Lymphatic System
1/61
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
62 Terms
What does antigen stand for?
Antibody Generator
What is an antigen?
Foreign Substance
Where can you find antigens?
Anywhere
Where are B-Cells Produced?
Bone Marrow
What are the 2 types of B-Cells?
Plasma Cells + Memory B-Cells
What does plasma cells produce?
Antibodies
How long do memory cells last?
Forever
How long do antibodies last?
Not forever (they have a half-life)
What is the first line of defense in innate immunity?
Skin + Mucosa and Secretions
What is the second line of defense in innate immunity?
Phagocytosis
What is milk, tear, saliva making up?
Lysozyme
what is the 3rd line of defense in innate immunity?
Inflammation
What are the 4 types of pathogens?
Viruses, bacteria, fungi, parasites
What are the 4 subunits of an antibody?
2 heavy chains and 2 light chains
What are the physical and chemical components of innate immunity?
Skin + Mucous Membranes
What are the cellular components of innate immunity?
(Phagocytic Cells) - Granulocytes, Monocytes, Macrophages, and Natural killer cells
What are soluble factors of innate immunity?
Complement proteins + cytokines
What are the four types of T - Cells ?
Helper T-cells, Cytotoxic T-cells, Regulatory T-cells, Memory T-cells.
What are the 4 ways to acquire adaptive immunity?
Natural Active, Natural Passive, Artificial Active, Artificial Passive
What is natural active acquired immunity?
The body becomes immune after being naturally exposed to a pathogen, gets sick, and then recovers.
What is natural passive acquired immunity?
Antibodies are passed from mother to child without the mother or child's immune system actively creating them.
What is Artificial active acquired immunity?
Your body produces its own antibodies in response to a weakened or dead form of a pathogen introduced through a vaccination.
What is artificial passive acquired immunity?
Antibodies are given directly to a person to provide immediate, temporary protection. This is done by injecting antibodies (immunoglobulin) produced in another person or animal.
What triggers antibody productions?
B-cell encounters its specific antigen, it becomes activated and begins to multiply
What part of the antibody combines with the antigen?
The variable region
Which organ is NOT part of the immune system?
Pancreas
True or false: red bone marrow, spleen, lymph node, and thymus are all part of the immune system?
True
IgM
IgE
IgG
IgA
IgD
These are all classes of what?
Antibodies
True or false:
-Release of inflammatory chemicals
-inactivation of the antigen
-phagocytosis of the antigen
are all the effects of the antigen + antibody combining?
True
Does fluid balance happen in the lymphatic system?
Yes, fluid balance happens in the lymphatic system
Does defense against pathogens happen in the lymphatic system?
Yes, defense against proteins happens in the lymphatic system.
Does protein absorption from the digestive tract happen in the lymphatic system?
No, the lymphatic system does not absorb protein from the digestive tract.
which of the following is NOT a process in the lymphatic system?
Protein absorption from the digestive tract
What induces the production of a specific antibody?
Antigens
What does b-cells produce?
Plasma and memory b-cells
What is caused by an adaptive response to self-antigens?
Autoimmune disease,
Exposure to an infectious agent in everyday activities leads to:
Natural Active immunity
What type of immunity is acquired from mom breastfeeding baby?
Natural Passive Immunity
Which is the mechanical barrier of innate immunity?
Skin (epidermis/epithelium) and mucous membranes
Which organ produces a hormone that promotes maturation of T cells
the thymus gland
Which of the following is produced in a cell-mediated immune response?
cytotoxic t-cells
Which of the following does NOT produce a chemical / physical barrier?
Macrophages
Which type of adaptive immunity will result from intravenous injections of immunoglobulins?
Artificial passive immunity
What is another name for innate immunity?
Non-specific
Which type of immunity defends against any type of invader?
Innate immunity / Non-specific immunity
In specific/adaptive immunity B cells perform what function?
Produce antibodies to neutralize specific antigens.
Which complement system action makes microbes more susceptible to phagocytosis?
Opsonization is the complement system action that makes microbes more susceptible to phagocytosis.
Which of the following is often needed to activate antibody-mediated immunity?
Helper T cells
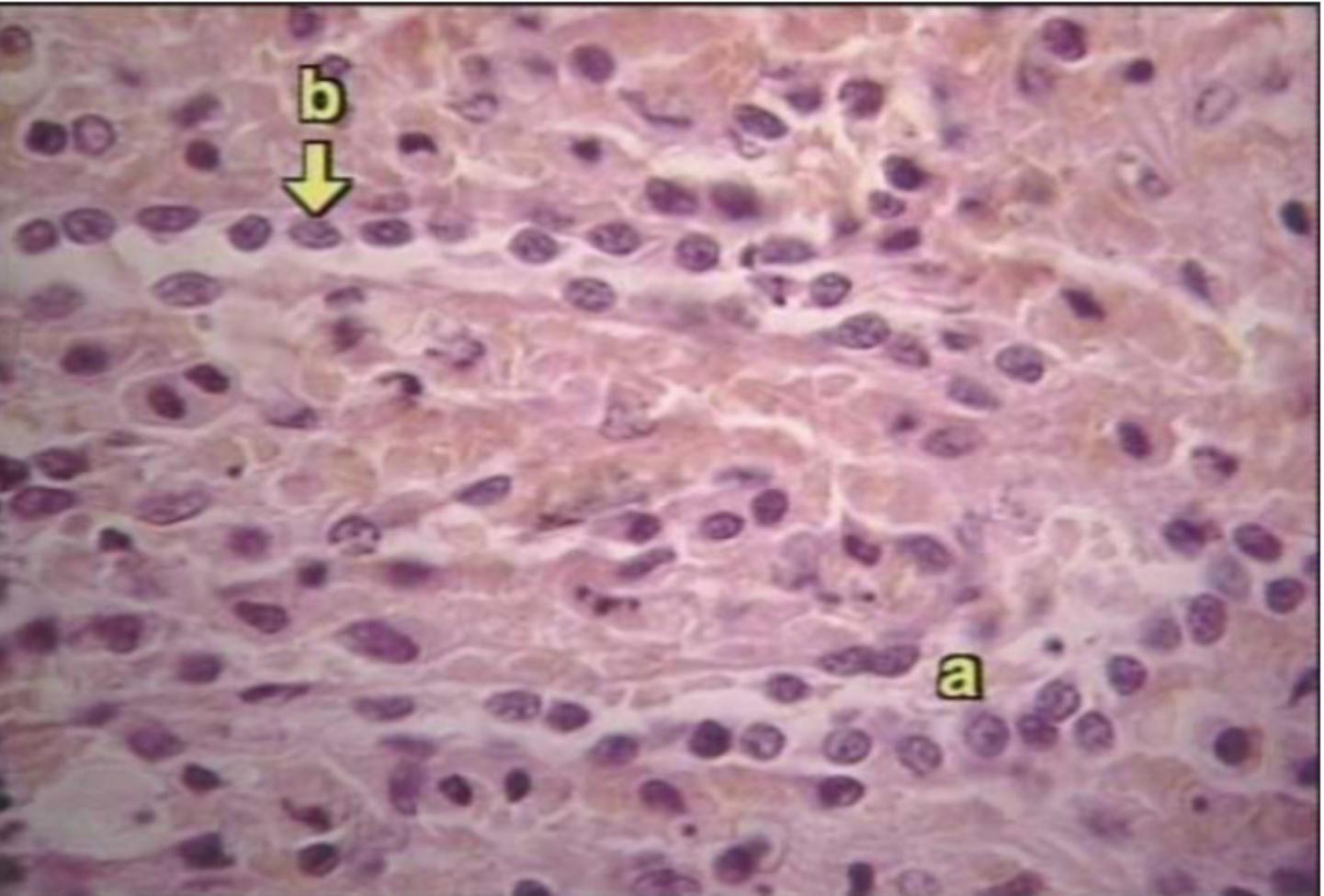
What organ is this?
