Unit 9 - the Gas Laws
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
14 Terms
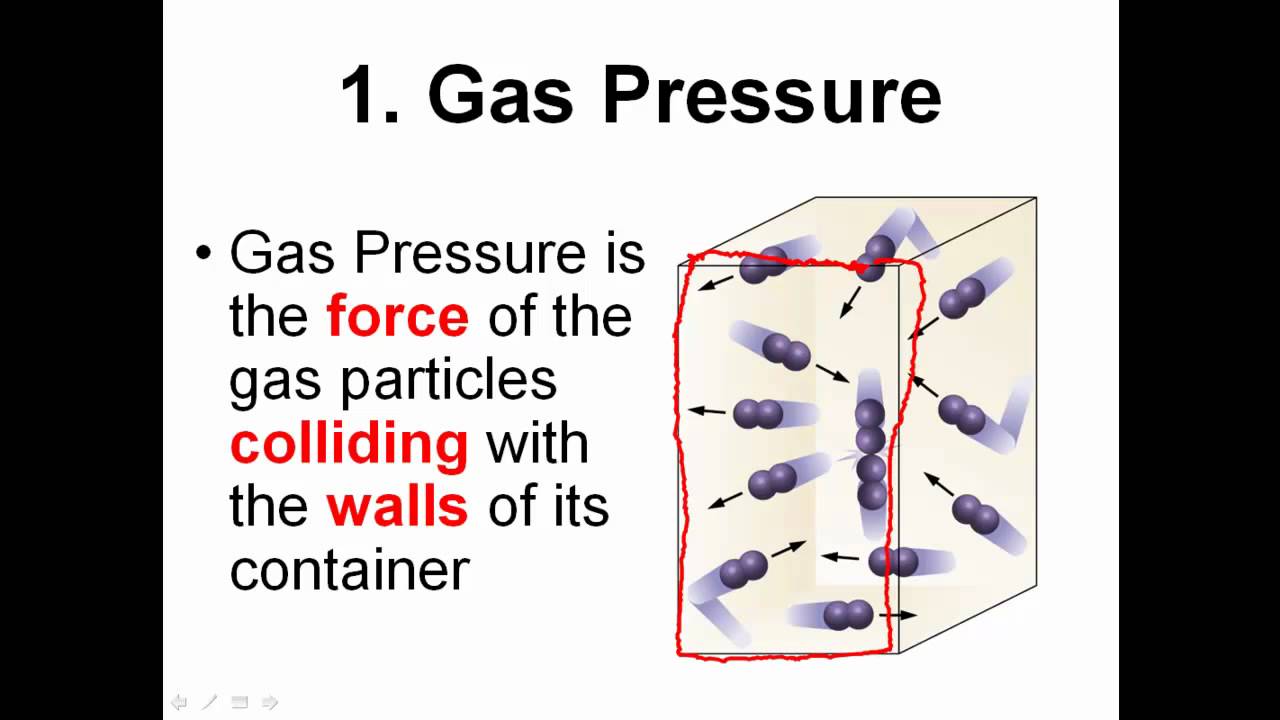
pressure
The force exerted by gases on the walls of their container, usually measured in atmospheres (atm) or pascals (Pa). It is affected by temperature, volume, and the number of gas particles.
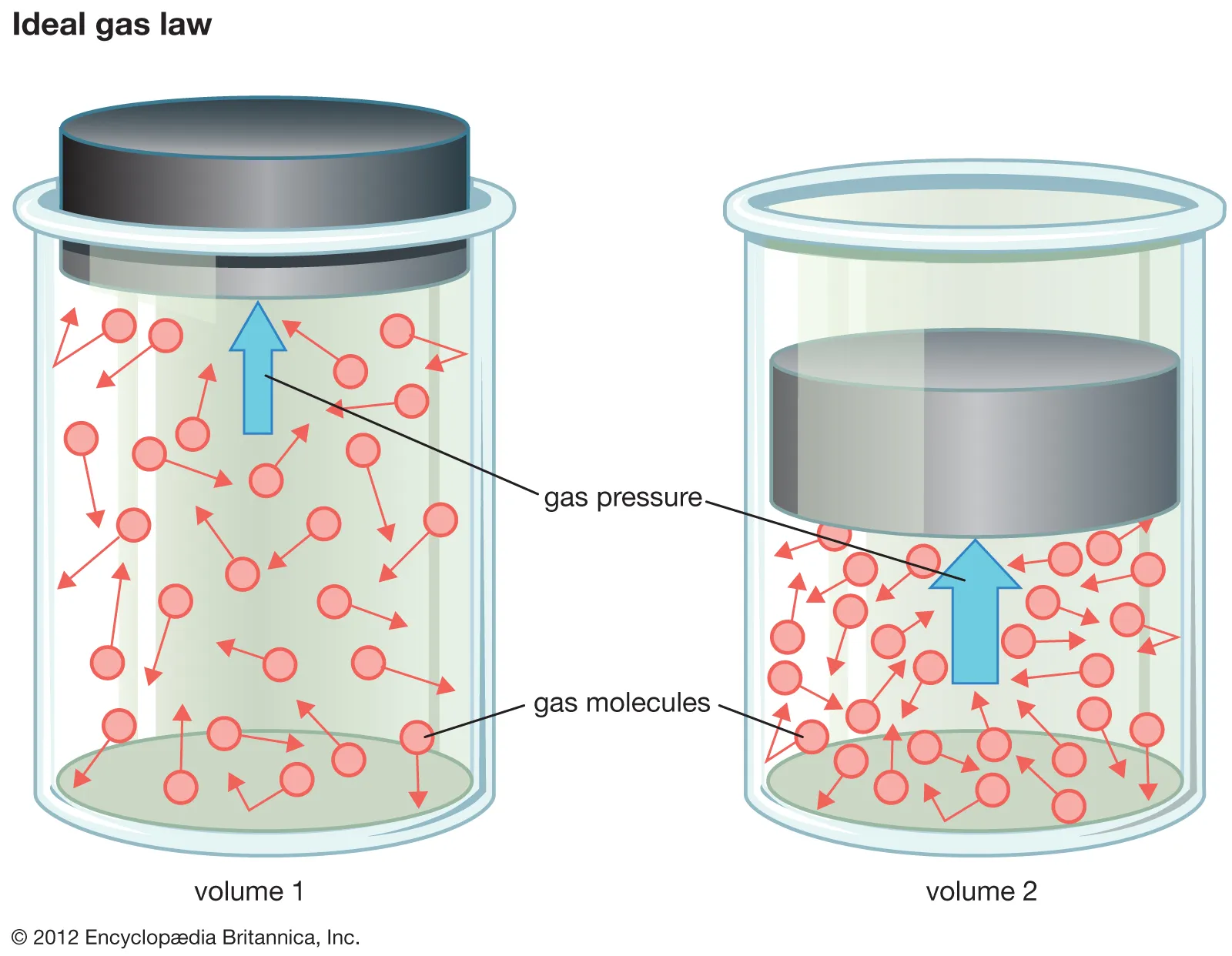
volume
The amount of space that a gas occupies, typically measured in liters (L) or cubic meters.
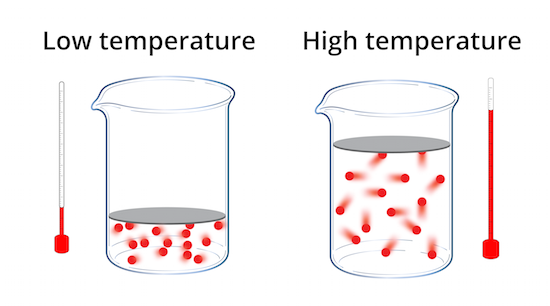
temperature
A measure of the average kinetic energy of gas particles, influencing pressure and volume. Measured in kelvin (K).
ideal gas law
