Lecture 29 - Planetary Atmosphere - Basics
1/40
Earn XP
Description and Tags
ASTR 1210 (Exam 3)
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
41 Terms
Erosion
Earth has been eroded at —> re-shaping its surface — not a good data point for what solar system looked like
Very geologically active — most eroded than other terrestrial worlds
Has a lot of water (liquid, solid, and vapor) — reshapes the Earth
Grand Canyon - formed from water erosion
Uplift causes the Earth to rise
Relatively young
Tributaries shape it
Rivers, rocks, mud create deltas — like Mars & Earth
Yosemite Valley
Ice river or glaciers flowing through the rock - carving at the land
Wind Erosion
Can create giant sand dunes
Ex. Great Sand Dunes National Park
Why don’t we see a lot of wind erosion on Venus?
Has flat rocks
Because it rotates slowly - weaker winds - less wind erosion
Role of Planetary Size
Smaller worlds cool off faster and harden earlier
Larger worlds remain warm inside - promoting volcanism and tectonics
Larger worlds also have more erosion because their gravity retains an atmosphere
Role of Distance from Sun
Too close to Sun - no atmosphere, no water
Earth is in Goldilocks zone for water to exist on surface
If we move closer to Sun, wouldn’t retain water — Venus
Earth has liquid water —> glacial erosion
Spins fast —> stronger magnetic field / atmosphere
Faster wind spins - stronger winds
Role of Rotation
Jupiter spins the fastest - lots of wind in equatorial regions (more weather, erosion, stronger magnetic field)
Planets with slower rotations have less weather, erosion and a weaker magnetic field
What is an Atmosphere?
Layer of gas that surrounds planets - atoms and molecules in gaseous vapor form
Considers clouds too
Venus has an incredibly thick atmosphere, thicker than Earth
Mars has thinner atmosphere
Moon and Mercury has no atmosphere
What’s the primary component of the Earth’s atmosphere?
Nitrogen (N2)
Makes up 80% of our atmosphere
Use oxygen to create energy though
Nitrogen doesn’t react with things - inert gas
Can use oxygen to cause chemical reactions to create energy - fire uses oxygen
Body can use it
Nitrogen will stick there and not get taken out of atmosphere
Oxygen gets removed quickly - but we still have a lot of oxygen in our atmosphere
Plants
Plankton, phytoplankton — life creates oxygen
What is in the Atmosphere?
Atmospheric pressure - weight of atmosphere pushing on surface of Earth
Weight: 1 atm or 1 bar
Higher/lower pressure region (lower) — hurricane
Pressure pushes in on you - all a result of the stuff above our heads
Can impact weather, climate, and gas giant planets
Gas pressure depends on temp and density - can change composition of states of matter
Pressure forces on Venus are higher than pressure forces on Earth
Pressure and Altitude
Less stuff, lower pressure
Higher and higher, pressure gets lower - not necessarily because of temp
Temp is higher at higher points
Density —> more gas particles at the bottom
Auroras
Particles smacking into Earth’s atmosphere
Effects of Atmosphere
Create pressure that determines whether liquid water can exist on the surface
Absorb and scatter light
Create wind, weather, and impact climate
Can make planetary surfaces warmer through the greenhouse gas
At 0 C - water freezes, 100 C - water boils
Change the pressure - change the freezing/boiling point
Triple point of water (6% of an atm pressure and 0.01 degrees C), water is a solid, liquid, and vapor
Any small changes can cause that solid to boil or to turn into a liquid as a result of pressure
Greenhouse Effect
Greenhouse gas is vital towards life on Earth
Heats up temp of Earth so liquid water could exist
Any gas that is transparent to visible but opaque to infrared — visible hits Earth and makes it warmer
When it radiates, radiates infrared
Layer holds onto infrared
Holds onto the energy
Which greenhouse gas contributes to the effect?
CO2, H2O, and methane (cows farting)
Planetary Temperature
Surface temperature is determined by balance between energy from sunlight it absorbs and energy of outgoing thermal radiation
Glaciers or Ice
Reflecting a lot of light
As Earth gets colder - icier - reflects more light - gets more colder - reflects more light
GHG effect makes it hotter
Planetary Temp: Rotation and Reflectivity
Planet’s rotation rate affects the temp differences between day and night
Planet’s albedo is fraction of incoming sunlight it reflects (0 = absorb, 1 = reflect)
Low albedo = absorb more light, leading to hotter temperatures
Black pavement = 0
White pavement = 1
Clouds reflect a lot of light
If Earth didn’t have an atmosphere, what would happen to its temp?
Got rid of its greenhouse layer and blanket - colder
Temperature of the Earth vs. Altitude
Higher you go, hotter and hotter temp - then colder and colder
Impacts where clouds can be, what types of clouds can form
Stratosphere: unique for terrestrial planets
Ozone layer creates this - absorbs energy in the stratosphere
3 oxygen molecules bound together
Ozone absorbs a lot of UV energy - UV blanket to hold It all together

Why Do Atmospheric Properties Vary with Altitude?
Convection - hotter at bottom, cold at top - cycle - troposphere
Doesn’t do it stratosphere - inverts it (no ice forming)
Light’s Effects on Atmosphere
Ionization: removal of an electron
Dissociation: destruction of a molecule
Scattering: change in photon’s direction
Absorption: photon’s energy is absorbed
Magnetosphere
A magnetosphere is the region of space around a planet that is controlled by its magnetic field. This magnetic field acts as a shield, deflecting the solar wind and protecting the planet from the charged particles from the sun
Exosphere
The exosphere is the outermost layer of Earth's atmosphere, starting around 600 km (375 miles) above the surface and gradually fading into space. It is extremely thin, composed mainly of hydrogen and helium, and is where satellites orbit Earth. Particles in this layer are so spread out they rarely collide, and the lightest ones can escape into outer space.
Thermosphere
The thermosphere is a layer of Earth's atmosphere above the mesosphere where temperatures increase with altitude, reaching thousands of degrees Celsius due to absorption of high-energy solar radiation. Despite the high temperatures, the air is so thin that it would feel cold to us. This layer is also where the aurora borealis and aurora australis occur and where satellites like the International Space Station orbit.
Which planet(s) have an atmosphere that consists mostly of carbon dioxide?
Venus and Mars
Which of the following is not caused by the Coriolis effect on Earth?
Water going down a drain swirls in opposite directions in the Northern and Southern hemispheres.
Why is the Coriolis effect so weak on Venus?
Because Venus rotates so slowly.
Why is thermal escape of atmospheric gas much easier from the Moon than from Earth?
Because the Moon's gravity is so much weaker than Earth's.
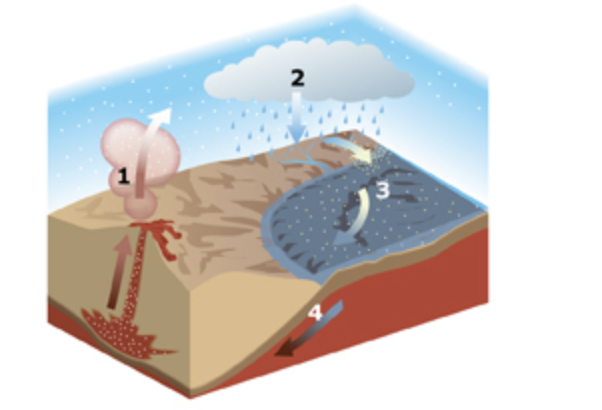
This diagram represents the carbon dioxide cycle. Which position in the diagram represents the part of the cycle in which carbon dioxide is turned into carbonate minerals and rock?
Position 3
Which of the following best describes the nature and origin of the atmospheres of the Moon and Mercury?
They have thin exospheres only, with gas coming from impacts of subatomic particles and photons.
What is the connection between core convection and a strong magnetosphere?
Core convection helps generate a magnetic field, and the magnetic field creates the magnetosphere.
What key process underlies why Mars changed so much from its early conditions to its conditions today?
Interior cooling
Why is Mars red?
Chemical reactions between surface rock and atmospheric oxygen literally rusted the surface.
What would happen to Earth if we somehow moved our planet to the orbit of Venus?
Earth would suffer a runaway greenhouse effect and become as hot as or hotter than Venus.
Which characteristic of Earth explains why Earth has the ozone necessary for an ultraviolet-absorbing stratosphere?
the existence of photosynthetic life
Why does Earth have so little carbon dioxide in its atmosphere compared to Venus?
Earth has just as much carbon dioxide as Venus, but most of it is locked up in carbonate rocks rather than being free in the atmosphere.
Which two factors are critical to the existence of the carbon dioxide (CO2) cycle on Earth?
plate tectonics and liquid water oceans
Listed following are characteristics of the atmospheres of Venus, Earth, and Mars. Match each atmospheric characteristic to the appropriate planet.
Venus - almost no surface winds, runaway greenhouse effect, sulfuric acid clouds; Earth - atmosphere composed primarily of nitrogen, ultraviolet-absorbing stratosphere; Mars - global dust storms, extremely low density atmosphere

All the following statements about Mars are true. Which one might have led to a significant loss of atmospheric gas to space?
Mars lost any global magnetic field that it may once have had. - This allowed the solar wind to strip atmospheric gas into space.
All the following statements are true. Which two represent the two facts that lead us to expect Earth to be warming up as a result of human activity? Be sure to choose two of the statements below.
Human activity is increasing the concentration of carbon dioxide and other greenhouse gases in the atmosphere.
Greenhouse gases make Earth warmer than it would be otherwise.