Spleen
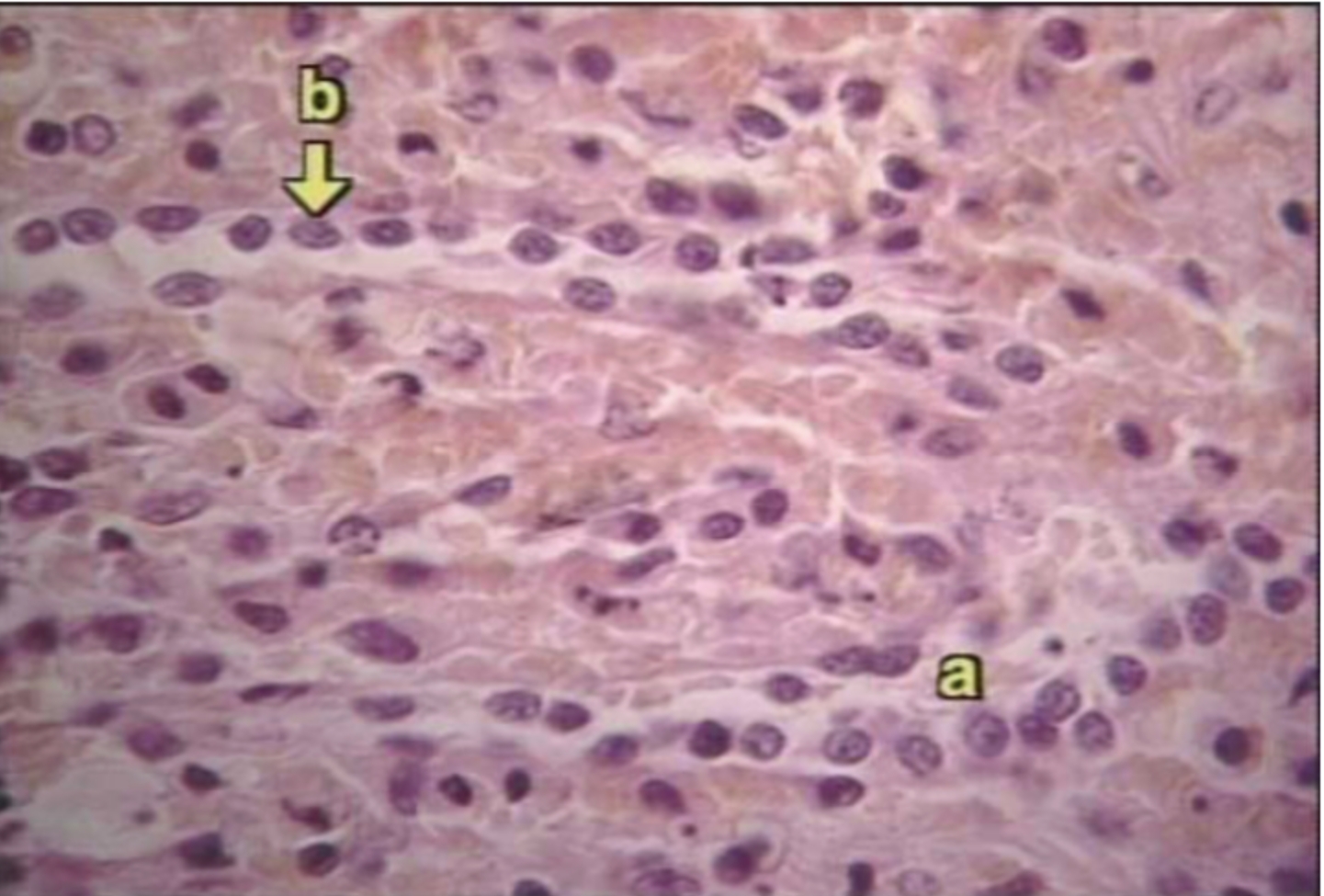
What is A?
