Botany Finals (Ethnobotany, Plant Adaptations)
1/90
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Part 2
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
91 Terms
Ethnobotany
is to study how and in what ways people use nature and how in what ways people view nature.
Ethnoecology
studies the interactions of the local people with the natural environment
Ethnobotany
Is the part that studies the interactions of local people with plants.
Ethnobotany
tries to get a holistic understanding of local knowledge on plants
Ethnobotany
_______ is a subset of Ethnoecology
Ethnobotany
The earliest, well developed, and currently fast expanding branch of ethnobiology
Ethnology
Study of culture
Botany
study of plants
Ethnobotany
is the scientific study of relationships that exist between people and plants
Egyptians
credited with inventing paper by pressing together strips of papyrus
Real paper
was made by separating plant fibers and matting them together in a thin sheet, was invented by the Chinese using mulberry.
Adaptation
is a characteristic which helps an organism to survive in its environment
Deserts
are dry and often hot. Annual Rainfall less than 10 inches, Soil is poor-sandy or rocky, Intense direct sunlight
Succulents
Store water in their leaves
Spines
modified leaves that discourage animals from eating this plant
Temperate Grasslands (Prairie)
Hot summers, cold winters, Rainfail can be sporadic, drought is common, Annual Rainfall between 10-30 inches/year, few tries, regular fires, Soil is rich in organic material, Soil is well suited for agriculture.
Tropical Rainforests
Hot, humid with rainfall between 80-180
inches annually.
• Poor soil due to leaching
• Plants grow quickly to use up any available
organic material
• Little sunlight at forest floor
• Intense sunlight in the canopy layer
