cell parts EXCEPT CELL MEMBRANE
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
17 Terms
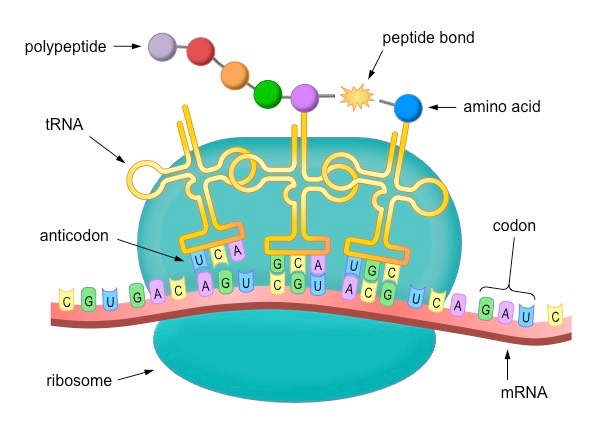
ribosomes
reads mRNA to create chain of amino acids, eventually becoming proteins
tRNA containing the opposite codon of mRNA decodes mRNA sequence into protein
ribosomal disease
diamond-blackfan anemia (DBA). Malfunction of ribosome assembly, causing anemia & bone marrow failure
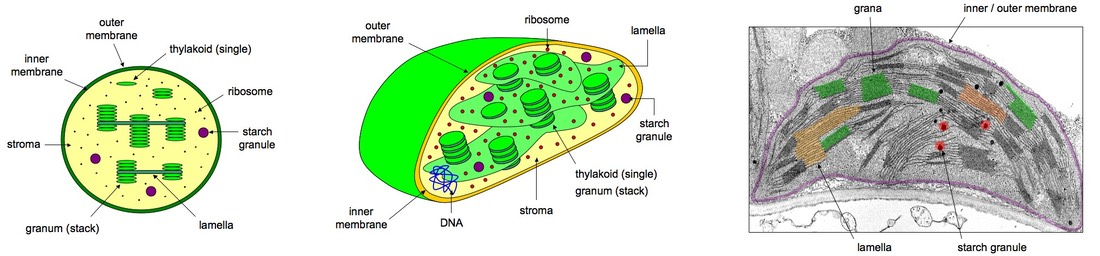
chloroplast
allow photosynthesis
has chlorophyll absborbs energy from the sun. Energy is used to convert CO2 & water into glucose and oxygen for plants to feed themselves.
chloroplast disease
chlorosis — plants become yellow. Caused by insufficient chlorophyll production so it can’t properly feed itself (chlorophyll - photosynthesis)