Venus sinusoid
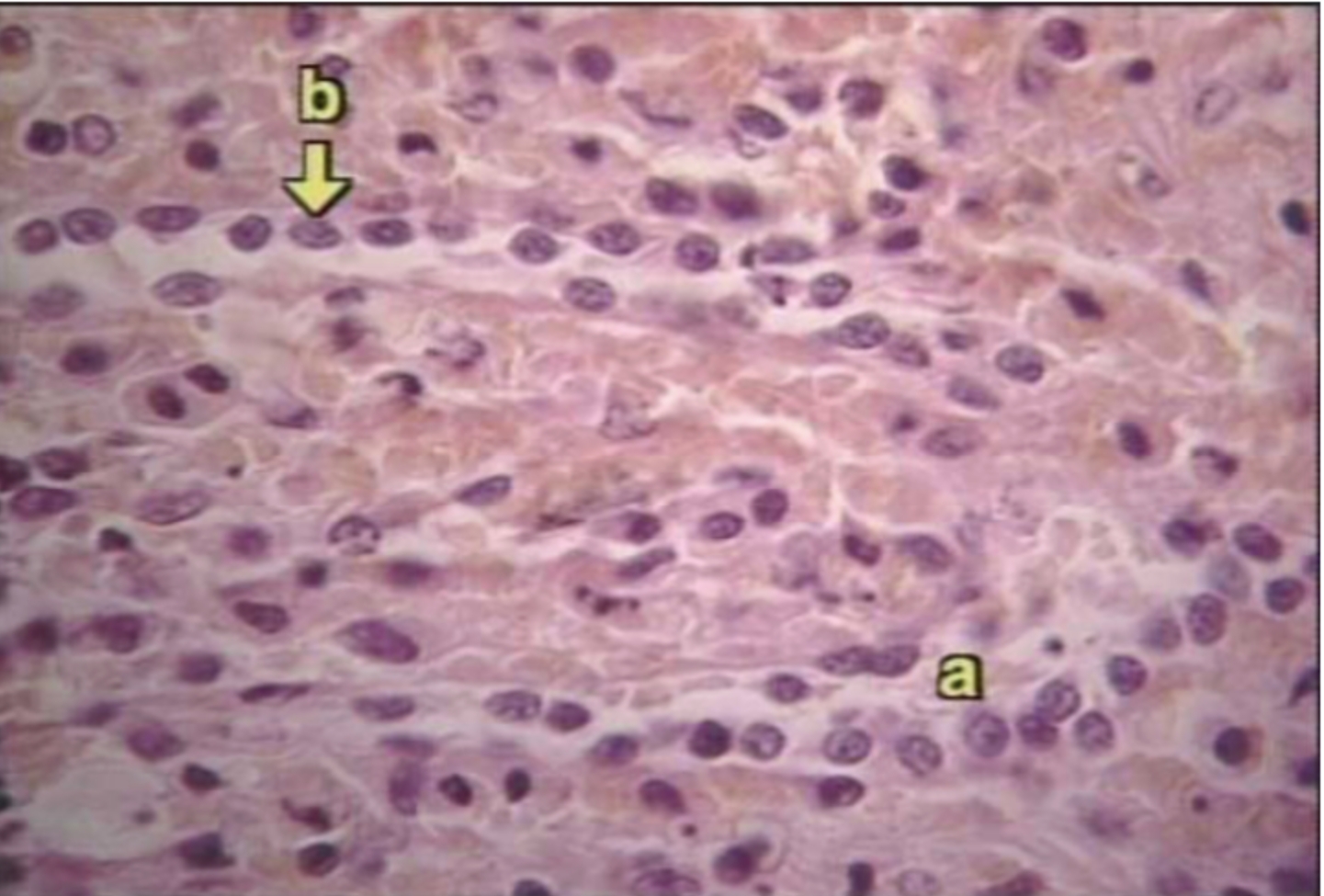
What is B?
Macrophages
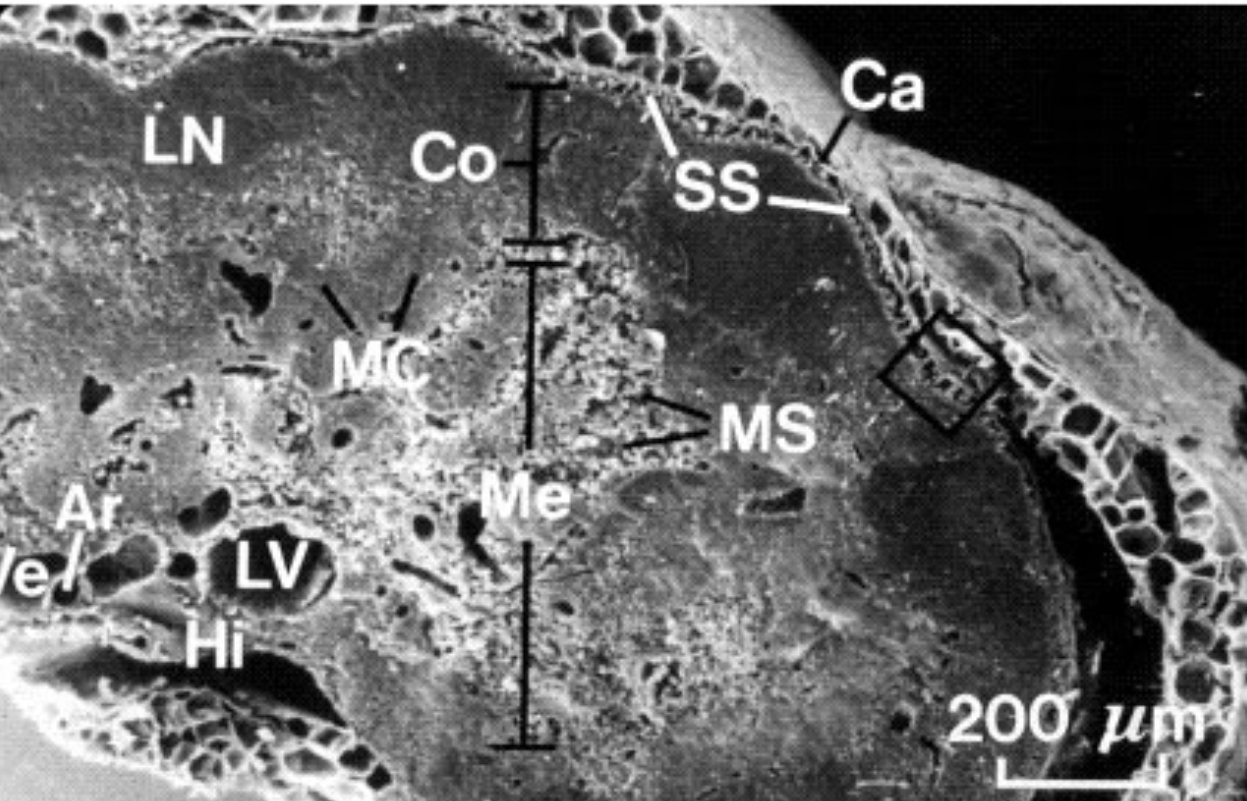
What is Ca?
