Geog1003 midterm
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
43 Terms
anthropocentrism
Human life holds intrinsic value
Natural resources should be used for economic gain and advancement
ecocentrism
humans are just part of a whole
Humans are equal to all living organisms
Nature and environment deserve specific consideration
social constructivism
nature = a mental construct of humanity
Nature is not separate from humanity
environmentalism
concern surrounding human impacts on environment
Ecological footprint
Human impacts on natural environment
quantified by the amount of land or sea required to produce human resources
Carrying capacity
Maximum population size Earth can sustain without depletion
I=PAT
total impact= population, affluence, technology
Development
the improvement of living standards in society
Sustainable development
development that meets our needs without compromising the needs of future generations
Sustainability
use of resources that maintains enough for the future
equitable
Bearable
Viable
Hydropsphere
Water in all its forms (precipitation, ocean, lakes, etc.)
Atmosphere
Gas layer
Litosphere/geosphere
Earth layer
Biosphere
all living organisms
Systems that shape biosphere:
axial tilt (seasons)
Glacial and interglacial tilts
Greenhouse effect
Biophysical systems (water cycle, carbon cycle, etc.)
Topography
natural and artificial features of an area
Relief
variations of shape and height of earth’s surface
slope
change in elevation between 2 points
Aspect
Direction slope is facing
Transpiration
moisture leaving vegetation
Evapotranspiration
moisture from the soil
Carbon source
puts out more carbon than it takes in
humans
Cows
carbon sinks
takes in more carbon than it puts out
trees
Coral reefs
Biome
plant and animal communities with distinct characteristics that cover large areas
Disturbance
short-term problems
fire
Extreme storm
succession
predictable, step-by-step change in the ecosystem
disruption
Disturbance with long term impacts
environmental history
study of human-environment relationships over time
paleoecology and paleoclimate
Study of long-term ecological change
Key periods in human history
Paleolithic and Neolithic
Ancient period
Middle Ages
Early modern era
Modern era
Industrial revolutions 1760-1840 and 1870-1914
Transnationalism
connections beyond political borders- culture, money, people, goods, etc.
Globalization
interdependence and integration with other nations for goods
“The designed Earth”
the theory that God/a higher power designed Earth
ecology
study of relations between organisms and the environment in the non-human world
policitical ecology
interdisciplinary study of humans and the environment that interpreters notes of power, specifically by looking at grassroots perspectives
cultural ecology
interdisciplinary study of how humans interact with their environment, specifically by starting at the grassroots perspectives
dependency theory
underdeveloped nations being exploited by countries with more power
world systems theory
distinguishes between core (developed), periphery (developing) and semi-periphery
post-structuralism
rejects universalizing of some theories in political ecology
the reason why we have environmental issues is due to power and colonialism
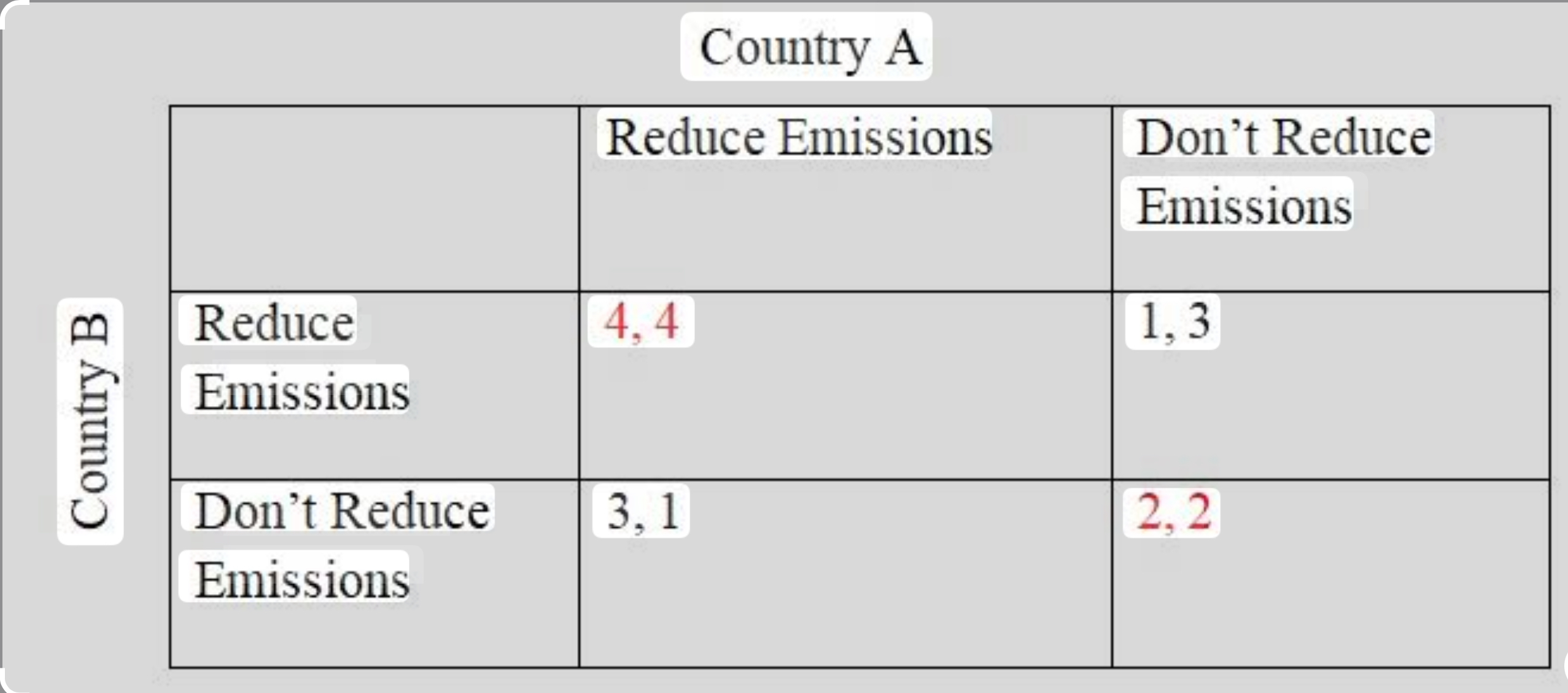
Prisoner’s dilemma
cooperations and incentive in pressure environment
1. If two nations both cooperate, then they both achieve good outcome
2. if one defects then it gets the biggest individual benefit without reaping reprecussions
3. If they both defect, then they end up in a worse outcome than if they had cooperated
Mary Douglass
anthropologist associated with cultural geography
individual perception heavily influenced by culture
Gilbert White
Ecologist who argued that we should accept trends of nature and human-environment interconnectedness
cowboy economics
popular approach prior to the 1860s where resources were seen as limitless in North America, and once those resources were exhausted, settlers simply moved (exploitation)
Rachel Carson
wrote Silent Spring (1962) which raised awareness about the detriments of pesticide use