ELE_IC Subatomic Particles/Structure of Hydrogenic Atoms
1/53
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
54 Terms
electron cloud
A region around the nucleus of an atom where electrons (-) are likely to be found.
nucleus
This is where protons (+) and neutrons (0) can be found.
electron (0.00054858) < proton (1.0073) < neutron (1.0087)
Rank neutrons, protons, and electrons according to increasing mass.
elements
Humphrey Davy passed electricity through compounds and noted and concluded that the compounds decomposed into?
electrical forces
Humphrey Davy passed electricity through compounds and noted and concluded that compounds are held together by?
amount of reaction that occurs during electrolysis is directly proportional to the electrical current passed through the compounds
Michael Faraday realized a directly proportional relationship between two parameters. What are these parameters?
very low P
Cathode ray tube experiments consist of 2 electrodes sealed in a glass tube containing a gas at very (high, low) pressure.
glow discharge
In cathode ray tube experiments, when a voltage is applied to the cathodes a _______ is emitted.
True.
Cathode rays (beam of electrons) produced by a cathode-ray (discharge) tube travel in straight lines.
T or F?
cathode (-end) to the (+end)
Cathode rays are emitted from ______ to the __________.
False. They must be negatively charged.
Cathode rays are not necessarily negatively charged.
T or F?
2
J.J. Thomson modified the cathode ray tube experiments in 1897 by adding how many adjustable voltage electrodes?
additional electric field
Following the addition of 2 adjustable voltage electrodes by J.J. Thomson, he studied the amount that the cathode ray beam was deflected by?
charge to mass ratio of electrons
Thomson used his cathode ray tube experiment modification to measure the?
e/m = -1.75882 x 10^8 coulomb/g
What is the value of the charge to mass ratio of an electron?
J. J. Thomson
He is considered to be the "discoverer of the electrons."
oil-drop experiment
Robert A. Millikan won the Nobel Prize in 1923 for what famous experiment?
charge and mass of the electron
In 1909, Millikan determine the ____ and _____ of the electron.
e = -1.60218 x 10^-19 coulomb
m = 9.10940 x 10^-28 g
Millikan determined that the charge on a single electron is equal to? Thus mass is equal to?
positively charged particles
Eugene Goldstein noted streams of _____ in cathode rays; these particles move in opposite direction of cathode rays.
because the positively charged particles passed through holes (channels or canals) drilled through the negative electrode.
The positively charged particles Eugene Goldstein noted were called canal rays because?
proton
Through Goldstein's experiment, he postulated the existence of a positive fundamental particle called?
α-particle scattering from thin Au foils
Ernest Rutherford directed Hans Geiger and Ernst Marsden's experiment which was called?
gave us the basic picture of the atom's structure
The α-particle scattering from thin Au foils experiment gave us what?
True.
Rutherford concluded from the α-particle scattering experiment that the atom is mostly empty space.
T or F?
nucleus
Rutherford concluded from the α-particle scattering experiment that an atom contains a very, small dense center called the _____ where nearly all of the atom's mass is in it.
1/10,000 to 1/100,000
Rutherford concluded from the α-particle scattering experiment that the nuclear diameter is _______ to _________ times less than the atom's radius.
thin beryllium films
James Chadwick in 1932 analyzed the results of α-particle scattering on which element?
neutrons
Through Chadwick's α-scattering experiment on thin Be films, he recognized the existence of massive neutral particles which he called?
# of protons in the nucleus
The atomic number is equal to the?
element
H. G. J. Moseley realized that the atomic number determines the _______; these differ from each other by the number of protons in the nucleus.
True.
The number of electrons in a neutral atom is also equal to the atomic number.
T or F?
wavelength (λ)
The _______ of electromagnetic radiation is the distance from the crest (top) of one wave to the crest of the next wave.
1 Å = 1 x 10^-10 m = 1 x 10^-8 cm
1 Å = _____ m = _______ cm
Frequency (f)
The ______ of electromagnetic radiation is the number of crests or troughs that pass a given point per second.
1/time, /s = Hz
Frequency is measured in units of?
velocity = λf or c = λf (for electromagnetic radiation)
The relationship between wavelength and frequency for any wave is?
c = 2.998 x 10^8 m/s
For electromagnetic radiation, the value for velocity, denoted by c, is?
