A Tour of the Cell: Structure and Function Overview
1/40
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
41 Terms
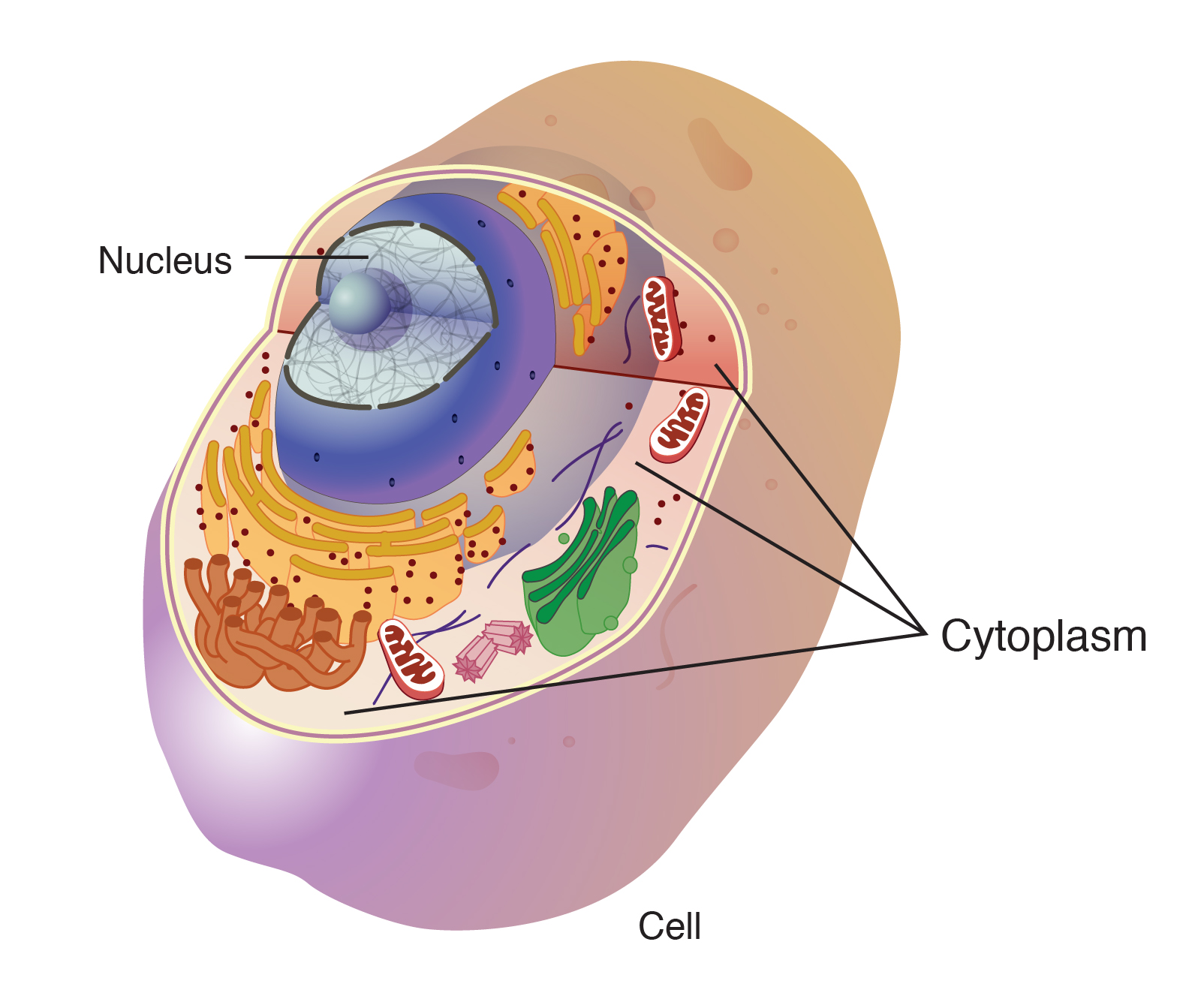
Cell
The fundamental unit of life.
Organelles
Specialized membrane-bound structures performing distinct functions.
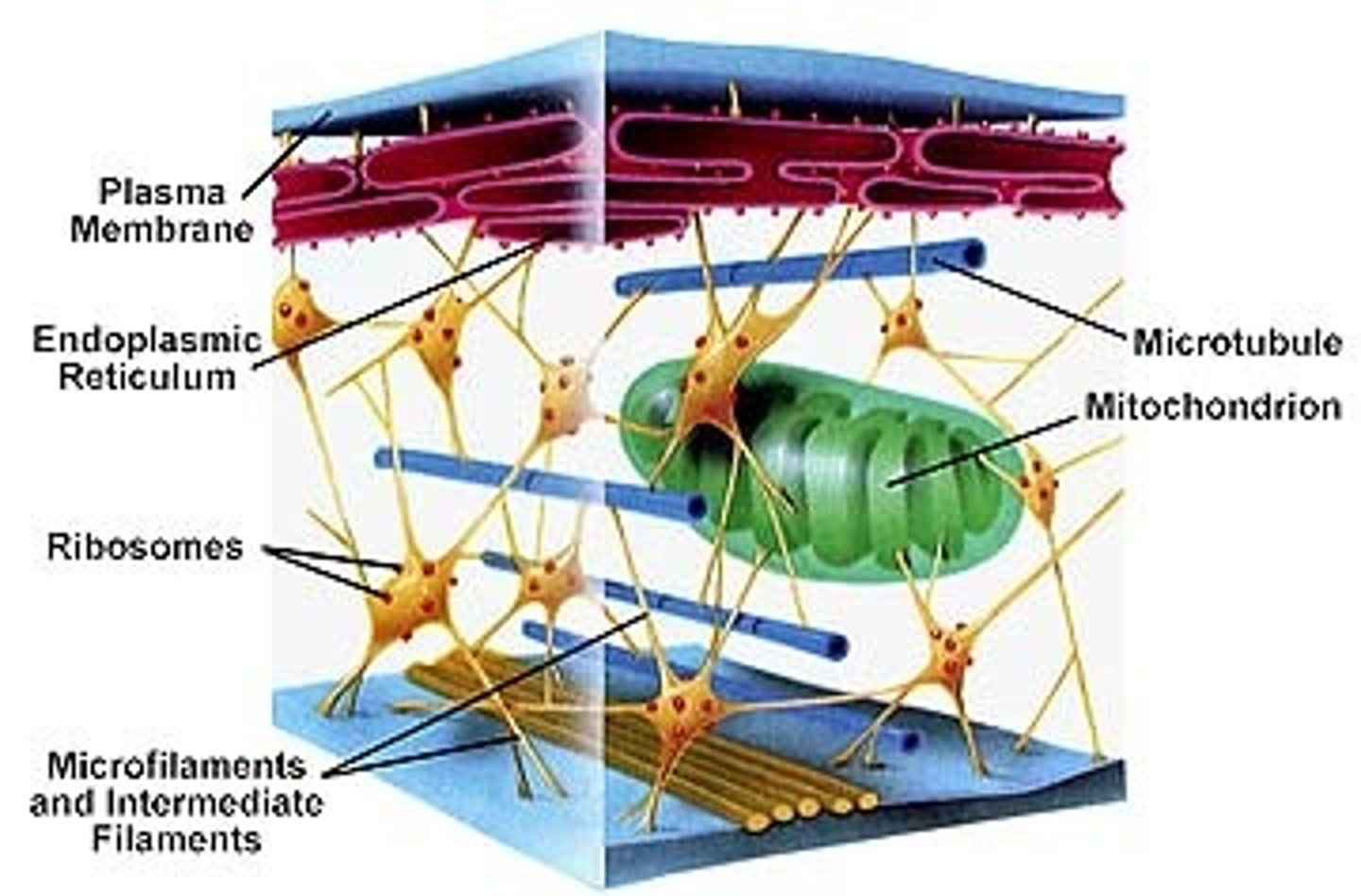
Cytoskeleton
Network of fibers provides structural support to cells.
Microscopy
Technique for visual examination of cells.
Cell Theory
Cells are life's basic units; arise from others.
Electron Microscopy (EM)
Technique using electrons for high-resolution imaging.
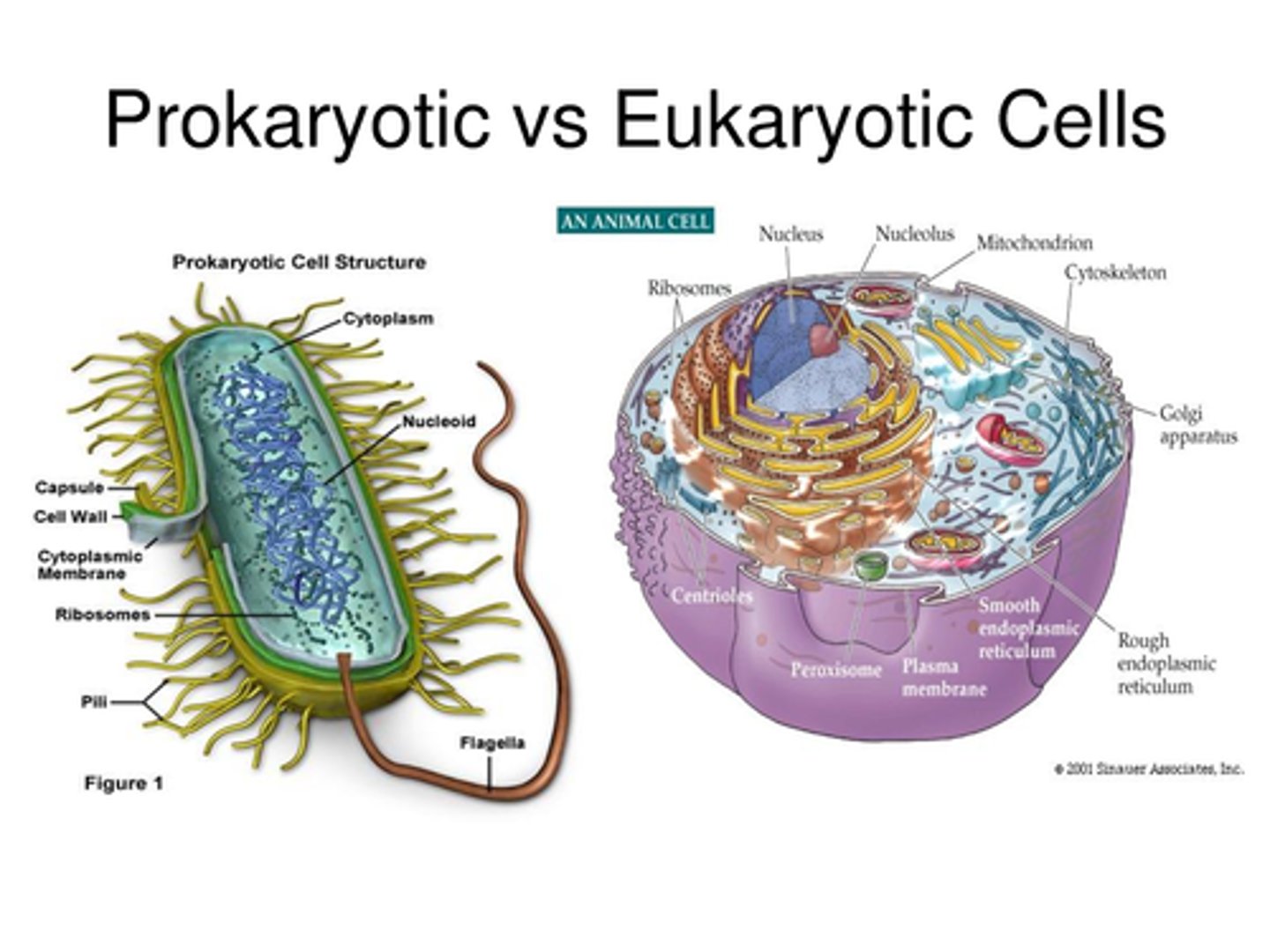
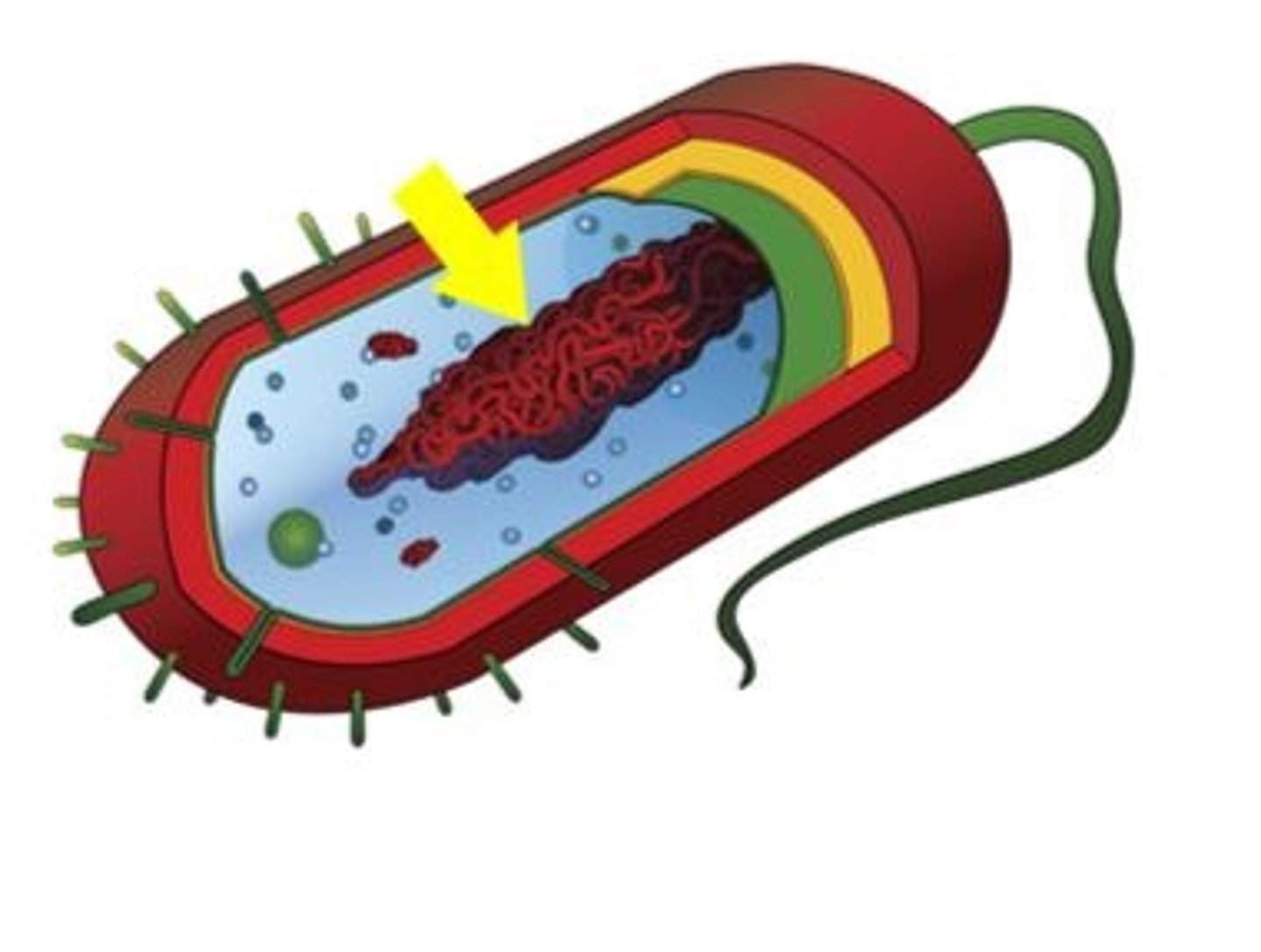
Prokaryotic Cells
Cells without membrane-bound organelles.
