phlt 304 test 1
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/101
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
102 Terms
1
New cards
Epidemiologic Triad
interaction between susceptible host, external agent, and environment that bring the three together
2
New cards
environmental contamination: natural
volcanoes, natural seepage, soil deposits, fires
3
New cards
anthropogenic causes
caused by humans, pollution
4
New cards
common effects of climate change
stronger storms, rising sea levels, damaged coral, warmer oceans, less snow, droughts and wildfire, food and water scarcity
5
New cards
water contaminants and waterborne illnesses
hepatitis A, cholera (killed by chlorine)
6
New cards
eutrophication
results in algae bloom, heavy production of algae
happens because of nutrient offloading, fertilizer runoff
body of water receives too many nutrients and elements such as nitrogen and phosphorous triggers heavy production
once algae dies, decaying process uses up a lot of oxygen, not leaving enough for the animals in the water
happens because of nutrient offloading, fertilizer runoff
body of water receives too many nutrients and elements such as nitrogen and phosphorous triggers heavy production
once algae dies, decaying process uses up a lot of oxygen, not leaving enough for the animals in the water
7
New cards
bioaccumulation
when an animal has a higher concentration of a chemical in its body than in the surrounding water (accumulation of a toxic chemical in the tissue of a particular organism
8
New cards
biomagnification
special kind of bioaccumulation where the animal is getting high amounts of the chemical through the food web, i.e fish and their mercury levels
9
New cards
bad fish
shark, swordfish, tiefish (fulf of MX), tuna (bigeye), marlin, orange roughey, king mackerel
10
New cards
onehealth
if we keep animals healthier, animal diseases won’t effect humans
11
New cards
ecosystem services
things we get from earth; water, air, lumber, etc
12
New cards
regulating services
help keep climate and resources stable, invisible until something goes wrong
13
New cards
ecosystem engineers
species that change biotic/abiotic materials to influence habitats i.e beavers and their dams
14
New cards
provisioning services
food and raw materials
15
New cards
supporting habitat services
a place to live for plants and animals
16
New cards
cultural services
benefits human get for being in the environment
cortisol levels improve
tourism, recreation
cortisol levels improve
tourism, recreation
17
New cards
keystone species\*\*
species that play a key role in the function and structure of an ecosystem
predator, prey, mutualists, host
predator, prey, mutualists, host
18
New cards
stressors affecting ecosystem services
chemical contaminants
biological factors
animal overexploitation
habitat loss: urban development, agriculture, fracturing
biological factors
animal overexploitation
habitat loss: urban development, agriculture, fracturing
19
New cards
greenhouse effect
not enough heat escaping the atmosphere
* carbon dioxide
* methane
* nitrous oxide
* gasses w fluorine
* carbon dioxide
* methane
* nitrous oxide
* gasses w fluorine
20
New cards
effects of each gas in the atmosphere depends on…
how much is in the atmosphere
how long it stays in the atmosphere
how much it absorbs/warms
how long it stays in the atmosphere
how much it absorbs/warms
21
New cards
potency on a molecular basis are
not equivalent
22
New cards
carbon dioxide (co2)
some removed quickly, but some stays for 1000+ years
GWP= 1 year
GWP= 1 year
23
New cards
global warming potential (GWP)
potency to stay in the atmosphere
24
New cards
methane (ch4)
12 year life in atmosphere
GWP= 25 years
GWP= 25 years
25
New cards
nitrous oxide (n2o)
114 year life in atmosphere
GWP= 298 years
GWP= 298 years
26
New cards
CO2 and ocean acification
affects animals with shells, shell is dissolving as the ocean becomes more acidic
27
New cards
environmental health
relationship between people and their environment
28
New cards
environmental risk assesmet
done when something is exposed to the environment
* how much of chemical is present
* how toxic is it
* how people are exposed and to what extent
* what is the likelihood of adverse effects (harm)
* how much of chemical is present
* how toxic is it
* how people are exposed and to what extent
* what is the likelihood of adverse effects (harm)
29
New cards
inhalation exposure
respiratory tract, surface area of lungs is large, rapid exchange of gasses/uptake of molecules
30
New cards
ingestion exposure
GI tract, small intestine has large surface area to facilitate nutrient absorption
31
New cards
skin exposure
depends if skin is damaged, warm, time on skin, properties,
32
New cards
concept of dose
central importance in determining health
adverse health effects when passing therapeutic level to toxic level
natural doesn’t mean good for you
adverse health effects when passing therapeutic level to toxic level
natural doesn’t mean good for you
33
New cards
particular contaminants
dust, fumes, mists, aerosols, fibers
34
New cards
top 10 causes of death environmentally
1. ischemic heart disease
2. chronic respiratory disease
3. cancers
4. unintentional injuries
5. respiratory infections
6. stroke
7. diarrheal diseases
8. diabetes
9. malaria
10. neo-natal conditions
35
New cards
clean air act
regulates many airborne contaminants
36
New cards
particulate contaminants/ particulate matter
less than 10 microns in diameter
* premature death
* nonfatal heart attacks
* irregular heart beat
* aggravated asthma
* reduced lung function
* increased respiratory symptoms
* premature death
* nonfatal heart attacks
* irregular heart beat
* aggravated asthma
* reduced lung function
* increased respiratory symptoms
37
New cards
genes
made of DNA
unit of inheritance
code for inherited variable traits
unit of inheritance
code for inherited variable traits
38
New cards
protein formation
gene (DNA) → transcription → mRNA transcript → translation → protein
39
New cards
beneficial mutation
duh benefits population through process of mutation
40
New cards
intron
noncoding sections of an RNA transcript
spliced out before RNA molecule is translated into a protein
spliced out before RNA molecule is translated into a protein
41
New cards
exon
region of the genome that ends up within an mRNA molecule
(what stays!!!!)
(what stays!!!!)
42
New cards
gene mutation
can change nothing, one amino acid, or a whole protein
43
New cards
genetic disorder
caused by mutation
deletion and insertion are more severe
deletion and insertion are more severe
44
New cards
Single Nucleotide Polymorphism (SNP)
variation in one nucleotide, single base position in DNA
45
New cards
CYP2D6
metabolizing
ex) when you consume morphine it's not an active therapeutic until the body enzyme metabolizes it
ex) when you consume morphine it's not an active therapeutic until the body enzyme metabolizes it
46
New cards
epigenetics
study of changes caused by activating or silencing genes (increasing or decreasing gene expression) without any change to the underlying DNA sequence
47
New cards
epigenetic modification
