02 Electrification & Digital Technology
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
41 Terms
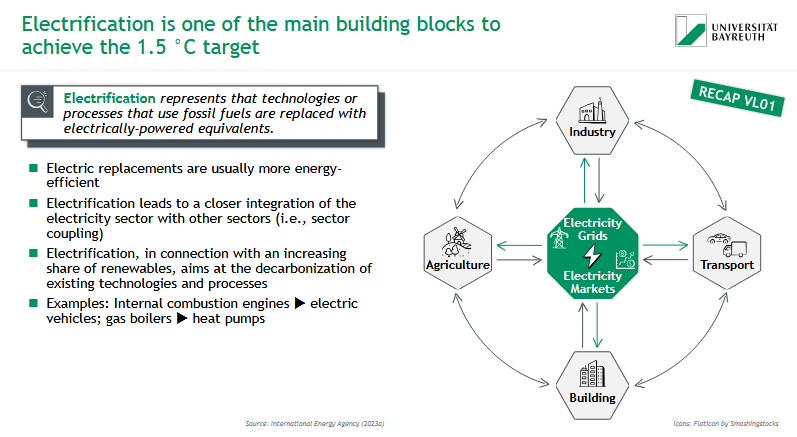
What is electrification & why is it one of the main building blocks to achieve the 1.5° target?
= technologies / processes that use fossil fuels are replaced with electrically-powered equivalents
more energy efficient
closer integration with other sectors
increase of renewables: decarbonization of existing technologies & processes
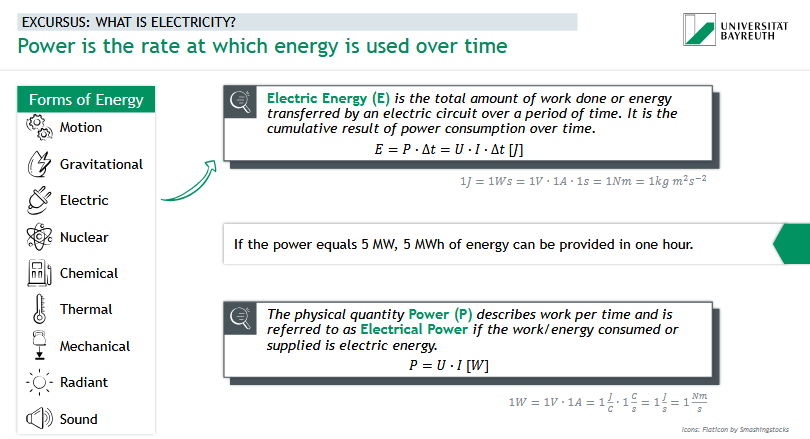
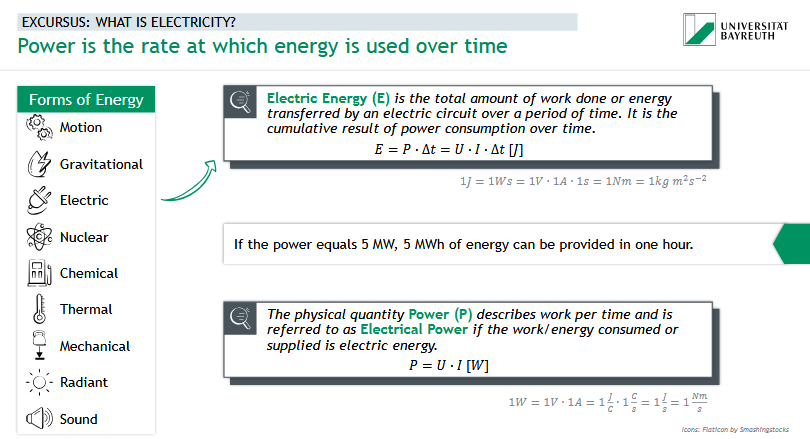
What is electricity?
electric energy
= total amount of work done / energy transferred by an electric circuit over a period of time
= cumulative resuls of power consumption over time
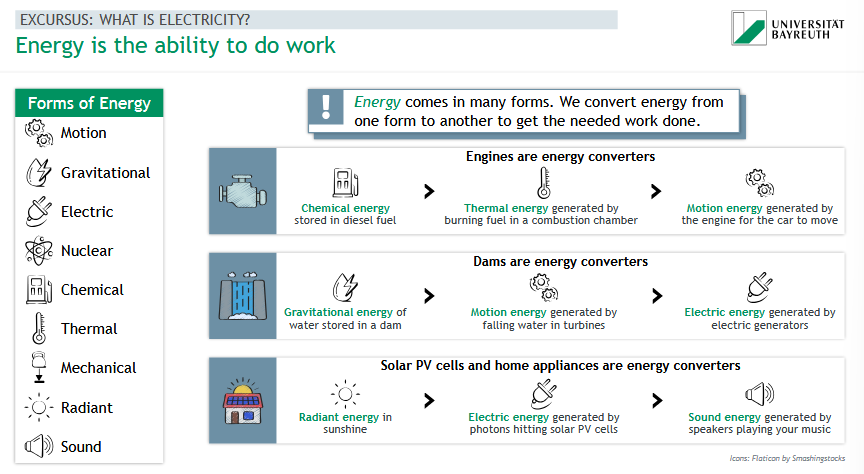
What are the 9 different forms of energy?
motion
gravitational
electric
nuclear
chemical
thermal
mechanical
readiant
sound
What is Electrical Power?
= work per time (physical quantity Power = P), electrical power if the work/energy consumed or supplied is electric energy
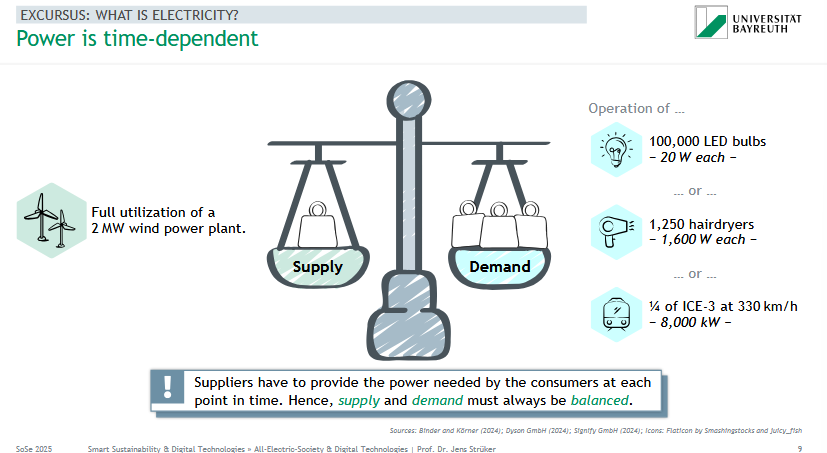
Why must electricity supply and demand always be balanced in real time?