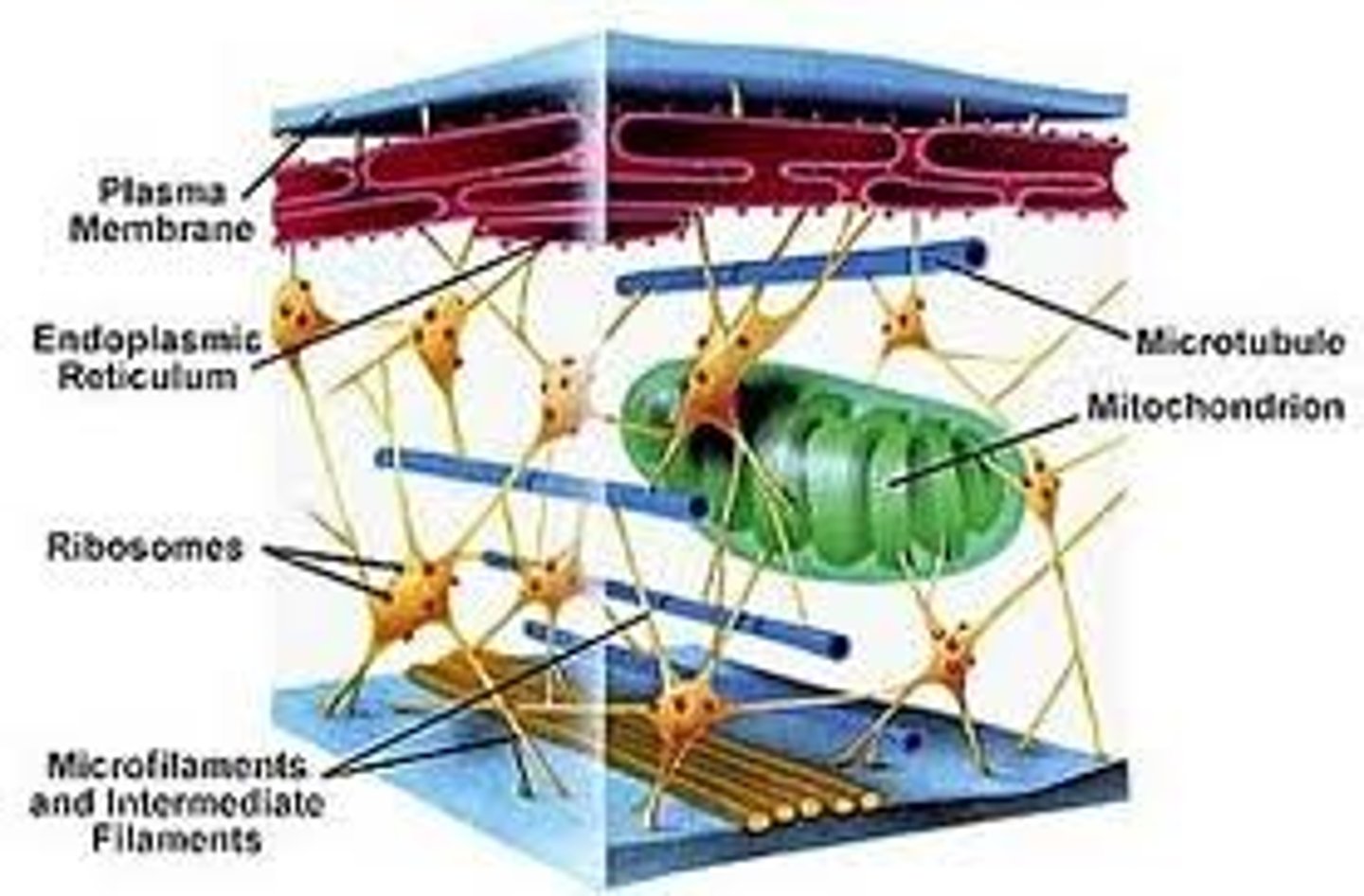
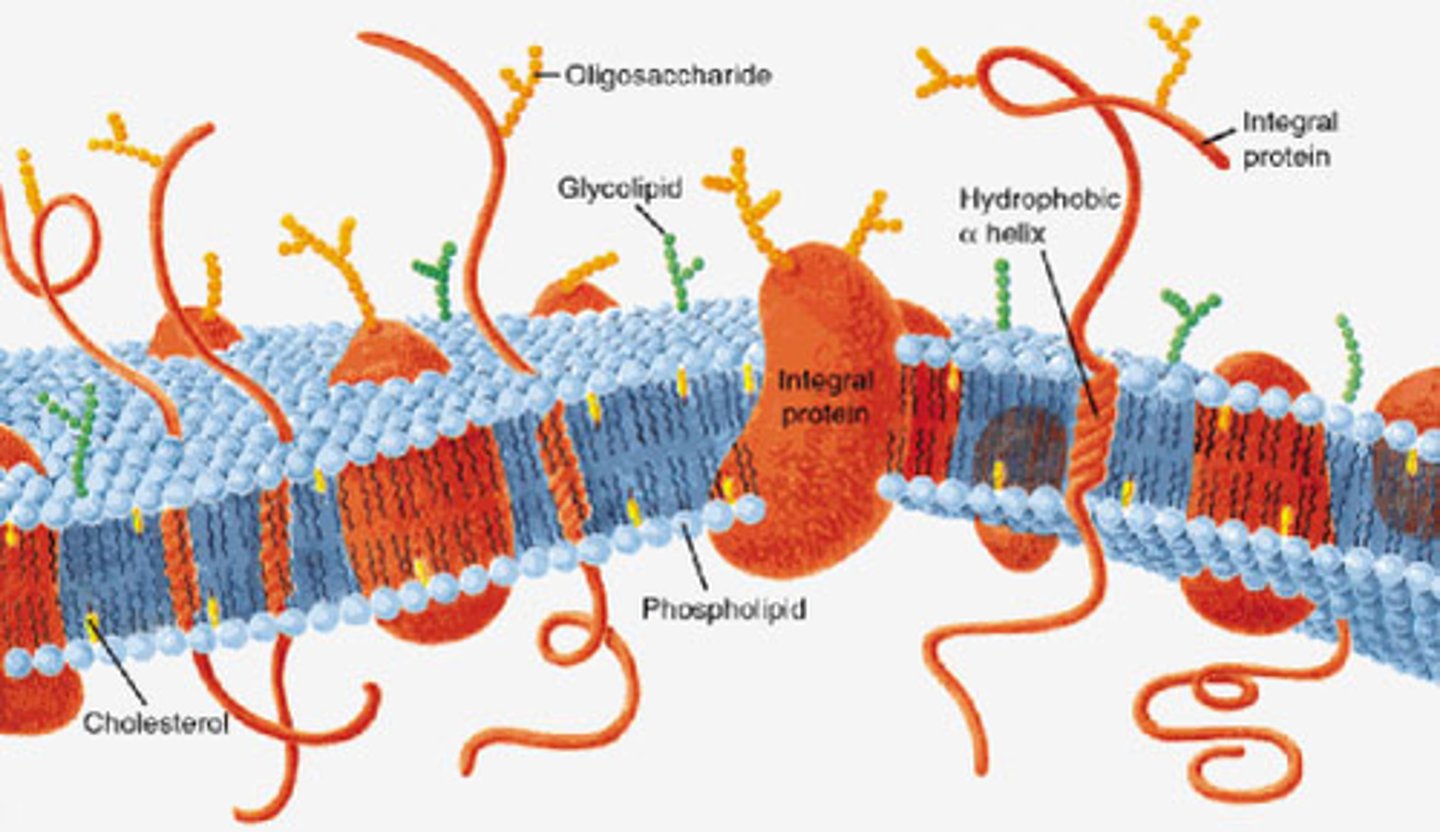
Plasma Membrane
Cell membrane controls substance entry and exit.
Cytosol
Cytoplasm's fluid substance containing free ribosomes, semifluid.
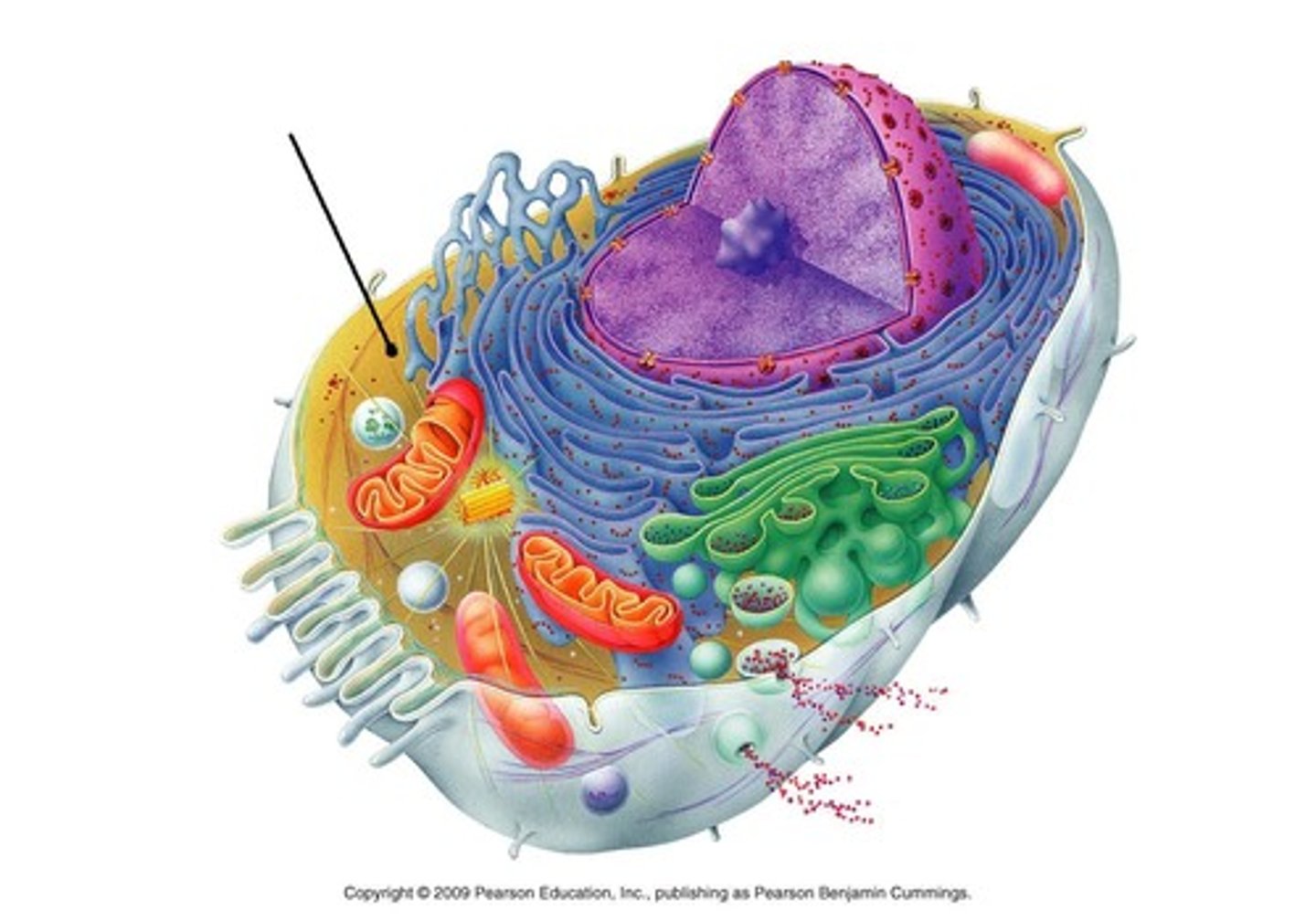
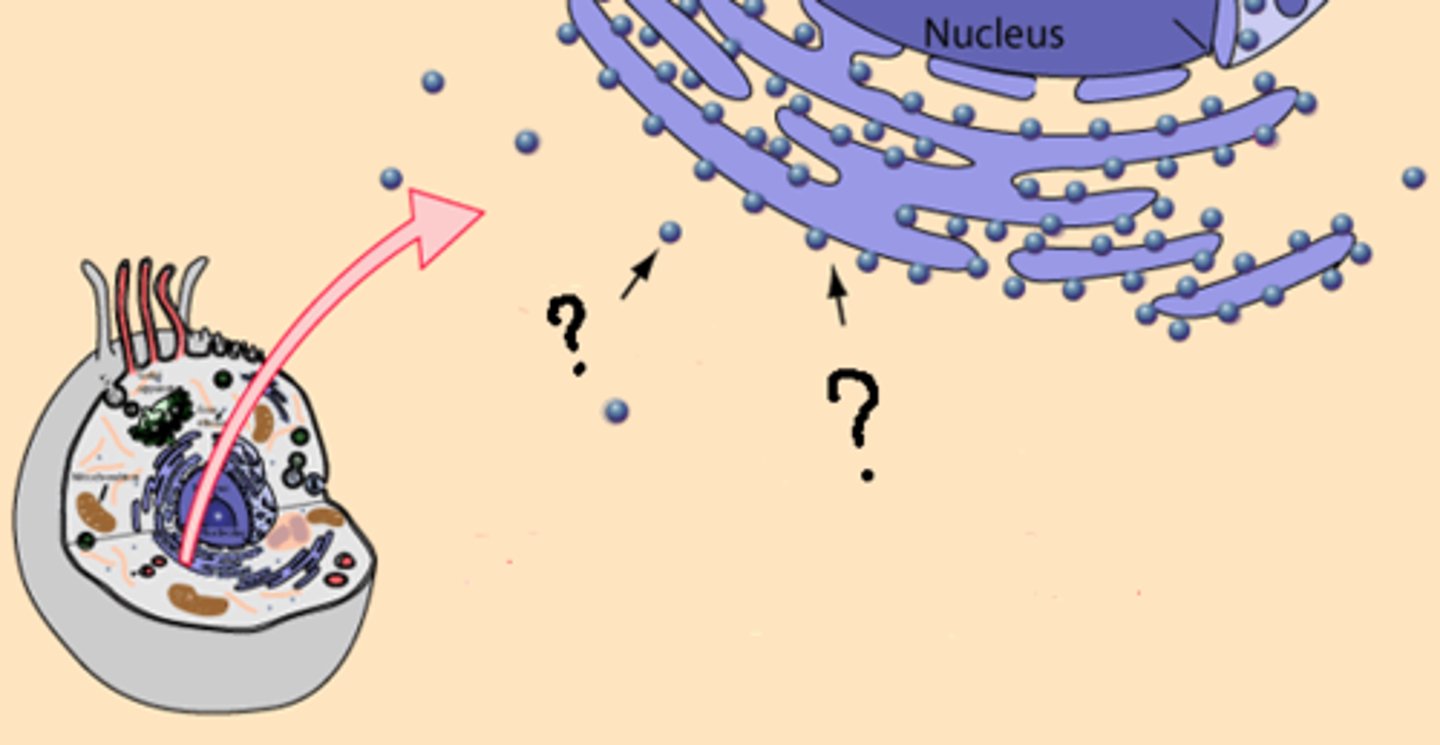
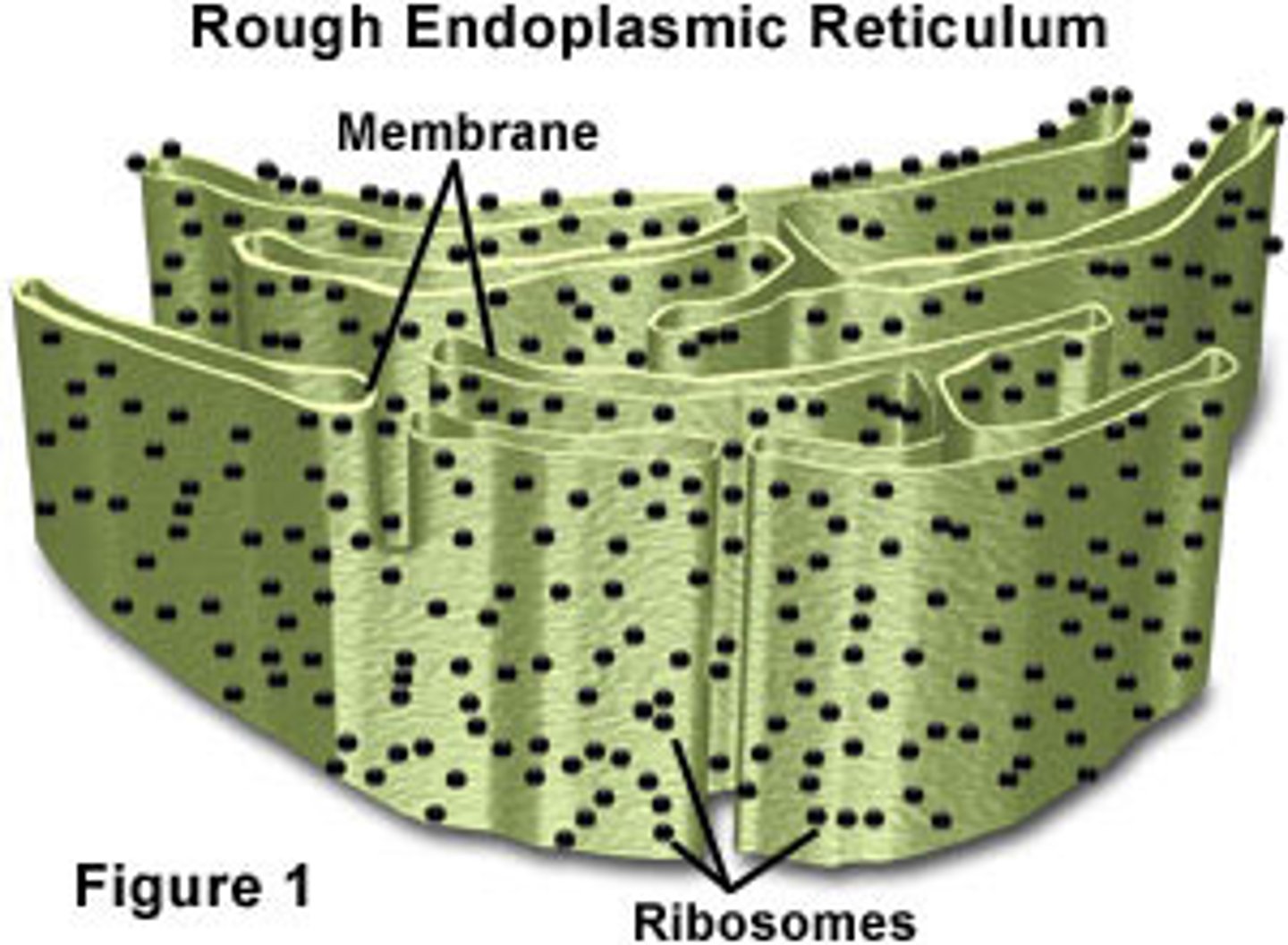
Ribosomes
synthesize proteins from mRNA, on Rough ER.