* consists of small molecules being attached to existing DNA
* small molecules added onto the DNA or histones, making it easier or harder to have gene expression
* does not change sequence in bases in DNA
* small molecules added onto the DNA or histones, making it easier or harder to have gene expression
* does not change sequence in bases in DNA
48
New cards
mutation
consists of change in the DNA sequence
ex) changes in the bases in the DNA
ex) changes in the bases in the DNA
49
New cards
DNA adduct
a piece of DNA covalently bonded to a chemical
isn’t a mutation but can cause mutations to form
DNA is damaged, resulting in abnormal replication
isn’t a mutation but can cause mutations to form
DNA is damaged, resulting in abnormal replication
50
New cards
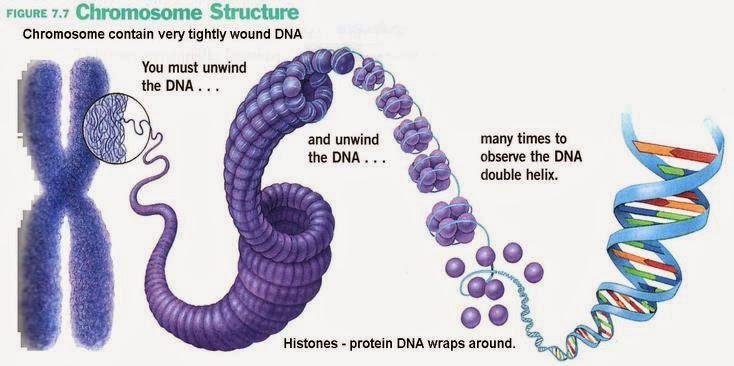
structure of DNA
* wrapped into histone protein core to form a nucleosome
* coiled further into solenoids
* solenoids organized into chromatin loops, each loop has 100,000 base pairs (ATGC)
* coiled further into solenoids
* solenoids organized into chromatin loops, each loop has 100,000 base pairs (ATGC)
51
New cards
methyl group
CH3 attachment, methyl group attaches directly to DNA but doesn’t change base sequence
when it gets close to the gene it SILENCES It
reversible
when it gets close to the gene it SILENCES It
reversible
52
New cards
DNA Methylation\*\*\*
\
Addition of methyl group ME onto DNA
when close to a gene, reduces expression
* histone acetyltransferase
* deacetylases
* acetylation
* methylation
Addition of methyl group ME onto DNA
when close to a gene, reduces expression
* histone acetyltransferase
* deacetylases
* acetylation
* methylation
53
New cards
DNA Acetylation\*
repairs proteins and is a dynamic epigenetic modification done by HATS (lysine acetyltransferase), effects DNA binding ability, protein activity
54
New cards
DNA deacetylation
histone tails, DNA becomes more tightly wrapped around the histone cores, making it harder for transcription factors to bind to the DNA
* gene silencing
* gene silencing
55
New cards
acetyl in methylation
makes it easier for gene expression to happen, loosens DNA for easier access
56
New cards
Bisphenol A (BPA)
associated! risks!
increased risk of miscarriage and gestational diabetes (women)
DNA damage to sperm/reduced fertility (men)
increased risk of miscarriage and gestational diabetes (women)
DNA damage to sperm/reduced fertility (men)
57
New cards
immunodeficiency
risk factor for certain kinds of cancer, specifically viral and lymphatic
58
New cards
Benzo(a)pyrene
changed into a very reactive molecule that covalently bonds with DNA
* mutation of the 12th codon of the Hras oncogene
* oncogene: gene which sometimes turns into a tumor cell
\
* mutation of the 12th codon of the Hras oncogene
* oncogene: gene which sometimes turns into a tumor cell
\
59
New cards
Initiation
mutation of somatic cell
these cells can remain static (nondividing)
eliminated by apoptosis
these cells can remain static (nondividing)
eliminated by apoptosis
60
New cards
somatic cell
every cell other than sperm and egg
61
New cards
progression
conversion of benign preneoplastic into neoplastic cancer
62
New cards
generation time
time needed for a quiescent cell to complete one cell division cycle to produce 2 daughter cells (amount of time for one cell cycle)
63
New cards
malignant cells
shorter generation time, smaller fraction of cells are in the resting and more are in the reproducing stage (too rapid!!)
64
New cards
proto-oncogene
managing normal cell growth, mutation turns it into just oncogene and then it’s bad!!!!!!
