7A- Membrane structure and proteins
1/35
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Cell Bio
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
36 Terms
Lipids are typically about what percentage of the 30% of chemicals in bacterial cells?
2%
There are numerous types of membranes in cells
true
What different types of membranes are in cells?
nucleus
Golgi apparatus
mitochondria
Endoplasmic reticulum
peroxisome
endosome
lysosomes
thylakoids
chloroplasts
Cell membranes are ( ), generally speaking, the lipids and integral membrane proteins can ( ) throughout the membrane
fluid mosaics
readily diffuse
mosaic meaning?
combination of many small pieces that create a whole object
mosaic nature of membranes means they have ( )- due to the ( )
various structures along their surfaces
various lipids and membrane proteins
what are the the main components lipids?
1)head
2)connector
3)tails
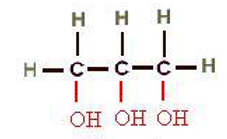
Structure of ( ), the connector/backbone group of ( )lipids which are by far the most ( )
glycerol
glycero
general structure of phospholipids:
lipids are ( )
amphiphilic/amphipathic
what is amphiphilic?
polar plus hydrocarbon non-polar components
what is amphipathic
polar and nonpolar parts
lipids comprise ( )% of mass of most animal cell membranes - other ( )% is ( )
50
50
protein
3 main components of lipids:
1) Head group: may or may not contain a phosphate, if it does, then it is a ( ). May or may not contain one or more sugars if it does, then it is a ( )
2) connector- if glycerol, then it is a ( )
3) tails-hydrocarbon so ( )
phospholipid
glycolipid
glycerolipid
hydrophobic
look at slide 13/14 and 16
okat
most abundant lipids- ( )
phospholipids
biological membranes are lipid bilayers that contain ( )
proteins
different cells have different ( ) compositions
lipid
lipids can form ( )layers or ( )layers
mono
bi
( ) surround cells and (usually) organelles within cells
lipid bilayers
phospholipids form a sphere because it is the most ( ) form in aqueous solution like ( )
energetically favorable
cytosol
( ) are the most energetically favorable configuration for lipids- in an ( ) environment
sealed bilayers
aqueous
a lipid bilayers is more like a “( )” hence a “( )”
two-dimensional liquid (semi-solid)
fluid mosaic
in which way do lipids move?
flexion
rotation
flip-flip (rarely occurs)
lateral diffusion
Biological membranes are lipid bilayers that have what main general characteristics?
1)they have hydrophilic surface layers (one on outside and one on inside)
2)they have a hydrophobic inner layer
3) they have proteins imbedded in them
-often these proteins have sugars chains attached (i.e. are glycosylated)
saturated fatty acids:
-tend to ( ) more ( ) and ( )
-( ) at relatively higher temperatures-compared to unsaturated lipids
pack
closely
tightly
solidify
Unsaturated fatty acids:
-tend to pack less ( )- so membranes composed of them are “looser”
-takes lower ( ) (vs.saturated) to start to solidity
closely
temperatures
The more kinked (not kinky!… tightly curled) unsaturated fatty acids are, the ( ) the membrane formed
looser
pure lipid bilayers serve are barriers for large and/or charged or polar molecules, this allows movement across membranes to be ( )
regulated
look at slide 27
okayyy
proteins can associate with a lipid bilayer in several ways:
1)( )
2( )
3( )
4( )
integral membrane proteins
peripheral membrane proteins
anchored membrane proteins
indirectly
( ) membrane proteins- tightly associated with membrane (i.e. cannot easily be removed)
-many (but not all) are ( )
-the ones that are not transmembrane penetrate into membrane and are ( )
integral
transmembrane proteins
tightly associated
( ) membrane proteins- more loosely associated (i.e. can be removed but relatively easy extraction methods)
can be just on ( ) or ( ) into the membrane
peripheral
surface
penetrate
( ) membrane proteins- attached by lipid-tail-like structures
anchored
( )- by interactions with membrane proteins
indirectly
look at slide 30
OKAY
some membrane proteins, are