Nucleoid
Region in prokaryotes containing concentrated DNA.
Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER)
Membrane network for protein and lipid synthesis, biosynthetic factory.
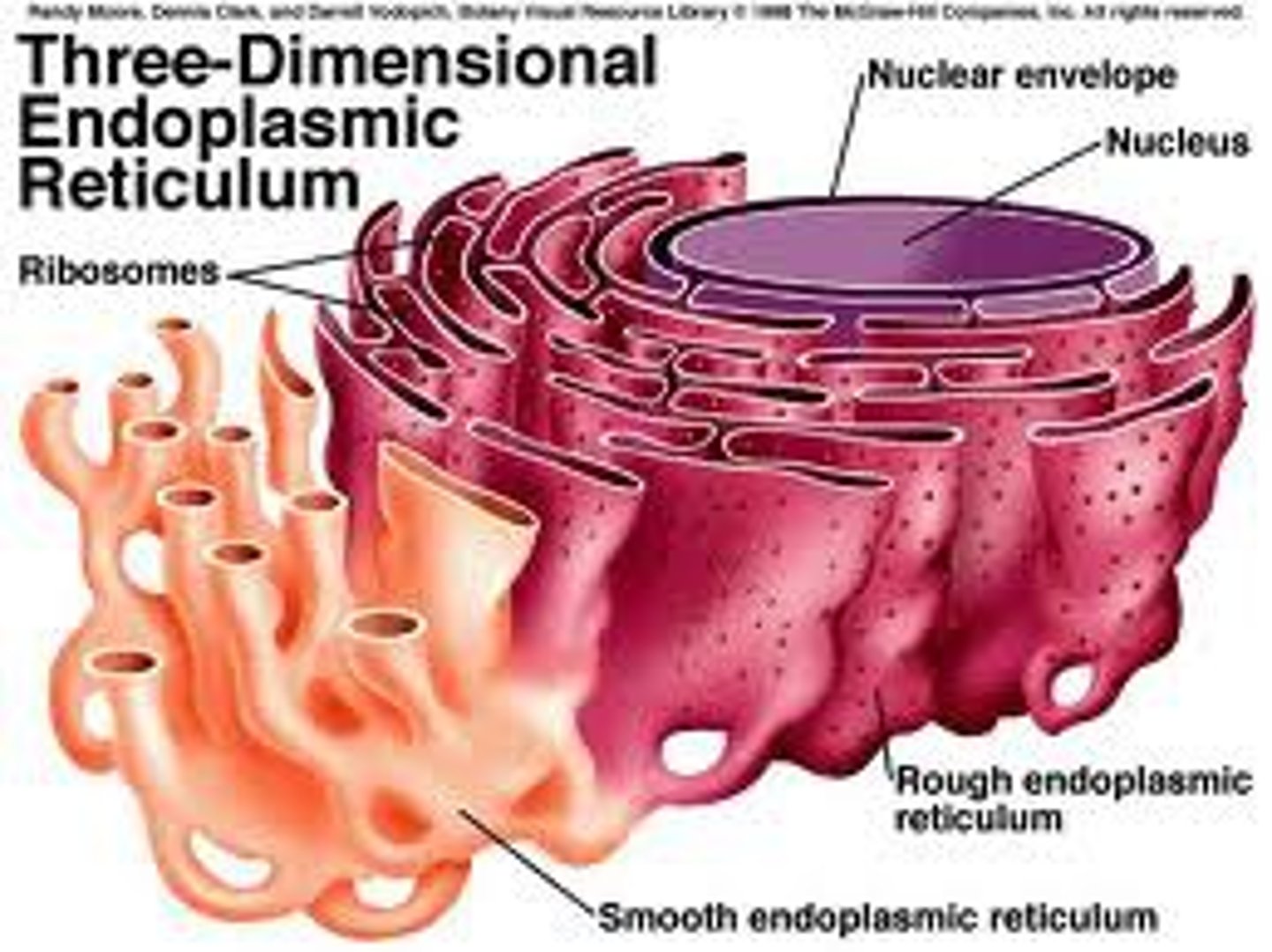
Rough ER
Ribosomes synthesize proteins for cellular export.
Smooth ER
ER without ribosomes, involved in lipid synthesis.
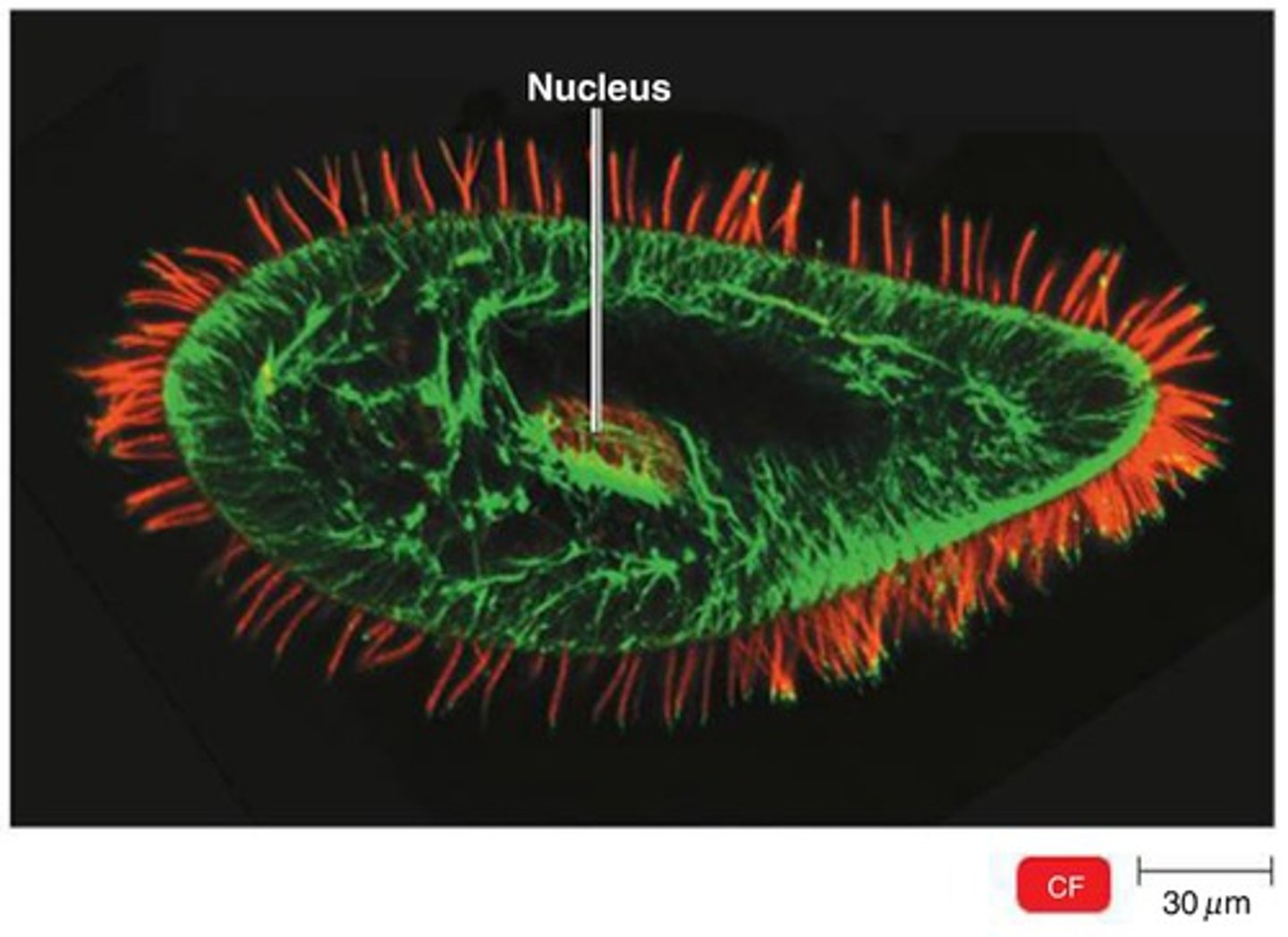
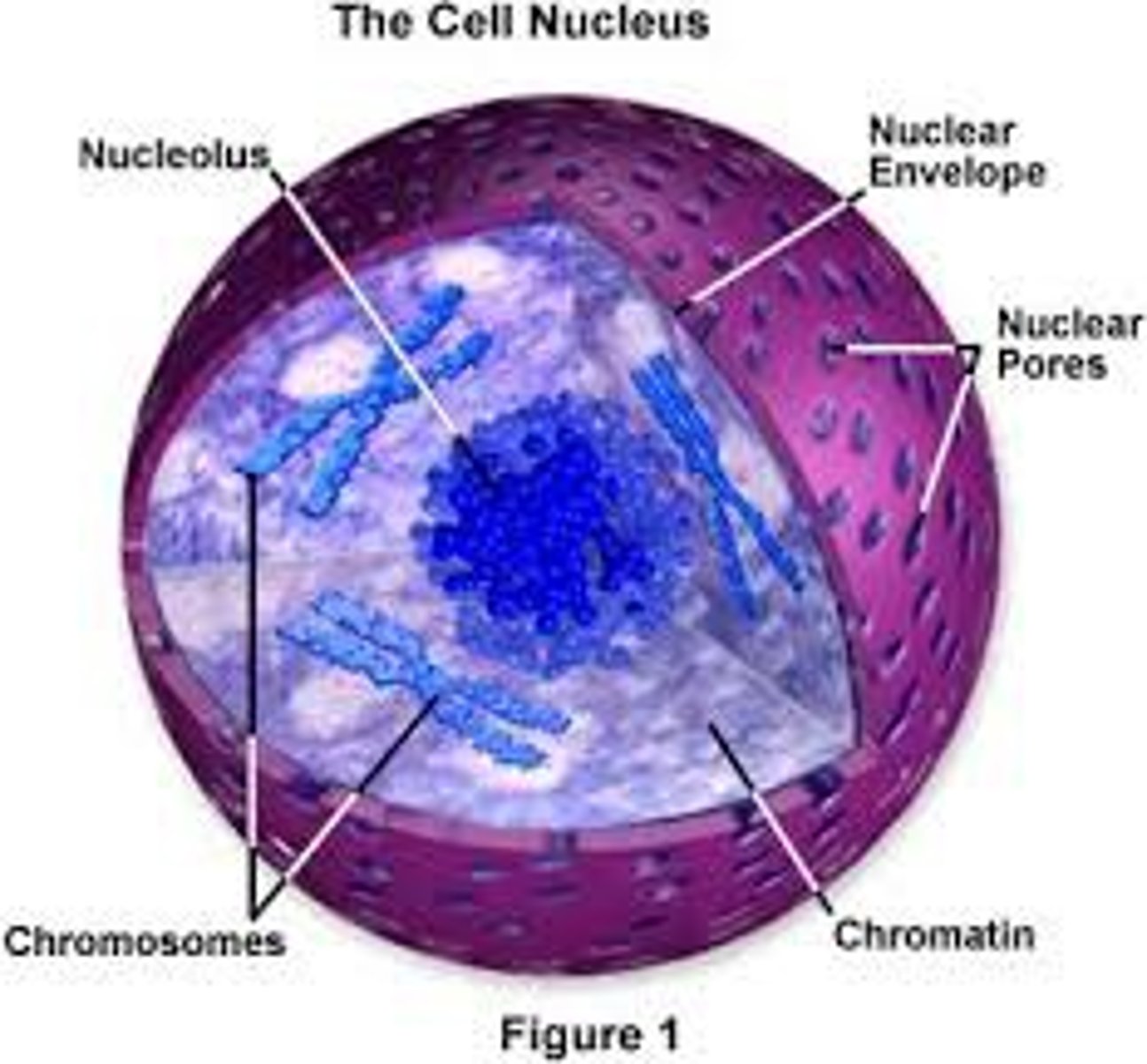
Nucleus
Organelle containing most eukaryotic cell genes. Averages about 5 µm in diameter.