Epiphytes, or “air” plants
have aerial roots that cling to a host plant
Temperate Deciduous Forest
Has four distinct seasons: spring, summer,
autumn, winter
• Average annual rainfall 30-50 inches
• Rich soil
• Forest made up of distinct layers: herb layer,
shrub layer, understory and canopy
Taiga (Boreal Forest)
Dominated by conifers (evergreens)
• Cold winters and warm summers
• Some areas have a layer of permanently
frozen ground called permafrost
• Poor drainage due to permafrost and layers of
rock just below the soil
• Annual rainfall of approx, 20 inches
Tundra
Short, cool summers and long, cold winters
• Has a permanently frozen layer called permafrost
• Poor drainage due to permafrost and cold
temperatures
• Annual precipitation low at only 4-10 inches,
usually as snow or ice
• Growing season has 24 hours of sunlight/day,
long nights in winter
Angiosperms
Reproduce Sexually and
Asexually
Flowers
are the
sex organs of
angiosperms
Asexual reproduction
is advantageous when conditions are
stable and plants are well-adapted to their surroundings.
Sexual reproduction
produces variable offspring,
increasing reproductive success in a changing world
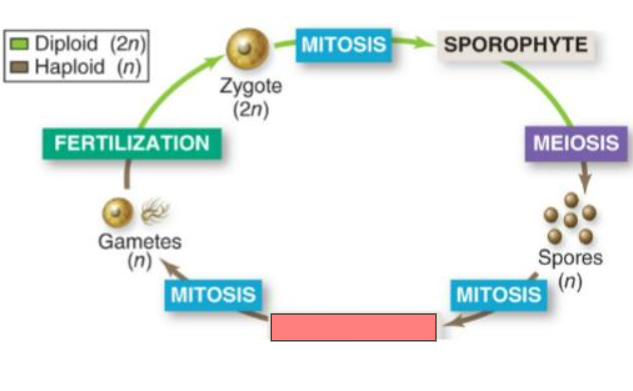
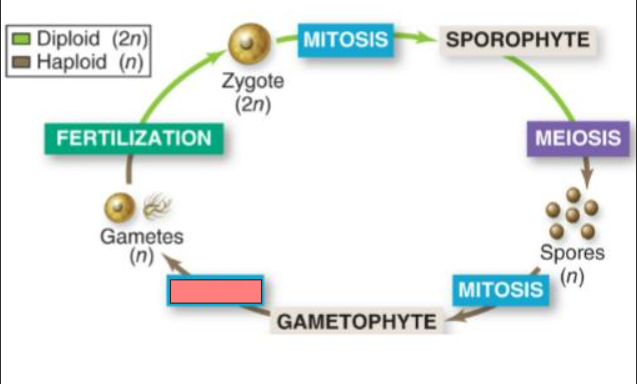
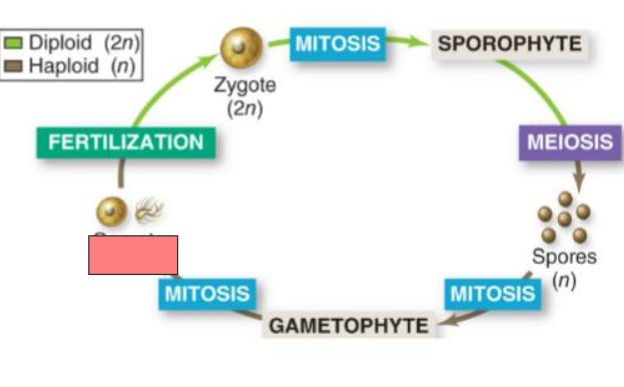
Mitosis

Sporophyte
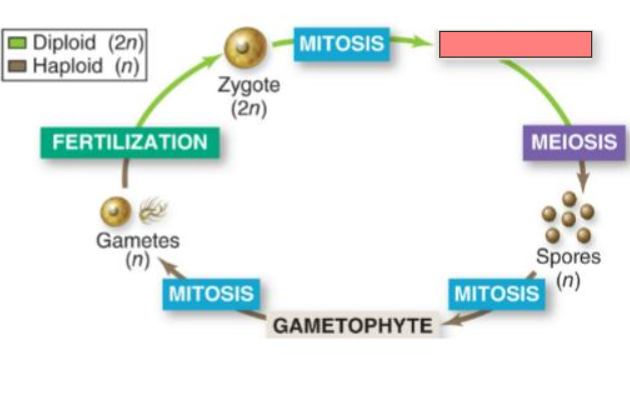
Meiosis
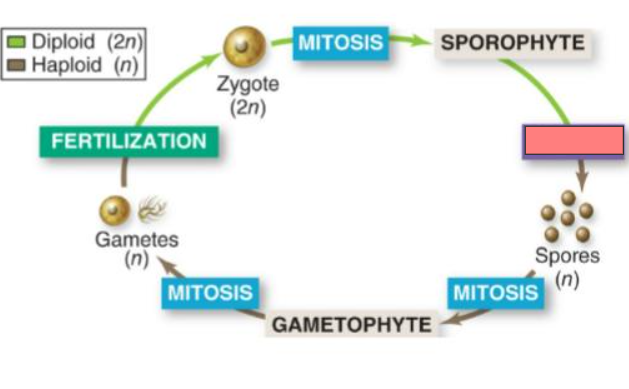
Spores
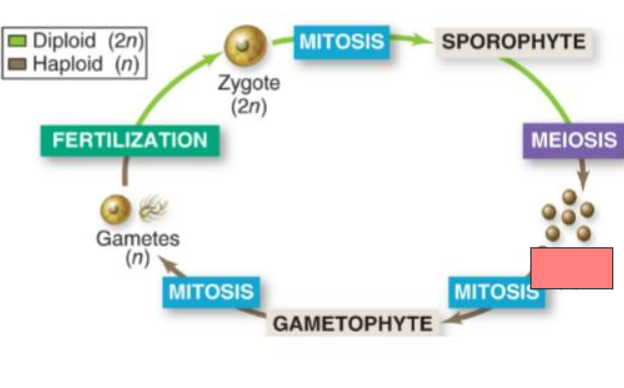
Mitosis
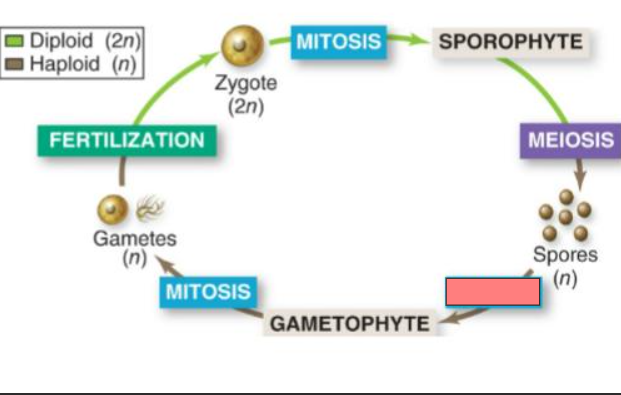
Gametophyte
Mitosis
Gametes
Fertilization

Zygote

Sporophyte (2n)
the multicellular
diploid form that
results from the
union of gametes
Gametophyte (n)
the multicellular
haploid form that
produces haploid
gametes by mitosis
Sporophyte
produces haploid
spores by meiosis
that develop into
gametophytes.
