Digestion and Absorption
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
What are the GI hormones
Gastrin
Gastric Inhibitory Peptide (GIP)
Vasoactive Intestinal Peptide (VIP)
Gastrin
Primarily by stomach when full
Increases secretion by parietal and chief cells of stomach
Increased mixing of stomach
Gastric inhibitory peptide (GIP)
Duodenum in presence of fats and glucose - carbohydrates
Inhibit gastrin (likely not major effect)
Increase secretion of insulin
Vasoactive intestinal peptide (VIP)
Duodenum in presence of chyme
Inhibits gastrin
Vasodilates intestinal capillaries
Increases intestinal secretions
Increases motility
Overall effect: aids in digestion/absorption
Recall, secretin and CCK increase…
Secretion of bile and pancreatic juice and inhibit gastric secretion and motility
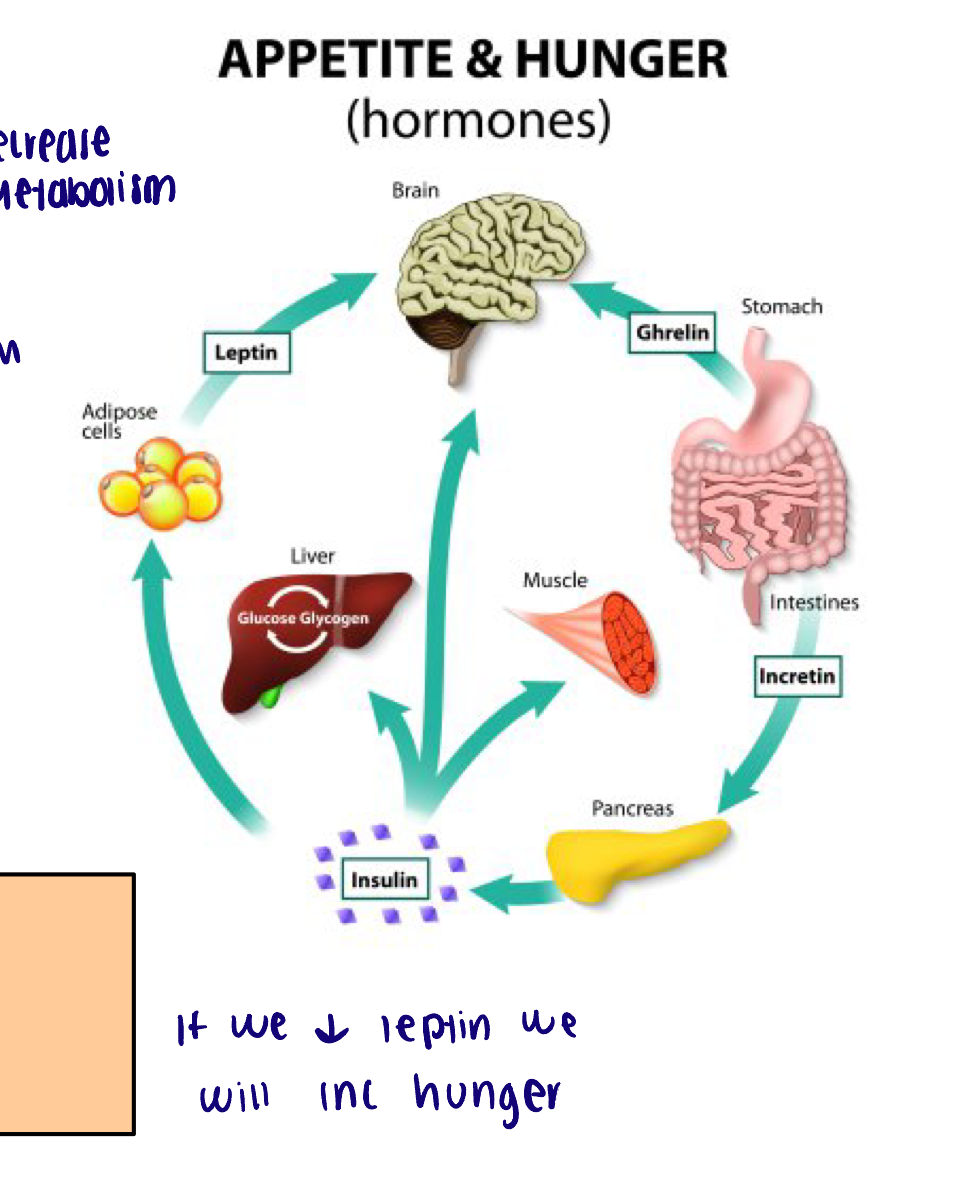
Hormones involved in hunger
Ghrelin
Leptin
Insulin
Ghrelin
Released by stomach when empty
Detected by hypothalamus
Stimulates hunger
Inhibits TSH which reduces ATP and ACTH which reduces glucose metabolism
Leptin
Released by adipocytes
Detected by hypothalamus
Inhibits hunger
Stimulates TSH and ACTH
Insulin
Released by pancreas
Same effect as leptin in the hypothalamus
Short term vs long term effects on hunger
Ghrelin and insulin have short-term effects on hunger and eating