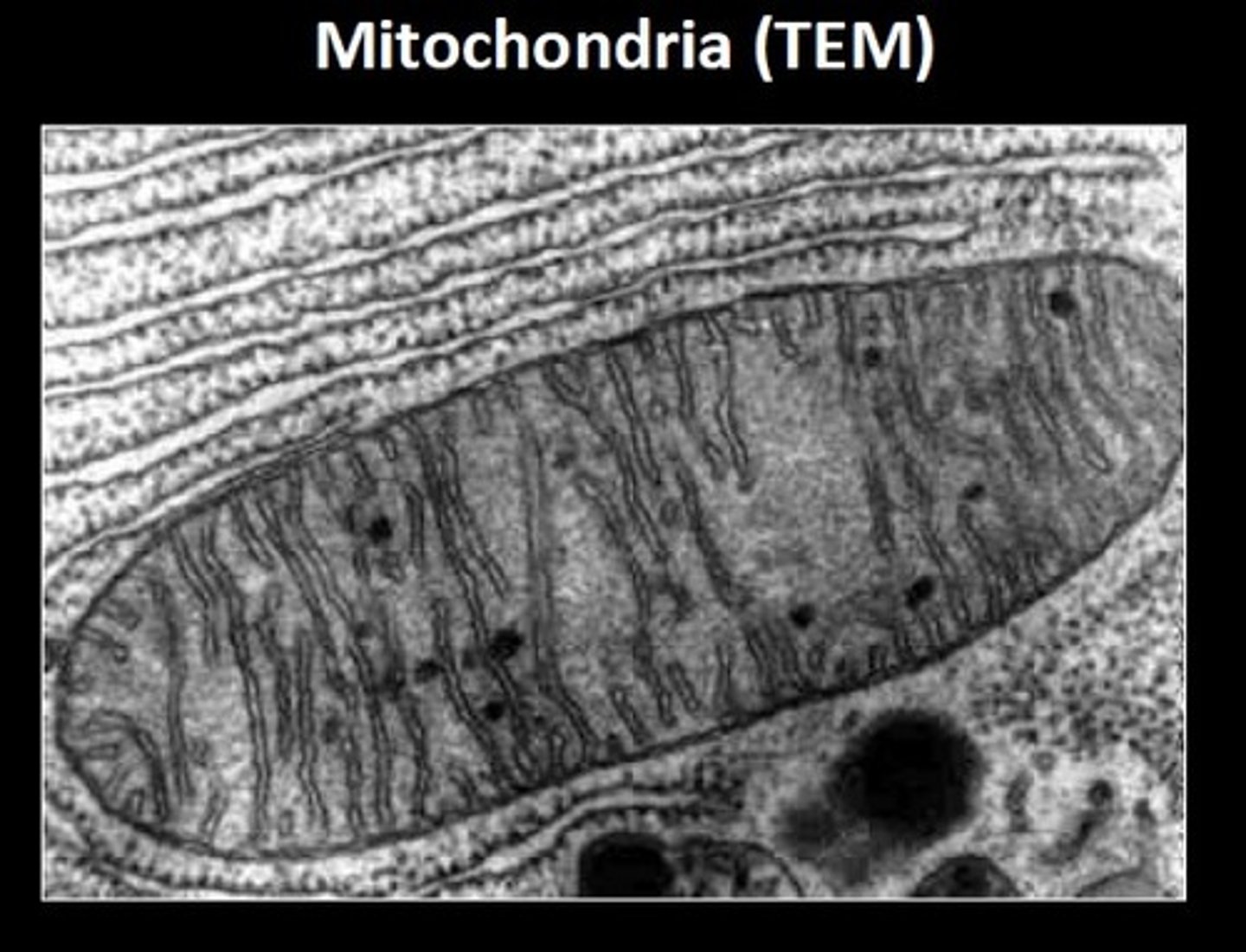
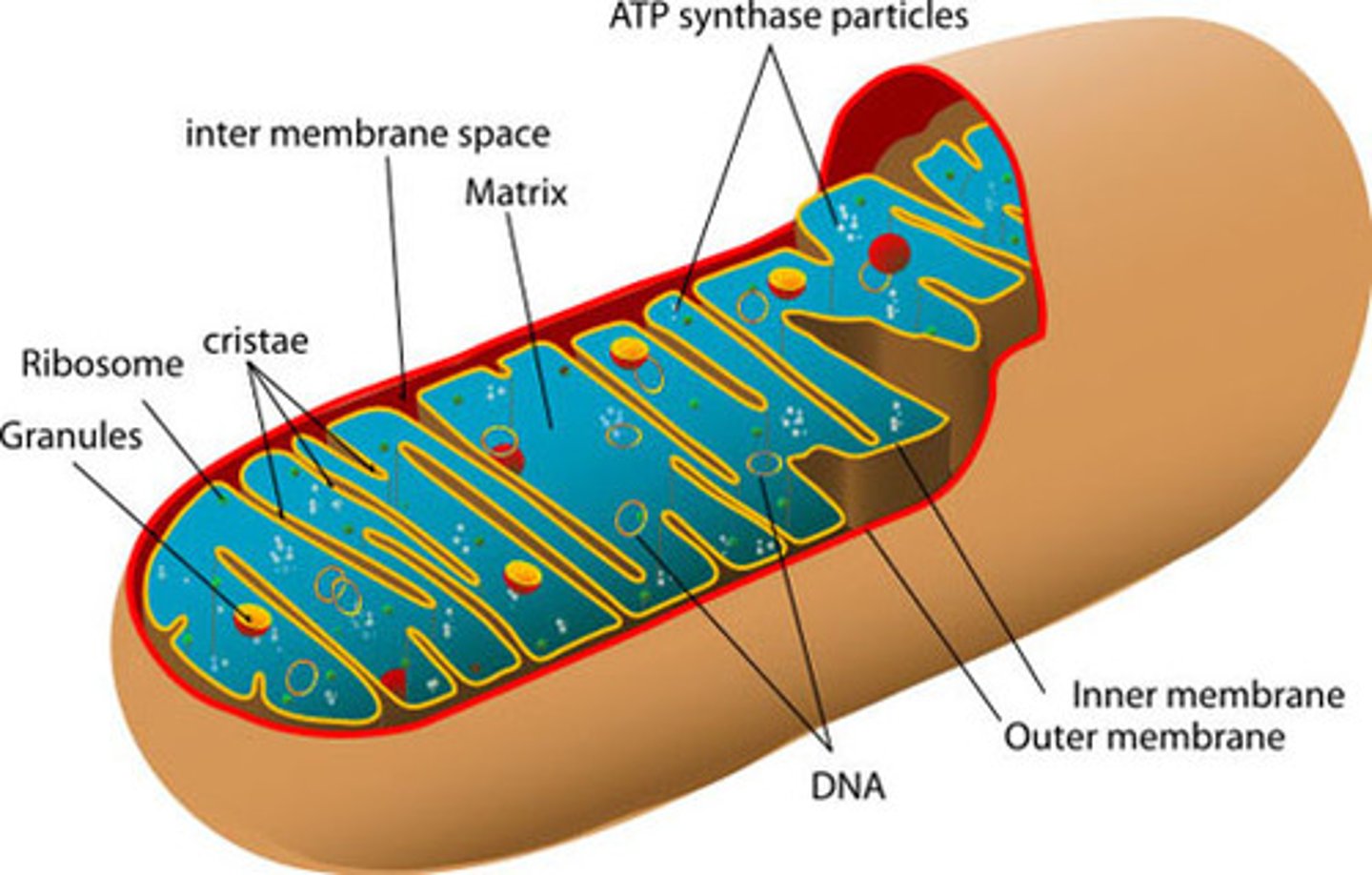
Mitochondria
produce ATP, powering cellular respiration processes. Typically 1-10 µm in length.
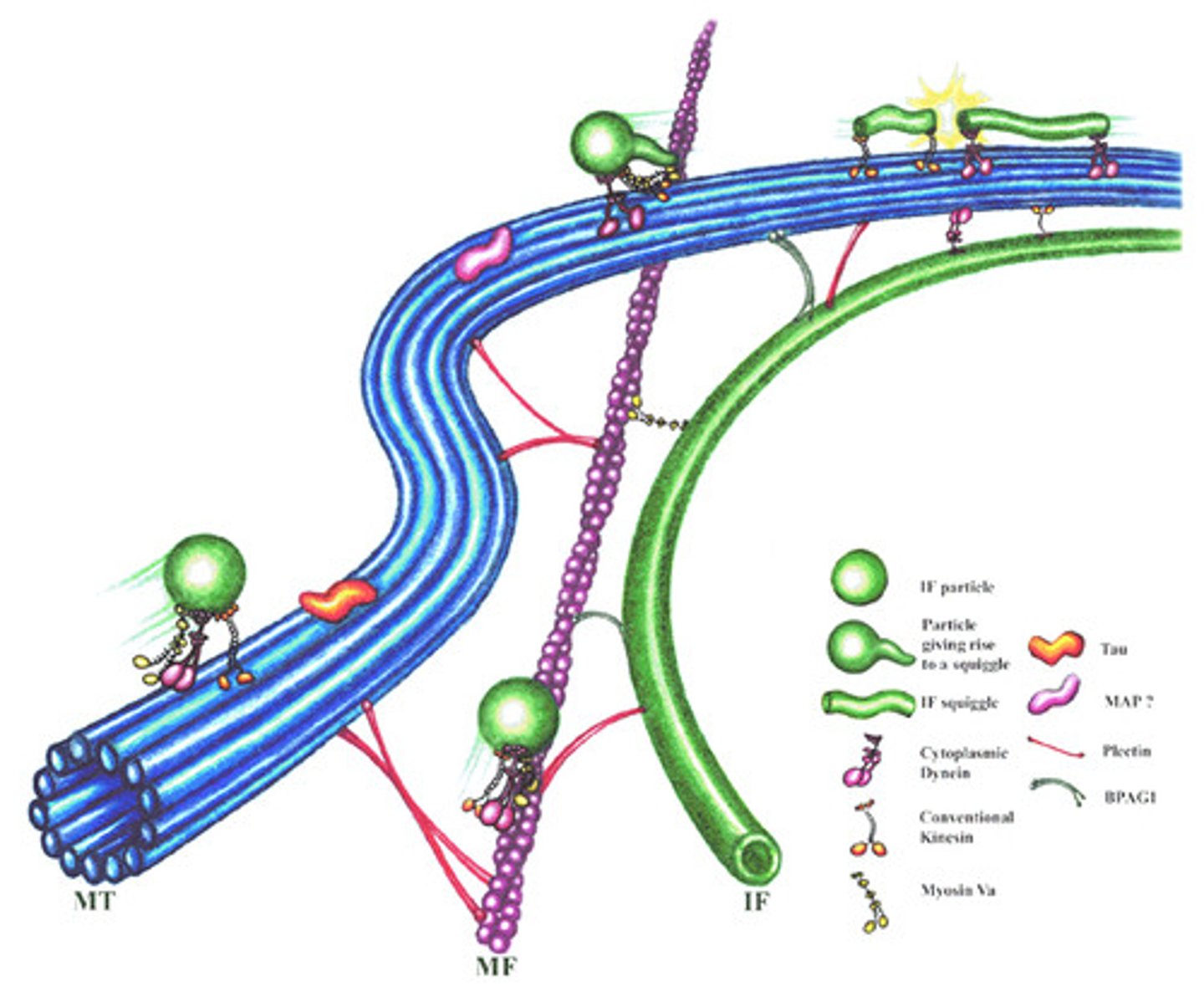
Microtubules
Thick cytoskeletal filaments made of tubulin for transport.
Intermediate Filaments
Fibers and fibrous proteins offer mechanical and structural support within cells, ensuring stability. Cytoskeletal components 8-12 nm in diameter.
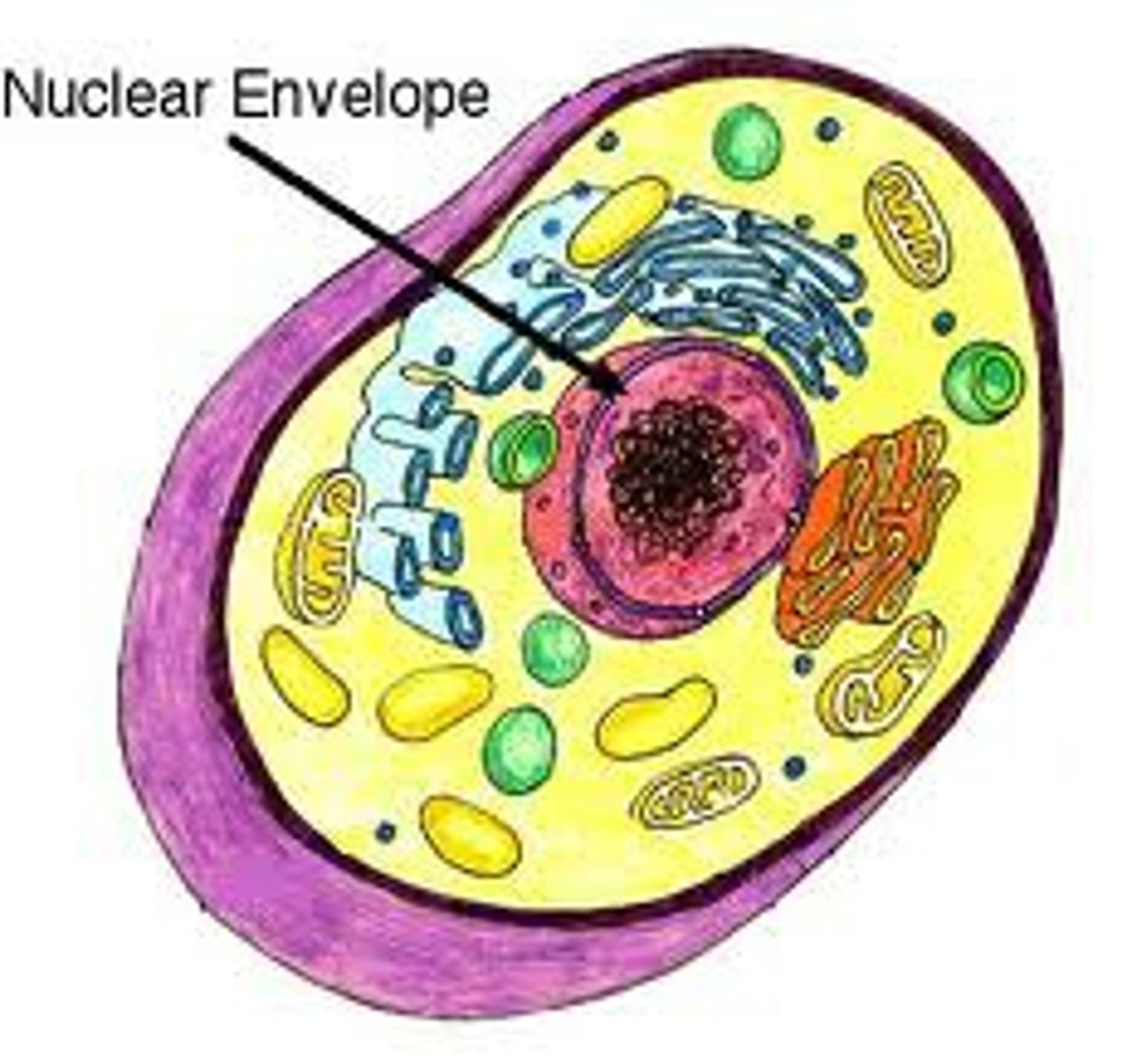
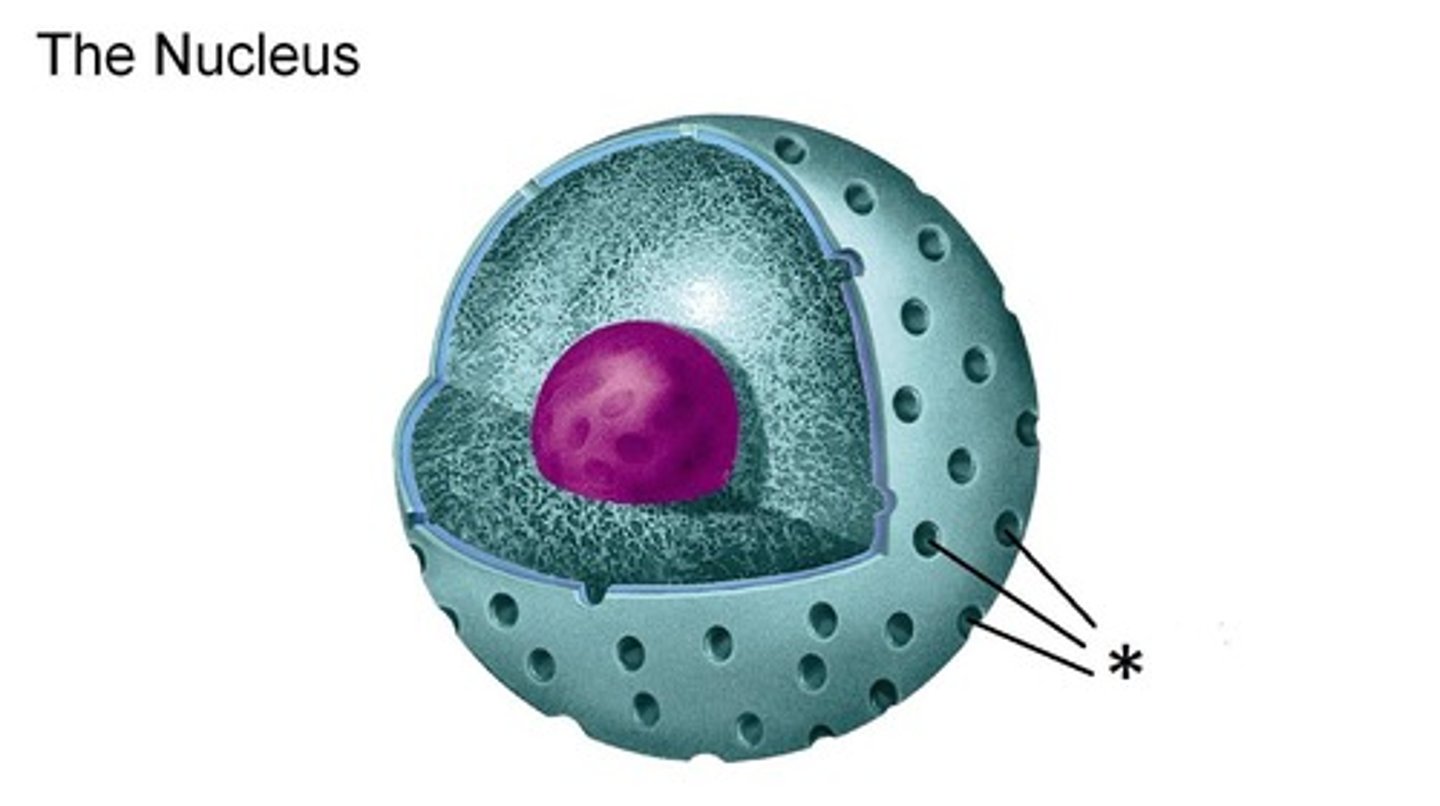
Nuclear envelope
Double membrane separating nucleus from cytoplasm.