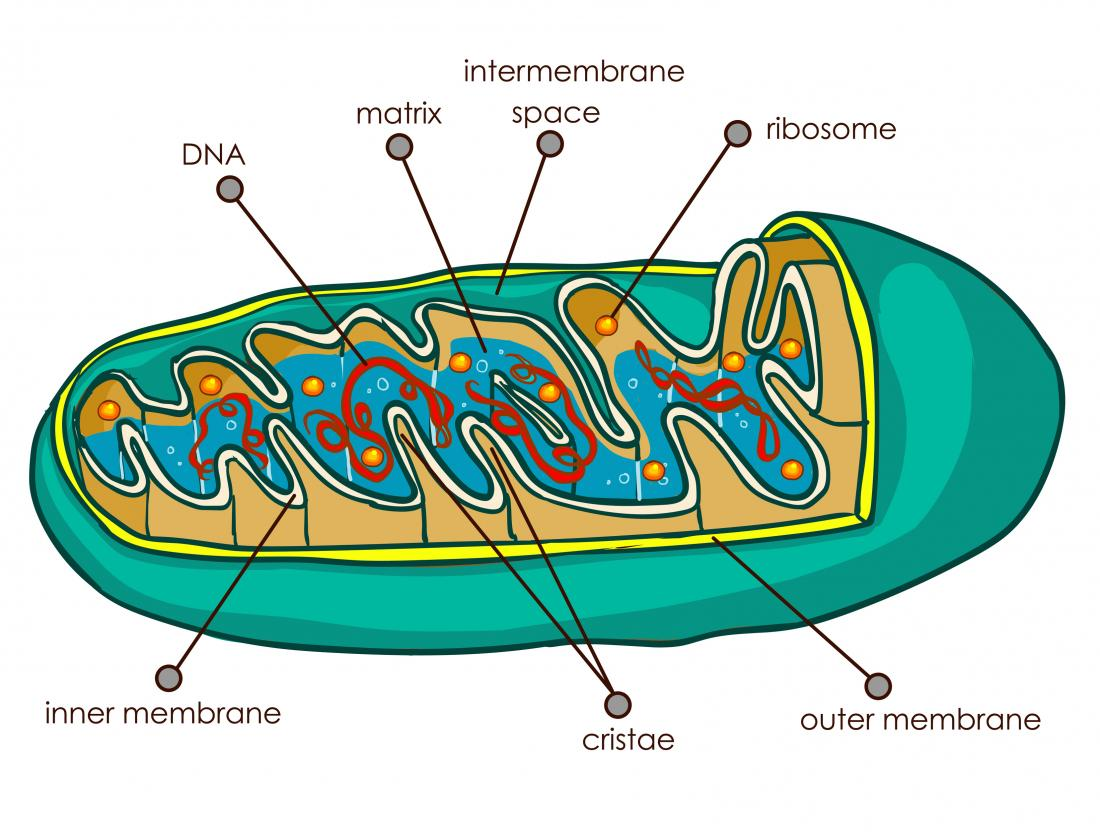
mitochondria
krebs cycle → makes ATP (energy)
uses cristae (inner folds) to increase surface area, has its own DNA & ribosomes
number of mitochondria depends on how much energy the cell needs (eg. muscle cells need more mitochondria)
mitochondrial disease
Leigh’s syndrome — mutation of DNA of mitochondria, can be passed on from the mother
symptoms — dementia, seizure, headaches, vomiting
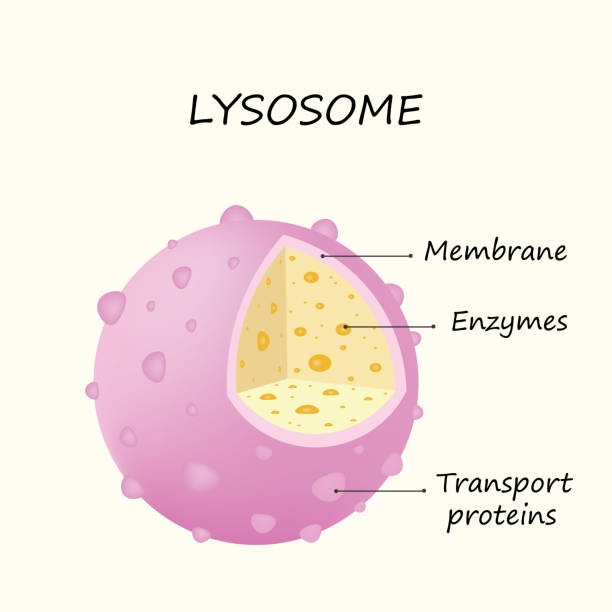
lysosome
STRUCTURE — phospholipid bilayer, hydrolytic enzyme, transport protein
breaks down substances, uses digestive enzymes to break down cellular debris, waste materials & foreign materials
autophagy — cell maintains health by digesting & recycling its own components
