Perception
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
13 Terms
Bottom-up processing
Begins with sensory receptors and works up to the brain (sensation first)

Top-down processing
Constructing perceptions using our experiences and expectations (expenses first)

Schema
A collection of basic knowledge about a concept or entity that serves as a guide to perception, interception, imagination, or problem solving.

Perceptual set
Tendency to see things in a certain way
Gestalt principles
Set of rules that describe how our brains organize and perceive visual information
Selective attention
Focusing our conscious awareness on one stimulus

Cocktail party effect
Ability to focus one’s listening attention on a single talker among a mixture of conversations and background noises

inattention blindness
failing to see visible objects when our attention is focused elsewhere
Change blindness
Failing to notices changes in the environment

Binocular depth cues
A depth cue, such as retinal disparity, that depends on the use of two eyes

Monocular depth cues
a depth cue, such as interposition or linear perspective, available to either eye alone

Perceptual constancies
perceiving objects as unchanging (having consistent color, brightness, shape, and size) even as illumination and retinal images change
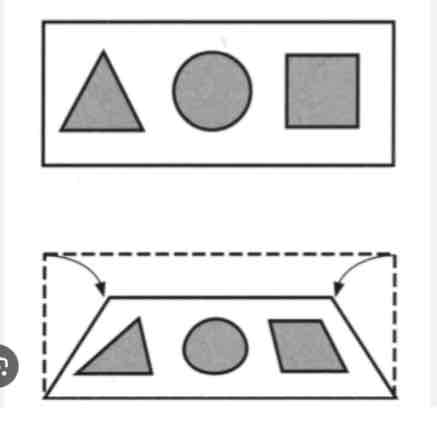
Apparent movement
An illusion of motion or change of size that is cued by visual tricks