Nuclear pores
Perforations allowing transport between nucleus and cytoplasm.
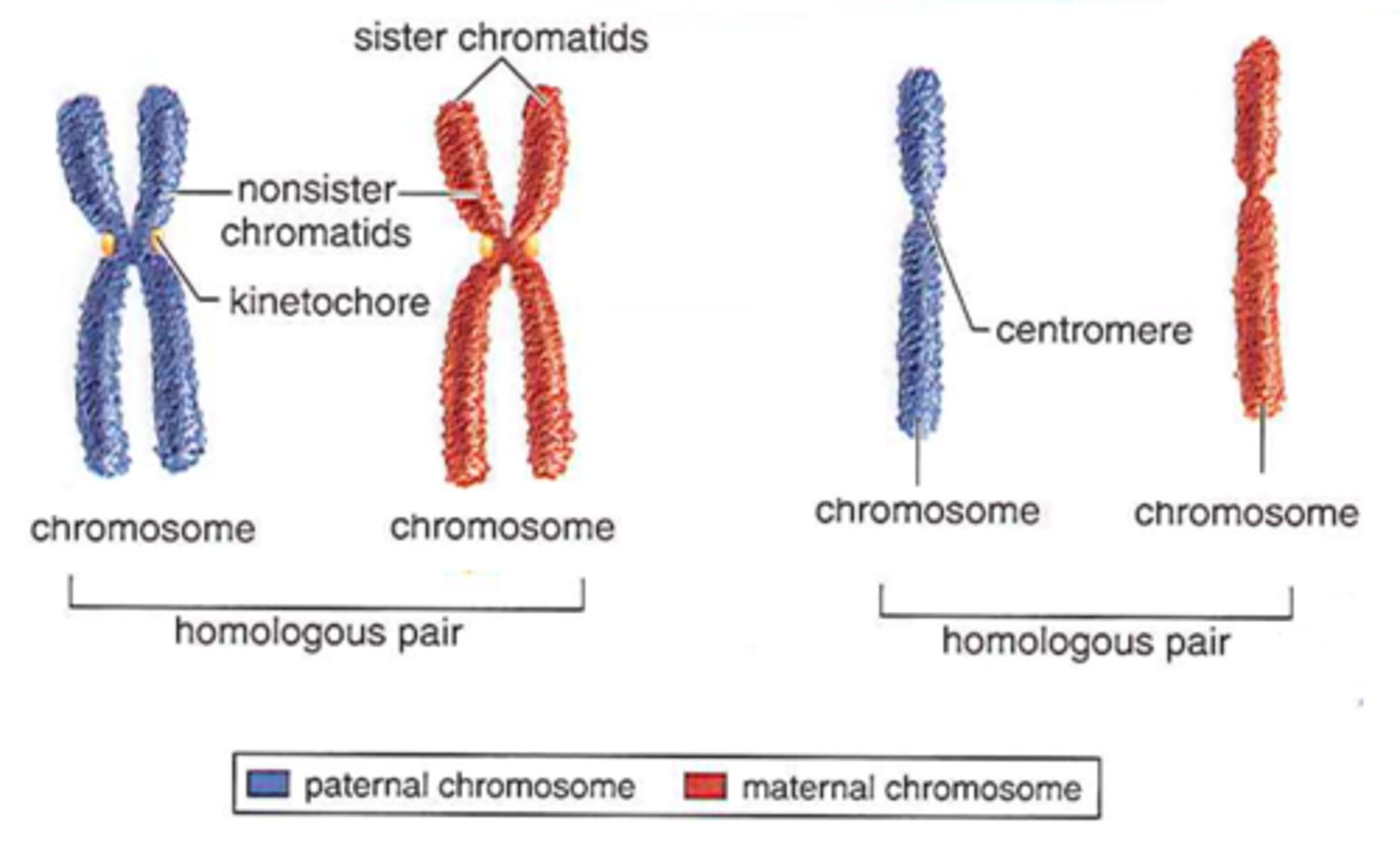
Chromosomes
Discrete units of DNA carrying genetic information.
Free ribosomes
Ribosomes synthesizing proteins for cytosol function.
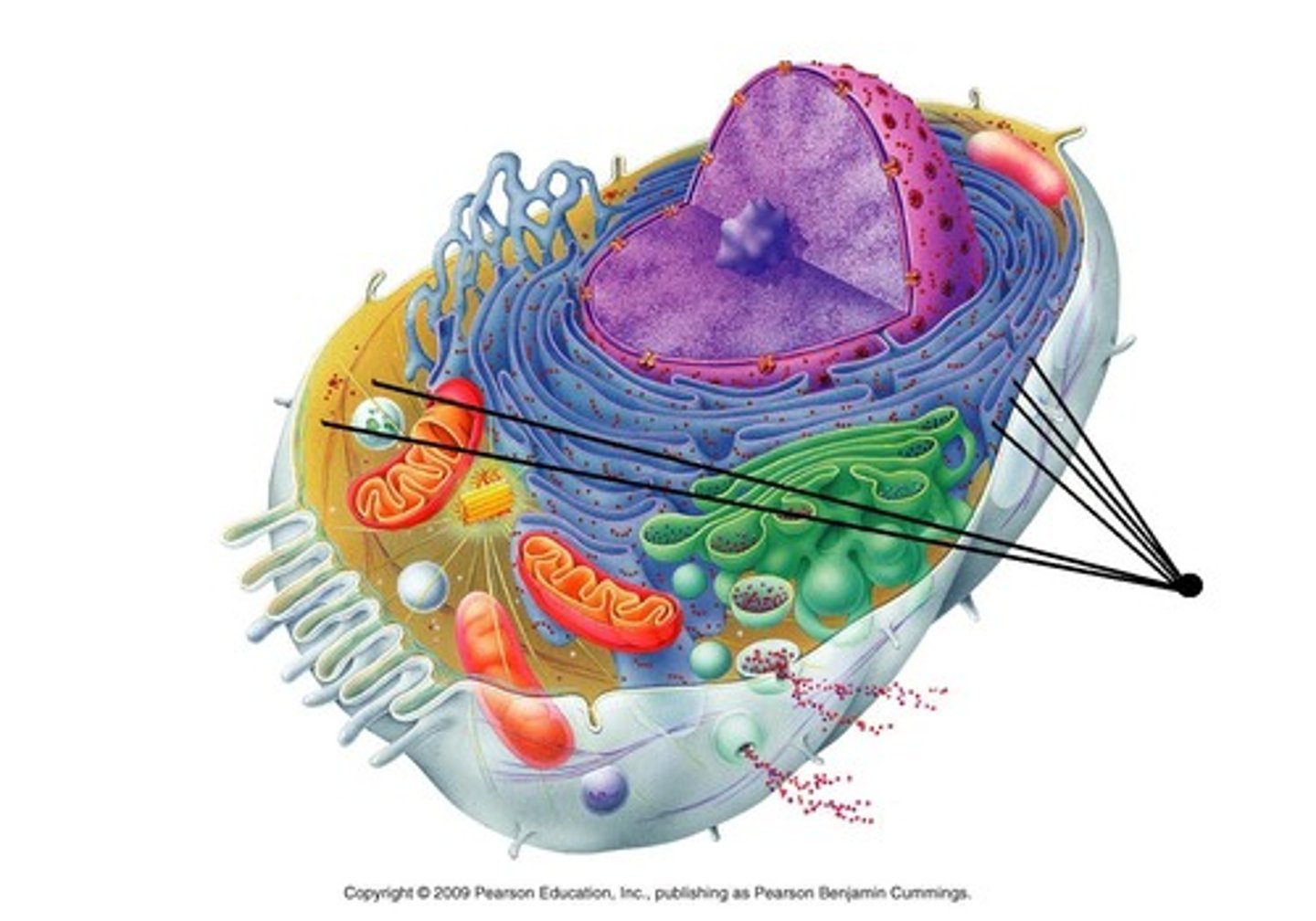
Bound ribosomes
Ribosomes attached to endoplasmic reticulum or nuclear envelope.
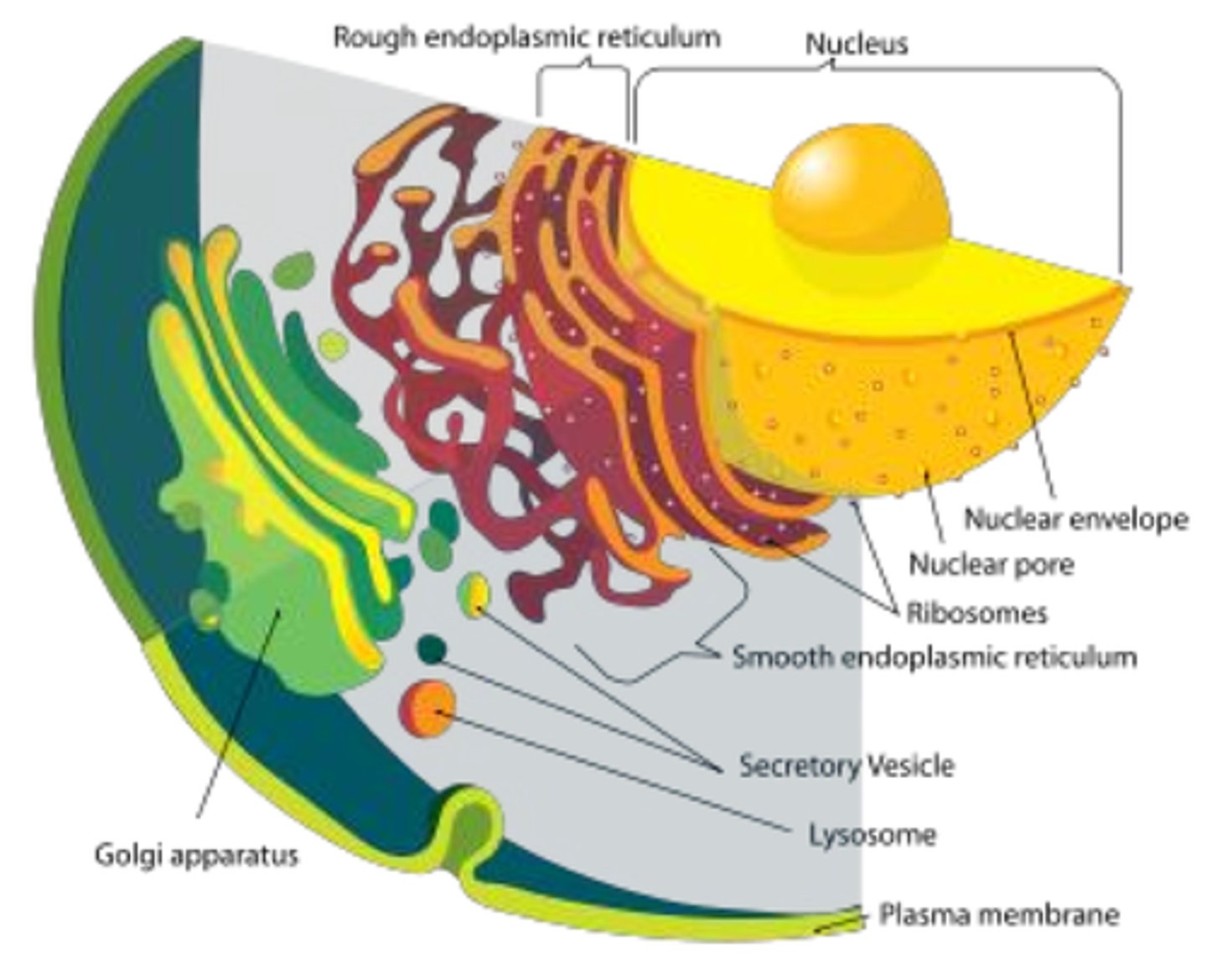
Endomembrane System
Network of membranes for protein synthesis and transport.