⚡ Power is time-dependent:
Supply must exactly match demand at every moment.
🟩 Example:
A 2 MW wind turbine can power:
💡 100,000 LED bulbs (20 W each)
💨 1,250 hairdryers (1,600 W each)
🚅 ¼ of an ICE-3 train at 330 km/h (8,000 kW)
📌 If supply ≠ demand → grid instability
Balance = essential for reliable power systems
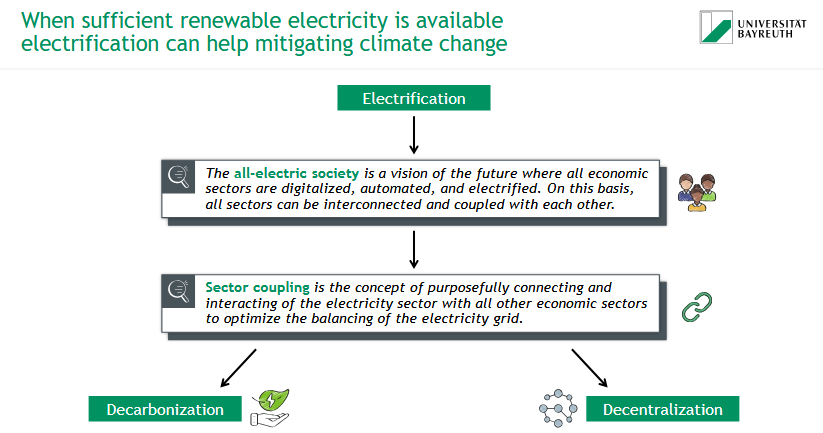
How can electrification help mitigate climate change?
all-electric society = vision of the future: all sectors digitalized, automated & electrified, interconnected & coupled
→ leads to decarbonization & decentralization
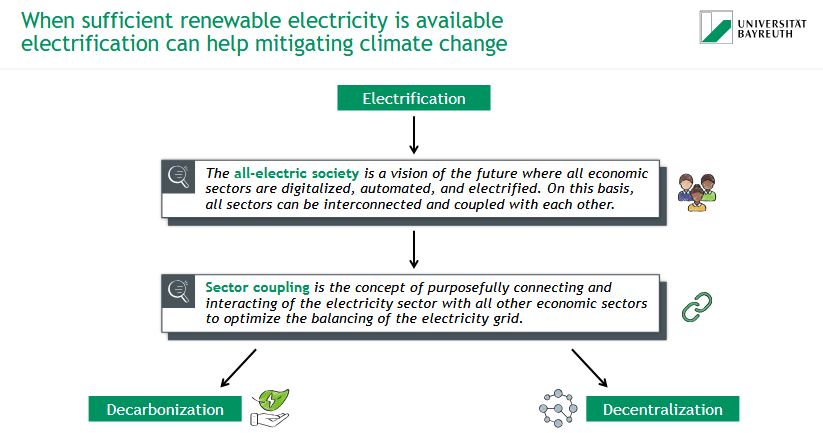
What is sector coupling?
= concept of purposefully connecting & interacting of electricity sector with all other economic sectors to optimize the balancing of the electricity grid
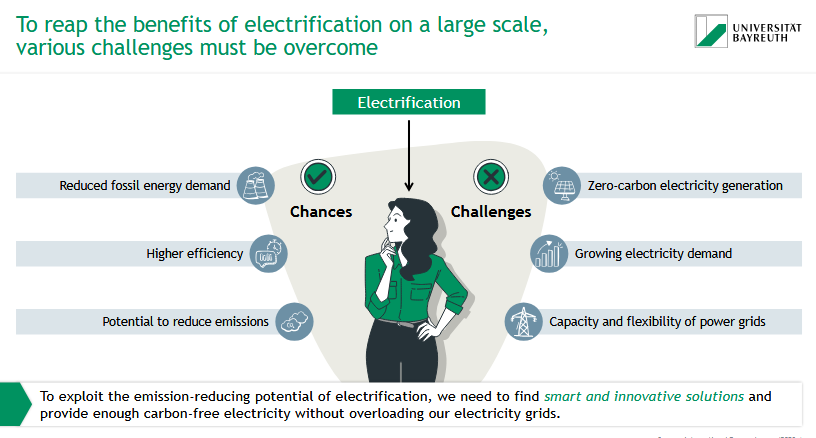
What are chances & challenges of electrification?
chances:
reduced fossil energy demand
higher efficiency
potential to reduce emissions
challenges:
zero-carbon electricity generation
growing electricity demand
capacity & flexibility of power grids
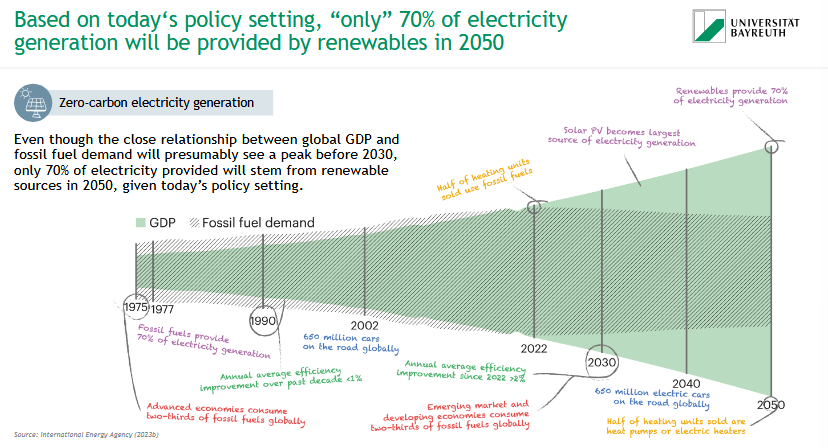
What share of electricity will come from renewables by 2050 under current policies?
🔋 Under today's policy setting, only ~70% of electricity will be renewable by 2050.
📉 Fossil fuel demand will peak before 2030, but remains significant:
1975–2022: strong link between GDP & fossil fuel use
2030: 650 million EVs & more heat pumps
2050: Solar PV = top energy source, but fossil fuels still used
📌 Efficiency gains help, but policy ambition must rise to fully decarbonize.