1. energy is quantized
2. light has a particle character
Max Planck studied black body radiation and realized that to explain the energy spectrum he had to assume that (2):
ΔE = hv = hc/λ
h = 6.626 x 10^-34 Js
Planck's equation is? where h is?
particle
In Einstein's explanation for the photoelectric effect, light behaves as a ______ when it collides with electrons on the metal surface which are then ejected.
wave
In Einstein's explanation for the photoelectric effect, light behaves as a _____ when it has quantized energy in discrete amounts sufficient to eject electrons.
emission spectrum (sometimes called a bright line spectrum)
A/an ________ is formed by an electric current passing through a gas in a vacuum tube (at very low pressure) which causes the gas to emit light.
absorption spectrum
A/an ________ is formed by shining a beam of white light through a sample of gas.
wavelengths of light
Absorption spectra indicate the _______ of light that have been absorbed.
True.
Every element has a unique spectrum.
T or F?
Rydberg equation
The _____ equation is an empirical equation that relates the wavelengths of the lines in the hydrogen spectrum.
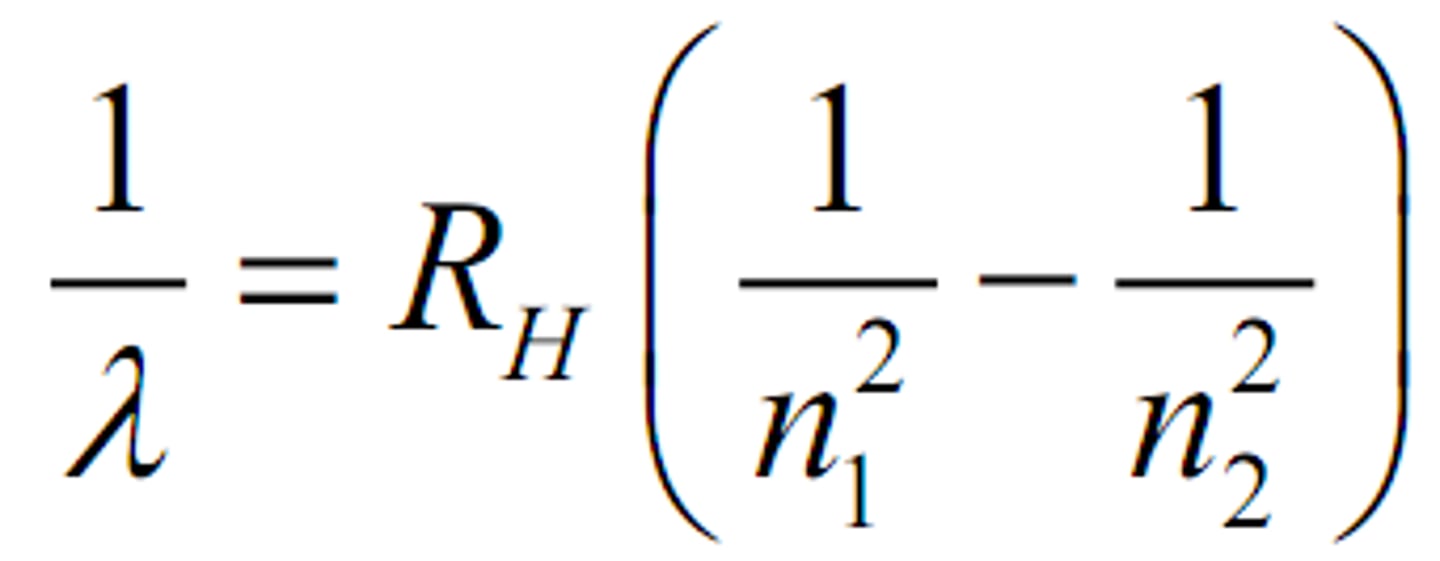
R = 1.097 x 10^-7 m^-1
R in Rydberg equation is equal to?
energy level in the emission spectrum of hydrogen
What does n stand for in the Rydberg equation?
r = (n^2)(a_o)
From mathematical equations describing the orbits for the H atom, together with the assumption of quantization of energy, Bohr was able to determine where the electron can be with respect the nucleus, as explained by this formula:
n = 3 --> n = 2
At what energy levels does red light jump from and to in the Balmer series?
n - 4 --> n = 2
At what energy levels does green light jump from and to in the Balmer series?
n = 5 -> n = 2
At what energy levels does blue light jump from and to in the Balmer series?
n = 6 -> n = 2
At what energy levels does violet light jump from and to in the Balmer series?