Micobiology Lab Quiz 2
1/124
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
125 Terms
Differential stain
uses more than one stain
Allows you to differentiate between different types of bacteria
Gram stain
based on bacterial cell wall properties
Differentiates between Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria
Peptidoglycan
Composes the bacterial cell wall
Peptides and sugars/carbohyrdates
Composes peptidoglycan
Carbohydrate backbone
Consists of repeating sugars
NAG and NAM
Repeating sugars of the carbohydrate backbone
Glycosidic bonds
Bonds that link NAG and NAM
Peptide bonds
Bonds that link carbohydrate backbones
Gram-positive bacteria
thick layer of peptidoglycan
Contains teichoic acid
No outer membrane
Wall teichoic acid
Connects peptidoglycan layers to each other
Iipoteichoic acid
Connects peptidoglycan to lipids in plasma membrane
Gram-negative bacteria
thin layer of peptidoglycan
No teichoic acid
Contains an outer membrane
Outer membrane composition
phospholipid bilayer
Porins
Lipoplysaccharide (LPS)
Porins
Channels that allow substances to enter /exit
Lipopolysaccharide (LPS)
Extends outward from phospholipid bilayer
Lipoproteins
Anchor outer membrane to cell wall
Crystal violet
Primary stain for Gram Stain ( ~2 min )
Secondary stain for Capsule Differential Stain
Stains purple
Gram’s Iodine
Mordant (binding agent) in Gram Stain (~2 min)
Acetone Alcohol
Detaining agent (destainer) in Gram Stain (~3-8secs)
Safranin
Secondary stain (counter stain) in Gram Stain and Endospore Differential Stain (~2min)
Purple
Gram positive stain
Pink
Gram Negative stain
Destain for too long
Gram-positive bacteria appear falsely gram-negative
Destain for too short
Gram-negative bacteria appear falsely gram-positive
Cells are too old
Cell wall can degrade or change
Capsule
gelatinous coat surrounding some bacteria
Uncharged polysaccharides
Composition of capsule
Functions of the capsule
increases bacterial virulence
Prevents desiccation
Adheres to surfaces
Resists phagocytosis
Nutritional reserve
Virulence
Degree of disease a pathogen can cause
Desiccation
Drying out
Capsule differential stain
Identify bacteria with capsule
Nigrosin
Negative stain in capsule differential stain (stains background black)
Acid-fast bacteria
Cell wall contains mycolic acid
Mycolic acid
Waxy lipid that makes cell impermeable to most stains
Functions of mycolic acid
Prevents desiccation and digestions after pathogenesis
Mycobacterium and Nocardia
Acid-fast genera
Mycobacterium tuberculosis
Tuberculosis
Mycobacterium leprae
Leprosy
Carbolfuchsin
Primary dye in Acid-Fast Stain
Contains phenol
Dark red basic dye
Must be added over steam
Acid Alcohol
destainer in Acid-Fast stain
Methylene Blue
Counterstain in Acid-Fast Stain
Blue
Non-acid fast bacteria stain color
Red
Acid-fast bacteria stain color
Vegetative body stain color
Vegetative body
Actively metabolizing
Endospore
Not actively metabolizing (only produced by certain bacteria)
Bacillus and Clostridum
bacteria types that produce endospores
Bacillus anthracis
Anthrax
Clostridium botulinum
Botulism
Clostridium tetanus
Tetanus
Clostridium difficile
Colitis
Sporogenesis
Process that endospores are formed through
Harsh environments
What causes sporogenesis?
One endospore
One vegetative body forms:
Endospore structure
Smaller and more compact that vegetative bodies
Endospore coat
Thick layer of keratin + calcium diplocholinate
Functions of endospore structure
resistant to heat, alcohol, UV, drying, etc.
