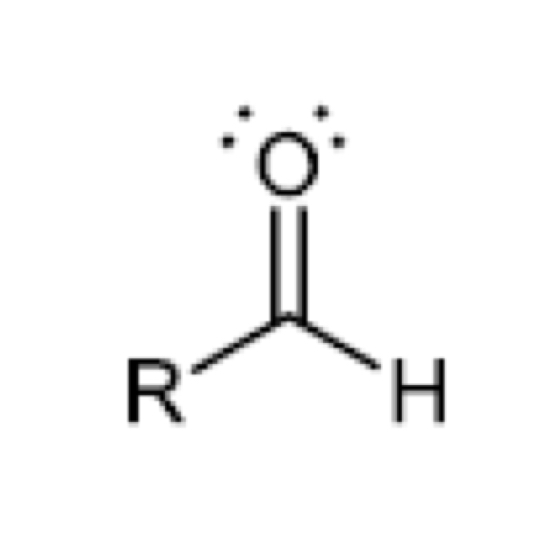
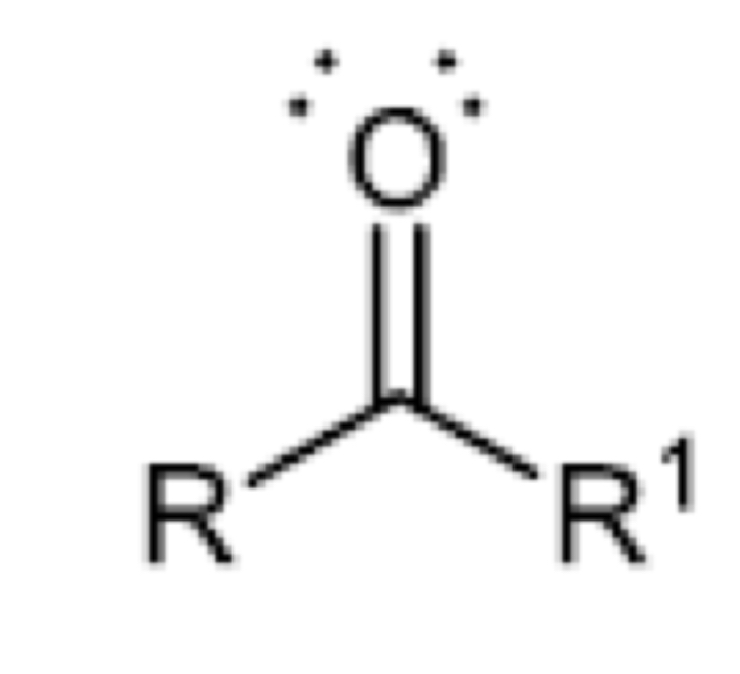
Functional group of ketone
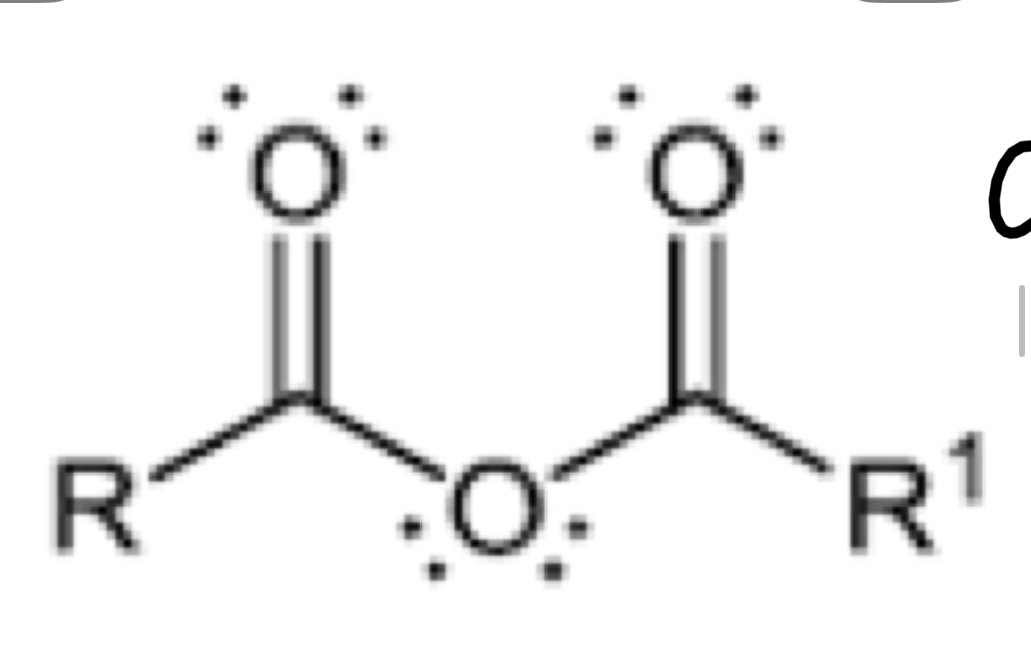