Haploid gametes
These gametes
unite and develop
into sporophytes.
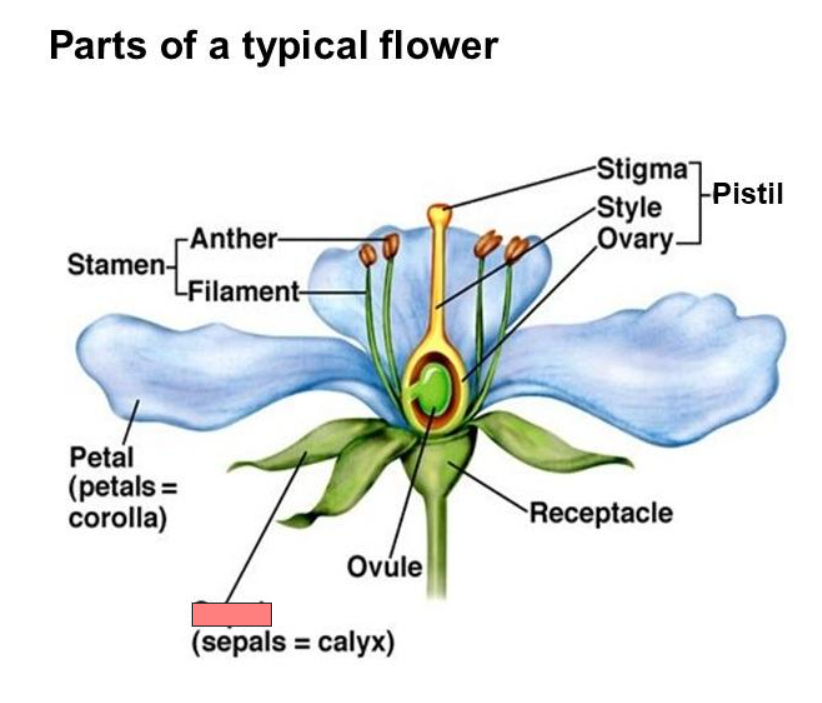
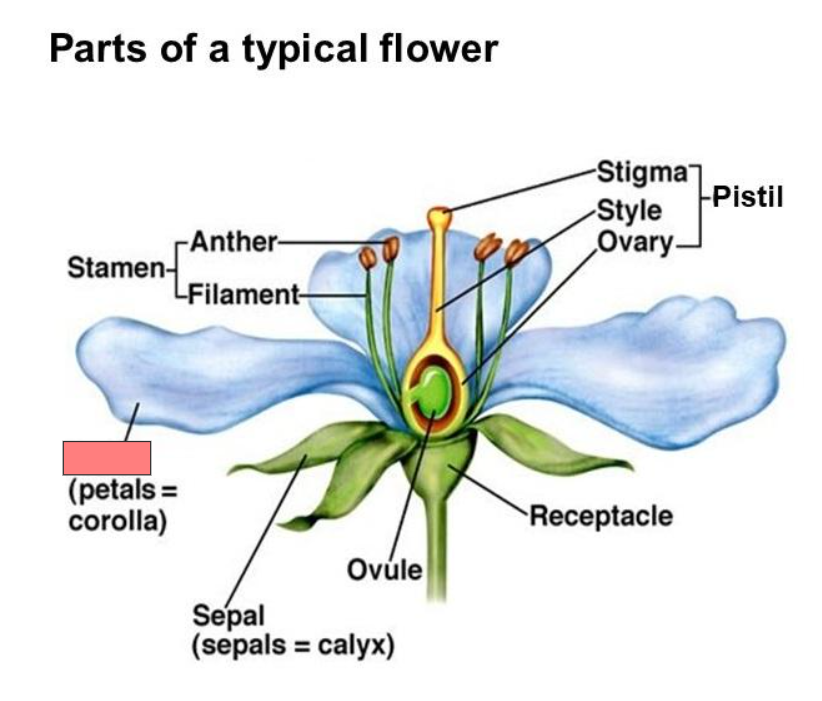
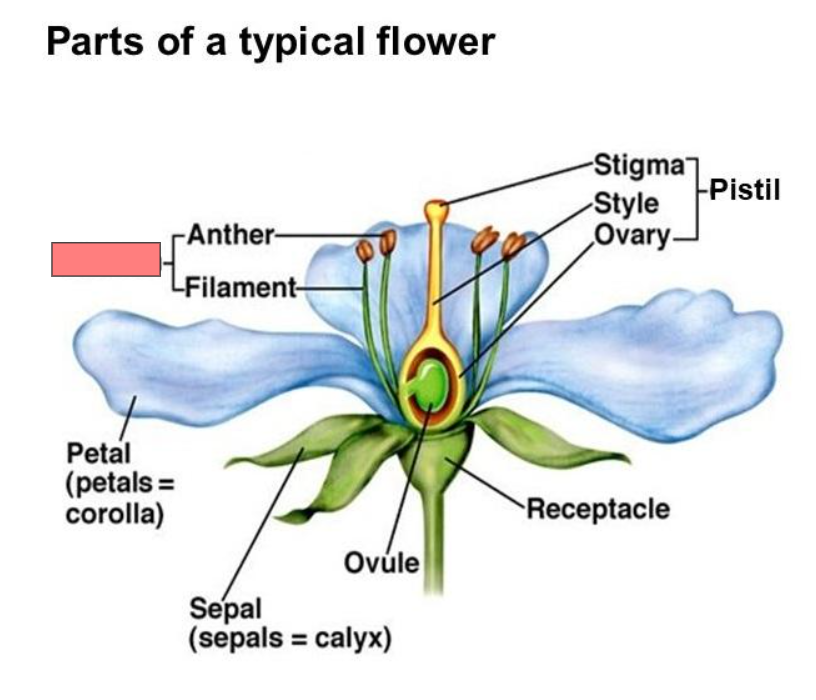
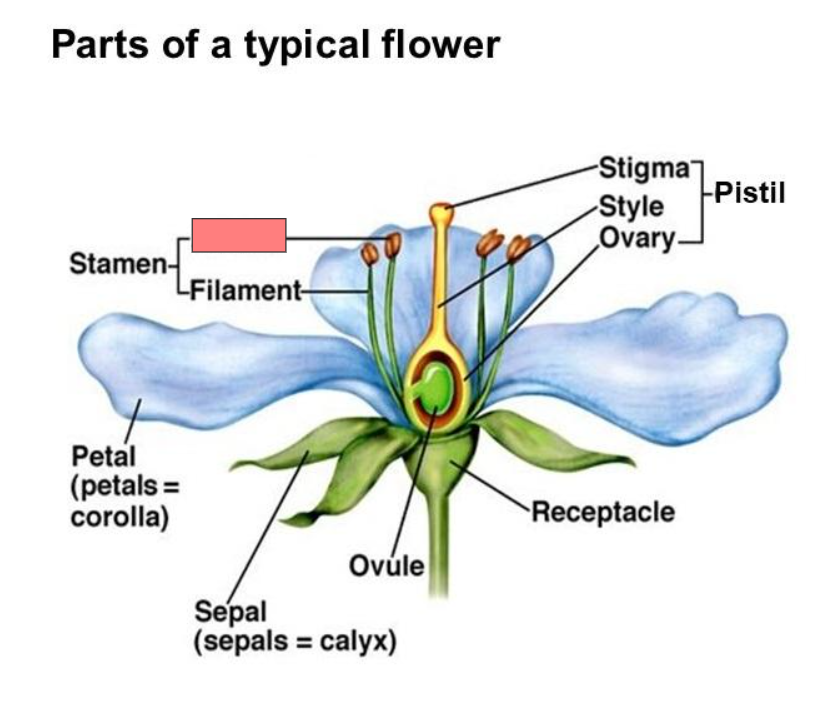
Receptacle
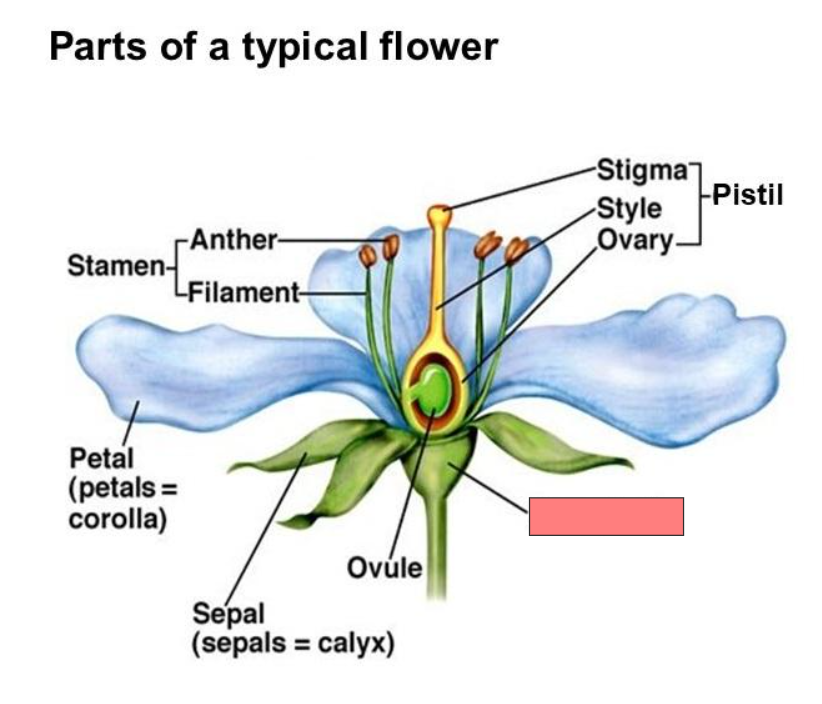
Pistil

