Psych Exam 5
1/173
Earn XP
Description and Tags
chapters 10-12
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
174 Terms
Motivation
describes wants and needs that direct behavoir towards a goal
intrinsic motivation
arise from internal factors such as personal satisfaction
autonomy
mastery
purpose
eg: completting a chore to feel accomplished
extrinsic motivation
motivated due to external factors
compensation
punishment
reward
eg chores because mom said so
William James (1842-1910)
called the father of pscyology in the US
theoriezed behavoir was driven by instincts
instinct
specific patter of behavior that is not learned
eg: maintaining of homeostasis
drive theory of motivation
deviations from homeostasis creates physiological needs
results in direct behavior to maintain homeostasis
eg: not eating, low blood sugar, hunger, consume food
habit
pattern of behavoir which we reuglarly engage
Yerkes-Dodson law
simple tasks are best preformed with high arousal levels
complex tasks best with lower arousal levels
self efficacy
an individuals belief in their own capability to complete a task
alfred bandura theorized that self efficacy is key in motivating behavior
more belif in ones ability = higher likleyhood to take on challanges
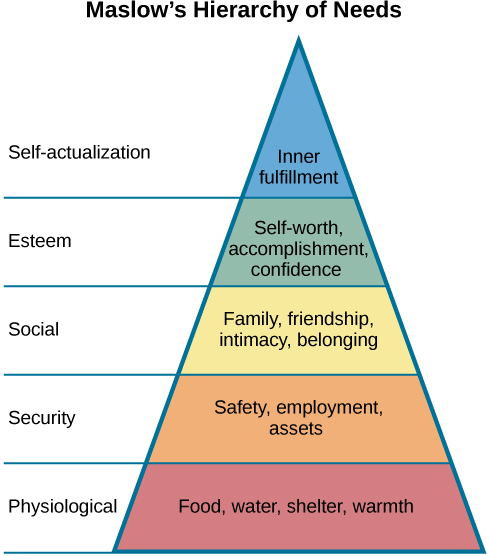
Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs
small percent of people actually achieve a self- actualizied state
satiation
fullness/satisfcation which stops eating bejavoir
regulated by physiological mechanisms
increase of glucose in blood, pancrease and liver sends signals to stop eating
leptin
satiation hormone acts as an appetite suppressant
secreted by fat cells
parts of the brain involved in eating
hypothalamus and hindbrain
metabolic rate
amount of energy expended in a given period of time
individual varaiblity
set-point theory
each indiviudal has a idea body weight which is resistant to change
genetically predetermined, efforts to change weight are resisted by energy intake/expenditure
lack of empirical support, fails to account for social.enviromental facots
overweight
BMI over 25 and 29.9
obese
BMI over 30
nearly one third of american adult population are obese
severe obseity
BMI over 40
risk of death
bariatric surgery
type of surgery for weight reduction
modification of gastrointestinal system to reduce the amount of food can be eaten/absorbed
bulimia nervosa
binge eating followed by purging of the food
usually through vomiting or laxatives
can lead to kidney failure, heart failure, tooth decay
binge eating disorder
binge eating followeed by distress guilt and embarrased
anorexia nervosa
starvation and excessive exersize
distorted body image of self= body dysmorphia
outcomes: bone loss, heart failure, kidney failure, amenorrhea, death
structures of the brain: sexual motivation
amygdala, nucleus accumbens
damage results in decreased sexual motivation while still able to do so
seen in rats
Dr. Alfred Kinsey
findings:
homosexuality is fairly common
masturbation without adverse health consequences
women= interest in sex as men
sexual orientation
is an individual’s emotional, romantic, and erotic attractions to other people or no people
sexual response cycle
excitement- arousal
plateau- blood flow increases to labia, erection
orgasm- ejaculation, contraction of pelvis
resolution- rapid return to unaroused
refractory peroid
time after orgasm capable of having another
older= longer refractory period
gender identity
ones senee of being male, female, neither or both, or another
Gender dysphoria
describes individuals who do not identify as the gender that most people would assume they are
emotion
subjective state of being that we often describe as our feelings
result from the combination of subjective experience, expression, cognitive appraisal, and physiological responses
components of emotion
combination of physiological arousal, psychological appraisal, and subjective experiences
our experiences, backgrounds, and cultures inform our emotions
James-Lange theory of emotion
emotions only arise from physiological arousal
such as fight or flight
cannon-bard theory
physiological arousal and emotional experience occur simultaneously, yet independently
eg: seeing snake, you feel fear at same time of fight or flight
emotion seperate/independant of physiological arousal
The Schachter-Singer two-factor theory
emotions are composed of physiological and cognitive factors
labels (im scared) sympathetic nervous systems feeling, type of cognitive appraise
polygraphs are accurate at differentiating emotions
appraisal
emotion depends on thoughts had
eg: positive thoughts
polygraph
lie decetor test measures the physiological arousal of an individual responding to a series of questions
vaildy and accuracy are questioned
the cognitive-mediational theory
asserts our emotions are determined by our appraisal of the stimulus.