equation that relates pressure, volume, temperature, and the number of moles of an ideal gas; PV = nRT.
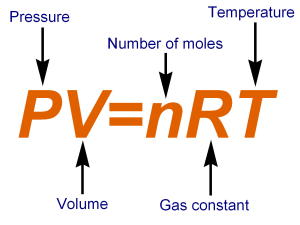
R
A constant used in the ideal gas law equation, typically valued at 0.0821 L·atm/(mol·K), representing the relationship between pressure, volume, and temperature.

n
the number of moles of gas in the ideal gas law equation.
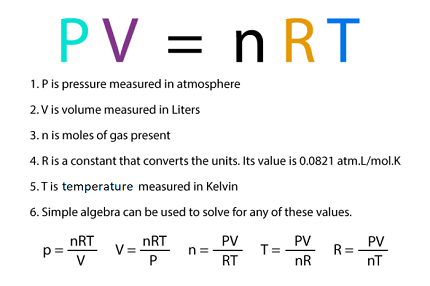
Kelvin
a unit of temperature used in science, based on absolute zero, where 0 K is equivalent to -273°C
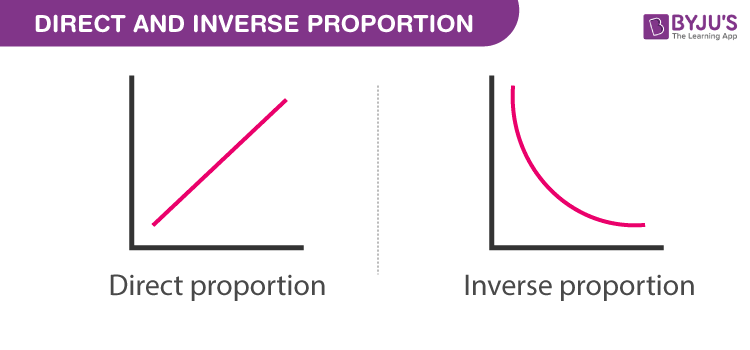
directly proportional
a relationship where an increase in one quantity results in a proportional increase in another quantity, commonly seen in gas laws regarding pressure and temperature.
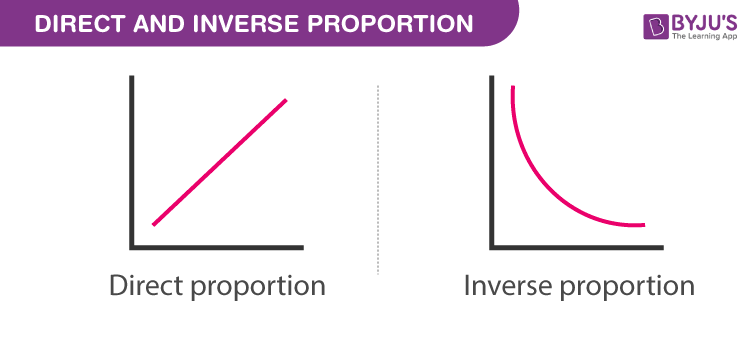
inversely proportional
a relationship where an increase in one quantity leads to a proportional decrease in another quantity, often observed in gas laws involving pressure and volume.
STP
Standard temperature and pressure, defined as 0°C (273 K) and 1 atmosphere (101.3 kPa) of pressure, often used as a reference for gas law calculations.

partial pressure
the pressure exerted by a single gas in a mixture, contributing to the total pressure of the gas mixture.
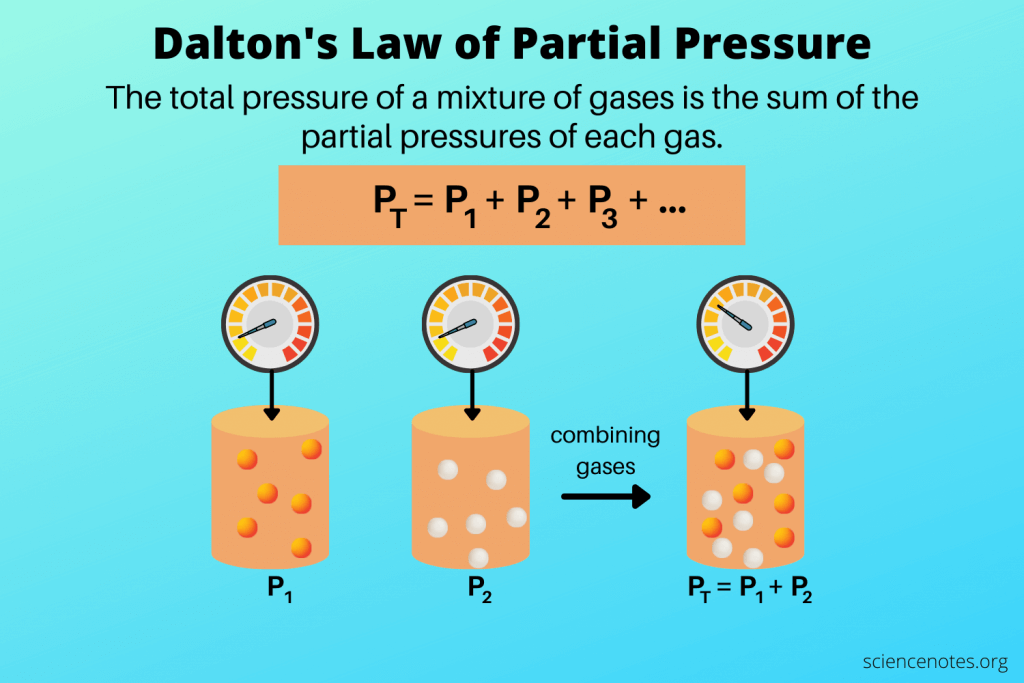
total pressure
the sum of the partial pressures of all gases in a mixture, representing the overall pressure exerted by the gas mixture.
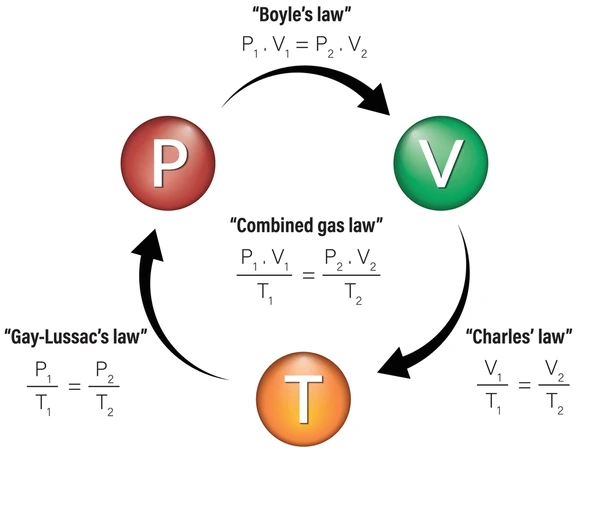
combined gas law
The combined gas law describes the relationship between the pressure, volume, and temperature of a fixed amount of gas, combining all three gas laws
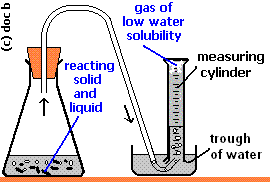
water displacement
is a method used to measure the volume of an object by observing the amount of water that rises when the object is submerged.