Fibrous Capsule
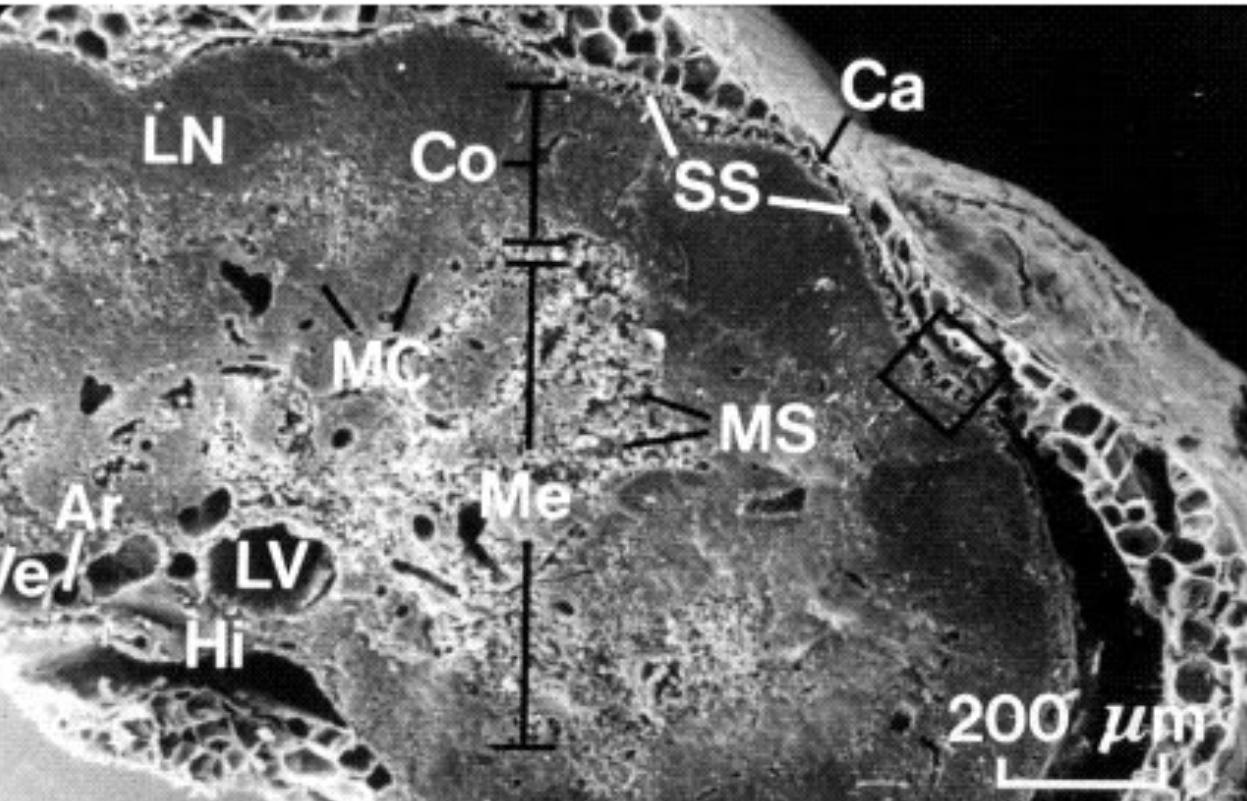
What is Me?
Medulla
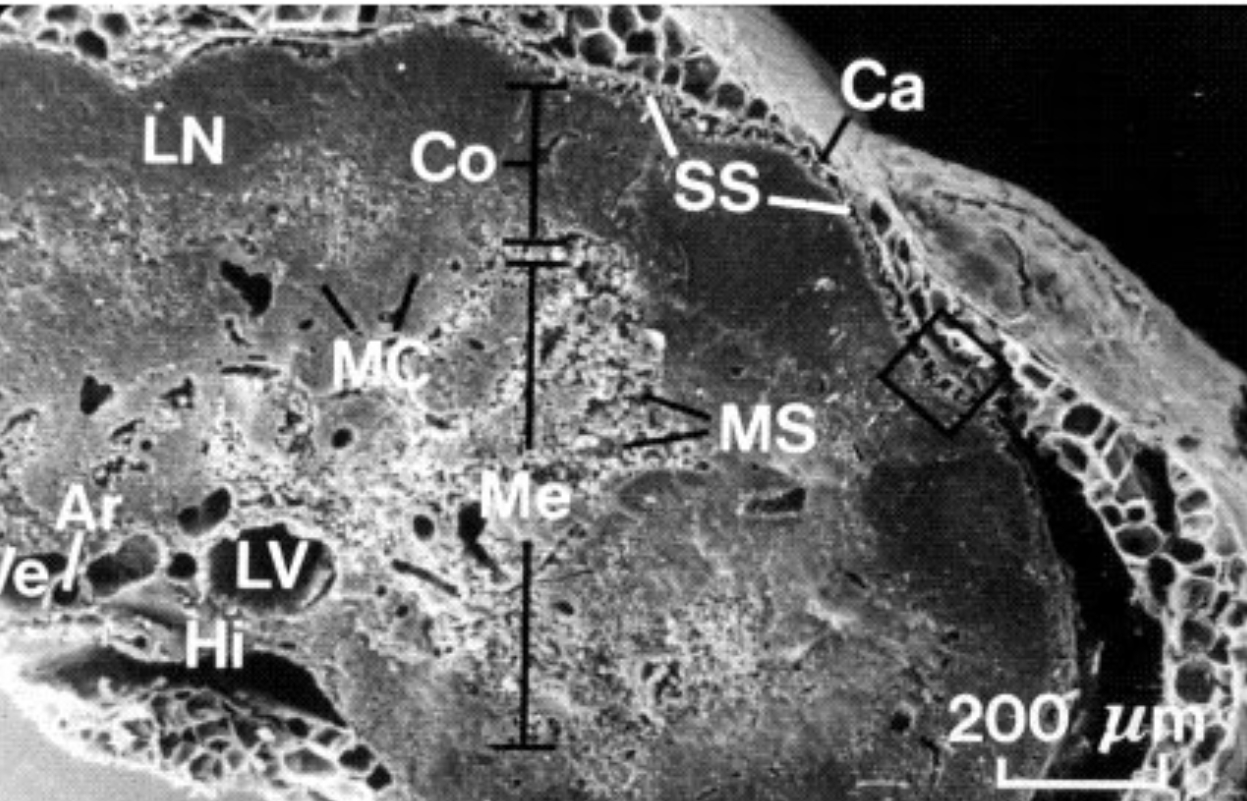
What is MS?