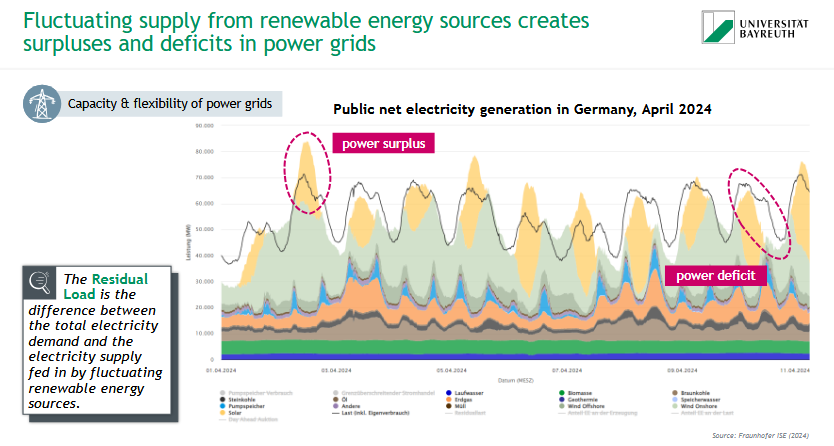
What is the residual load?
= difference between total electricity demand & electricity supply fed in by fluctuating renewable energy sources
→ fluctuating supply from renewable energy sources creates surpluses & deficits in power grids
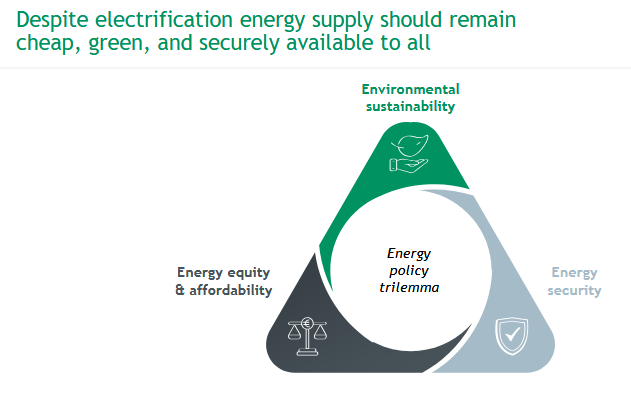
What is the energy policy trilemma?
environmental sustainability vs. energy security vs. energy equity & affordability
→ despite electrification energy supply should remain cheap, green, and securely available to all
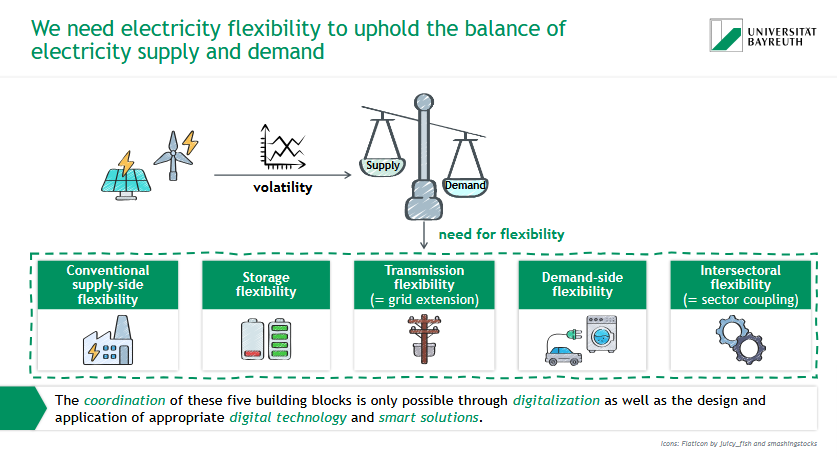
Why is electricity flexibility essential, and what are its main types?
⚖ Flexibility balances fluctuating supply & demand in the power grid — critical with rising renewables.
5 Flexibility Types:
Conventional supply-side
Storage (e.g. batteries)
Transmission (grid expansion)
Demand-side (e.g. smart appliances)
Intersectoral (sector coupling)
💡 Coordination needs digital tech & smart solutions
What are smart solutions? What is smart?
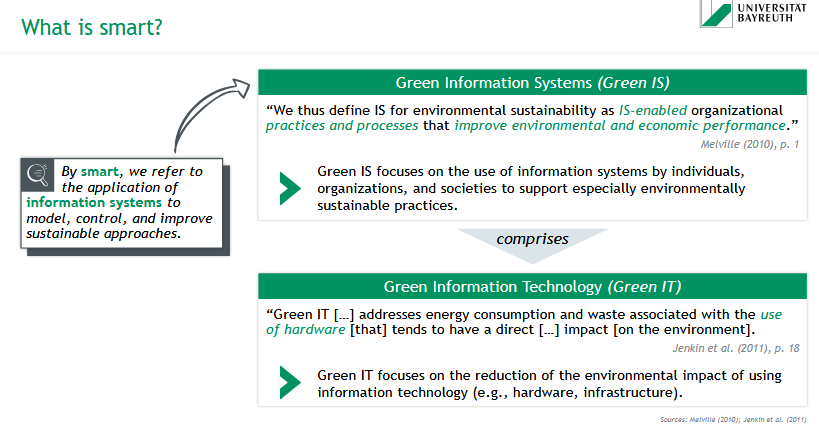
= the application of information systems to model, control, and improve sustainable approaches
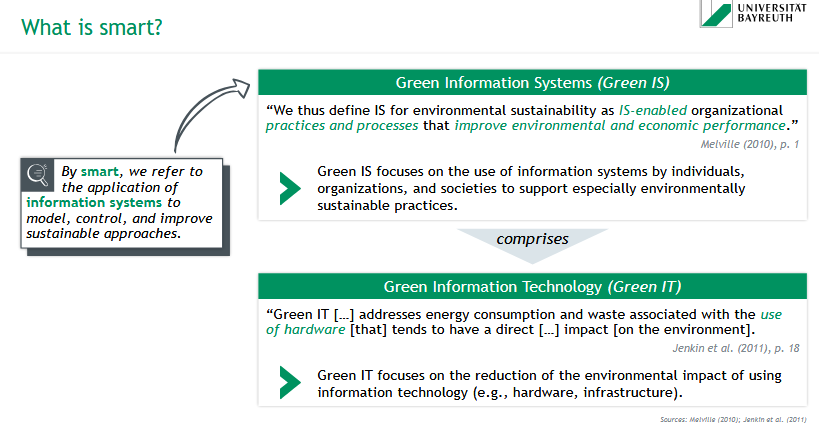
What are Green Information Systems (Green IS)?
