Ch. 24 Special Theory of Relativity
1/65
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
66 Terms
Why do different colors appear (like a rainbow in a pool of water)?
different colors correspond to different wavelengths of light bending/overlapping because each wavelength bends/interacts differently
Is light a wave or a particle?
light has a wave-particle duality
When looking in a parking lot after a rain storm you notice swirls of color…what causes these colors?
Light waves reflected from the top and bottom of the oil constructively interfere
What is a refraction?
a wave front that bends a wave as it passes from one medium into another (ex: air into water)
What rule explains refraction?
Snell’s Law
What are wave fronts?
they are a crest of a wave as it travels (surface of the wave basically)
Every point on a wave front can be considered as a source of __________ wavelets that spread out in the forward direction at the speed of the wave itself.
Every point on a wave front can be considered as a source of TINY wavelets that spread out in the forward direction at the speed of the wave itself.
What is the Huygen’s Principle?
every point on a wavefront acts like a new “source” of tiny waves
wavelets combine to form next wavefront
What is diffraction?
when wave bends around/through an obstacle/obstacle
How does light move in the following scenarios:
Sharp Edge
Large Hole
Small Hole
Sharp Edge = light bends around
Large Hole = less bending
Small Hole = strong bending
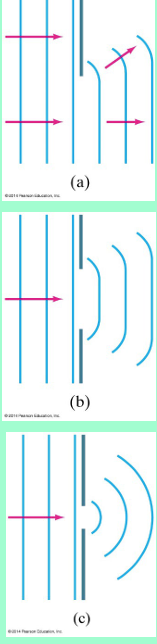
Whenever light enters a new material, what happens to the light?
(speed, time, distance)
light bends because the speed is different
time is the same
distance changes
if speed decreases = shorter d
if speed increases = longer d
What explains why the light ray bends?
when the distance changes due to the change in speed!!!
What is Snell’s Law?
tells us exactly how much the light bends at the boundary between 2 materials
What is a mirage? Does this fall under refraction or diffraction?
Mirage = light bends due to changes in air temperature
under refraction
How does light bend in respect to density of the air?
Warm air (near ground) = less dense
light travels faster
Colder air (up) = more dense
light travels slower
In terms of air, light bends gradually __________ because ________ affects air density causing a change in the light _________ leading to refraction
In terms of air, light bends gradually UPWARD because TEMPERATURE affects air density causing a change in the light SPEED leading to refraction
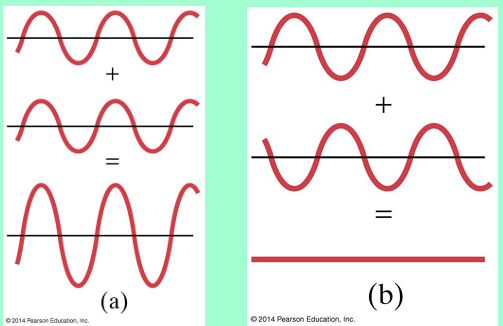
What is interference (waves)?
when 2 waves meet at the same time, they combine
What are the 2 types of wave interference?
Constructive
In Phase (same)
results get bigger
Destructive
Out of phase (opposite)
cancel out/smaller wave
Whenever you have 2 slits, what actually happens to the light particles?
you get many bright but decreasing bands of light (pattern)
showing that light behaves like a wave NOT a particle
How in a double-slit experiment does light react the way it does?
each slit produces a new wave front when it passes through each slit
each slit acts like a “new source” of a wave front
wave spreads out and interferes with each other (making them screen out)
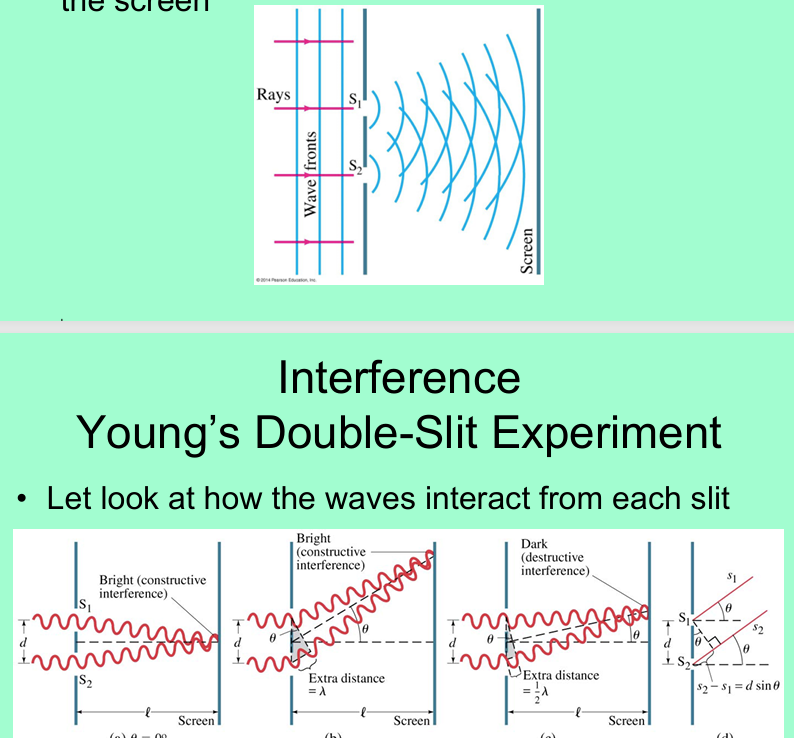
If you have a whole wavelength, waves will arrive in phase, resulting in a ______ spot.