Medullary Sinus
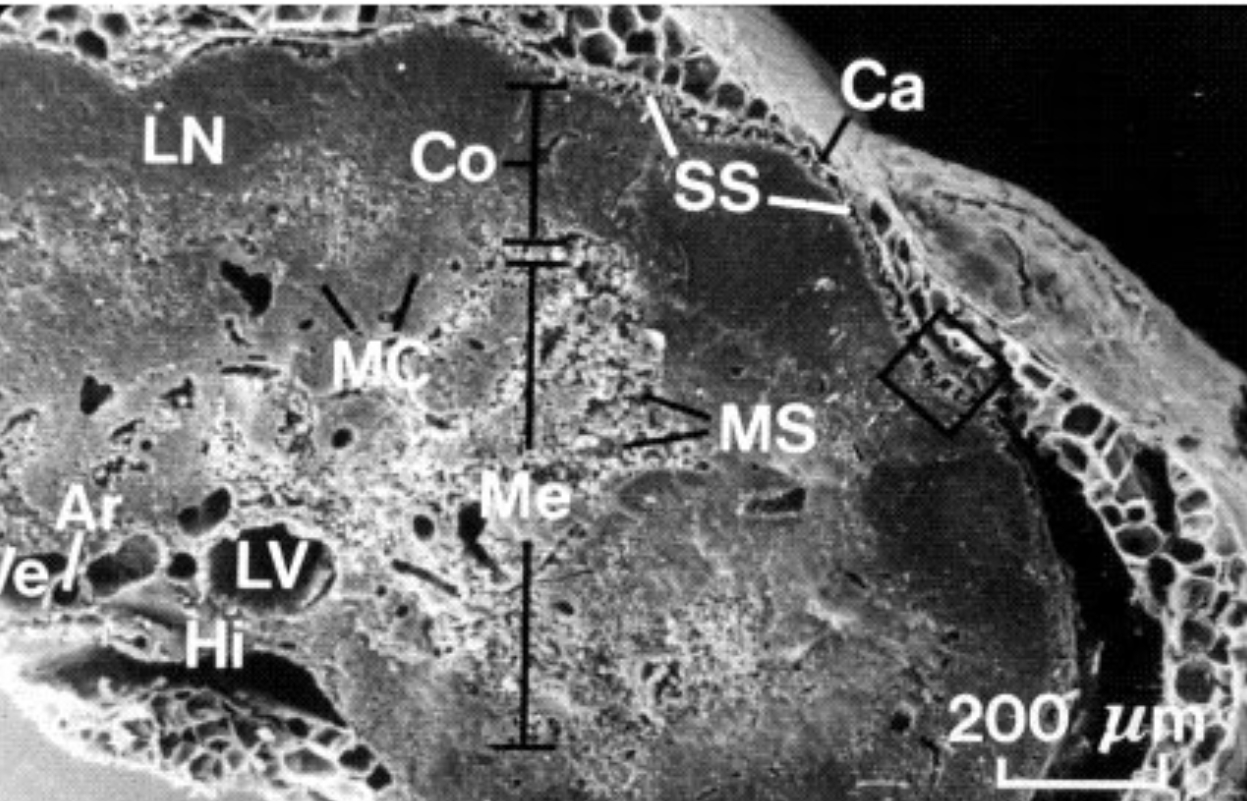
What is Co?
Cortex
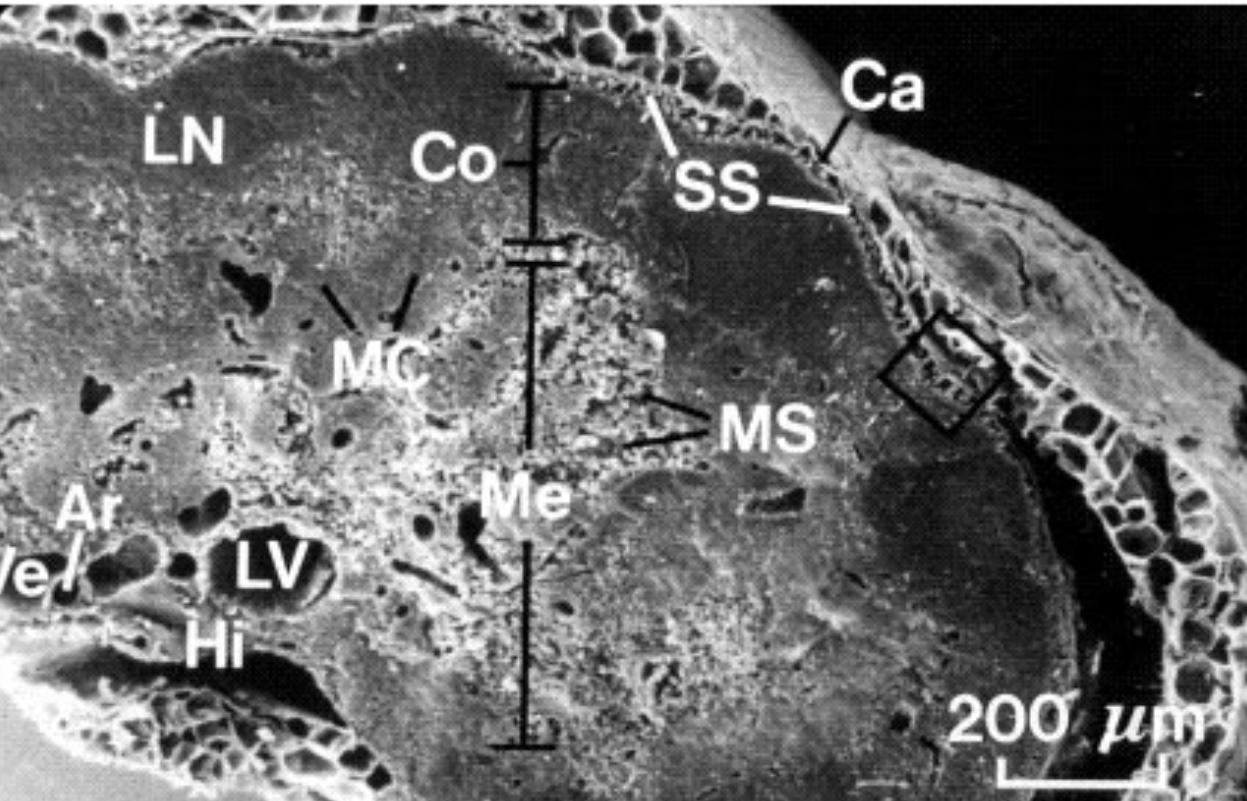
What is SS?