Green IS = IS-enabled organizational practices and processes that improve environmental an economic performance
→ focuses on the use of information systems by individuals, organizations, and societies to support especially environmentally sustainable practices
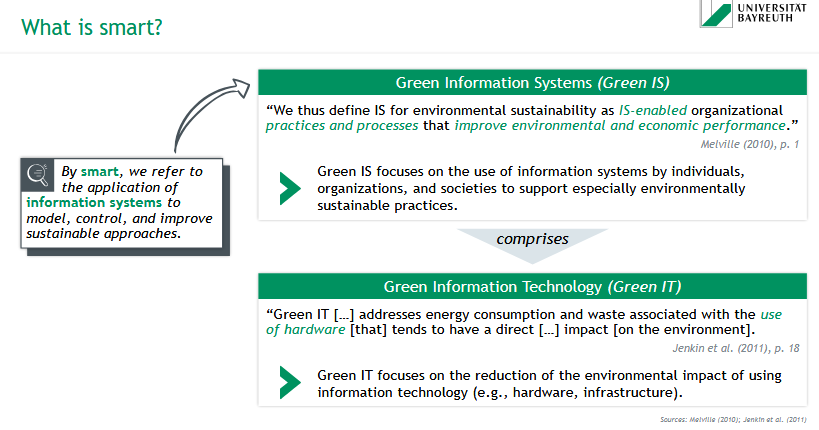
What is Green Information Technology (Green IT)?
Green IT addresses energy consumption & waste associated with the use of hardware that tends to have a direct impact on the environment
→ focuses on the reduction of the environmental impact of using information technology (e.g. hardware, infrastructure)
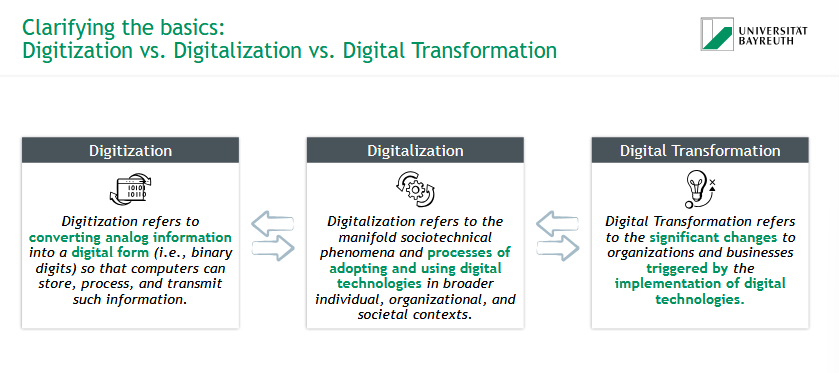
What is Digitization?
= converting analog information into a digital form so that computers can store, process, and transmit such information
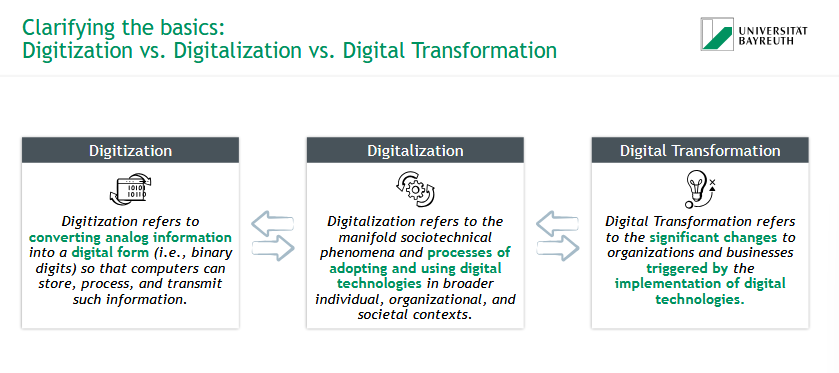
What is Digitalization?
= sociotechnical phenomena & processes of adopting & using digital technologies in broader individual, organizational, and societal contexts
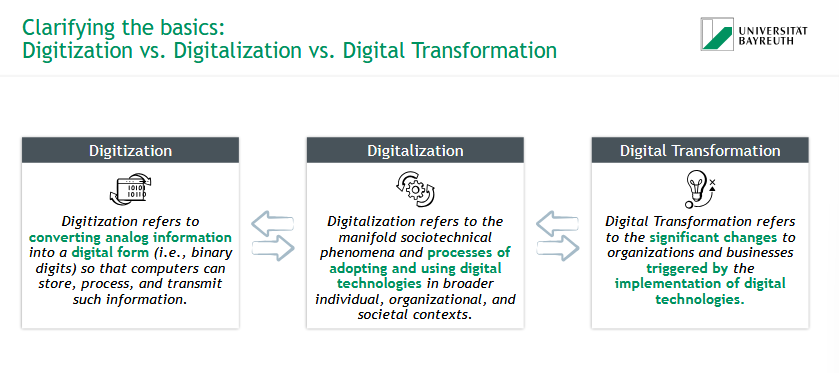
What is Digital Transformation?
= significant changes to organizations and businesses triggered by the implementation of digital technologies
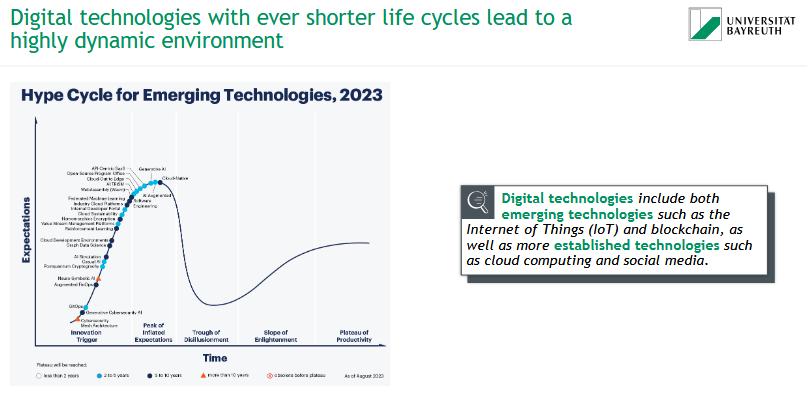
What characterizes digital technologies in today’s dynamic environment?
📈 Digital technologies have short life cycles and evolve rapidly.
They include:
🔄 Emerging tech: IoT, Blockchain, AI, etc.
🌐 Established tech: Cloud computing, social media
🌀 Illustrated by the Hype Cycle:
From Innovation Trigger → Peak of Inflated Expectations → Trough of Disillusionment → Slope of Enlightenment → Productivity
⚠ Rapid change demands adaptability and ongoing innovation.