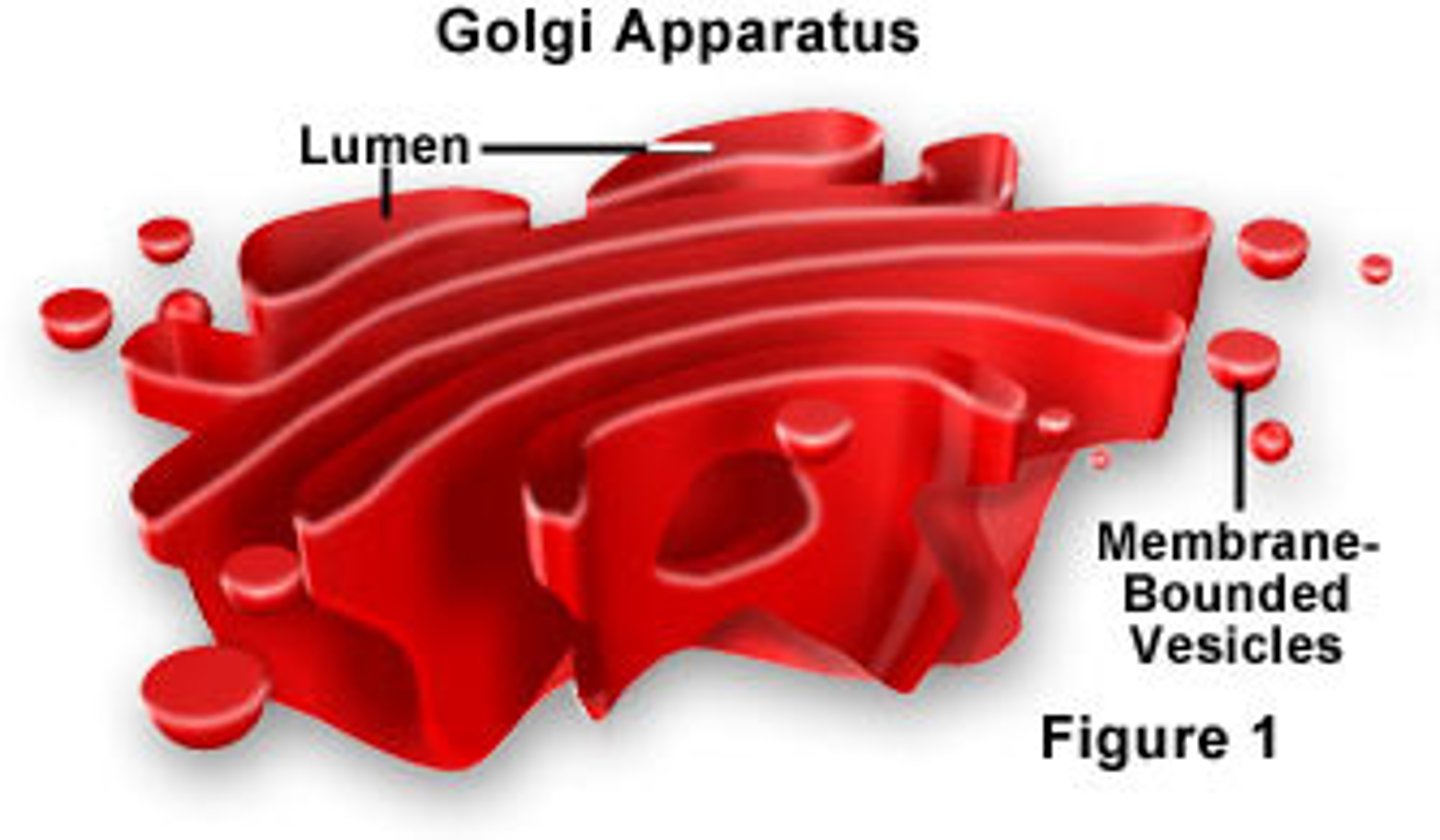
Golgi Apparatus
Center for manufacturing, sorting, and shipping proteins.
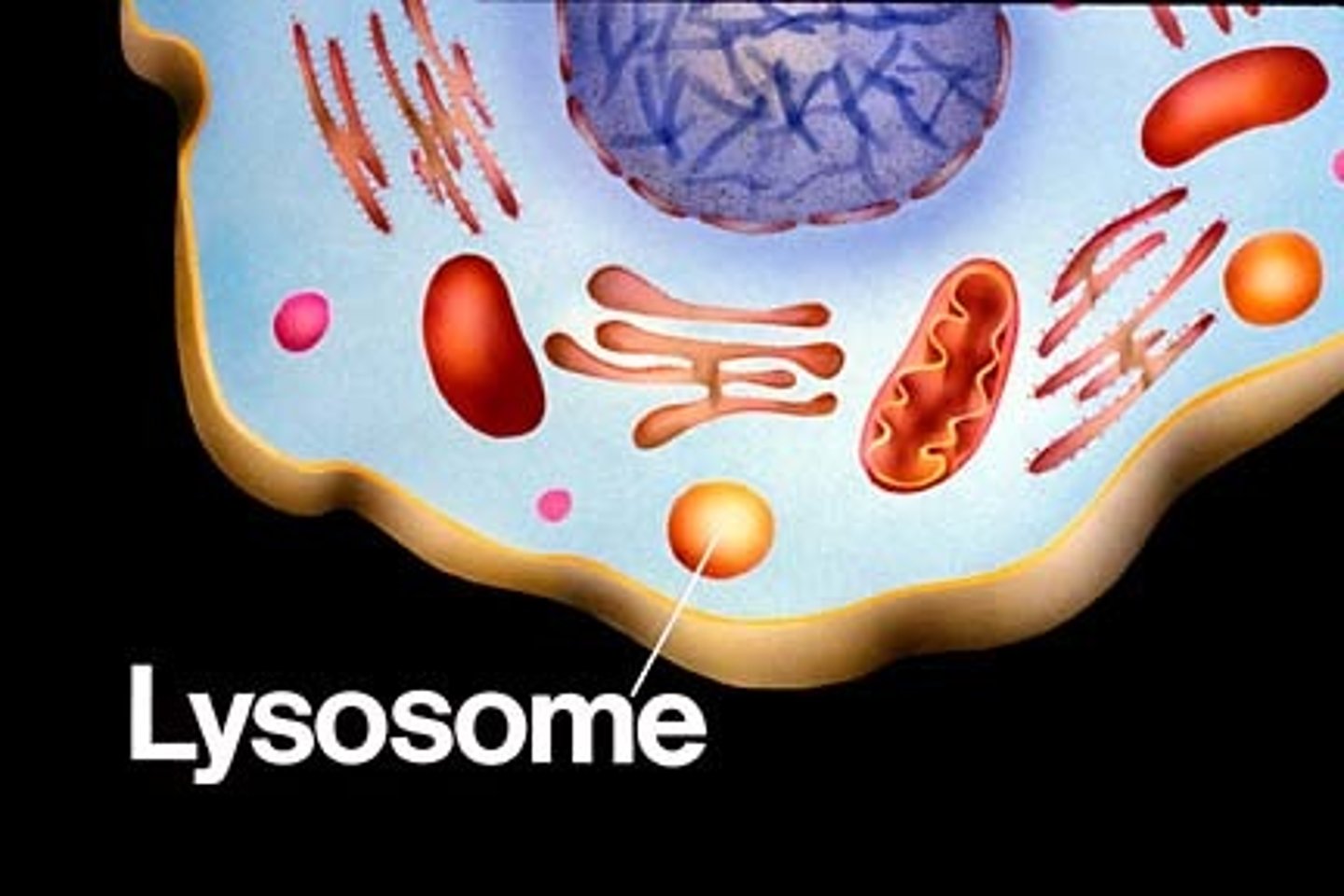
Lysosome
Intracellular organelle for digestion and waste processing.
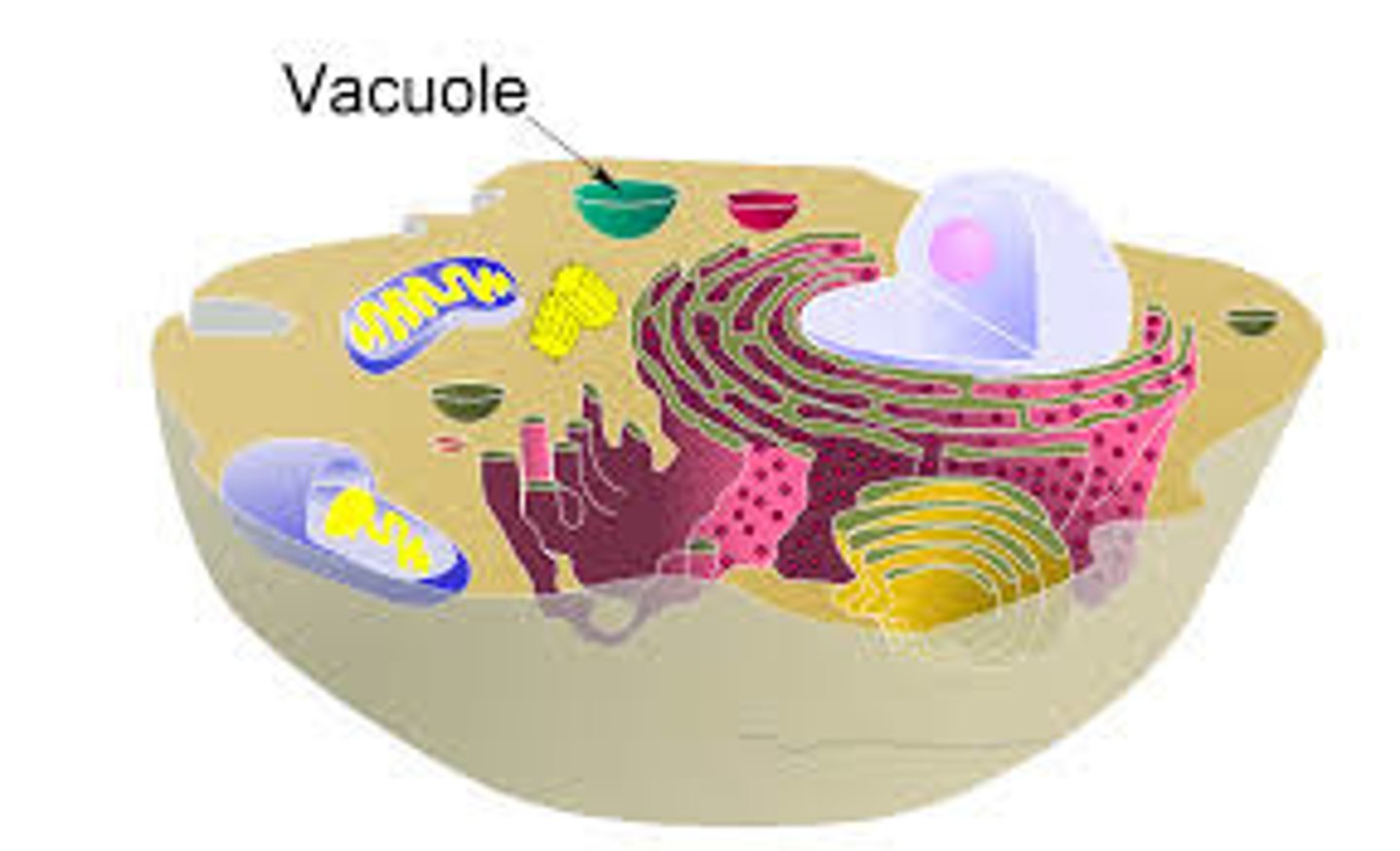
Vacuoles
Vesicles for storage organelles for nutrients and waste functions.
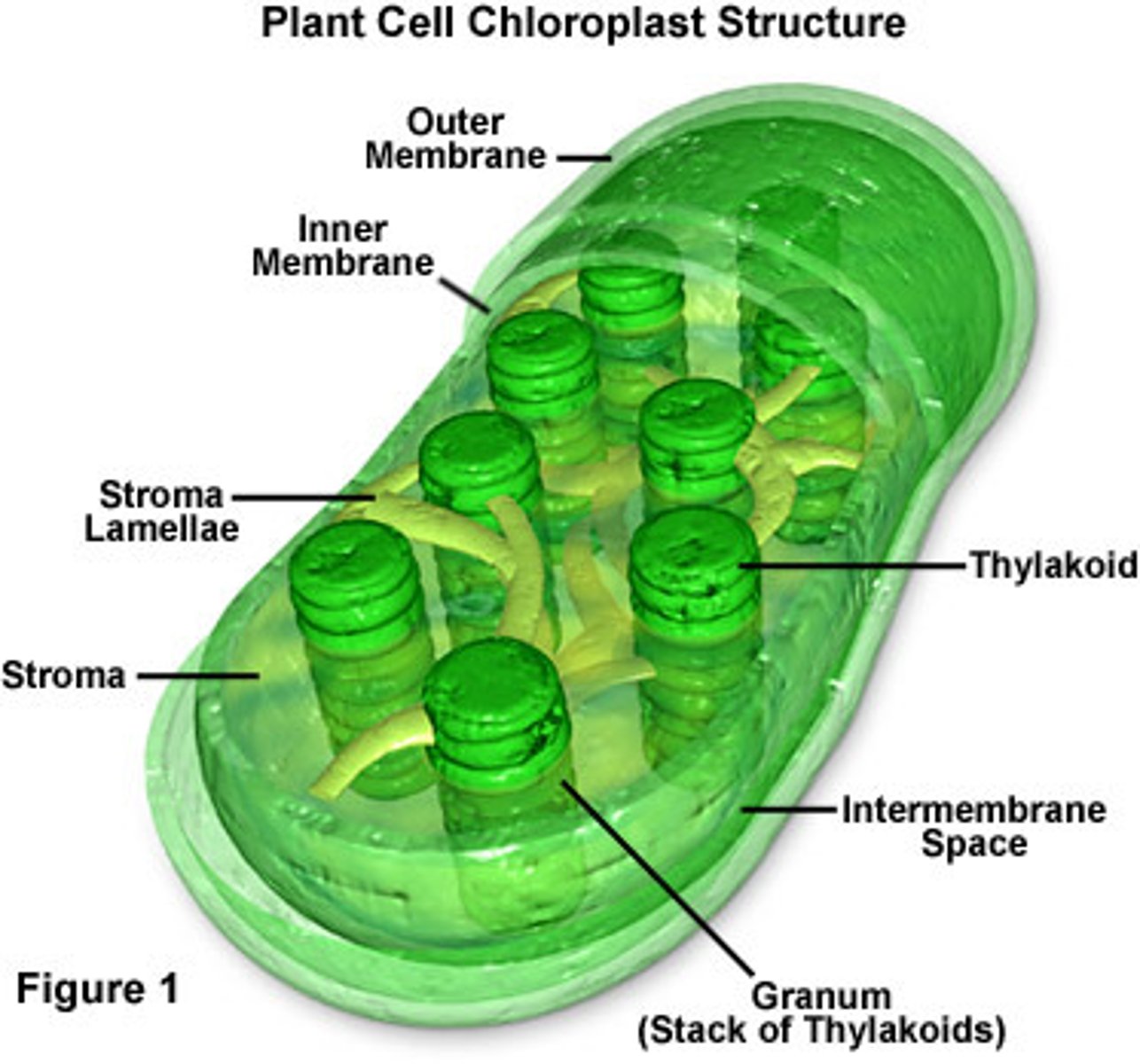
Chloroplasts
Sites of photosynthesis in plants and algae. Ranges from 3-6 µm.