Subscapular sinus
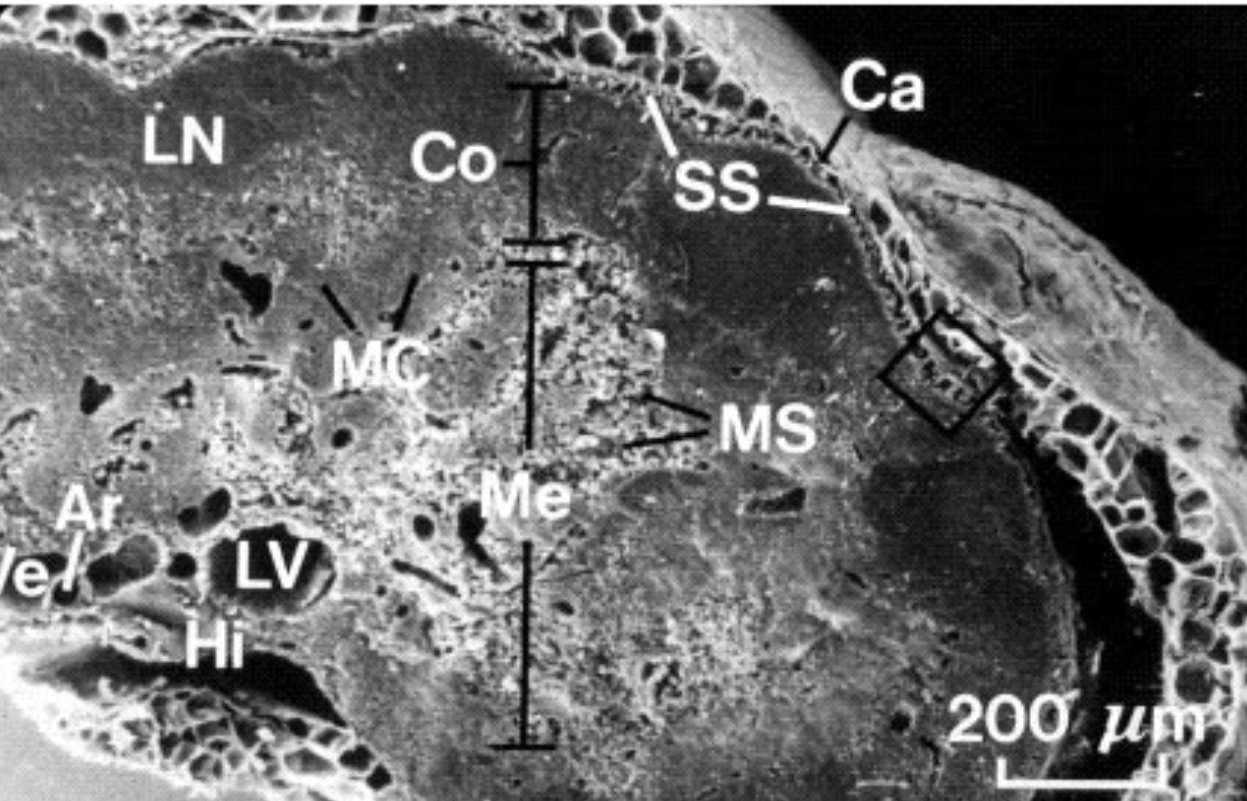
What is LN?
Lymphatic nodule
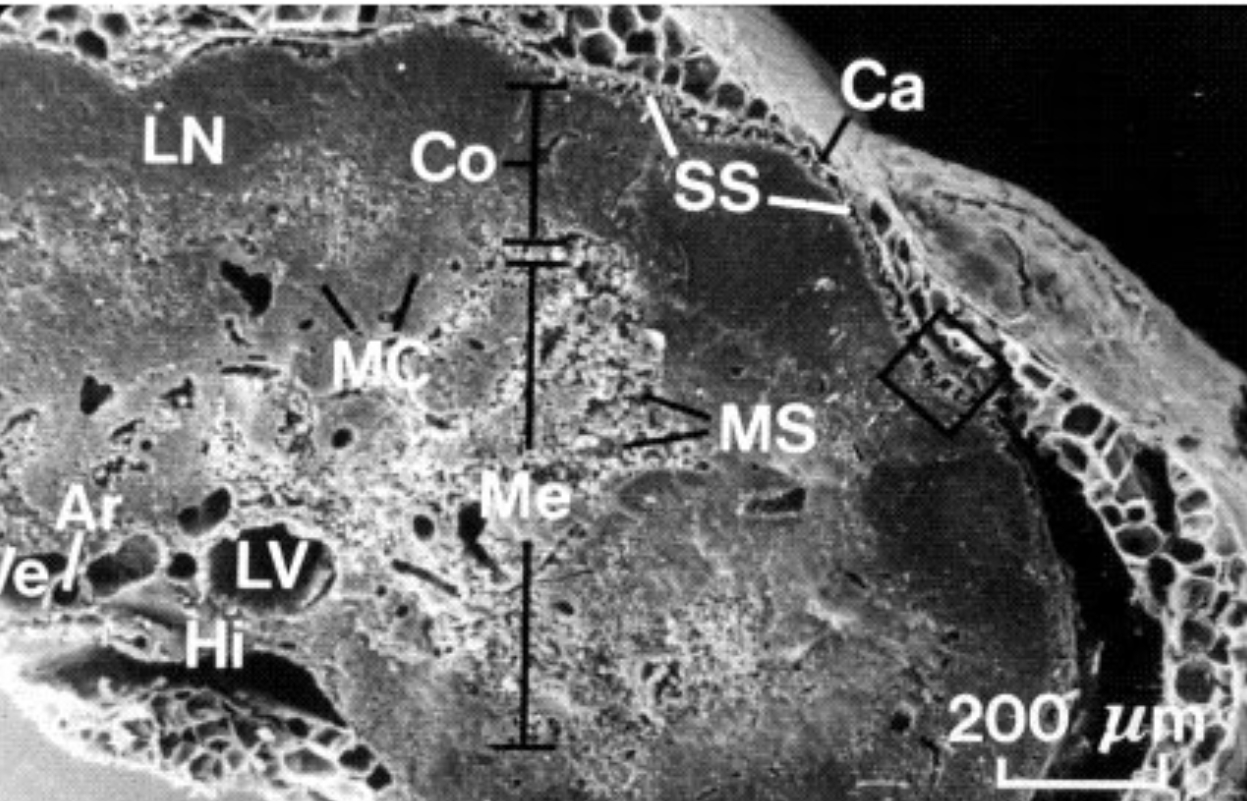
what is MC?