lysosome disease
tay-sachs — degenerative genetic disorder, common in Jewish ppl
deficiency of enzyme breaking a certain fatty substance in nervous system so fat accumulates in nerve cells → progressive neurological damage
symptoms — muscle weakness, motor skill loss, visual/hearing loss, death
peroxisome
breaks down substances, detoxify harmful substances
break down fatty acids leaving hydrogen peroxide by-product, by-product is turned into water & hydrogen by catalase enzyme
especially important in liver & kidney cells
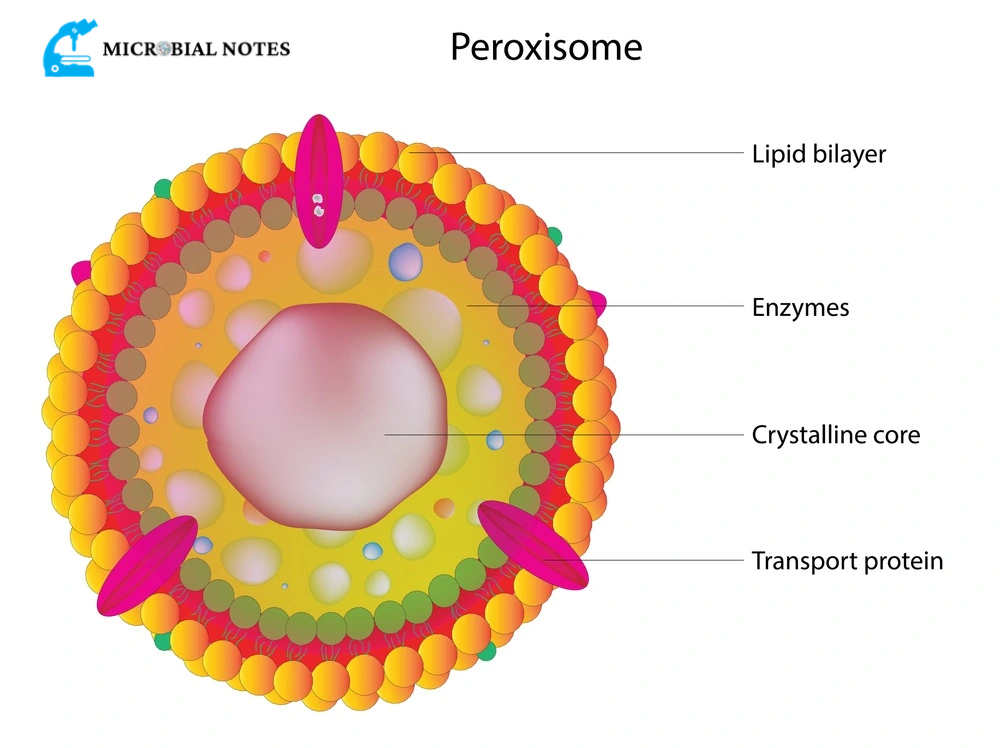
peroxisome disease
Zellweger syndrome — peroxisome doesn’t function right, fatty acid & toxins accumulate in the body.
symptoms — developmental delays, muscle weakness, seizures, early death
golgi apparatus