Functional group of anhydride
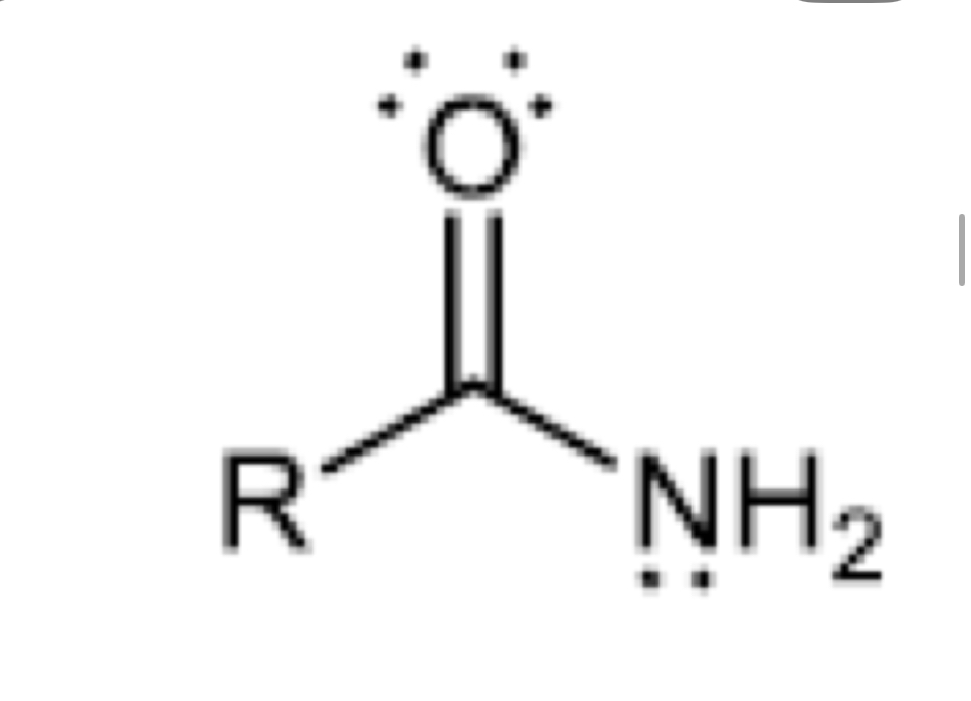
Functional group of primary amide
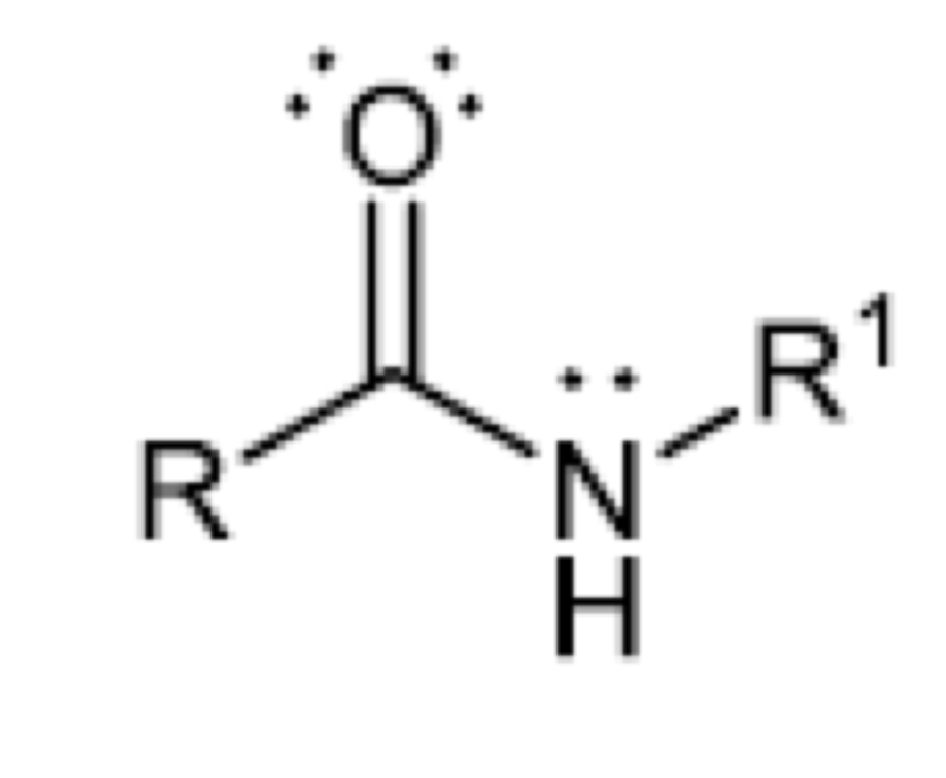