Medullary cords
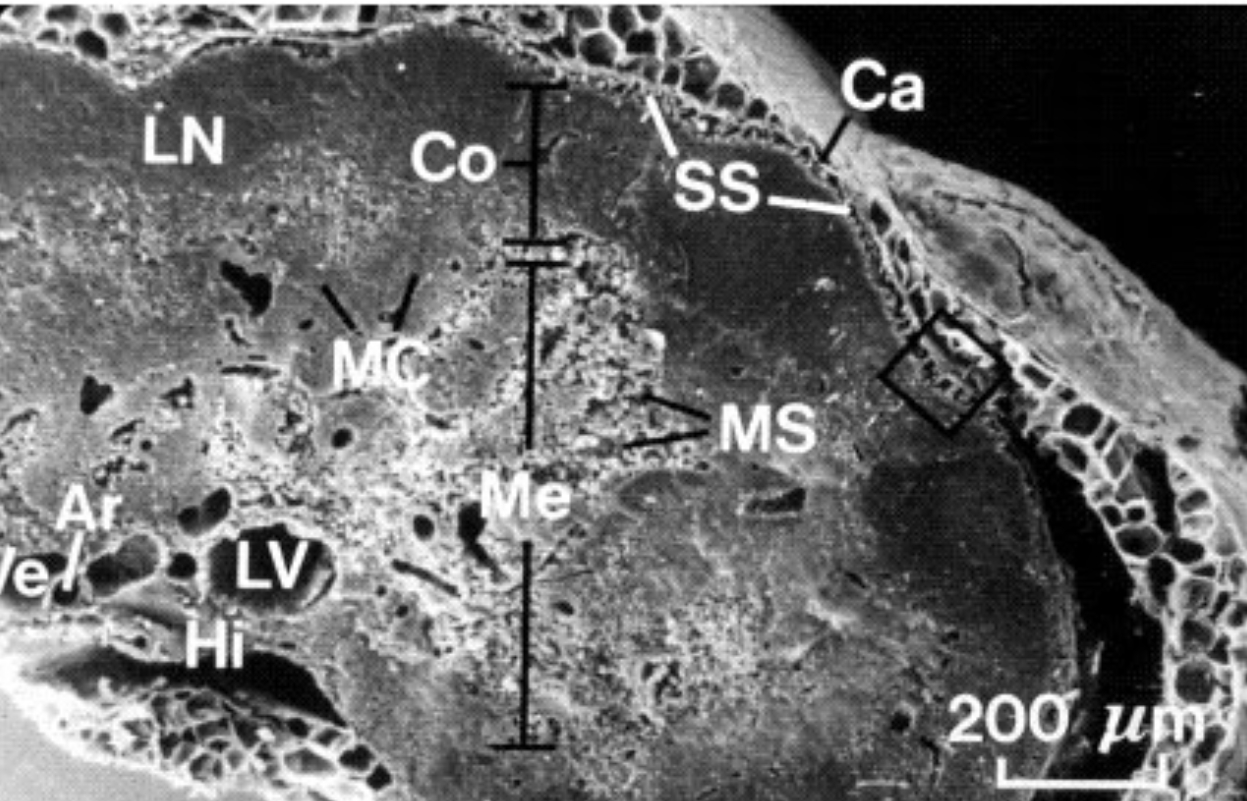
What is LV?
Lymphatic vessels
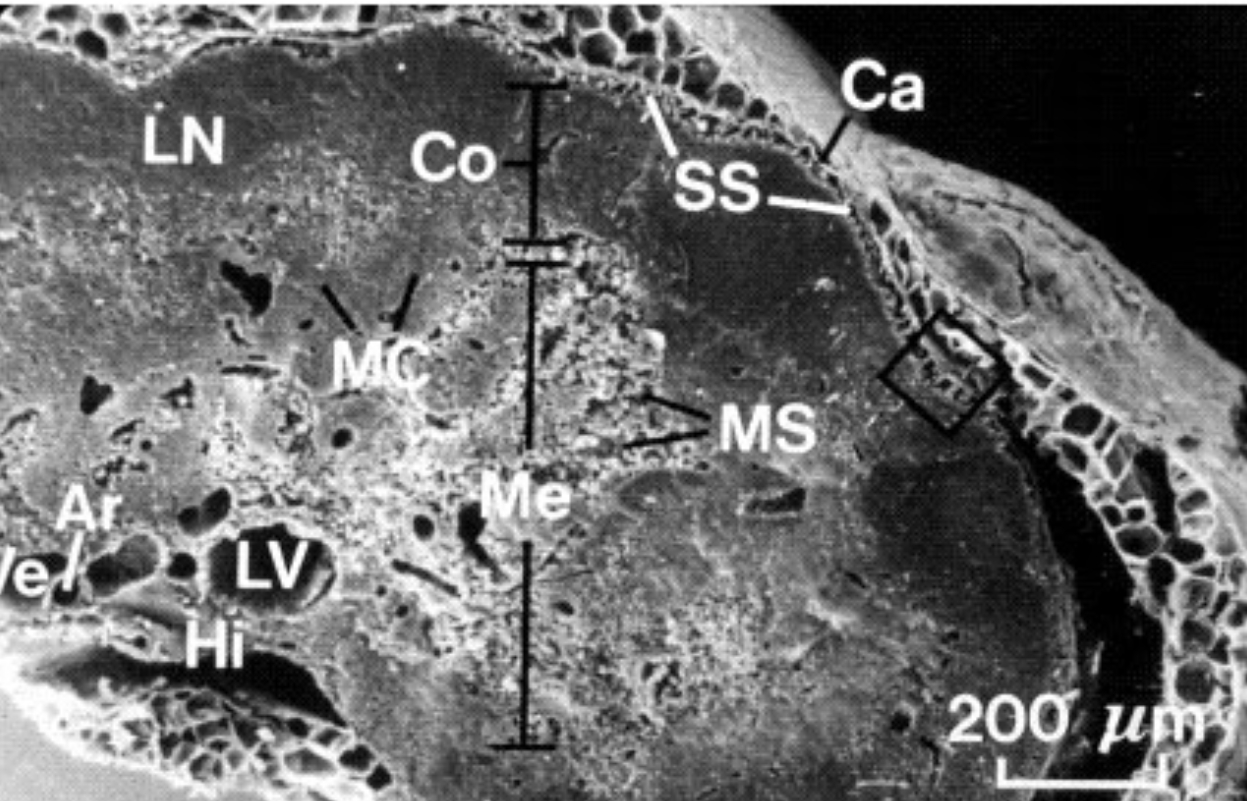
What is Hi?
