Chapter 11 - Carbonyl Compounds and Redox Reactions
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
dehydrogenation
a reaction in which an organic compound loses two hydrogen atoms, creating an alkene grp
alkane loses 2 hydrogen atoms to make room for additional carbon-carbon bond to become alkene
is an oxidation reaction
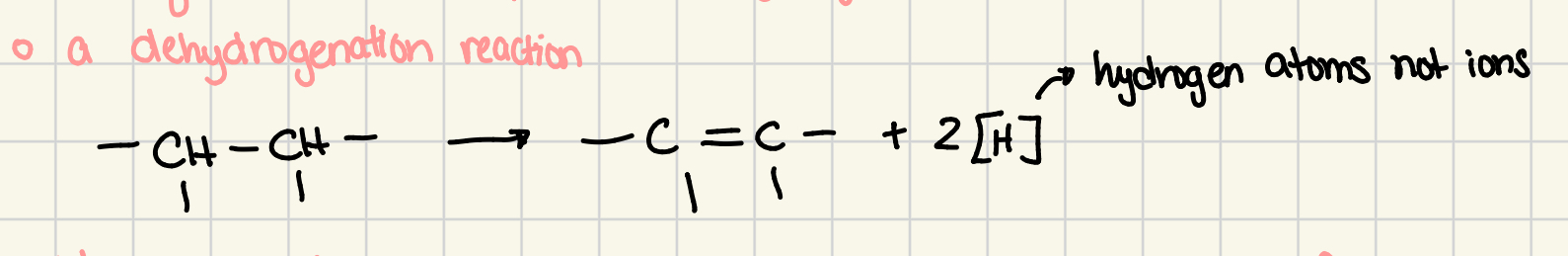
[H]
symbol that is used to represent a hydrogen atom that is attached to an organic molecule
oxidation reaction
any reaction that removes 2 hydrogen atoms from an organic compound
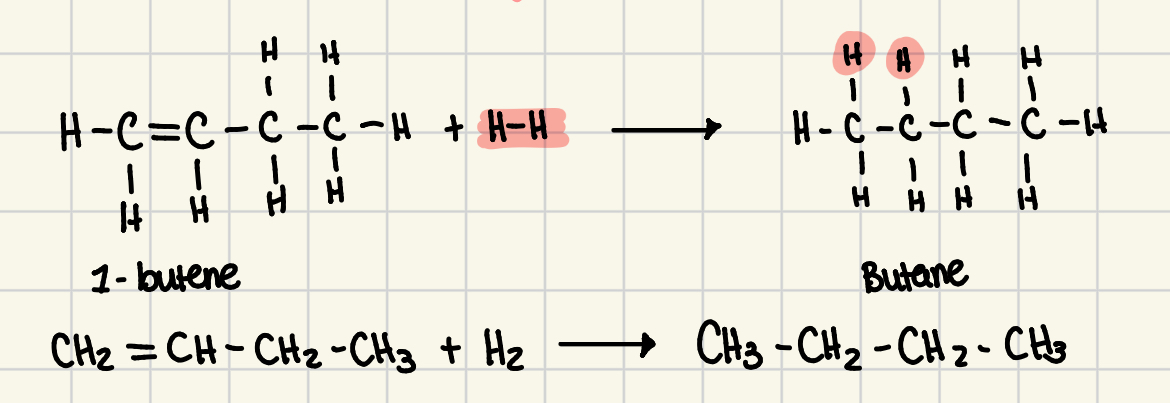
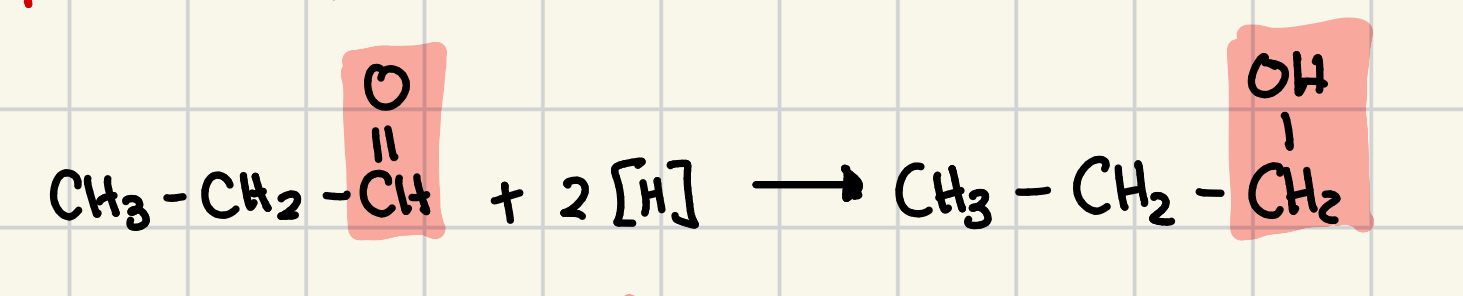
hydrogenation reaction
a reaction in which an alkene or alkyne gains hydrogen atoms, becoming an alkane or an alkene respectfully
reverse of the dehydrogenation reaction