Can remain dormant for long periods of time
Endospore germination
occurs when environment improves
One Endospore—> one vegetative body
NOT a reproductive process
Endospore differential stain
Differentiate between vegetative cells and endospores
Malachite green
primary stain in Endospore differential stain
Added over heat
Allows stain to penetrate thick endospore coat
Water
Detainer of endospore differential stain
Green
Endospore stain color
Aerobe
Utilize O2
Obligate aerobe
Require O2
Microaerophiles
Prefer low O2 and high CO2
Anaerobes
Do not utilize oxygen
Obligate anaerobe
Cannot tolerate the presence of O2
Aerotolerant
Cannot utilize O2, but tolerate it fairly well
Facultative anaerobe
Capable of living with or without O2, but prefer it
Sodium thioglycollate
Reducing agent that bonds to some of the O2 —> H2O
Small amount of agar
Reduces the diffusion of O2 from the air into medium
Resazurin
O2 indicator (changes color depending on if O2 is present or not)
O2 present
Resazurin turns pink
O2 absent
Resazurin is colorless
Anaerobic Pouch
Creates anaerobic environment
Gas Pak
absorbs O2
Produces CO2
Blue
Methylene Blue color when O2 is present
White
Methylene Blue color when O2 is absent
Candle Jar
Add lit candle to a jar
Candle consumes most of the O2 and generates CO2
Creates microaerophilic environment
Motility
Self-directed movement of an organism via cilia, pseudopods, or flagella
Cilia
Short-hair like processes (eukaryotic)
Pseudopods
“Fake foot” projection of cytoplasm (eukaryotic)
Spirillum volutans
Flagellated bacteria example
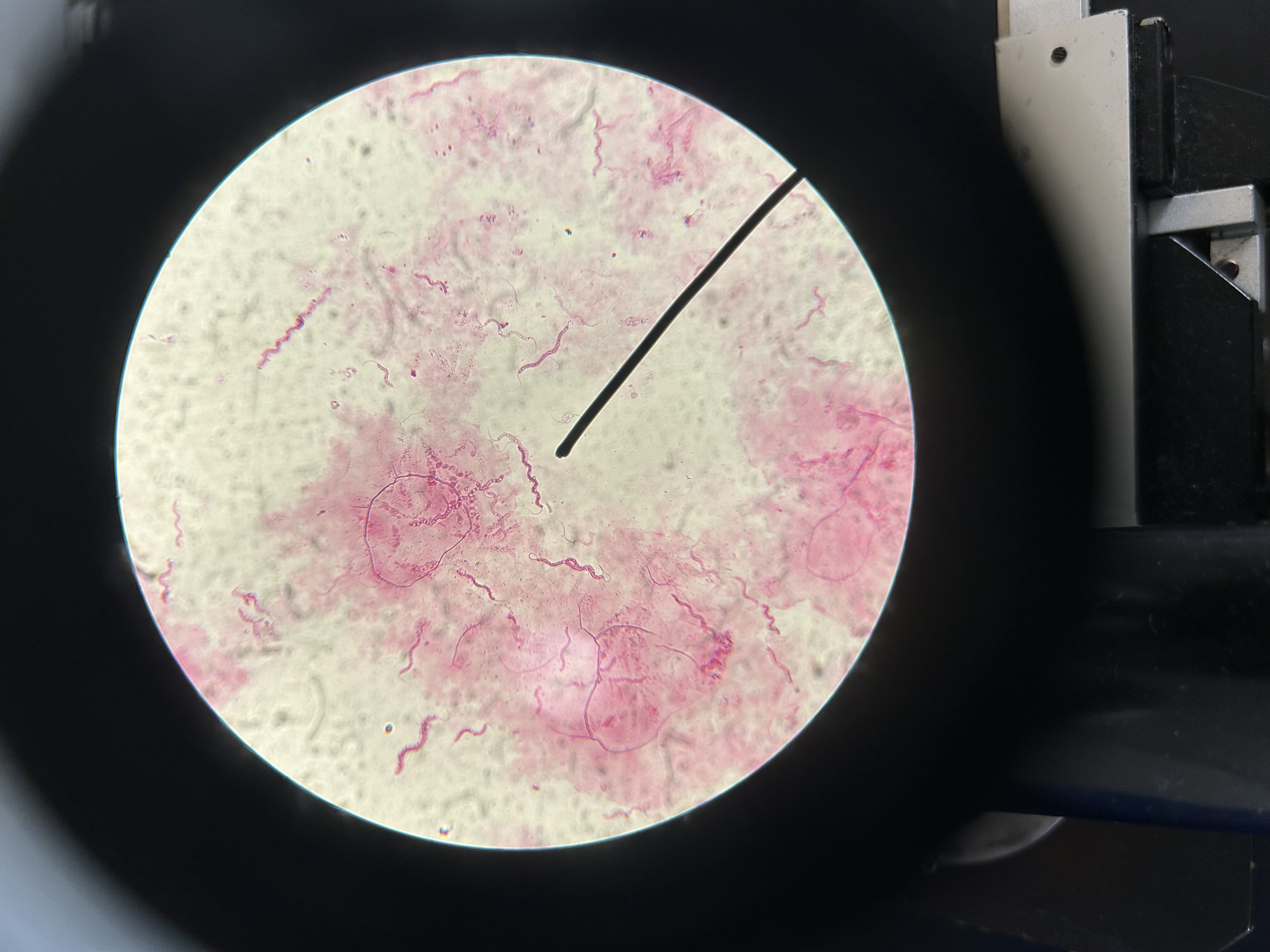
Flagella
Longer whip-like appendages (prokaryotic)
Brownian motion
Vibrational movement caused by collision with H2O molecules
Monotrichous
One single flagellum
Amphitrichous
Flagella on both ends
Peritrichous
Flagella surround entire cell
Lophotrichous
Multiple flagella at one end
Ways to check for motility
wet mount (microscopic)
Hanging drop (microscopic)
Semi-solid agar (culture)
0.5% agar
Agar percent for semi-solid agar
1% agar
Normal solid media agar %
Non-motile
Crisp line of growth
Motile organism
Hazy growth away from stab line
Only accounts for living organisms
Advantage of semi-solid agar test
Disadvantages of semi-solid agar motility test
requires overnight incubation
Results can be difficult to interpret
Heterotrophic
Must get carbon form other sources
Saprophytic
Can obtain nutrients from dead, organic matter
Mycosis
Fungal infection
Chitin
Cell wall of fungi
Low pH and high sugar
Preferred environment of fungi