Stigma
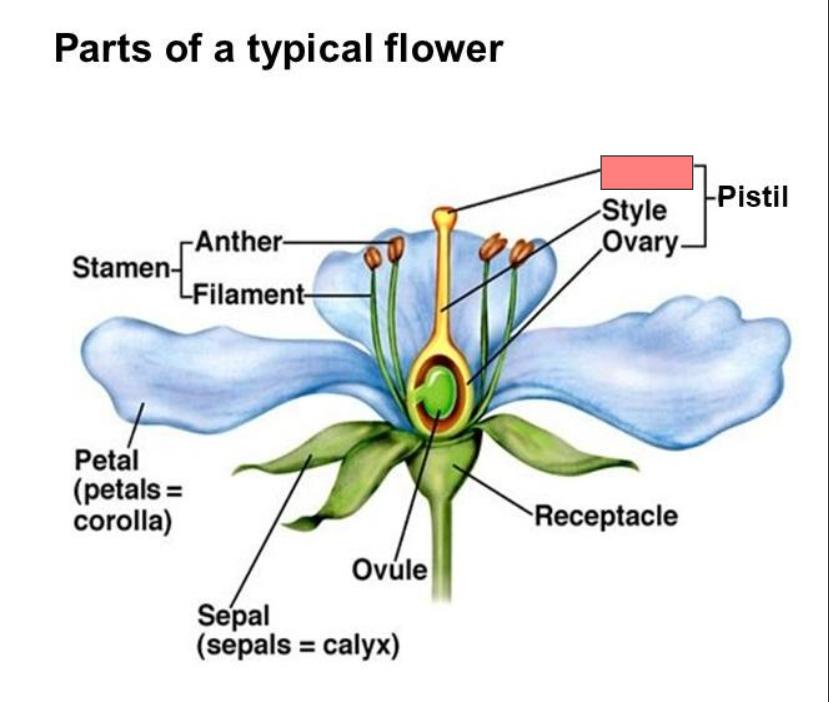
Style
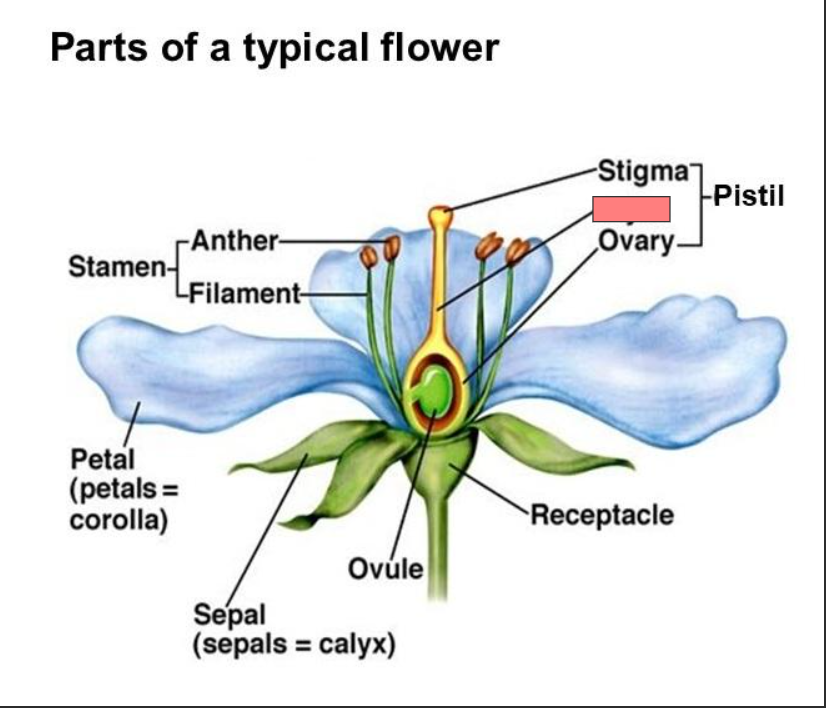
Ovary
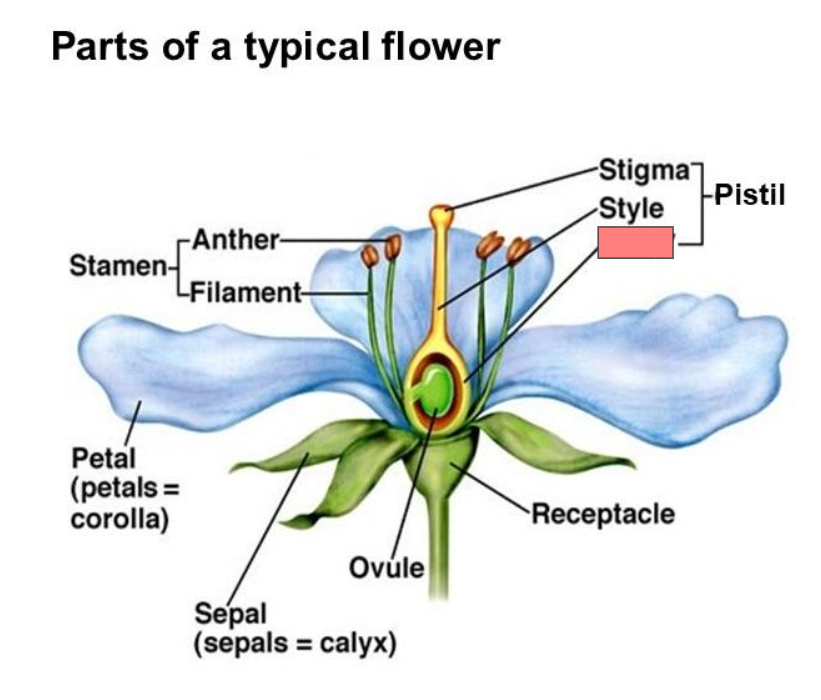
Ovule
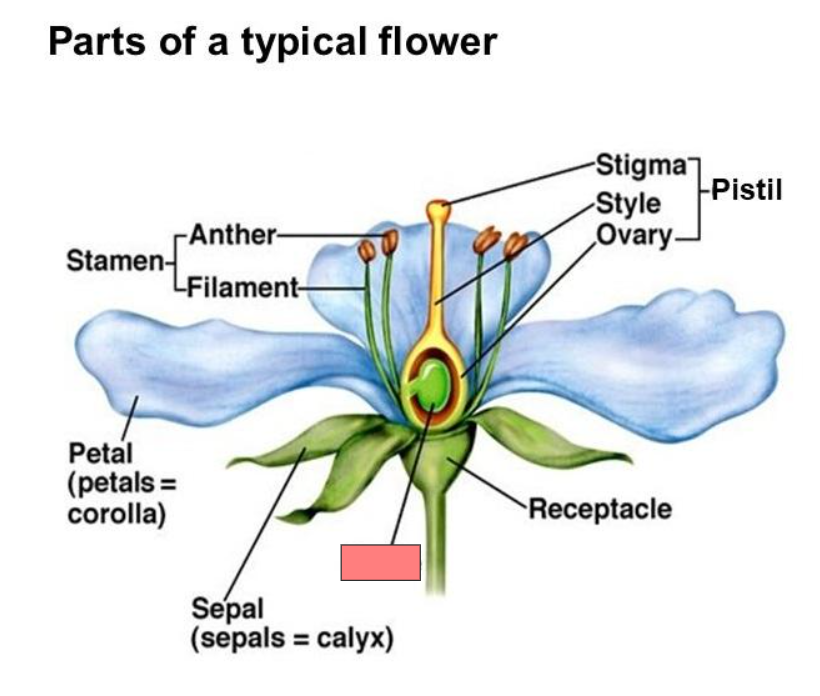
Sepal
Petal
Stamen
Anther
Filament
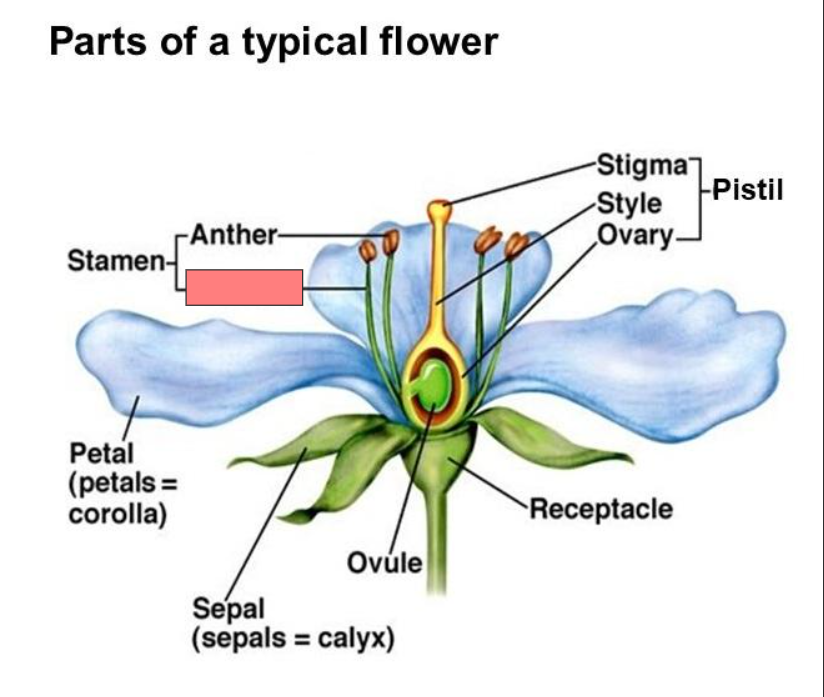
Corolla
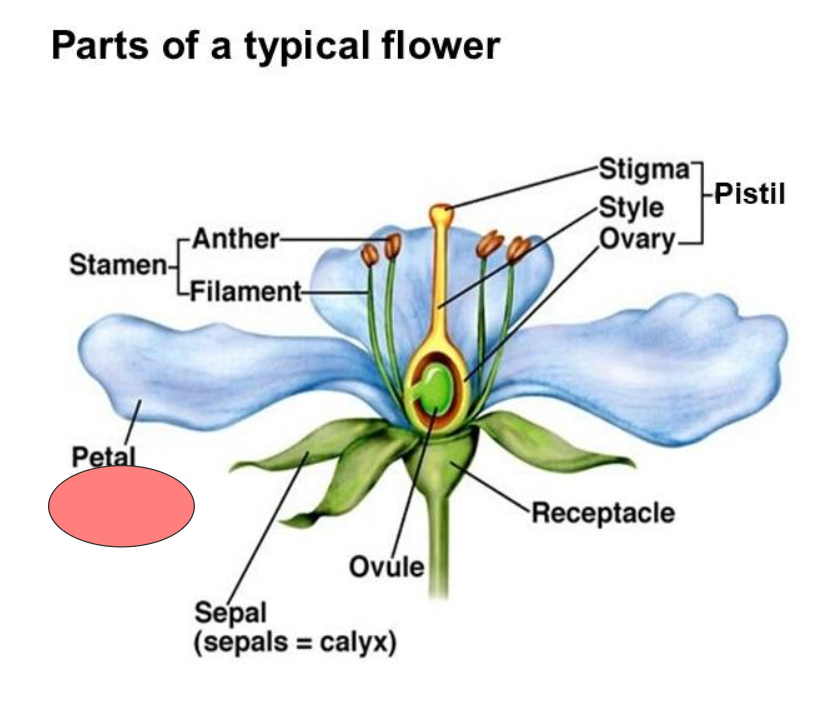
Calyx
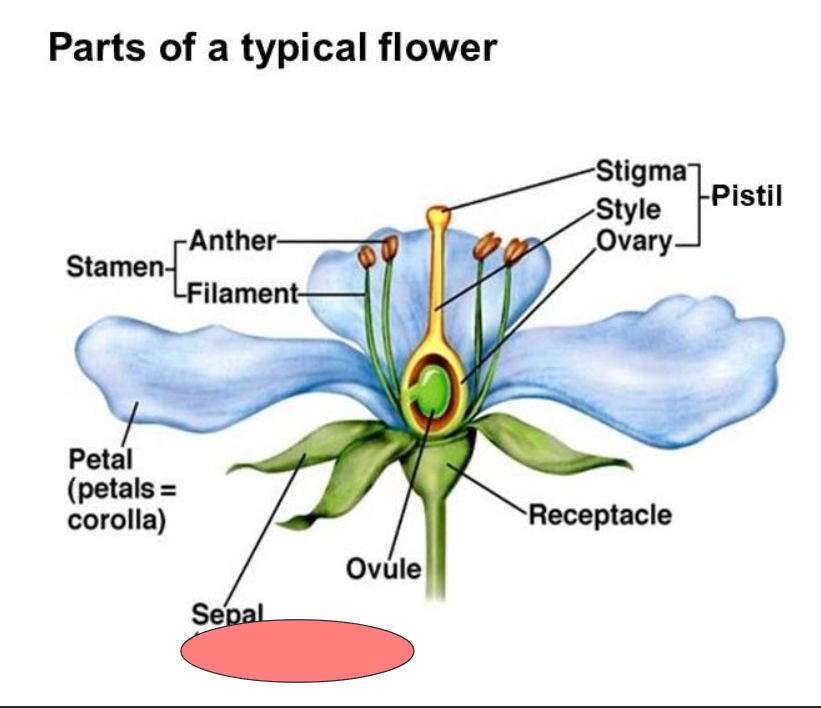
Stigma
located at the top of the style, receives pollen.
Anthers
produce male gametophytes (pollen grains)
Ovules
produces female gametophytes (embryo sacs)
Pollination
What occurs if a pollen grain lands on a receptive stigma.
Double fertilization
In ________ these sperm nuclei fertilize the egg and the two polar nuclei.
Double fertilization
results in a diploid zygote and triploid endosperm nucleus
Double Fertilization
ensures that the endosperm develops only in the ovules where the egg has been fertilized, there by preventing angiosperms from squandering nutrients on infertile ovules.
seed coat
is a tough outer layer that protects
the embryo from damage, dehydration, and predators.
fruit
develops from
the ovary enclosing
the developing
seed(s
Monoecious
male and female parts are in one flower
Dioecious
male and female parts are seperate
Ploidy
Number of chromosome sets
Haploid (n)
Half the amount of chromosomes an organism should have
Diploid (2n)
Base amount of chromosomes that an organism should have
Triploid (3n)
In Angiosperms causes the development of the Endosperm