is a reduction reaction

reduction reaction
any reaction in which hydrogen atoms are added to an organic molecule
summary
oxidation reactions remove hydrogen atoms from organic molecule
reduction reactions add hydrogen atoms to an organic molecule
whenever one compound is oxidized, another must be reduced
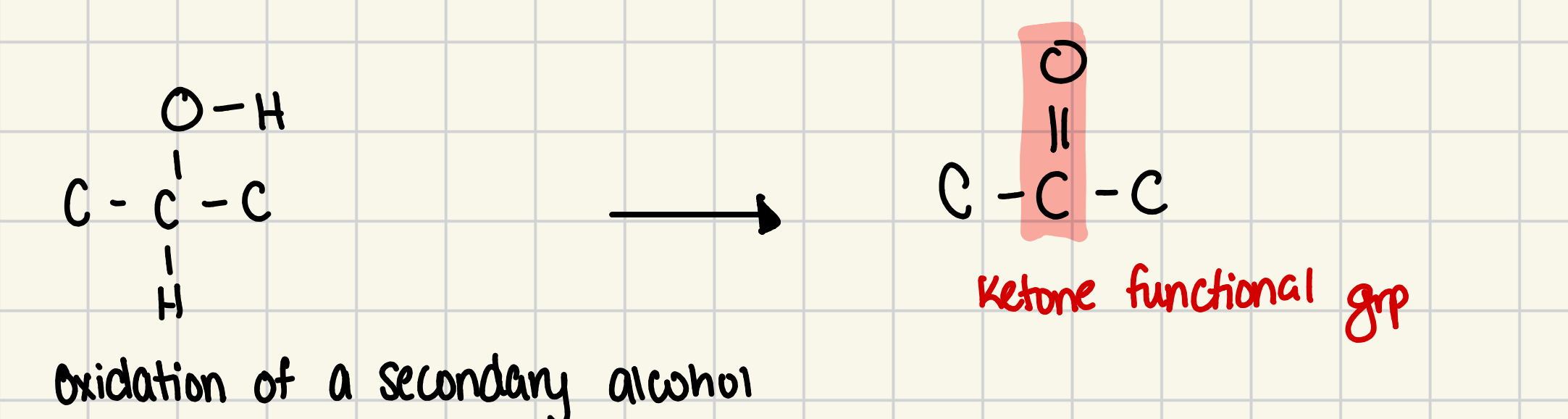
oxidation of an alcohol
remove 2 hydrogen atoms from the organic compound, and we convert a single bond to a double bond
carbonyl group is the product
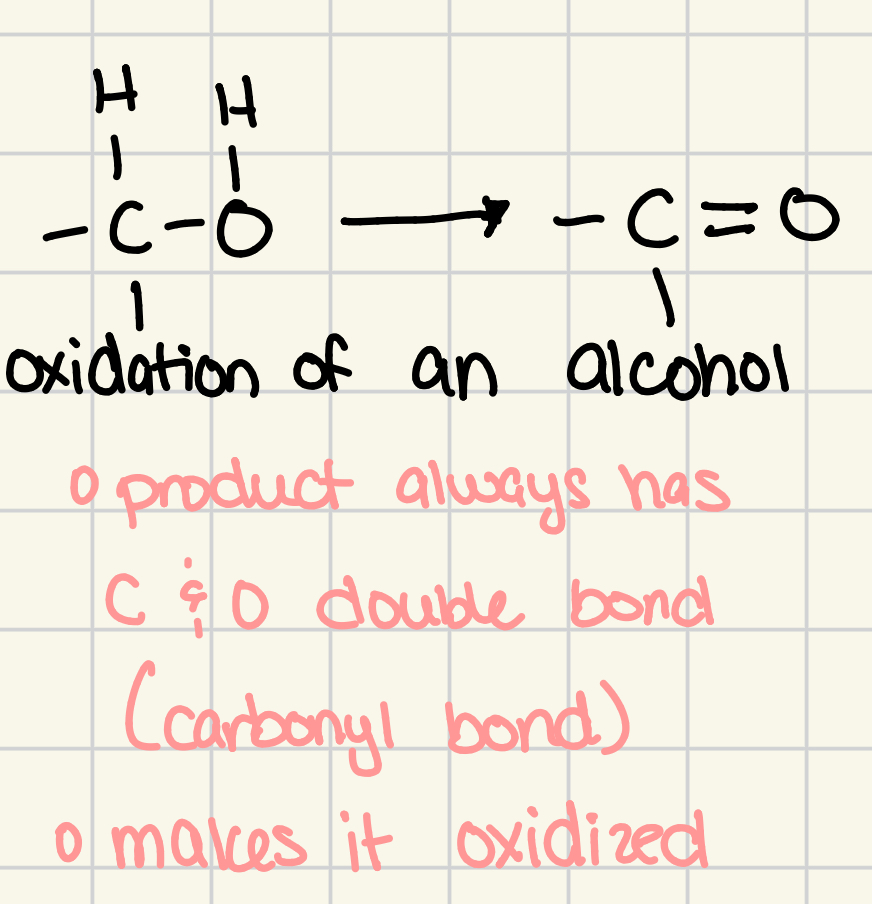
carbonyl group
C = O
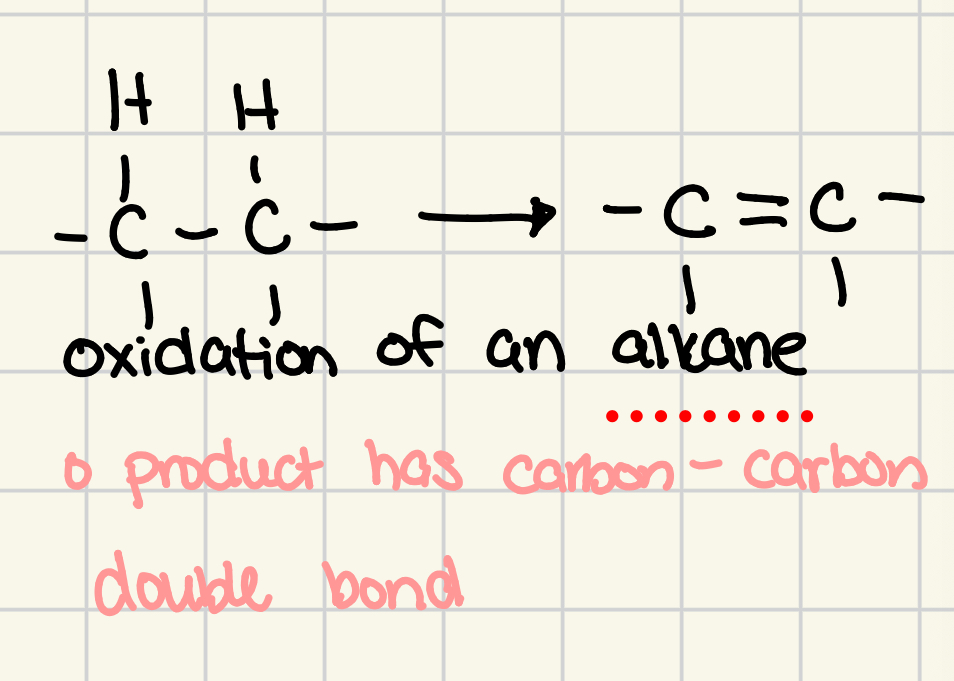
oxidation of an alkane
product has carbon-carbon double bond
teritiary alcohols cannot be oxidized
to be oxidized an alcohol must have a hydrogen atom directly bonded to the carbon of the functional group