process & modify proteins received from ER by adding carbohydrates & lipids. Sorts proteins into vesicles to transport to different locations so enzymes can be produced to break down waste such as those destined for lysosomes
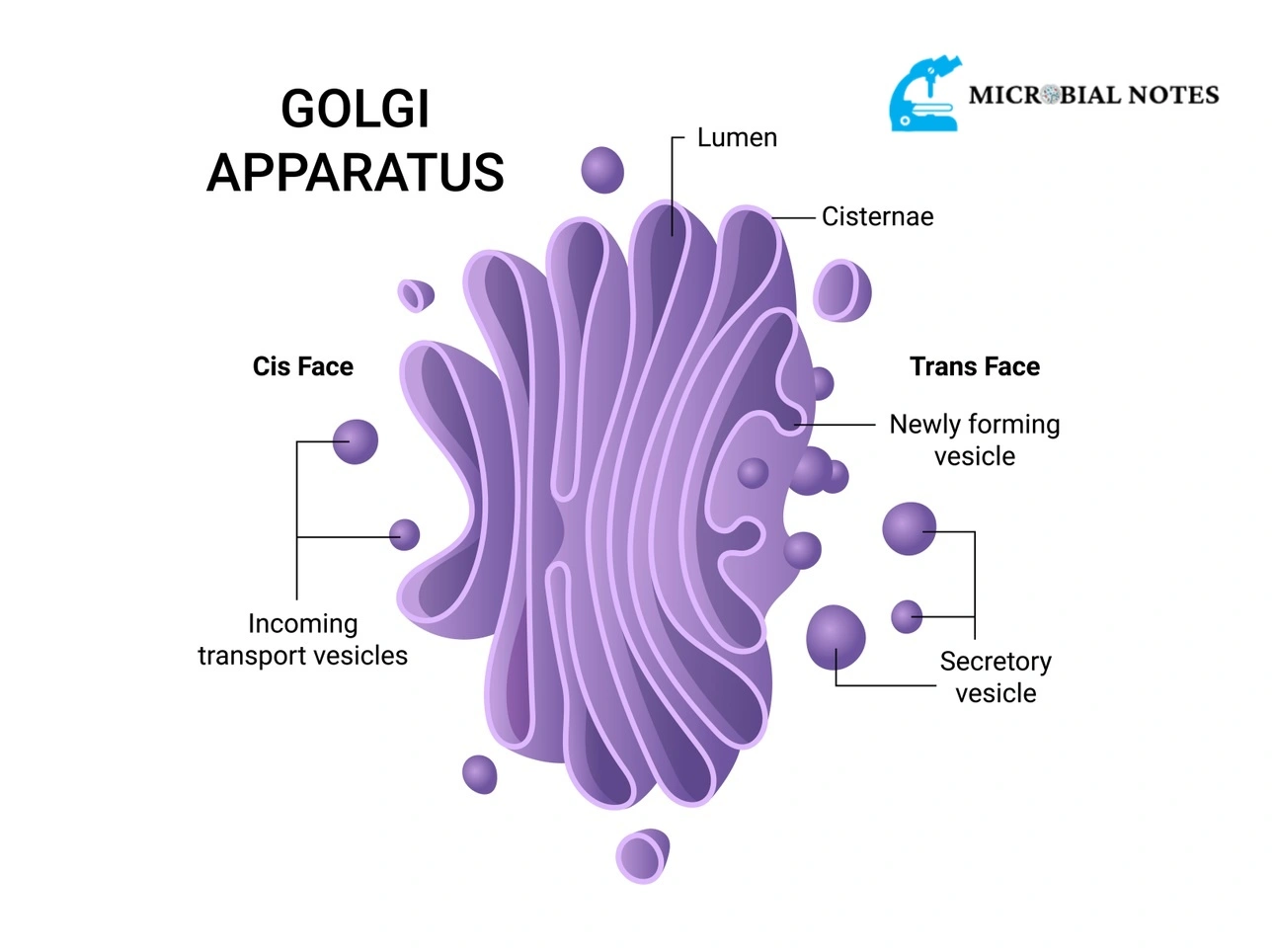
golgi appartus disease
Congenital Disorders of Glycosylation (CDG) affects ability of golgi neurological process protein & lipid molecules
symptoms: developmental delays, neurological issues, digestive problems
nucleus
store & replicate genetic info of cell. Nucleolus has RNA, protein, chromatin
nuclear pores → groups of proteins attach to envelope & form small openings
nuclear envelope has 2 phospholipid bilayers, double membrane, serves to separate nucleus from the rest of the cell