Functional group of secondary amide
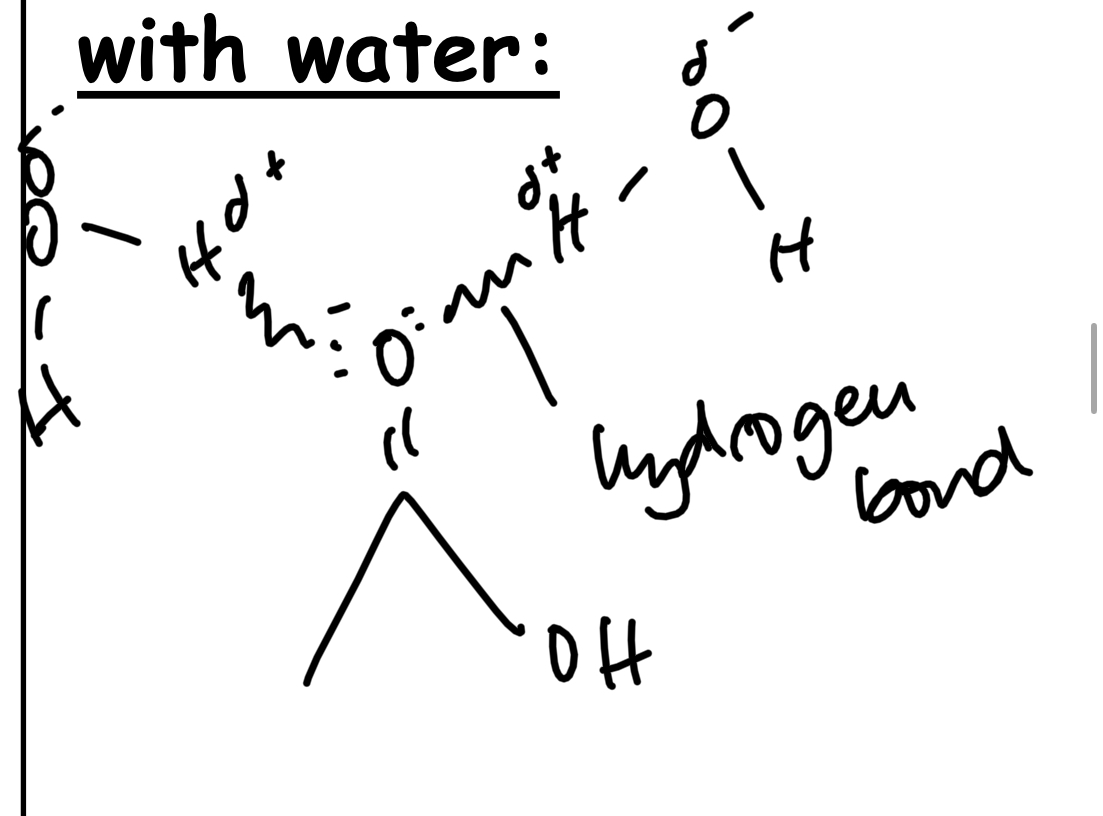
Draw a compound showing how a carbonyl compound can hydrogen bond with water.