picture cannot be oxidized because there is no H atom bonded to the functional group carbon
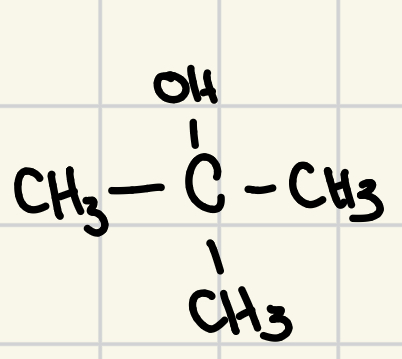
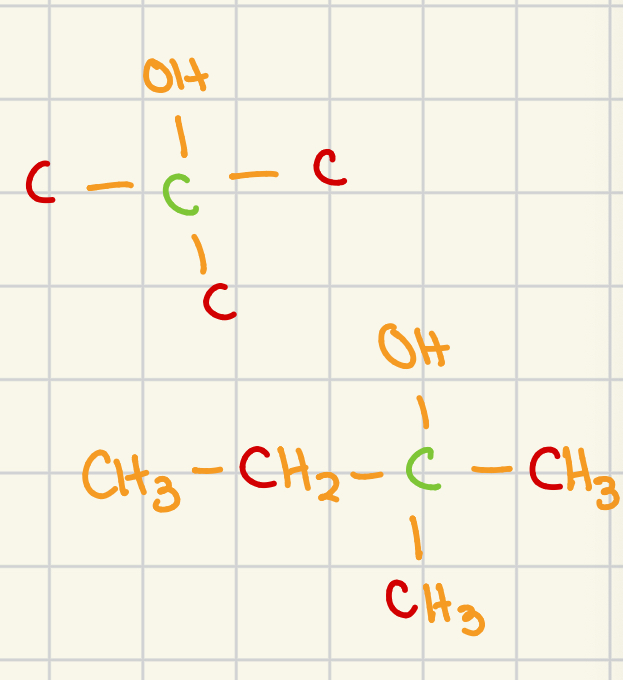
classification of alcohols
methanol
primary
secondary
tertiary
methanol
carbon atoms adjacent to the functional grp: 0
general structure (adjacent carbon atoms are shown in red
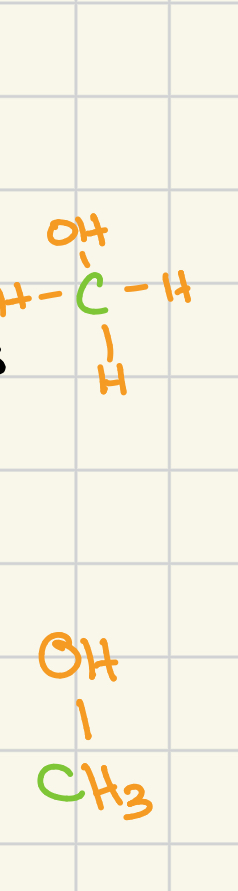
primary
carbon atoms adjacent to the functional grp: 1
general structure (adjacent carbon atoms are shown in red
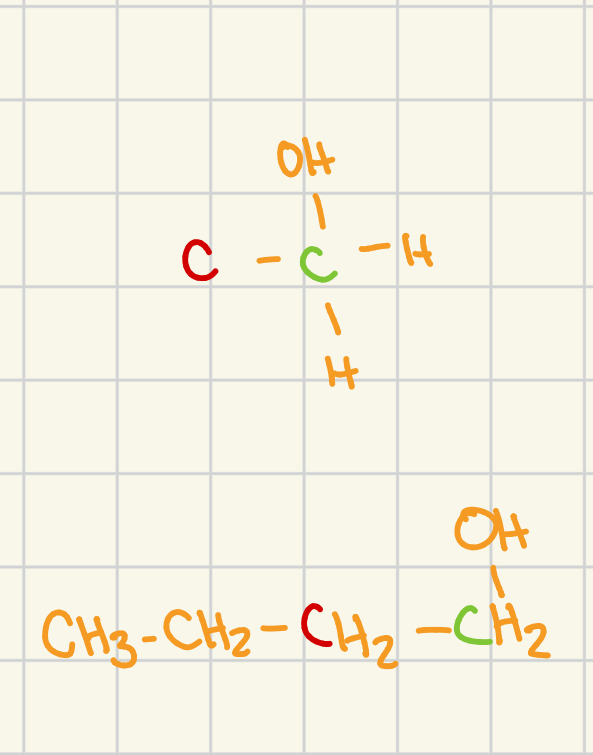
secondary
carbon atoms adjacent to the functional grp: 2
general structure (adjacent carbon atoms are shown in red
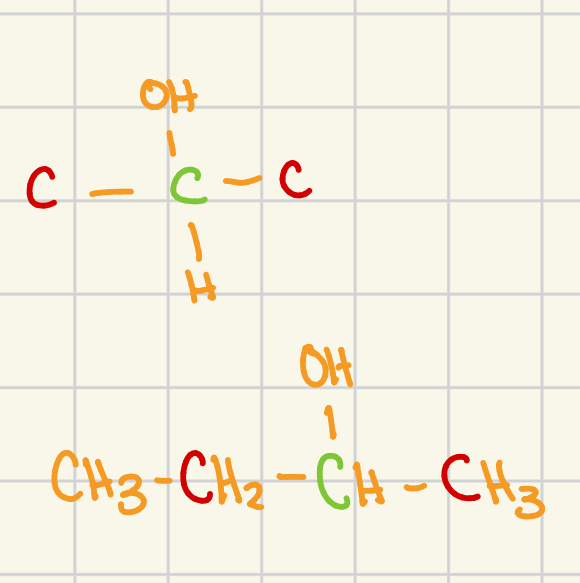
tertiary
carbon atoms adjacent to the functional grp: 3
general structure (adjacent carbon atoms are shown in red
carbonyl groups
compounds that contain carboxyl grp can be reduced
double bond becomes a single bond and carbon and oxygen of the original group each gain a hydrogen atom
specific example of a reduction
reduction reactions often convert an achiral molecule into a chiral molecule
aldehydes
oxidized PRIMARY alcohol or methanol with the product of a carbonyl group on the END of the carbon chain
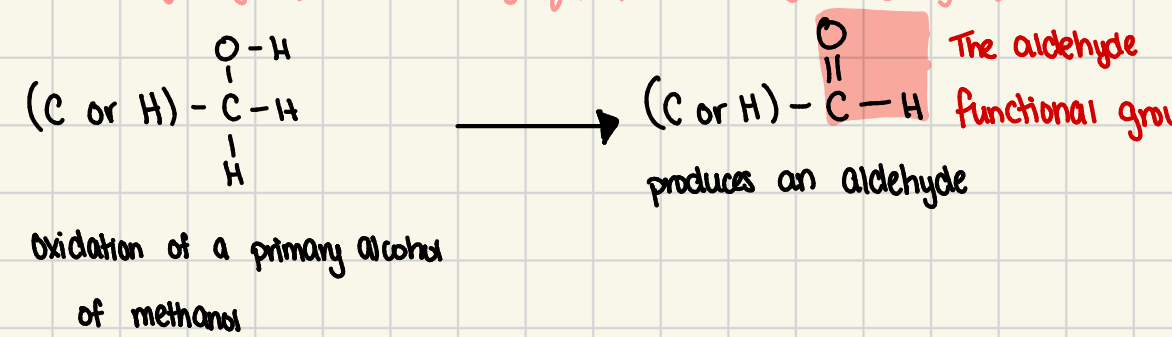
aldehyde group
the carbonyl grp plus its neighboring hydrogen
to name an aldehyde using IUPAC rules
first name the carbon chain, include the aldehyde chain
replace the final “-e” of the alkane name w “-al”
do not need to write a # to show the location of the functional grp bc aldehyde group must always be at the end of the carbon chain
drawing aldehydes
drawn structure of an aldehyde, they abbreviate the aldehyde group to -CHO

acetaldehyde
trivial name for ethanal aldehyde

formaldehyde
trivial name for methanal
ketones
compounds with structure where oxidized SECONDARY alcohol, the product has a carbonyl group in the interior of carbon chain
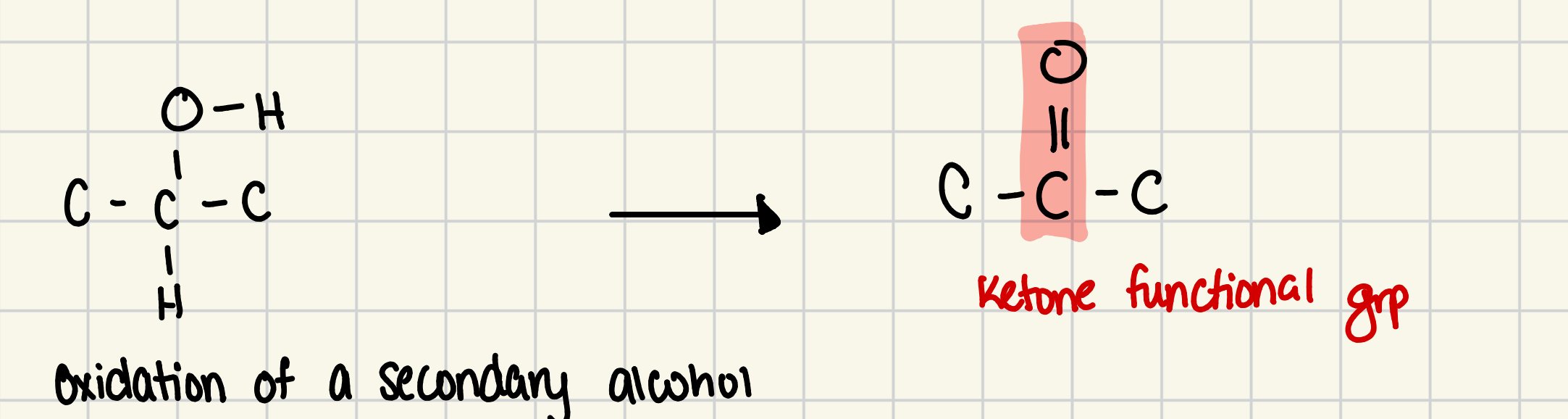
ketone grp
is the funcitonal grp
To name a ketone using IUPAC rules
start with naming carbon chain
replace the final “-e” w/ “-one”
have to include a # to show location of functional ketone grp because the oxygen atom can be bonded to any internal carbon atoms in a ketone (# chain from side thats closest to functional grp)
cyclic ketone
naming it don’t use a #
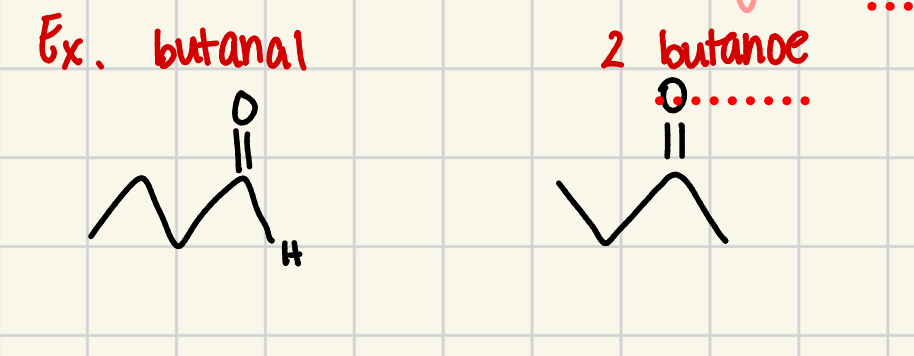
drawing line structure of an aldehyde or ketone
draw carbon chain as a zigzag line, then add oxygen atom with its double bond
for aldehydes add functional grp hydrogen to structure
aldehydes and ketones have similar physical proerties
boiling points
solubilities
boiling points
molecules containing a carbonyl group are more strongly attracted to one another
aldehydes and ketones have HIGHER BP’s then normal hydrocarbons but LESS than alcohols (hydrogen bonds
all common aldehydes and ketones are liquids at 20 degrees
solubilities
aldehydes and ketones have similar solubilities to alcohol and are greater than regular hydrocarbons
1. alcohol, 2. A and K, 3. regular hydrocarbons
increase # of carbon atoms = decrease
increase of carbonyl grps = increase