appraisal mediates between the stimulus and the emotional response, and it is immediate and often unconscious.
appraisal precedes a cognitive label
basolateral complex
dense connections with a variety of sensory areas in the brain
critical for classical conditioning and attaching emotional value to learning processes and memory
central nucleus
role in attention
connections with hypothalamus and various brainstem areas to regulate the autonomic nervous and endocrine system
hippocampus
involved in emotional processing
inked to mood and anxiety disorders
PTSD = REDUCED COUMED IN HIPPOCAMPUS
cultural display rule
diffrent cultures have dfirrent expressions and displays of emotion
eg: negative emotional suppression in frowned upon in Japan
ability to engage in sexual behavoir: rats
medial preoptic area of the hypothalamus
does not affect motivation
7 universal emotions
Charles Darwin’s: "The Expression of Emotions in Man and Animals
happiness
surprise
sadness
fight
disgust
contempt
anger
personality
traits and patterns that propel individuals to think, feel and behave in certain ways
concioussness : freud
only one third of our mind is concious
rest is unconscious
repression
unaccpetable urges and desires are kept in our unconscious
freudian slip
expressing unacceptable unconcious through slips of the tounge
freud says these are sexual or agressive urges
id- freud
primative drives and urges
hunger thirst sex
pleasure princaple and immediate gratification
constant conflict with superego
superego
occours through socalization
controls the id
moral compass and conscience
strives for perfectionism
ego
rational personality
the self
personality seen by others
satisfies the id in rational ways
neurosis- freud
imbalance between ID and ego
results in negative emotions, anxiety disorders, or unhealthy behavior
eg: dominant superego= guilt lack of pleasures
or lack of superego= psychopath
defense mechanisms
unconscious protective behaviors that aim to reduce anxiety
protects the ego from anxiety
unaware of using defense mechanisms
denial
refusing to accept real events because they are unplesant
eg: refusing to admit you have a drinking problem even though you drink every day
displacement
transferring inappropriate urges onto a more acceptable or less threathening target
eg: taking out anger from boss onto co worker
projection
attributing unnacceptable desires from ones self onto others
pointing out someones bad makeup because youre insecure about your own
rationalization
justifiying behavoirsoirs by subsitituing accpetable reasosn for less acceptable real reasons
eg: failing french because you didnt study but saying its cuz your prof was bad
reaction formation
reducing anxiety by adopting belifs contraru to yout own belifs
being mad at someone for coming late to work and hungover but saying that her partying is “cool”
regression
returing to coping strategies for less mature stages of devlopment
being sad and cuddling your childhood toy
repression
supressing painful memories and thoughts
not being able to remember truamtic experinces
sublimation
redirecting unaccpetable desires through socially acceptable channels
eg: wanting to hurt someone but going to boxing class instead
stages of Psychosexual Development
Freud’s Stages of Psychosexual Development
Stage | Age (years) | Erogenous Zone | Major Conflict | Adult Fixation Example |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Oral | 0–1 | Mouth | Weaning off breast or bottle | Smoking, overeating |
Anal | 1–3 | Anus | Toilet training | Neatness, messiness |
Phallic | 3–6 | Genitals | Oedipus/Electra complex | Vanity, overambition |
Latency | 6–12 | None | None | None |
Genital | 12+ | Genitals | None | None |
oral stage
birth- 1 year
pleasure from mouth/sucking
adult fixation: smoking, drinking biting nails
anal stage
1-3 years
bowel and bladder pleasure
adult fixiation: messy, careless, disorganized, emotional outburts
phallic stage
3-6 years
awareness of bodies/genitals
oedipus complex: attract to parent of other sex/attention
latency period
6 years to puberty
sexual feelings are dormant
freindships with same sex
genital stage
final stage: puberty onwards
sexual reawakening
desire for opposite sex
indiviudal psychology
alfred adler
focuses on our drive to compensate for feelings of inferiority
people attempt to gain superiorty on life
inferiority complex
persons feelings that they lack worth and dont measure up to the standards of society
could be from childhood
Alfred: Fundemental social tasks
all humans must experince
occupational tasks- career
societal tasks- frienships
love- finding a partner
Erik Erikson
Erikson’s Psychosocial Stages of Development
Stage | Age (years) | Developmental Task | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