How is the adoption of digital technologies reshaping business models?
leads to change in business models
provides new revenues & value-producing opportunities
process of moving to a digital business

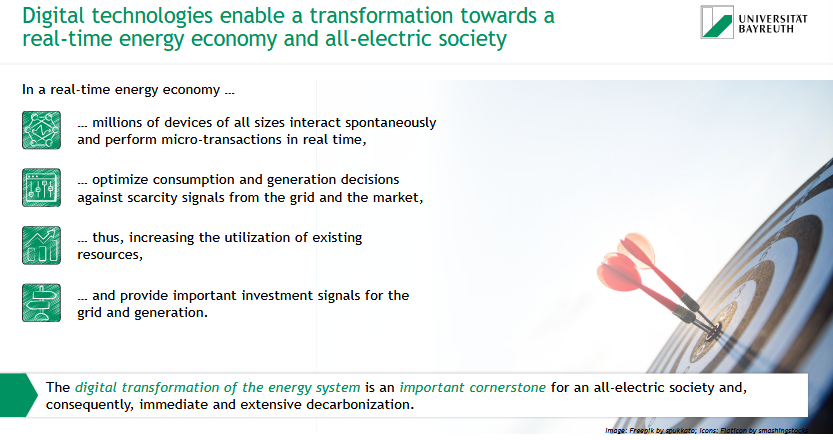
How do digital technologies enable a transformation towards a real-time energy economy and all-electric society?
💡 In a real-time energy economy, digital tech enables:
🔁 Millions of devices to interact & transact in real time
📊 Smart decisions on consumption & generation
🔧 Better use of existing resources
📈 Investment signals for grid & generation
✅ The digital transformation of energy is key for fast and deep decarbonization.
What is the Internet of Things (IoT)?
= networking everyday physical objects - equipped with sensors, actuators and computing logic - with the internet
→ enables new interactions between things, companies & individuals
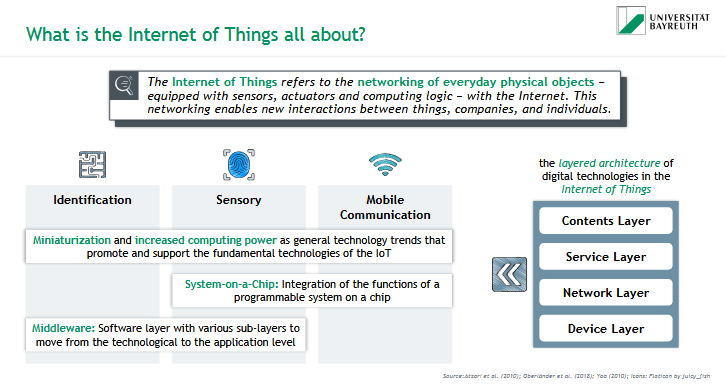
What are the 4 layers of the IoT architecture?
contents layer
service layer
network layer
device layer
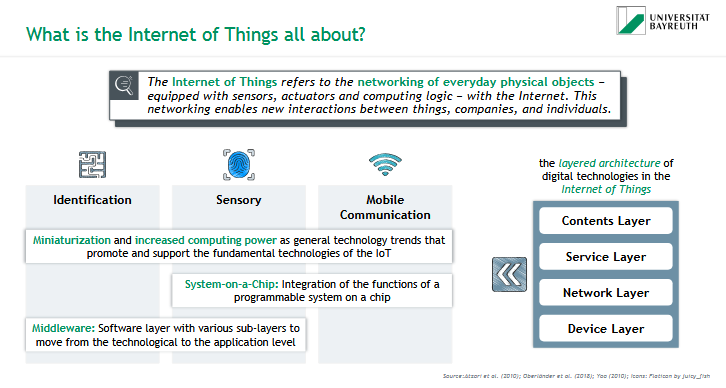
What is Artificial Intelligence and what are the different levels of AI?
= intelligent use of data and self-learning algorithms that mimic & simulate human behavior, decision-making and interactions. AI is therefore a toolbox of applications that were previously mostly performed by humans and not machines (e.g. specific predictions, decision-making, automation, optimization and solving complex tasks).
levels of AI:
weak AI
strong AI
Artificial Superintelligence
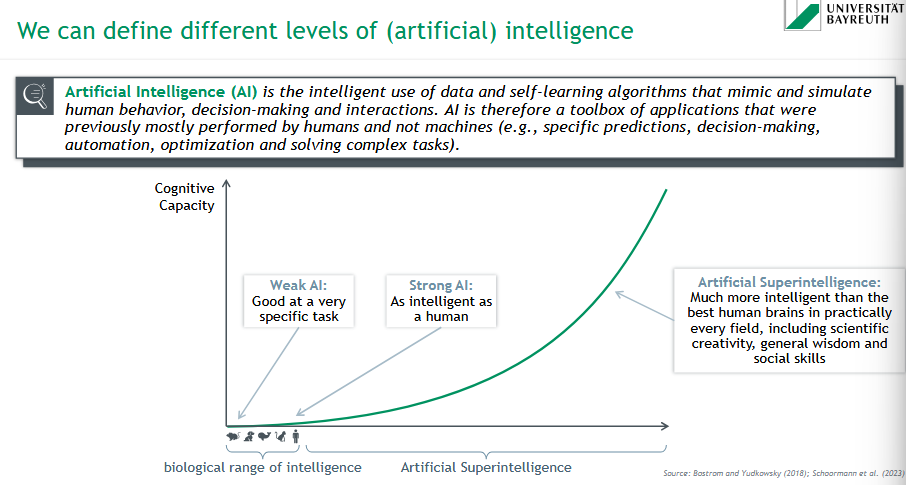
On which type of algorithms is AI based?
supervised learning = learning the mapping from input to output
unsupervised learning = recognizing previously unknown patterns in data
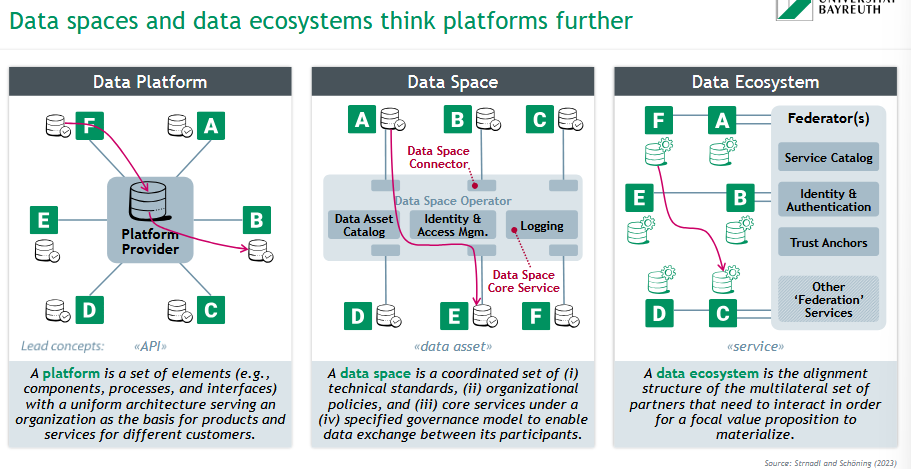
What is a data platform?