If you have ½ a wavelength, waves will arrive out of phase, resulting in a _______ spot
If you have a whole wavelength, waves will arrive in phase, resulting in a BRIGHT spot.
If you have ½ a wavelength, waves will arrive out of phase, resulting in a DARK spot
what does “m” represent in terms of waves?
m = integer starting at 0
represents the distance b/w the slips
0 = central bright area
True or False: sin(theta) cannot exceed 1
true
As you move away from the center maximum (bright spot), what happens to the brightness/intensity?
decreases!

What happens when the wavelength increases/decreases?
wavelength INC = angle/distance INC
wavelength DEC = angle/distance DEC
What does white light mean?
means all colors/wavelengths overlap there
going to left/right = results in rainbow-looking interference pattern
What would happen if the 2 slits were replaced by 2 lightbulbs and why?
no interference would happen!!
light from 2 separate bulbs are NOT IN PHASE
light waves are different so interference pattern is different
What are the 2 most important characteristics of light?
intensity (W/m²)
“how much energy light has”
color
look at frequency/wavelength
What is the wavelength and frequency range?
Wavelength → (frequency)
400 nm (violet) →HIGH [uv]
750 nm (red) → LOW [ir]
Whenever a white light passes through a prism, why is a rainbow seen?
each color has a different angle (n = different for each)
True or False: n depends on frequency
n depends on wavelength
If there is a shorter wavelength, the light will ben _____ and this represents the colors _______, meaning n is _________
If there is a shorter wavelength, the light will bend MORE and this represents the colors BLUE/VIOLET meaning n is HIGHER
what is dispersion?
the way a color bends because it is by a different amount and they all have different wavelength
What happens if light passes by a single slit or around a disk?
diffraction occurs
bright spot/pattern appears around the shadow
What is a diffraction pattern?
pattern of light/dark stripes
wavelets interfere with each other after passing the obstacle
How does light travel when the angle is 0?
light rays travel same distance = in phase
constructive interference → bright center
How does light travel when the angle is ½ ?
the paths differ in lengths = out of phase
destructive interference → dark fringe
How does light travel when the angle is 3/2 ?
only 1/3 of the waves constructively interfere
show weak bright fringe
How is the formula different for diffraction compared to the one for double-slit?
Diffraction
m = integer (NOT 0 ~ looking for minimum)
D = width of slit
Double-slit
d = distance between 2 slits
If you have a rectangular slit (narrow part along vertical) that line shines through, would the light spread out more horizontally or vertically?
more vertically
what happens if light is passed through many slits?
interference occurs b/w the light waves coming from each slit
What is diffraction grating?
device with many slits that are equally spaced and parallel to each other
shows where bright lines appear on screen
When there are many slits, the bright spots are brighter/dimmer and narrower/wider.
When there are many slits, the bright spots are BRIGHTER and NARROWER.
there is a lot of destructive interference
what does a spectrometer measure?
measures light
define what emission + absorption spectra means
Emission spectra
bright lines
Absorption spectra
dark lines (lines missing)
________ absorb and emit light when electrson change energy levels
ATOMS absorb and emit light when electrons change energy levels
Does each atom have its own set of lines?
yes!
True or False: if multiple elements are present, their lines will interfere
FALSE
…..their lines will NOT INTERFERE
How does reflection occur?
when light hurts a surface and the waves interfere with each other to give bright/dark areas
what determines whether a wave is in phase or out of phase
the index of refraction (n)
when going from low n to high n, is the reflection in/out of phase??
out of phase (180 degree shift)
When going from high n to low n, is the reflection in/out of phase?
in phase (no shift)
what 3 things does interference of waves depend ong?
index of refraction (n)
thickness (t)
in/out of phase
How are Newton’s Rings created when a rounded glass is placed on a flat piece of glass?
light interferes with each other when…→ results in bright/dark spots (NR)
light reflects off bottom of curved glass
light reflects off top of flat glass
What type of light pattern is created when 2 flat pieces of glass are placed on top of each other but separated by a small wire on one end?
light rays will reflect and interfere with each other
cause alternating bright/dark fringes
What does a Michelson Interferometer do?
splits a beam of light transmitting half the light to a movable mirror and the other half to a fixed mirror
sensitive to bright fringes
what is polarization?
shows the electric field along a wave (it is perpendicular)
What is the difference between polarized and unpolarized light?
Polarized
oscillations (plane of electric field) are in ALL directions
Unpolarized
oscillations (plane of electric field) are in MANY directions, but perpendicular to the direction of travel
What does a polarizer do?
material that only allows light vibrate in 1 direction to pass through
What happens when unpolarized light hits a polarizer?
50% of unpolarized light is transmitted
results in linearly polarized light
after light is polarized, what does the intensity of the light transmitted depend on? This is known under what law?
depends on angle between electric field and polarize → Malus’s Law
Why does light reflect from water become polarized?
reflected light becomes polarized (in the direction that is parallel to the surface)
what happens when you rotate a polarizer?
can block horizontally polarized glare (reflected off the water)
how do LCD screens work ? What happens if you turn on the voltage?
inside of them they have liquid crystals that twist light if no voltage is applied
voltage on = crystals stop twisting light/no more light and screen dark
why is the sky blue?
light scatters and hits tiny air molecules
blue scatters more than red
at sunset, light travels farther, so more blue scatters and red/orange seeni
is the light in the sky polarized?
scattered light in the sky is partly polarized (so mostly 1 direction)