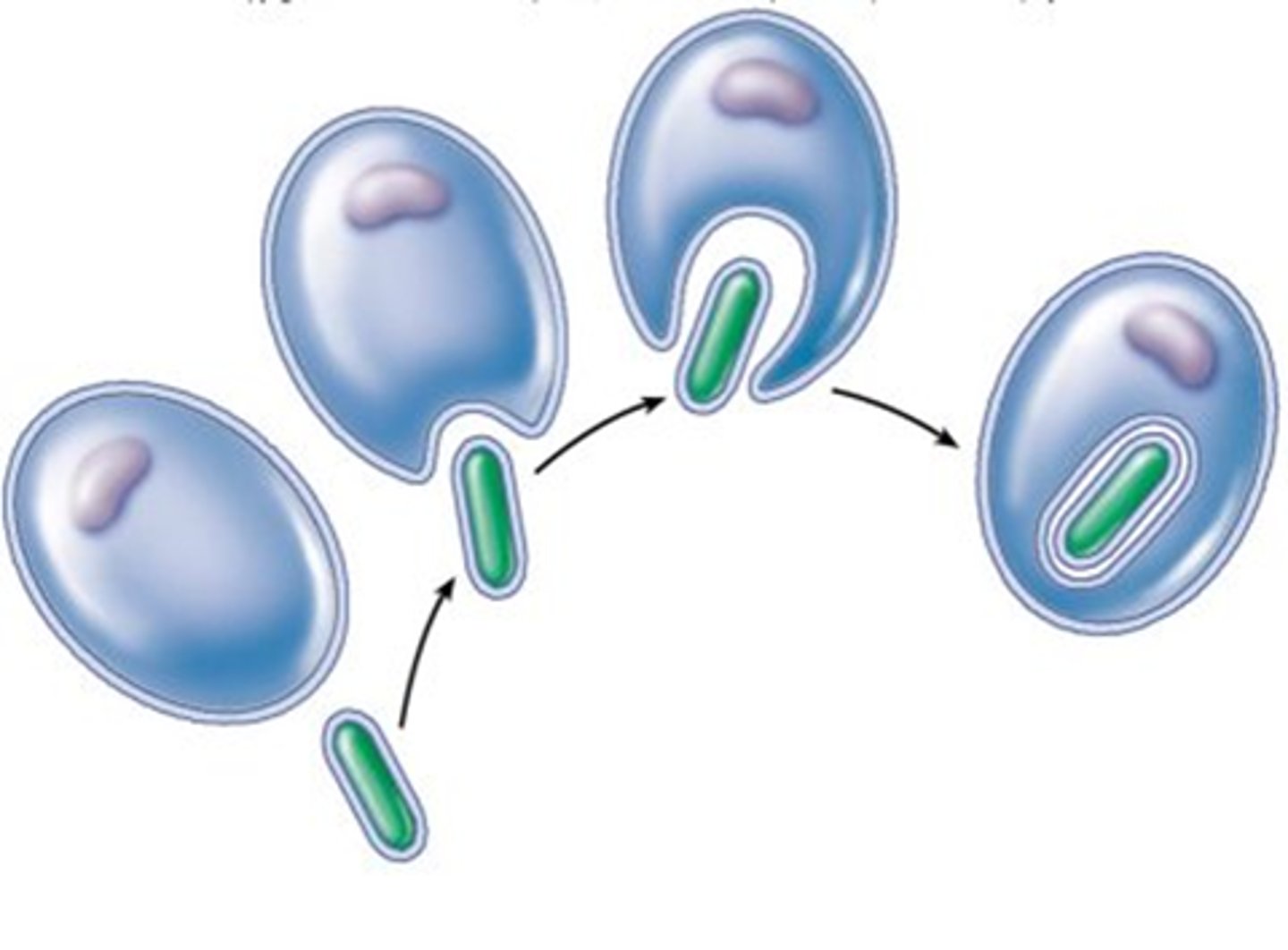
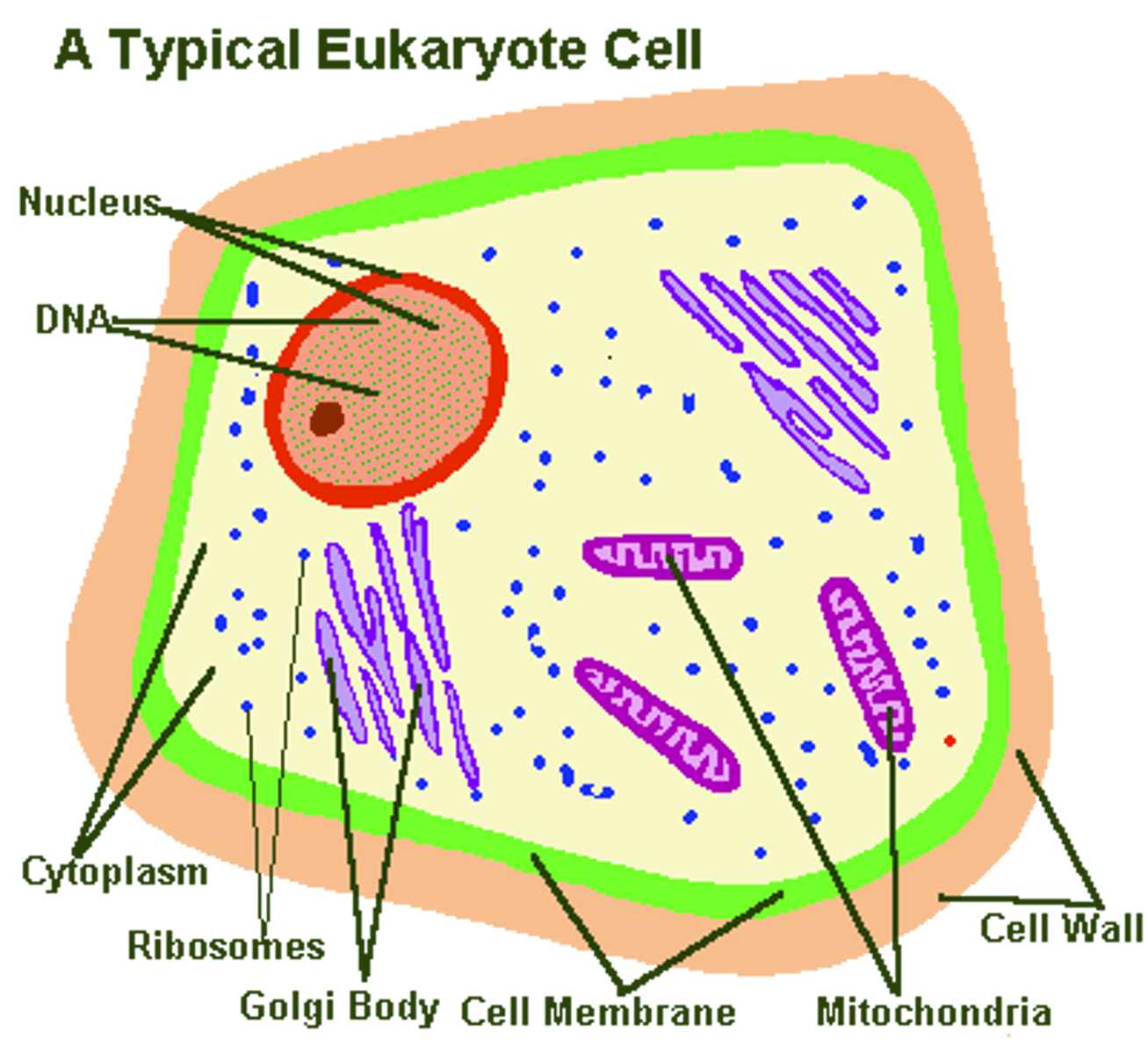
Eukaryotic cells
Cells that contain internal membrane-bound organelles, including mitochondria.
Cilia
Short extensions for cell movement, differing in motion.
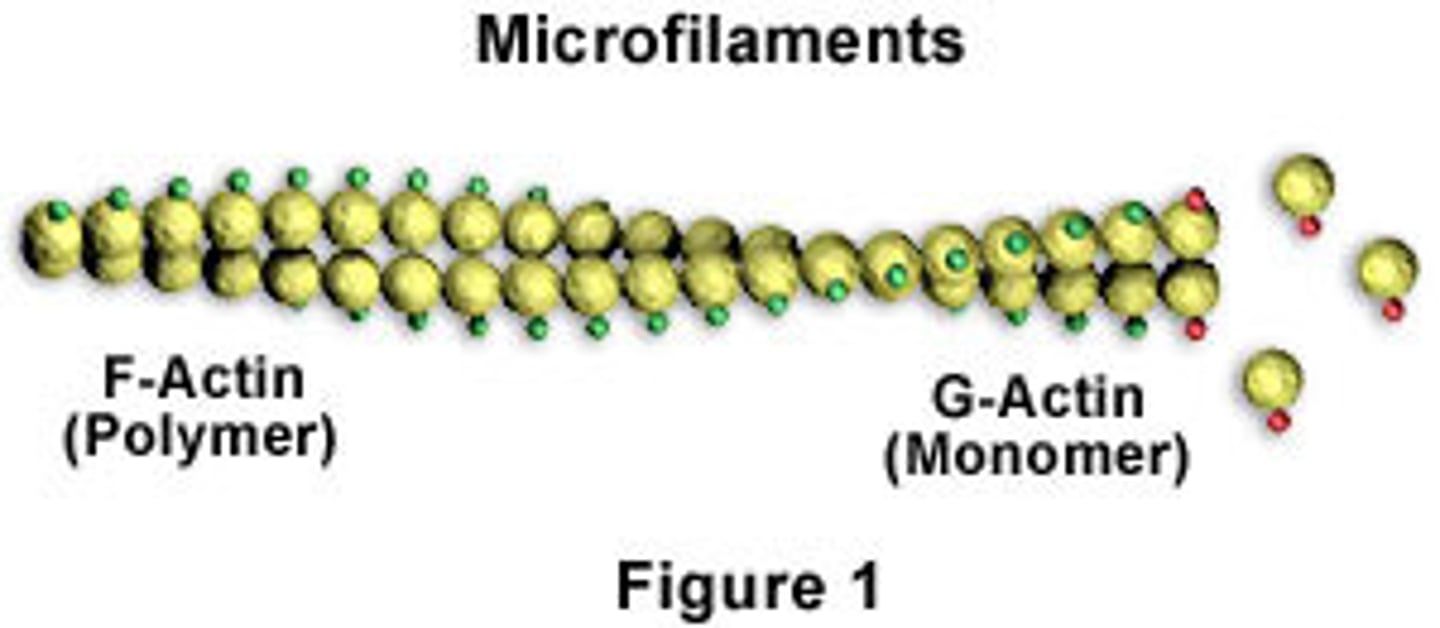
Microfilaments
Actin microfilaments aid cell movement, thinnest fibers.
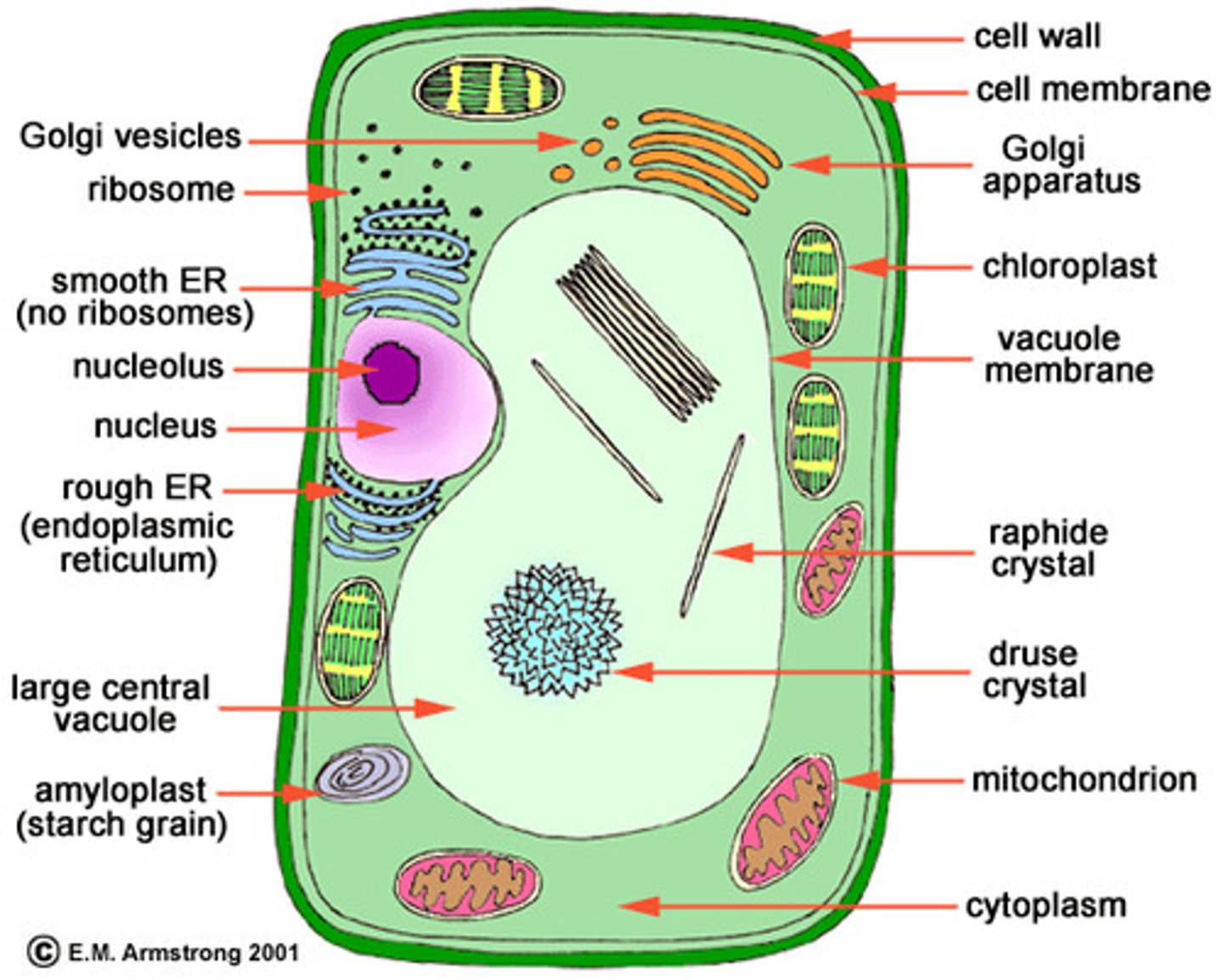
Cell Wall
rigid support for plants. Ranges from 0.1 µm to several micrometers
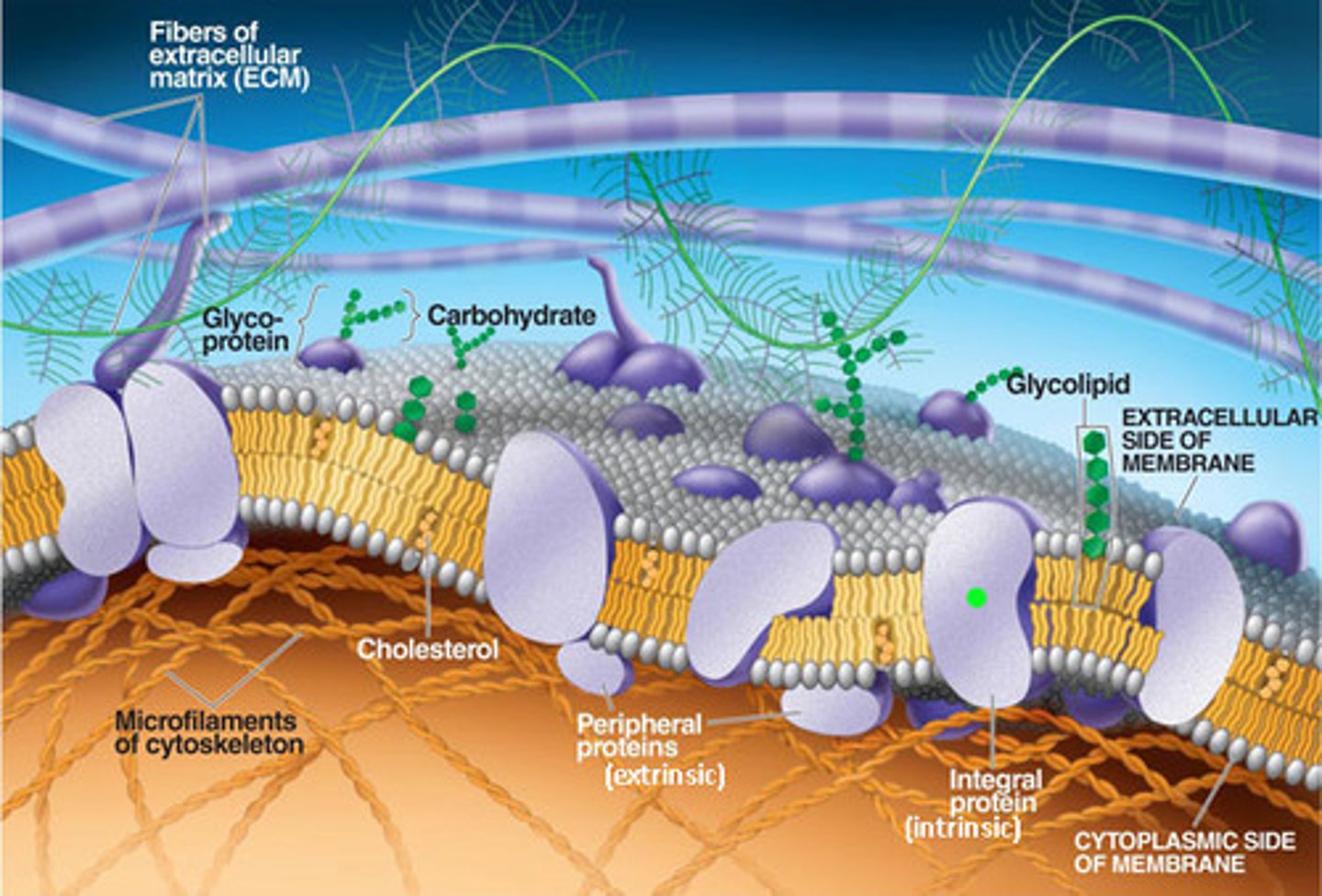
Extracellular Matrix (ECM)
Network of glycoproteins outside surrounding animal cells providing support and signaling.