A platform is a set of elements (e.g., components, processes, and interfaces)
with a uniform architecture serving an organization as the basis for products and services for different customers.
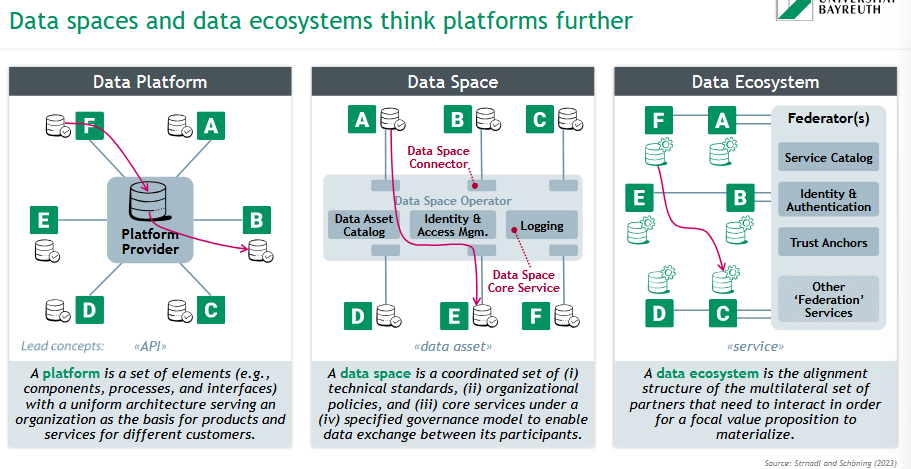
What is a data space?
A data space is a coordinated set of (i) technical standards, (ii) organizational
policies, and (iii) core services under a (iv) specified governance model to enable data exchange between its participants.
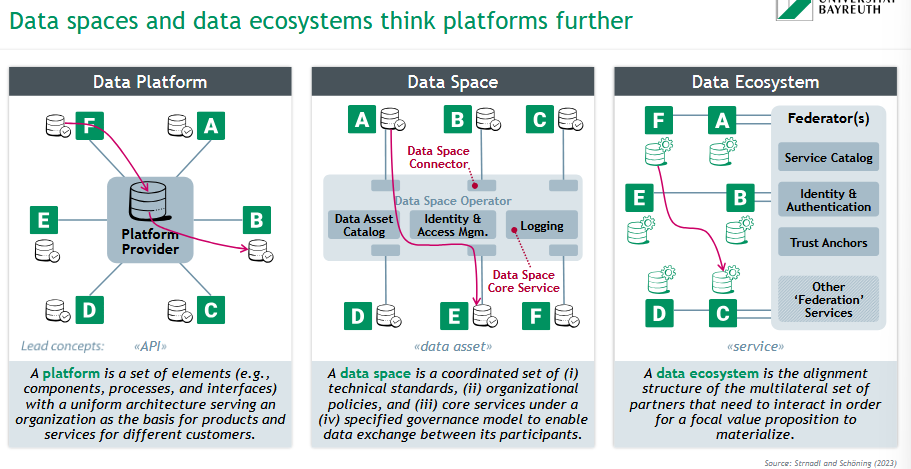
What is a data ecosystem?
A data ecosystem is the alignment structure of the multilateral set of partners that need to interact in order for a focal value proposition to materialize.
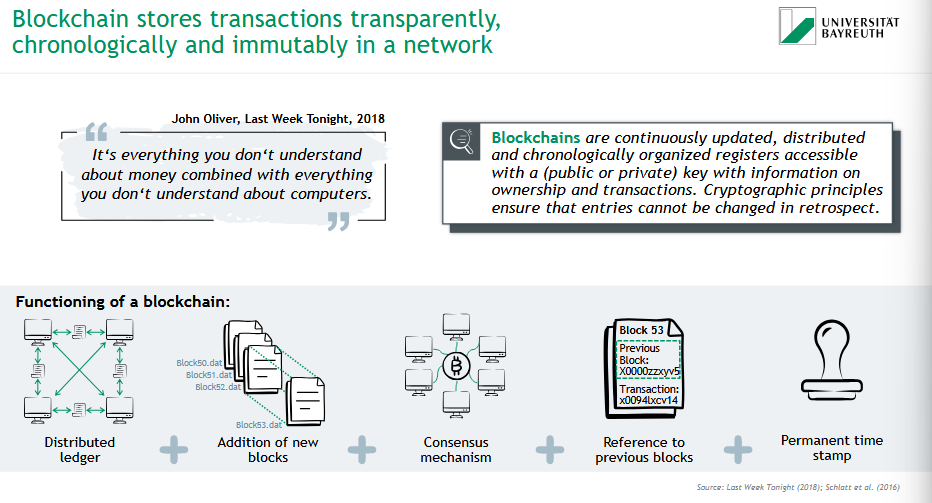
What is blockchain & how does it work?
🔗 Blockchain = a secure, distributed digital ledger that stores transactions transparently, chronologically, and immutably.
📌 Key features:
✅ Distributed ledger
➕ New blocks added regularly
🤝 Consensus mechanism
🔁 Reference to previous blocks
🕒 Permanent timestamp
🔐 Cryptography ensures data can’t be altered in retrospect.
Public/private keys allow secure access.
💬 “It’s everything you don’t understand about money combined with everything you don’t understand about computers.” – John Oliver
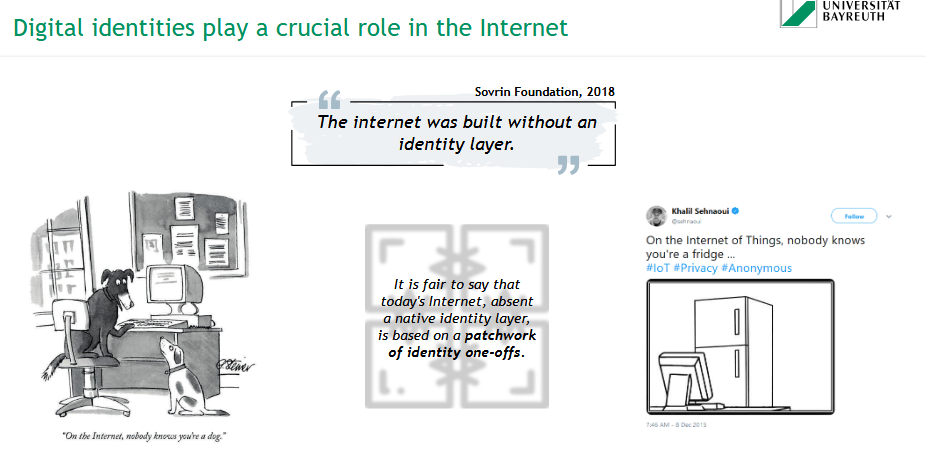
What is a digital identity and why is it important for the internet?