Why do many drug compounds contain carbonyl groups ?
there is an abundance f hydrogen bonds within the human body therefore hydrogen bonding can occur between a drug containing a carbonyl group and a receptor on a human body cell.
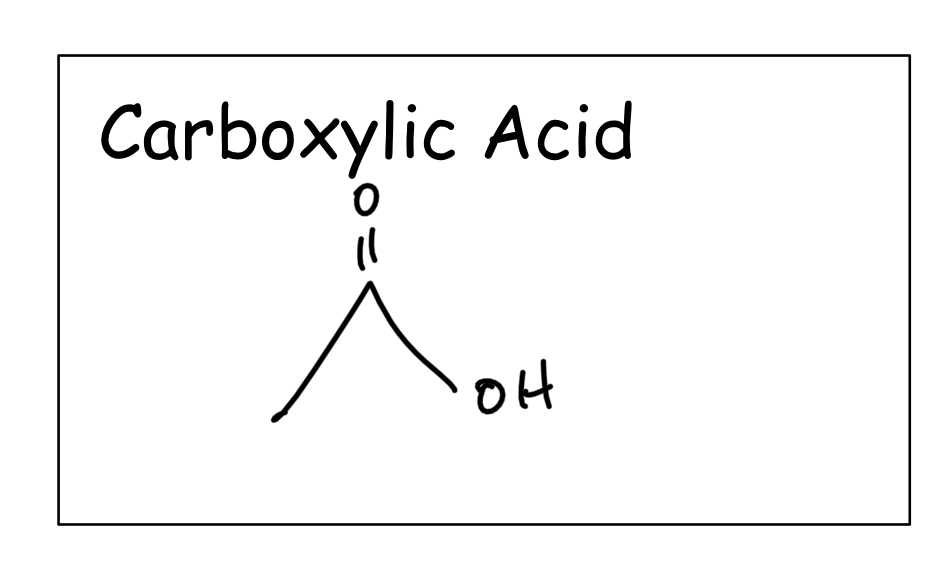
Draw the structure of a carboxylic acid .
Describe the location of the two nonbonding electron pairs on the carbonyl oxygen.
Both nonbonding pairs are in the sp2 orbital.
Explain why carboxylic acids are stronger acids than alcohols.
Due to the resonance stability of the carboxylate ion ( conjugate base of carboxylic acids) - a more stable conjugate base means a stronger acid as the acid is reformed more readily.
In an alcoxide ion the negative charge is localised on the oxygen making it less stable.
Why do nucleophiles add to carbonyl compounds ?
The carbon of the carbonyl group has a partial positive charge, which attracts nucleophiles.
Explain the difference in acidity between trifluoroacetic acid and methanoic acid.
The CF3 group is electron withdrawing, which stabilises the conjugate base carboxylate ion and increases the acidity.
Name a reagent used for the reduction of aldehydes and ketones.
NaBH4
What do you need to make an amide from a aci chloride?
An amine and a base
Why does nucleophiles elimination not occur when H and R are leaving group from a carbonyl compound ?
H and R do not form stable anions so are not good leaving groups.
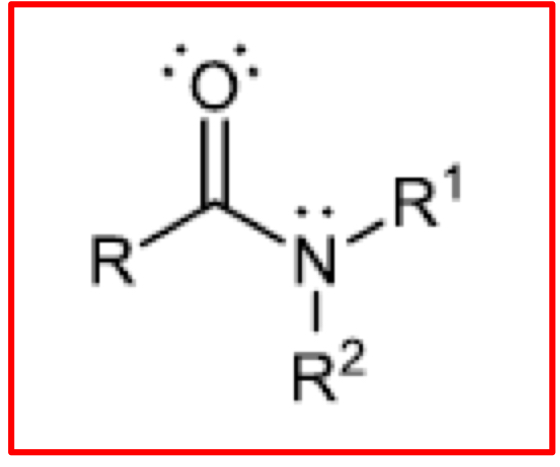
Structure of a tertiary Amide
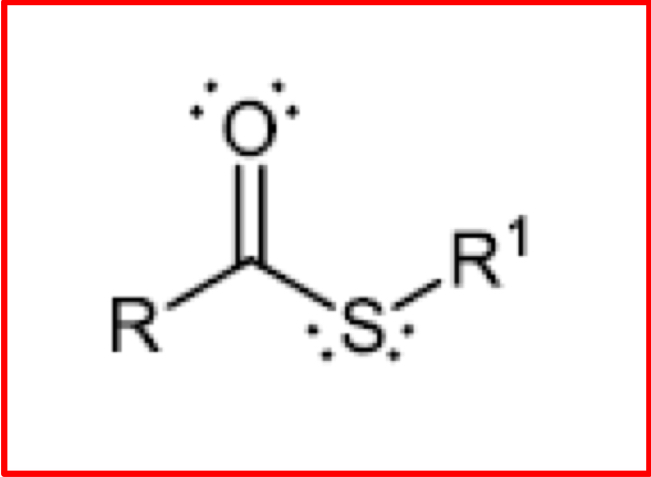
Structure of a Thioester
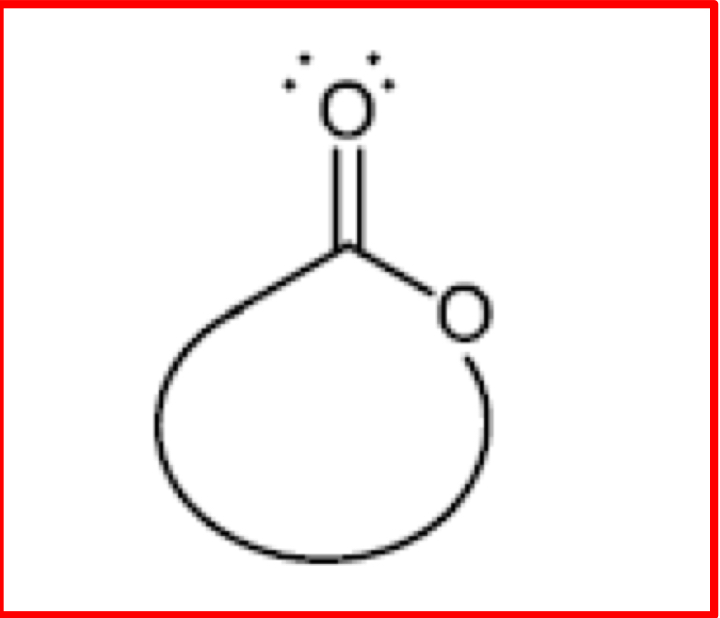
Structure of a Lactone
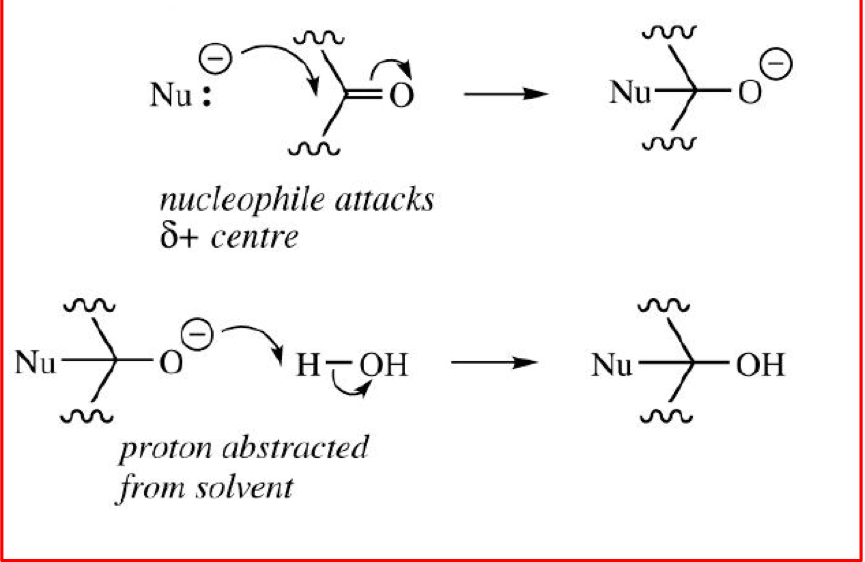
Draw the mechanism for the nucleophilic addition to a carbonyl group
Draw the Mechanism for the acid hydrolysis of an ester.
Draw the mechanism for the base catalysed ester hydrolysis
Draw a mechanism for the lydrolysis of an acid chloride
Draw the reaction mechanism for the reduction of an aldehyde.