Unit 4 - Psychodynamic and Humanistic Theories of Personality
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
28 Terms
Personality
an individual's characteristic patterns of thinking, feeling, and acting
Psychodynamic theories view of personality
view human behavior as a dynamic interaction between the conscious mind and the unconscious mind, including associated motives and conflicts
Sigmund Freud
personality is attributed to thoughts and actions due to unconscious motives and conflicts
Expose and interpret unconscious tensions
Free association
Unconscious
Beneath our conscious mind is a larger mind with mostly unacceptable thoughts, wishes, feelings, and memories that we are unaware of
Free Association
psychoanalytic therapy method of exploring the unconscious in which the person relaxes and says whatever come to mind, not matter how trivial or embarrassing
This would lead to painful unconscious memories from childhood that could be retrieved.
ID
Unconscious portion of personality
Primitive & Instinctive component
Seeks immediate Satisfaction
SUPEREGO
Tells us what we should and should not do
Values/ Morals
too much SE guilty, shy, fearful, withdrawn… it monitors the id and hands out rewards (pride, satisfaction) or punishments (shame, guilt)
Develops first 5 years of life
Ego
the largely conscious, “executive” part of personality that, mediates among the demands of the id, superego, and reality
Develops during first 5 years
Defense mechanisms
are unconscious strategies that people use to protect themselves from anxiety or threats to their self-esteem
Repression
the banishment of threatening thoughts, feelings, and memories into the unconscious mind; unconsciously forgetting information that is too painful to recall
ex: witness a murder and when the police ask you what happened, you forget
Regression
reverting back to childlike behavior to get the attention you got when you were younger or to get your way
ex: anxious on a first day of school, a child may result to a “thumb sucking” phase to help him/her get through
Reaction Formation
the tendency to act in a manner opposite to one's true feelings
ex: “I hate him” may really mean, “I love him”
Projection
the attribution of one's undesirable feelings to others; blaming another person for the feelings you have
ex: “He doesn’t trust me,” may mean “I don’t trust him.”
Rationalization
the providing of socially acceptable reasons for one's inappropriate behavior
ex: students who don’t study may think, “All work and no play makes me a boring person”, or someone who is an alcoholic may say, “I only drink in social settings.”
Displacement
the expression of feelings toward a person/thing who is less threatening than the true target of those feelings; taking out one’s anger or frustration on a person or object that is not the cause of the offense
ex: bullying
Denial
Refusing to acknowledge or accept reality, often to avoid painful or threatening information
ex: see your boyfriend cheating, but still don’t believe it
Sublimation
the expression of sexual or aggressive impulses through indirect, socially acceptable outlets
It is possible that smokers have graduated from earlier stages of thumb-sucking and pencil-chewing, neither of which would be acceptable behavior in adult society. Smoking is a socially acceptable outlet for oral needs.
Alfred Adler
Childhood tensions are social, not sexual.
Healthy individuals overcome inferiority by engaging with society, fostering self-worth and concern for others.
Some prioritize selfishness over social interest.
Inferiority Complex: Persistent insecurity from perceived inferiority, impacting life and relationships.
Birth Order Theory: Birth order influences personality.
Karen Horney
Psychoanalytic Social Theory: Social and cultural conditions in childhood shape personality.
Lack of love in childhood → basic hostility → leads to basic anxiety.
To cope, people adopt one of three styles:
Moving toward people: Seeks affirmation, appears needy/clingy.
Moving away from people: Avoids others, appears cold/aloof.
Moving against people: Controls others, appears domineering/unkind.
Personality Types:
Aggressive: Sees others as enemies, self-serving.
Compliant: Prioritizes others' needs.
Detached: Seeks independence, may become isolated.
Carl Jung
Jung & Freud: Initially Freud’s protégé but later criticized his Oedipus complex theory in 1912.
Collective Unconscious: Shared human reservoir of images from our past.
Archetypes: Universal symbols in myths, art, and literature (e.g., Hero vs. Villain).
Personality Types: Four opposing pairs, with one dominant in each person:
Extroversion/Introversion
Sensing/Intuition
Thinking/Feeling
Judging/Perceiving
Balance: Ideal self-realization comes from balancing extroversion and introversion.
Introverts: Reflective, insightful, inward-focused.
Extroverts: Engage with the external world, action-oriented.
Projective Test
personality test that provides ambiguous stimuli and test-takers tell a story about it
Thematic Apperception Test (TAT)
Developed by Henry Murray
A test in which people express their inner feelings and interests through the stories they make up about ambiguous scenes

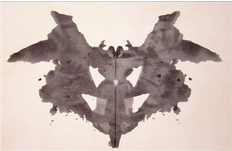
Rorschach Inkblot Test
Designed by Hermann Rorschach
Most widely used projective test with a set of 10 inkblots
It seeks to identify people’s inner feelings by analyzing their interpretation of the inkblots
What do you see?
Projective Test: Criticism
Critics argue that projective test lack both reliability (consistency of results) and validity (predicting what it is supposed to)
Preconscious
includes stored information about yourself or your environment that you are not currently aware or thinking of but can easily call to mind when asked
Humanistic Psychology
emphasized human potential, focused on the ways “healthy” people strive for self determination and self-realization
Unconditional Positive Regard
we are all born with a need for acceptance and love from others independent of how we behave, and positive self-regard from ourselves
Self-Actualization
motivation to fulfill potential and to become a fully functioning person