🆔 A digital identity is the online equivalent of a person’s or object’s identifiable presence — used to verify and authenticate access.
📌 Problem:
The Internet was built without a native identity layer, leading to:
Fragmented identity solutions (“identity one-offs”)
Privacy risks (e.g., IoT devices)
💡 Quote:
“The internet was built without an identity layer.” – Sovrin Foundation (2018)
🧠 On the Internet, even a fridge or a dog may stay anonymous.
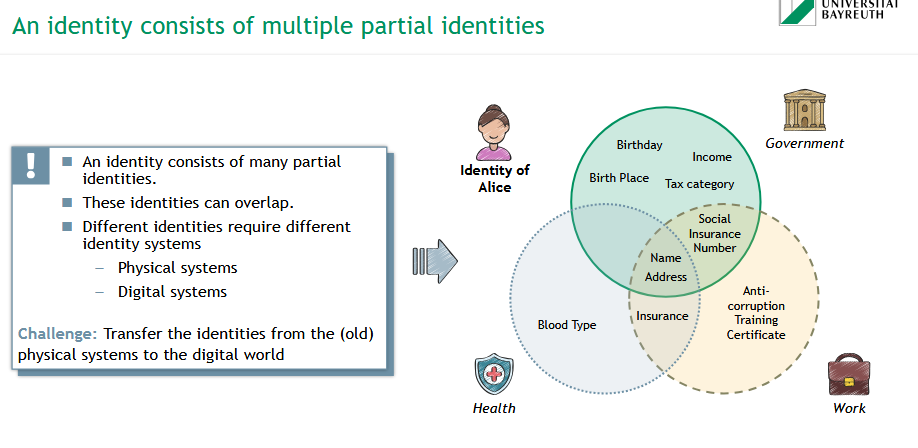
What are partial identities, and why are they important in the digital world?
🧩 An identity = a collection of partial identities across different domains:
👩 Government: birthday, income, tax category
🏥 Health: blood type, insurance
💼 Work: training certificates
💡 These identities may overlap (e.g., name, address) and exist in:
Physical systems (paper, ID cards)
Digital systems (databases, apps)
⚠ Challenge: Transfer & integrate identities from physical to digital systems securely.
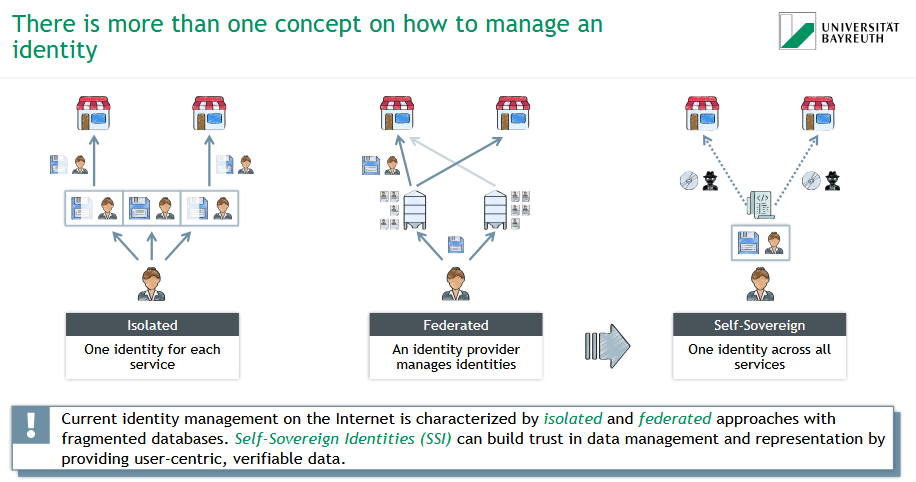
What are the different concepts on how to manage an identity?
isolated
federated
self-sovereign
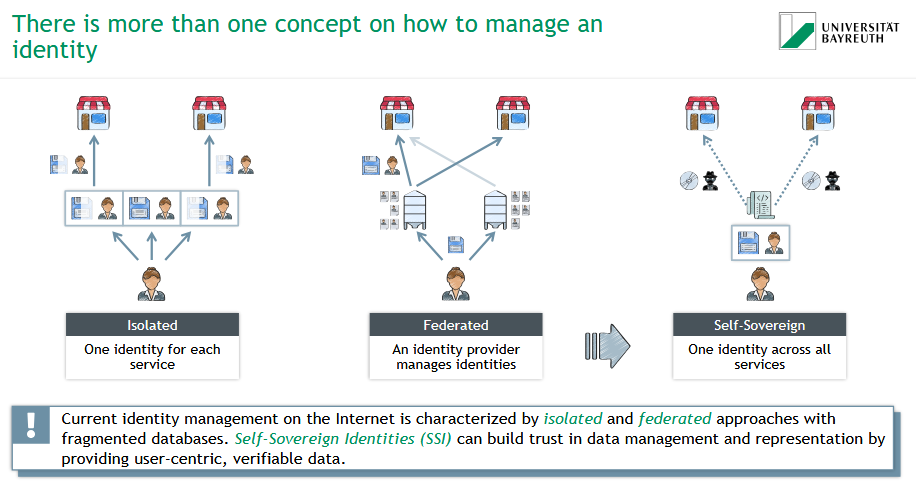
What is a Self-Sovereign Identity (SSI)?
🔐 Self-Sovereign Identity (SSI) = A user-centric identity model
▸ One identity for all services
▸ User fully controls their own data
▸ Verifiable & trustable digital credentials
✅ SSI enables secure, privacy-friendly, and interoperable identity management.
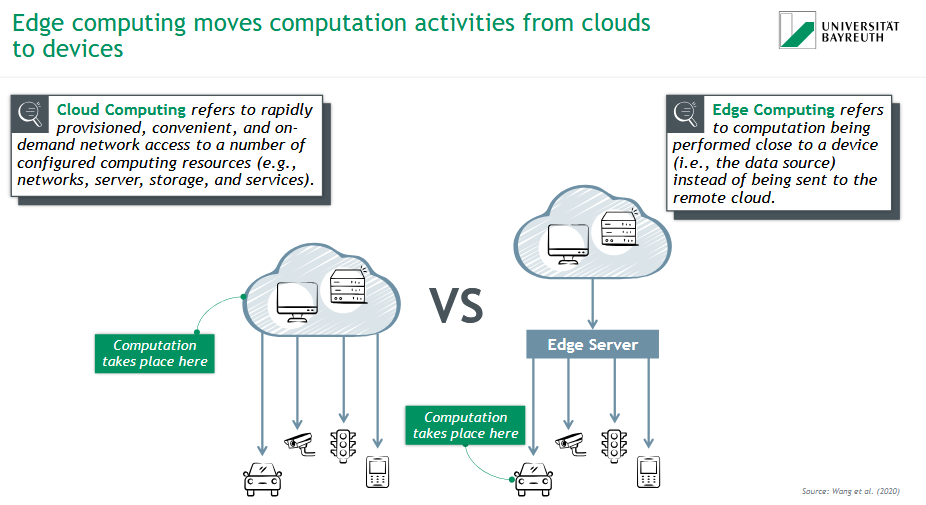
What is Cloud Computing?