1 | 0–1 | Trust vs. mistrust | Trust (or mistrust) that basic needs, such as nourishment and affection, will be met |
2 | 1–3 | Autonomy vs. shame/doubt | Sense of independence in many tasks develops |
3 | 3–6 | Initiative vs. guilt | Take initiative on some activities, may develop guilt when success not met or boundaries overstepped |
4 | 7–11 | Industry vs. inferiority | Develop self-confidence in abilities when competent or sense of inferiority when not |
5 | 12–18 | Identity vs. confusion | Experiment with and develop identity and roles |
6 | 19–29 | Intimacy vs. isolation | Establish intimacy and relationships with others |
7 | 30–64 | Generativity vs. stagnation | Contribute to society and be part of a family |
8 | 65– | Integrity vs. despair | Assess and make sense of life and meaning of contributions |
Carul Jung- Analytical psychology
working to balance opposing forces of conscious and unconscious thought and experience within one’s personality.
collective unconcious
jung
universal version of the personal unconscious, holding mental patterns, or memory traces, which are common to all
archetypes
universal themes s expressed through literature, art, and dreams
these themes reflect common experience: death, becoming independent, and striving for mastery
eg: the hero, maiden, trickster
extrovert
energized by being with others
seeks attention
speaks out loud, quickly and loudly
introvert
energized by being alone
avoids attention
thinks before speaking
cautious
behaviorist perspective on personality
do not believe in biological determinism: personality traits are inborn
Skinner argued that personality develops over our entire life- not just first years
cognitive perspective on personality
emphasizes both learning and cognition as sources of individual differences in personality
reciprocal determinism, observational learning, and self-efficacy all play a part
Reciprocal Determinism
Bandura
one’s environment can determine behavior, but at the same time, people can influence the environment with both their thoughts and behaviors
eg: going bungee jumping, cognitive factors and context (reward structure) come into play
Self-efficacy
is our level of confidence in our own abilities, developed through our social experiences
affects how we approach challenges and reach goals
locus of control
our beliefs about the power we have over our lives
internals: believe that most of our outcomes are the direct result of our efforts
externals: lives as being controlled by factors outside of our control- other people, luck, or chance
Walter Mischel and the Person-Situation Debate
a person’s personality traits are not consistent across situations
but behavoir it is likely to be repeated in diffrent situations
self-regulation.
the process of identifying a goal or set of goals and, in pursuing these goals, using both internal and external feedback
aka will power
self-concept
carl rogers
our thoughts and feelings about ourselves.
How would you respond to the question, “Who am I?”
high self concept = congruence
ideal self
carl rogers
person you would like to be
real self
the person you actually are
congruene
consistency between the real self and ideal self
high confruence= greater self worth
parents can help children through unconditional postive regard/love
incongruence
can lead to maladjustment
humanism
carl rogers and maslow
individuald choices
biology is not determanistic
Minnesota Study of Twins Reared Apart
researchers found that identical twins, whether raised together or apart, have very similar personalities
suggest heritability of some personality traits
Heritability
refers to the proportion of difference among people that is attributed to genetics.
temperment
how a person reacts to the world, including their activity level, starting when they are very young
babies:
easy
difficult
slow to warm up
2 types of temparment
reactivity
how we respond to new or challenging environmental stimuli
self-regulation
our ability to control such response
traits
characteristic ways of behaving
eg: optimistic, pessemistic, passive, agressivw etc.
Gordon Allport found 4,5000 traits to describe people
narroweded down to 171 by raymond cattell
cardinal trait
dominates your entire personality and life
such as Ebenezer Scrooge’s greed and Mother Theresa’s altruism.
few people have cardinal traits
multiple traits.
more common as personality is comprised of multiple traits
loyal, kind, agreeable, friendly, sneaky, wild, and grouchy
Secondary traits
not quite as obvious or as consistent as
present under specific circumstances and include preferences and attitudes
eg: angry when getting rickled
Eysencks’ theory
divides people into four quadrants.
melancholic, choleric, phlegmatic, and sanguine