65
New cards
cancer cells have a lower level of…
methylation
66
New cards
autoimmune disease
immune system cannot differentiate self and non-self
67
New cards
lymph nodes
lymphocytes recognize and eliminate invading pathogens
68
New cards
spleen
assists body in protecting against bacterial infections
69
New cards
innate immunity
nonspecific immunity
had since birth
first line of defense
fast
* not effected by vaccines
* stomach, stomach acid
had since birth
first line of defense
fast
* not effected by vaccines
* stomach, stomach acid
70
New cards
complement
plasma proteins that kill foreign cells, increase inflammatory response and attach phagocytes
71
New cards
natural killer cells
cytotoxic action against cancer cells
72
New cards
interferons
antiviral proteins
73
New cards
NK cells
effector lymphocytes of the innate immune system
74
New cards
Adaptive Immunity
acquired or specific immunity
* antigens
* slower than the first time exposed to pathogen, develops immunologic memory
* slower than innate immunity
* antigens
* slower than the first time exposed to pathogen, develops immunologic memory
* slower than innate immunity
75
New cards
antigen\*
molecule or substance that is foreign to the body that provokes an immune response
76
New cards
Cell mediated immunity
primarily involves T lymphocytes/ t cells
77
New cards
cytotoxic t cells
(CD8 cells) destroy infected host cells (cancer, transplant organs
78
New cards
helper t cells
(CD4) cells
* increase and support antibody production. cytotoxic t cells, natural killer cells, increase phagocytosis
* increase and support antibody production. cytotoxic t cells, natural killer cells, increase phagocytosis
79
New cards
long lived memory t cells
made after you first get sick, works fast for future exposure to same antigen
80
New cards
cytotoxic
cell killing, factors destroy cell once infected
81
New cards
humoral (anti-body mediated) immunity\*
encounter pathogen and remember antigen (non-self indicator to B cells)
82
New cards
plasma cells
make antibodies that are specific for the antigen that initiated their production, can make 2000 per second
83
New cards
antibody function
proteins secreted into plasma to help eliminate foreign organisms
84
New cards
active immunity
after exposure to a foreign organism, immune cells produce antibodies and memory cells
85
New cards
passive immunity
transfer of antibodies from someone else to the vulnerable person
* no memory cells formed → short terms protection until antibodies consumed or catabolized
* no memory cells formed → short terms protection until antibodies consumed or catabolized
86
New cards
tolerance
body’s ability to correctly recognize self and not attack it
immune system’s appropriate lack of response to “self”
immune system’s appropriate lack of response to “self”
87
New cards
autoimmunity
when tolerance fails and body develops autoantibodies to own tissues, no known cause and no preventative methods available
* sjorn’s syndrome (4 million US women, dry eyes & mouth) can occur with lupus or rheumatoid arthritis
* sjorn’s syndrome (4 million US women, dry eyes & mouth) can occur with lupus or rheumatoid arthritis
88
New cards
inflammation
body’s response to injury, infection, certain environmental exposure
89
New cards
intestinal dysbiosis
perturbation in the composition of the gut microbiome relative to the composition of the gut microbiome in healthy individuals
90
New cards
circadian rythms
physical, mental, behavioral changes that occur over a 24 hour period
91
New cards
suprachiasmatic nucleus (SCN)
overall master clock
* located in the brain
* controls production of melatonin
* located in the brain
* controls production of melatonin
92
New cards
insufficient sleep
changes in mood, memory, cognition
* increased risk of obesity because less sleep decreases leptin, making you hungry and wanting carbs
* type 2 diabetes and high tension and high blood pressure
* sleep hygiene
* increased risk of obesity because less sleep decreases leptin, making you hungry and wanting carbs
* type 2 diabetes and high tension and high blood pressure
* sleep hygiene
93
New cards
which chromosome determines sex
23rd
94
New cards
color blindness
recessive and sex-linked
95
New cards
alcohol dehydrogenase (ADH)
converts ethanol to acetaldehyde (toxic)
96
New cards
aldehyde dehydrogenase (ALDH)
oxidized aldehydes to acetate (less toxic)
* acetate is broken down into CO2 and H2O
* acetate is broken down into CO2 and H2O
97
New cards
asian flush
50% of Chinese, Koreans, and Vietnamese populations have high incidence of atypical form of ADH (rapidly metabolize, red)
98
New cards
lead
children of ages 0-6
* reduced IQ
* can be stored in the bones with calcium, during pregnancy it’s released from bones and exposed to fetus
* reduced IQ
* can be stored in the bones with calcium, during pregnancy it’s released from bones and exposed to fetus
99
New cards
ground-level ozone
health effects of breathing this
* chest pain
* coughing
* throat irritation
* airway inflammation
* worsen bronchitis, emphysema, asthma
* chest pain
* coughing
* throat irritation
* airway inflammation
* worsen bronchitis, emphysema, asthma
100
New cards
ground level ozone compounds
* carbon monoxide (CO)
* sulfur dioxide (SO2)
* nitrogen dioxide (NO2)
* sulfur dioxide (SO2)
* nitrogen dioxide (NO2)