Tight Junctions
Prevent leakage of extracellular fluid between cells.
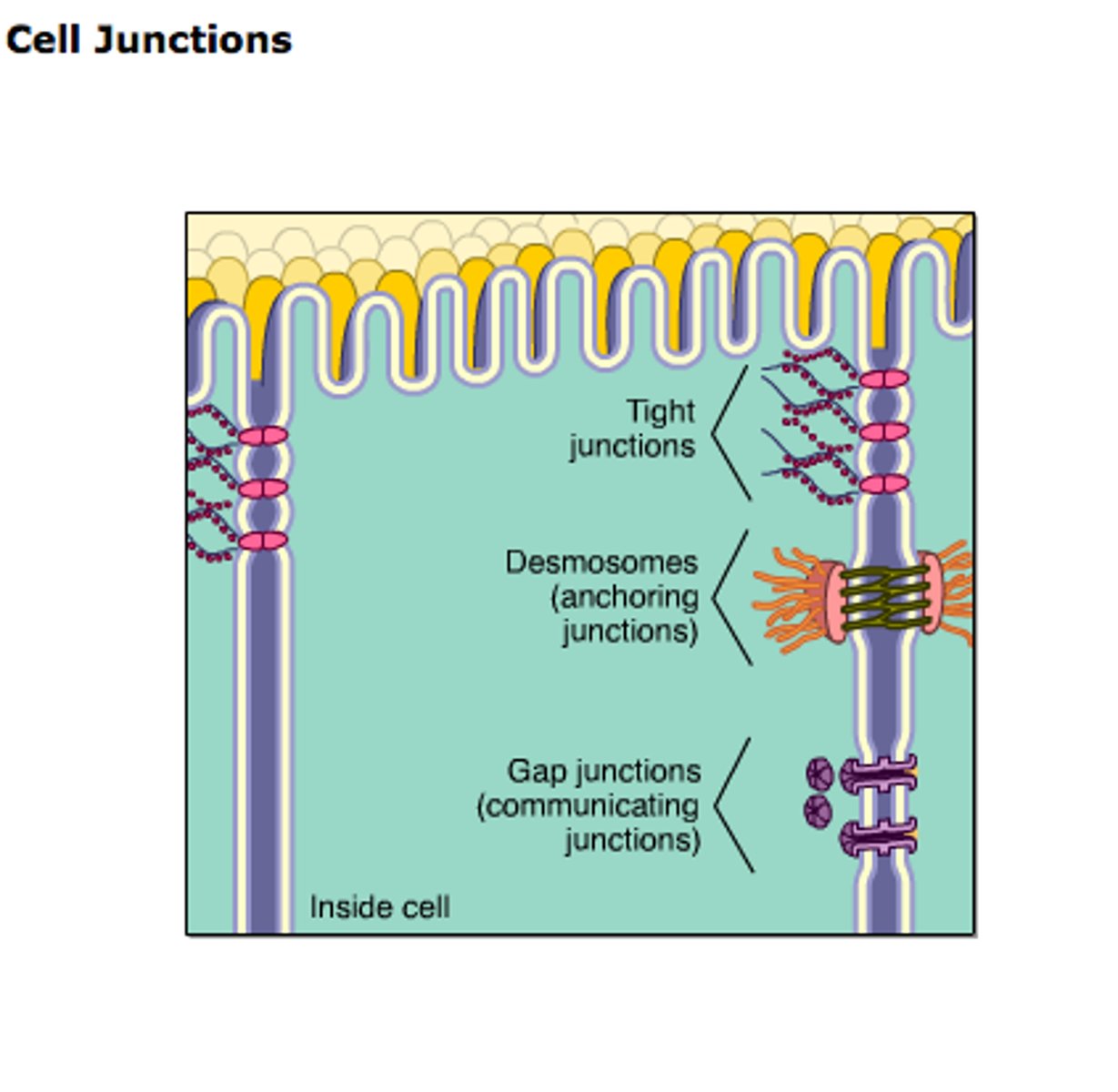
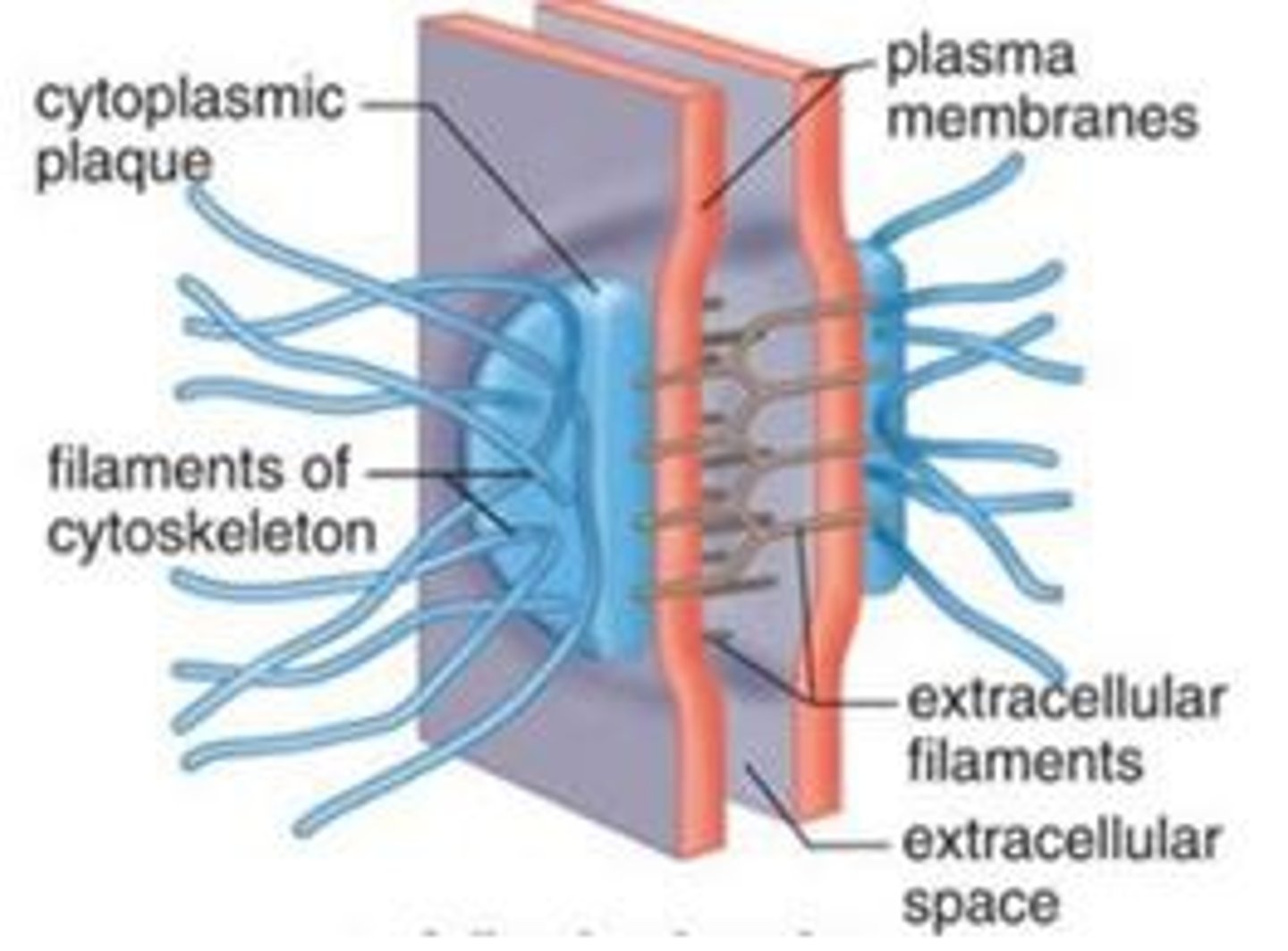
Desmosomes
Anchoring junctions fastening cells into strong sheets.
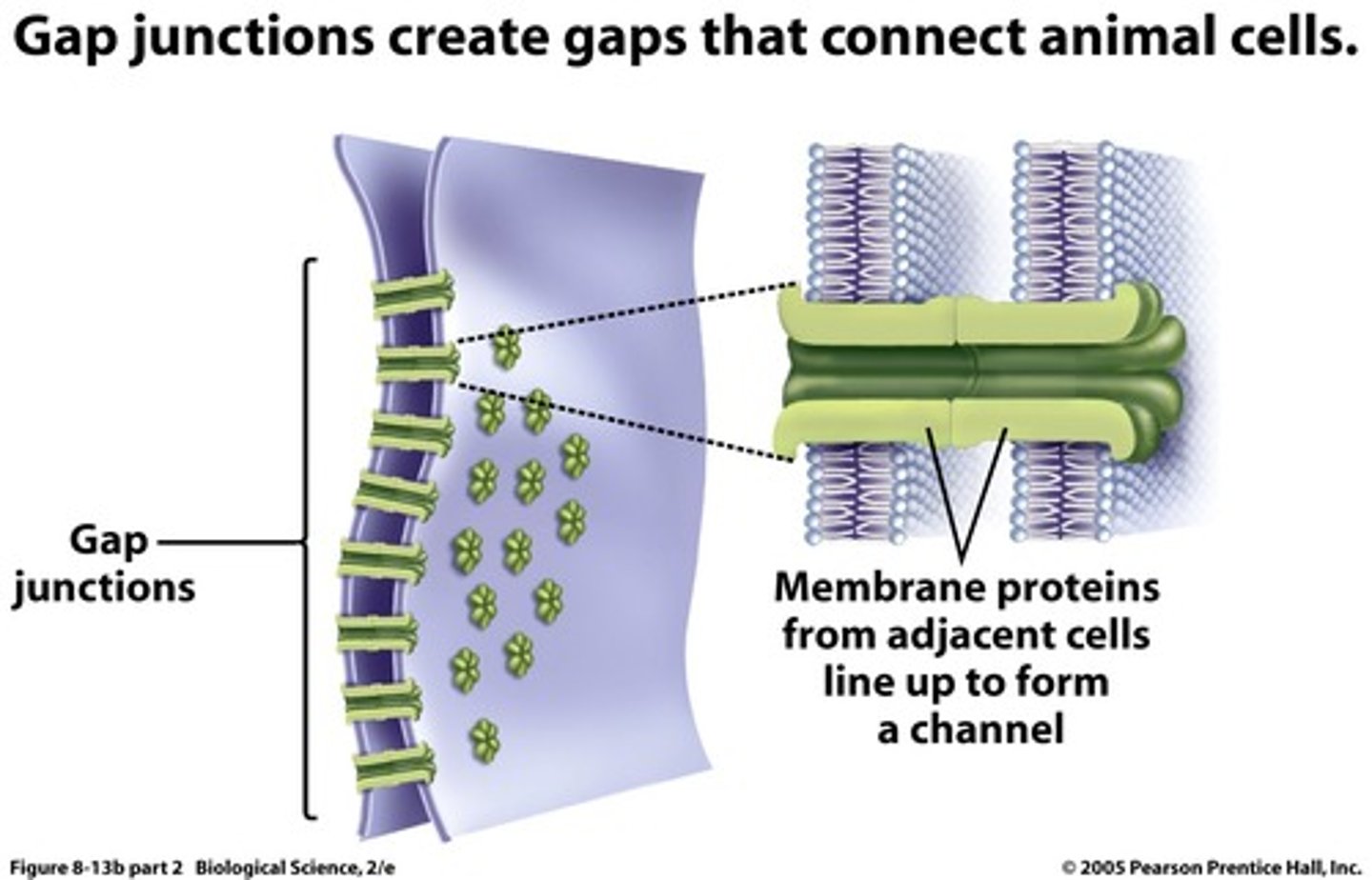
Gap Junctions
Cytoplasmic channels allowing communication between cells.
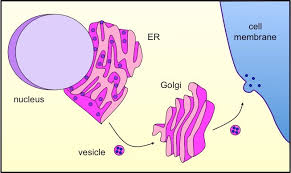
Transport Vesicles
Membrane-bound sacs that transport materials within cells, including proteins and lipids.
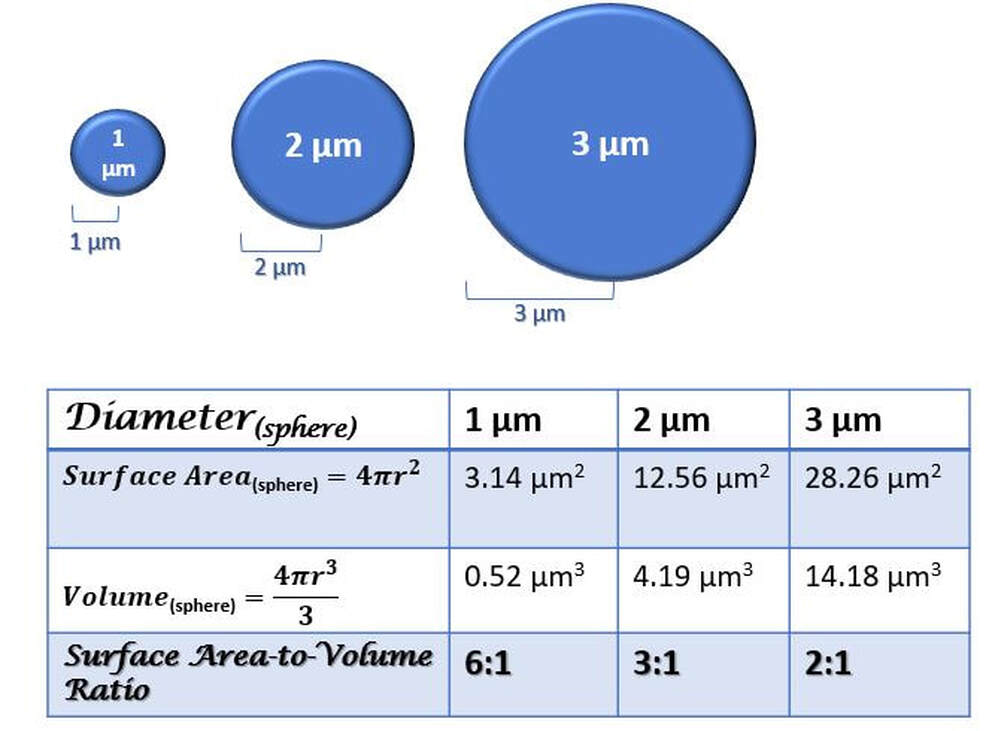
Surface area to volume ratio
Large vacuoles, smaller cells, efficient exchange.
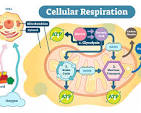
Cellular respiration
breaks down glucose for ATP energy, using oxygen and releasing carbon dioxide and water.
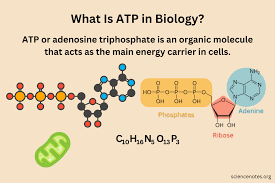
ATP
Energy currency of the cell.
Cytoplasm
Interior of prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells.