Psych 202 Module 1
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
30 Terms
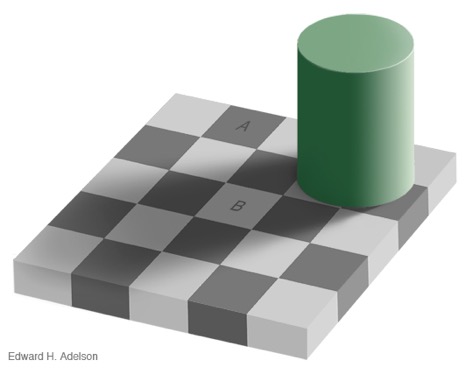
The bottom-up information from the squares marked A and B respectively is ____, which is ____ for the two squares
the raw number of photons coming off the two squares and entering your eye; the same
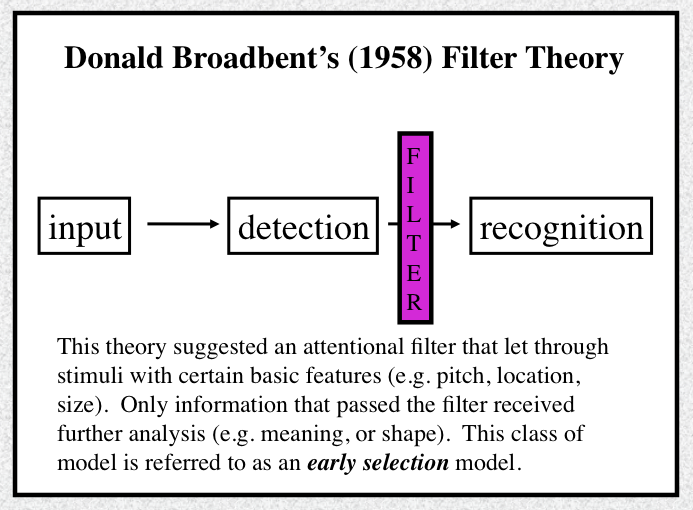
Which model of attention is this and what does it do
early selection model theory; attentional filter that let through stimuli with basic features and any information passed was analyzed
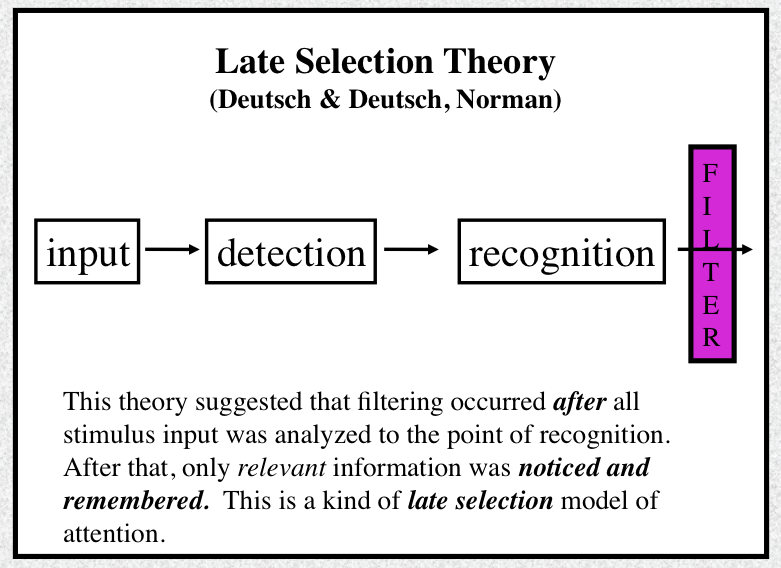
Which model of attention is this and what does it do
late selection model theory; filtering occurred after all the stimulus input was analyzed and only relevant information was noticed and remembered
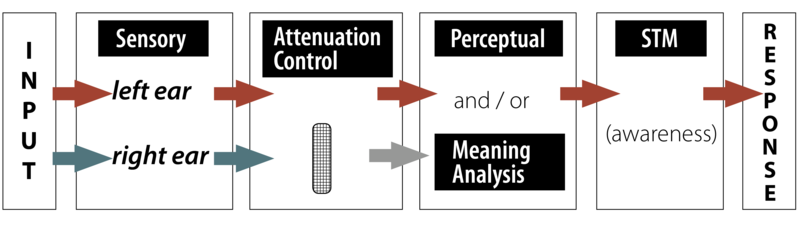
Which model of attention is this and what does it do
Attenuation model; information that is weak will totally be blocked, but strong information will be passed through and analyzed
misinformation effect
Occurs when misleading information distorts memory of an event, often due to post-event information.
suggestibility definition and example
the tendency to incorporate misleading information from external sources into personal recollections; an example is when a witness remembers details from a crime based on incorrect/biased sources on the internet…the way things are worded impact our memories
egocentric bias
remembering the past in a self-enhancing manner
cognitive dissonance
discomfort you feel when there is a mismatch between various beliefs you have and the actions you take, resulting to resolve by changing our beliefs or actions
consistency bias
misremember past attitudes or behaviors in line with the attitudes currently held
misattribution
information is remembered correctly, but the source is remembered incorrectly
overconfidence
to be too certain about their ability to accurately remember events and make judgements
serial position effect
aspect of forgetting when people remember the beginning and end of the list but forget the middle items
Patient HM
removed hippocampus, lost ability to form many types of new explicit memories, kept procedural memories
rational choice theory
maximize gains and minimizes losses
availability bias
more available in memory are judged as more common
representative heuristic
base judgements on what we expect to happen
conjunction fallacy
the conjunction of two events makes the process more “representative”
gamblers fallacy
if something happens more frequently than expected, then it will happen less in the future, vice versa
hot hand fallacy
experience success means greater chance of further success
ignoring the base rate
focusing on specific information instead of the general information presented
information bias
the tendency to seek information even if the information isn’t useful in determining what to do
framing
people react to particular choice in different ways depending on whether it is presented as a loss or as a gain
loss aversion
prefer avoiding losses over gaining
risk aversion
prefer certain gains to uncertain gains
sunk cost fallacy
sticking with an original decision because the original investment would be “wasted”
endowment effect
things have more value if you own them
anchoring
relying on the first piece of information (anchor) when making decision
temporal discounting
don’t value things in the future as much as things in the present
belief perseverance
facts don’t change our minds
bias blindspot
we aren’t aware of our bias