Hilus
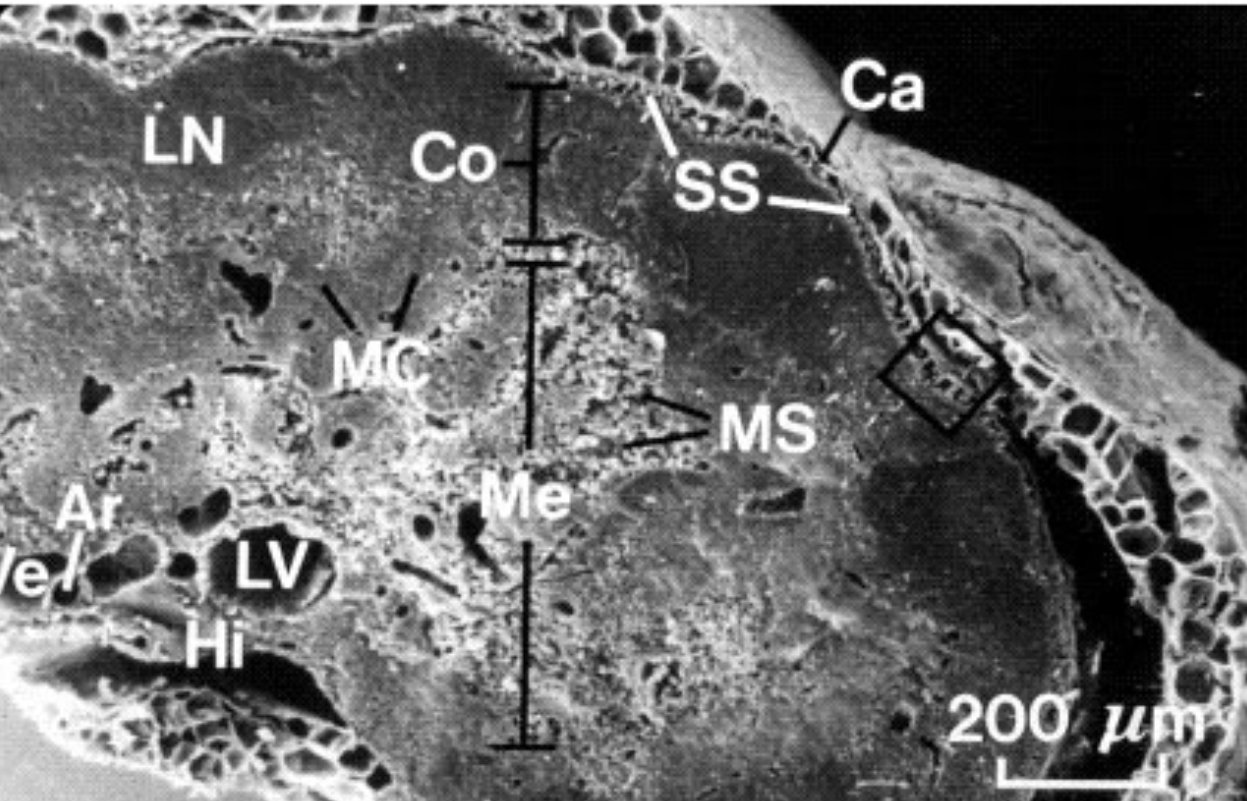
What is Ar?
Artery
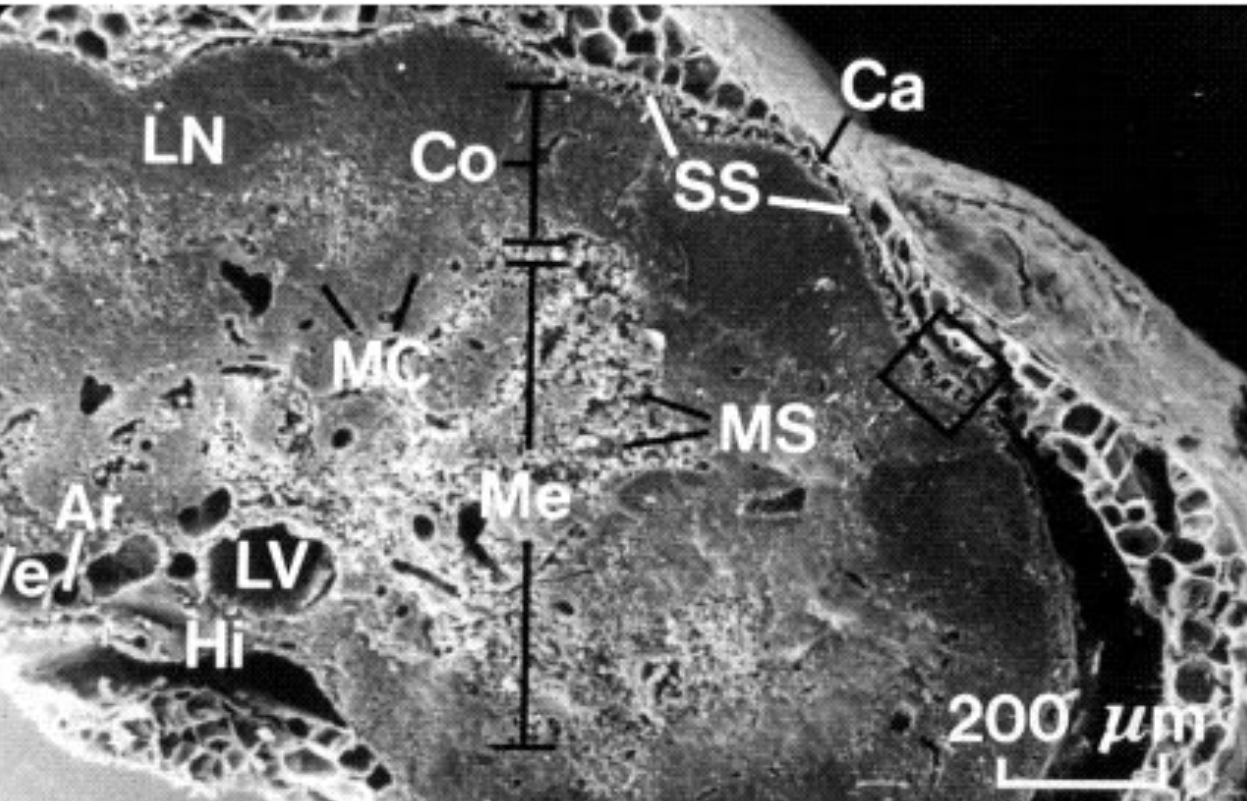
What is Ve?
Vein