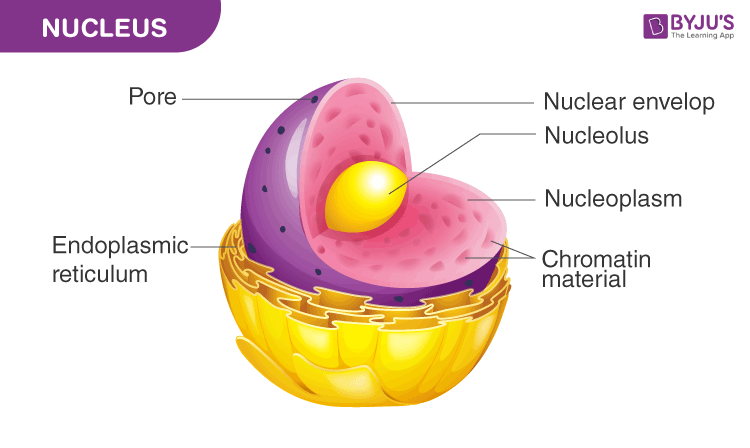
nucleus disease
Huntington’s disease — inherited, mutation in gene that codes for Huntington protein, and mutated proteins build up in muscles
rough endoplasmic reticulum (RER)
studded w/ RER proteins or ones intended for export
folds & processes proteins & packages them in vesicles to golgi
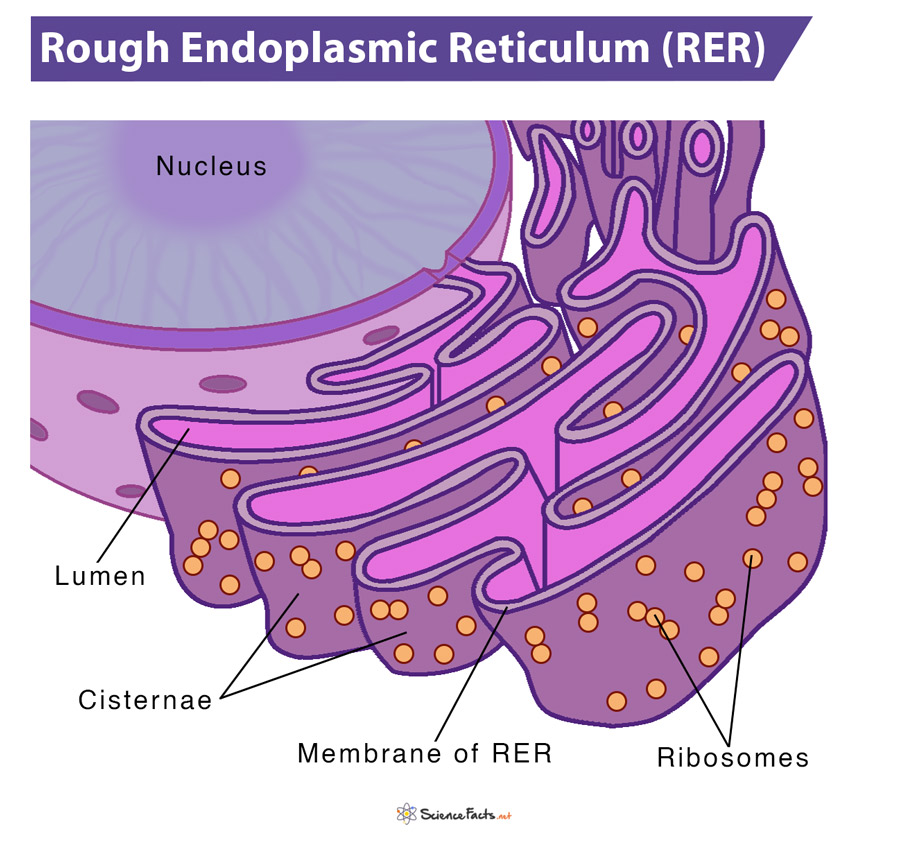
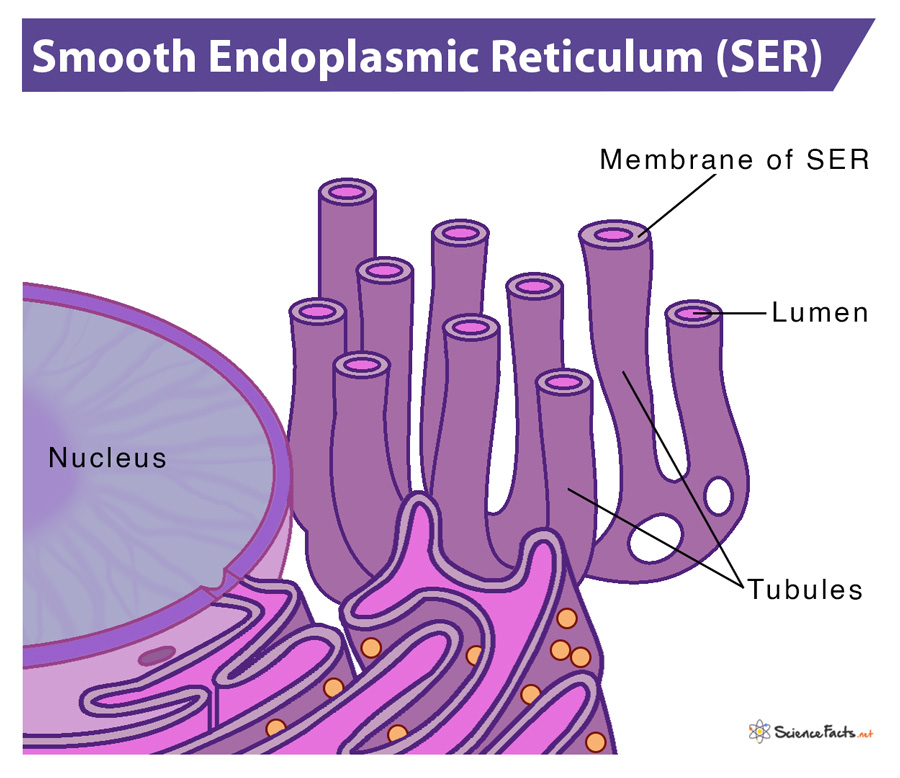
smooth ER
make lipids, steroids, products associated with metabolism, and carbohydrates (glycogen → glucose)
Detoxifies molecules to be water-soluble and safe. NO RIBOSOMES
ER disease
ER stress — disruption in normal function of ER, causing apoptosis & adaptive signals, & goal for that is homeostasis
causes — type 2 diabetes, liver, disease, atherosclerosis, and cancer