☁ Cloud Computing
= Remote computation via networked data centers.
Computation happens in centralized cloud servers
Offers scalable resources like storage, services, and processing
Used in applications needing large computing power, but higher latency
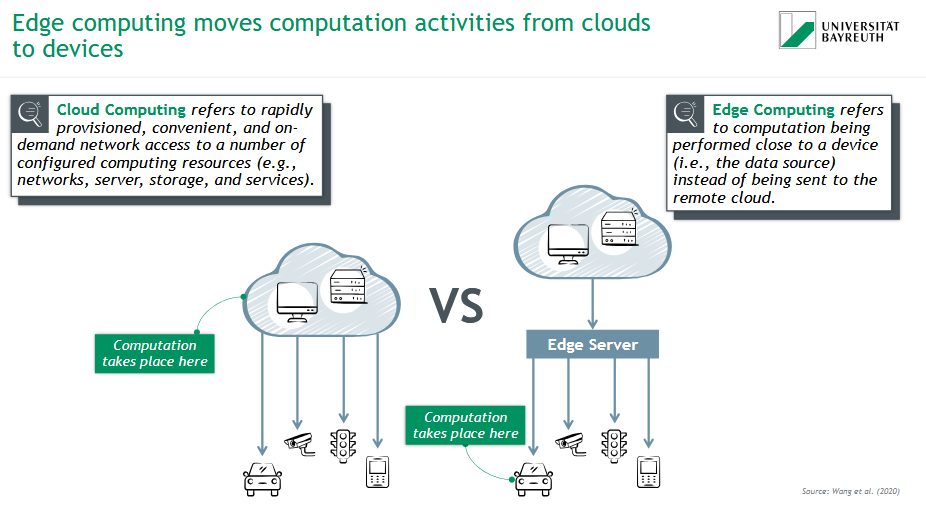
What is Edge Computing?
📶 Edge Computing
= Computation happens close to the data source, like sensors or devices.
Reduces latency and network load
Enables faster, localized responses
Ideal for IoT, smart vehicles, and real-time systems
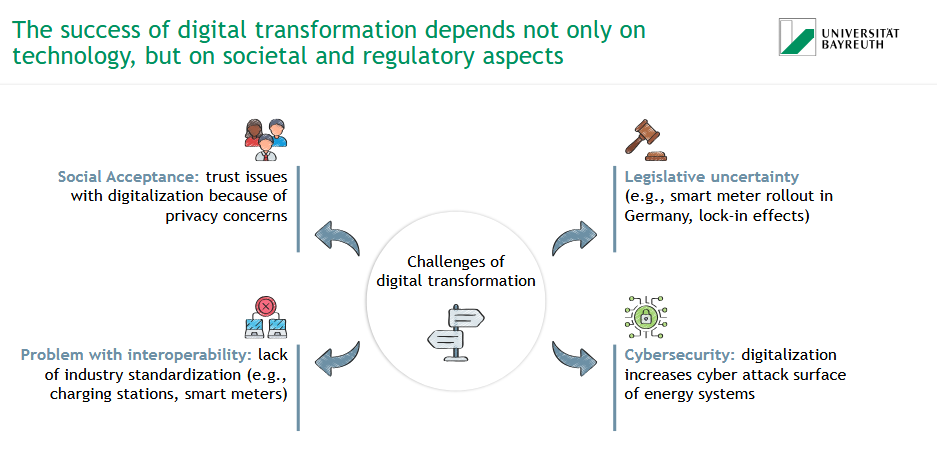
On which aspects does the success of digital transformation depend?
technology
societal aspects
regulatory aspects
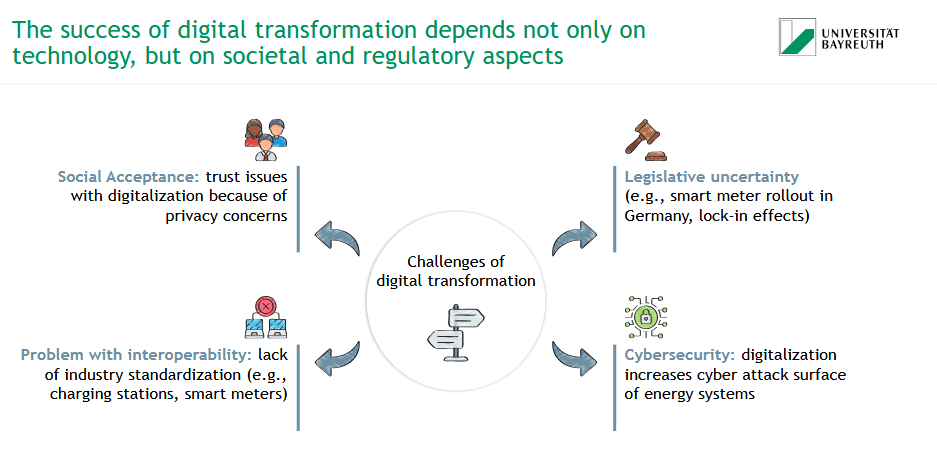
What are challenges of digital transformation?
social acceptance (trust issues, privacy concerns)
legislative uncertainty
problem with interoperability (lack of industry standardzation)
cybersecurity
What is an all-electric society?
The all-electric society is a vision of the future where all economic sectors are digitalized, automated, and electrified. On this basis, all sectors can be interconnected and coupled with each other

What challenges come together with electrification?
Electrification with the objective of decarbonization requires zero- or at least low-carbon electricity generation while simultaneously accounting for an increasing electricity demand. Further, the capacity and flexibility of the transmission grid must be adjusted to enable electrification.

How can we balance the electricity grid?
We can refer to multiple kinds of flexibility to balance supply and demand in the electricity grid with an increasing share of renewables: Conventional supply-side flexibility, storage flexibility, transmission flexibility, demand-side flexibility, and inter-sectoral flexibility.

What role do digital technologies have in an all-electric society?
Digital technologies enable a transformation towards a real-time energy economy and all-electric society by connecting an increasing number of devices to the grid and optimize their consumption (or provision) of electricity.