Leptin is associated with more long-term regulation
Carbohydrate digestion
Two step procedure:
Salivary and pancreatic amylase
Brush boarder enzymes
Salivary and pancreatic amylase of carbohydrate digestion
Function at neutral pH
Begins in the mouth, inactivates at stomach pH
Begins again in duodenum
Break down complex carbs to di and trisaccharides
Brush boarder enzymes of carbohydrate digestion
Produce monosaccharides → hydrolysis reactions
Maltase - breaks down maltose
Sucrase - breaks down sucrose
Lactase - breaks down lactose
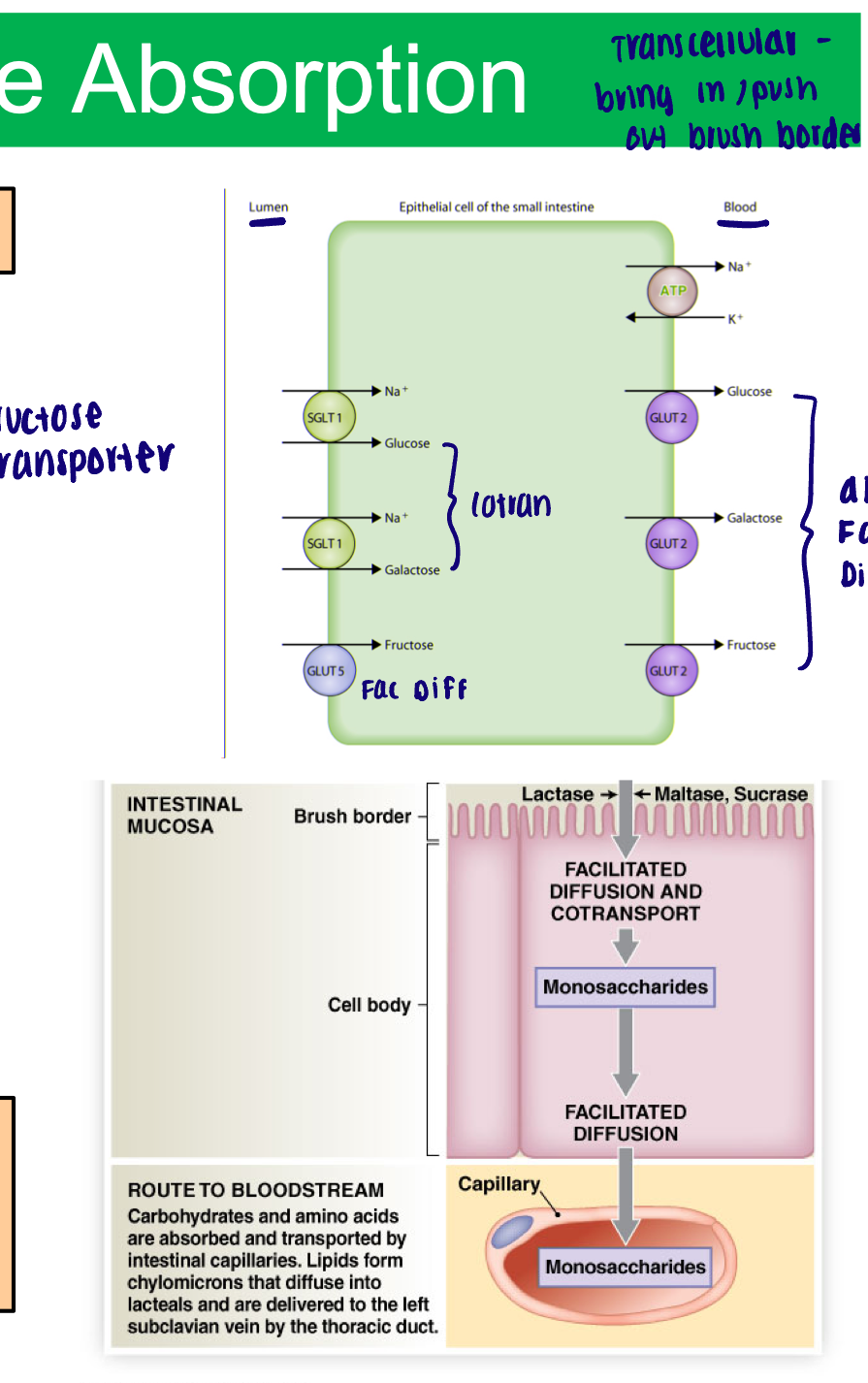
Carbohydrate absorption
Requires carrier proteins
Facilitated diffusion
Fructose
1 molecule through plasma membrane at a time
Co-transport
Glucose and galactose
Follows concentration gradient of Na+
All three removed to capillaries of intestinal villi via facilitated diffusion
Lipid digestion
Pancreatic lipase
Bile salts
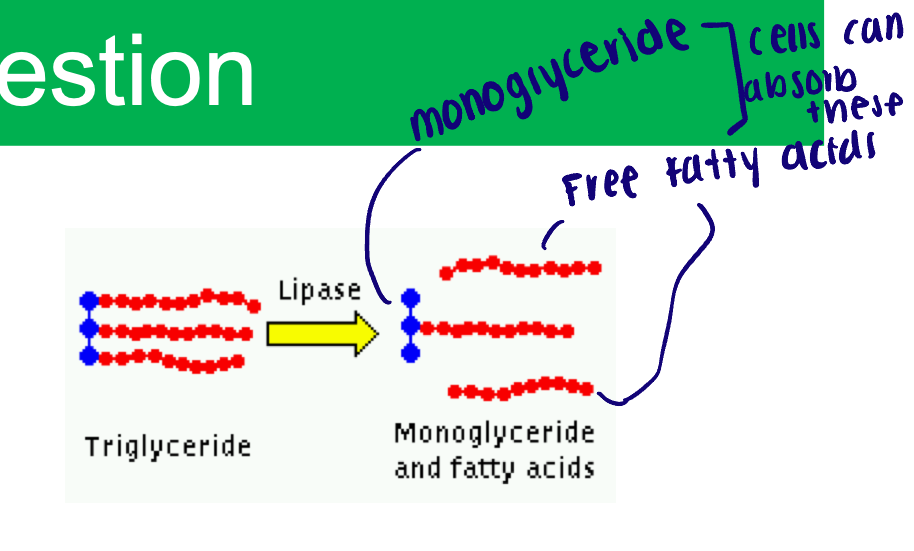
Pancreatic lipase of lipid digestion
Unlimited activity of lingual lipase
Functions at neutral pH
Water-soluble enzyme
Break down triglycerides into mono-glycerides
Bile salts of lipid digestion
Emulsify large lipid drops into tiny droplets
Creates surface area for lipase to work → break apart triglycerides - now there is more area to interact with the triglycerides
Lipids absorption
Micelles: bile salts (amphipathic) - surrounding fatty acids (hydrophobic)
Attach to plasma membrane - fatty acids diffuse into epithelium
ER of the epithelial cell:
Converts free fatty acids and monoglycerides back into triglycerides
Protein coat added
Now known as chylomicrons
Secreted from epithelial cell
Move into lacteals
Travel in lymph to enter circulation
Protein digestion
Mechanical digestion in mouth and acidity in stomach disrupt structure (folding) of proteins
Stomach acid activates pepsinogen → pepsin
Active at pH of 1.5-2.0
Breaks peptide bonds in polypeptide chains
Trypsin, chymotrypsin, elastase, carboxypepidase secreted from pancreas into duodenum (trypsin activates the others)
Cleave into short peptides and amino acids
Dipeptidases in the brush border cleave short peptides into amino acids
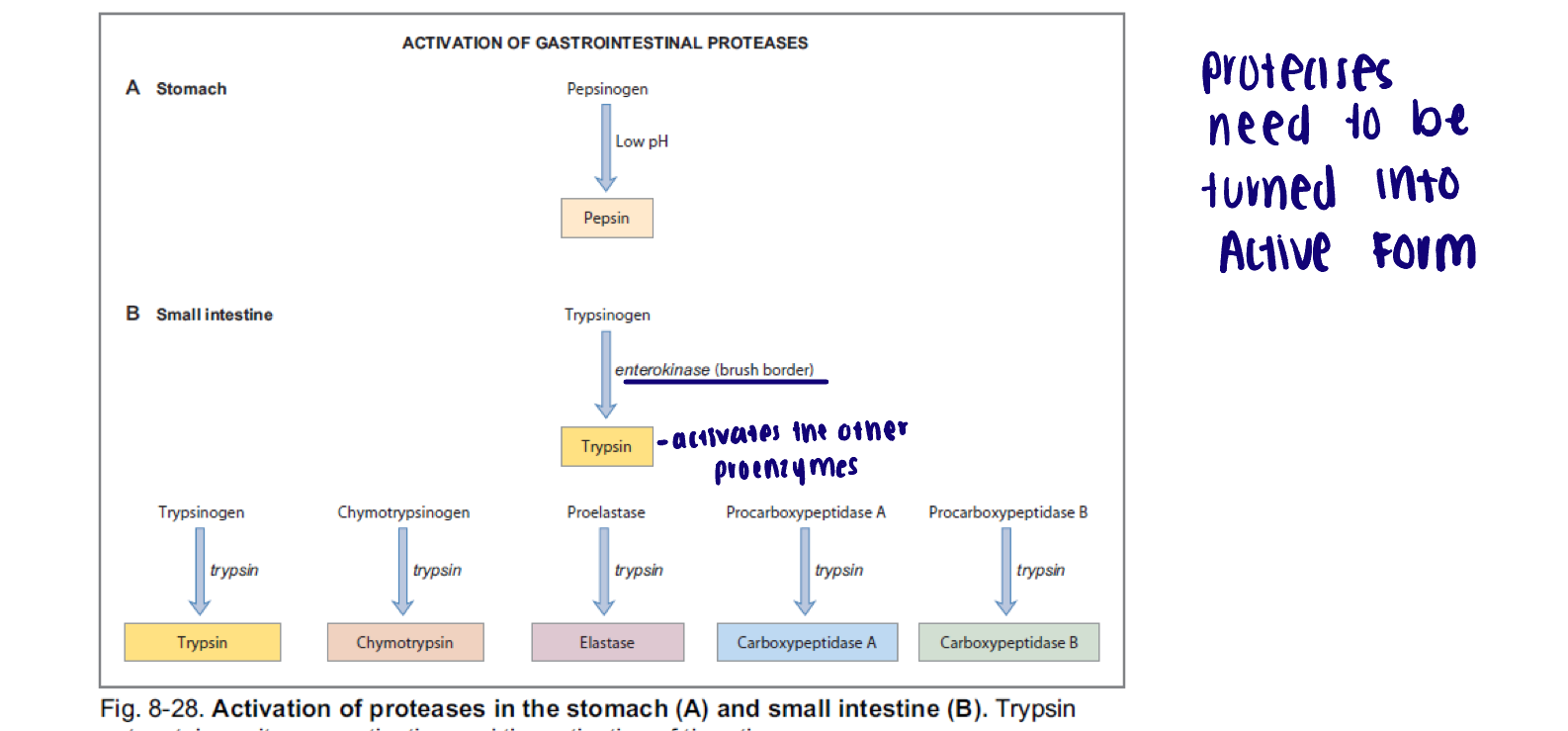
Activation of proteolytic enzymes
Stomach: low pH
Small intestine: Enterokinase, an enzyme in the brush border of the small intestine catalyzes the conversion of trypsinogen to trypsin
Trypsin then catalyzes conversion of multiple proenzymes into active forms
Protein absorption
Epithelium of small intestine will absorb amino acids, dipeptides, and tripeptides
Facilitated diffusion:
Basic amino acids only
Co-transport:
Acidic and neutral amino acid via Na+ co-transport
Di and tri peptides via H+ co-transport
Broken down into amino acids within the epithelial cell
Amino acids removed to capillaries of intestinal villa via facilitated diffusion and co-transport (depends on the amino acid)
Water absorption
Not actively absorbed or secreted
Follows osmotic gradient
If chyme is dilute (watery) water will move across intestinal wall to interstitial fluid
If chyme is concentrated water will move into the lumen of the intestine
As nutrients are absorbed in the small intestine - lowers solutes present in the lumen
Water follows
90% reabsorbed in the small intestine
8-9% reabsorbed in the large intestine
Ions absorption
Na+ (most abundant and the more we eat the more is absorbed)
Active transport, facilitated diffusion, co-transport
Aldosterone can increase Na+ absorption (insertion of Na+/H+ exchanger in small intestine)
Calcium and phosphate
Active transport
Calcitriol (active vitamin D) increases Ca2+ and phosphate absorption (variety of calcium transporters and Na+/PO4- co-transporter)
Magnesium, potassium, chloride, ion, bicarbonate
Facilitated diffusion/carrier proteins
Vitamin absorption
Water soluble (B [8], and C)
Diffusion
Exception - B12, which must bind intrinsic factor and then be actively transported
Fat soluble (A,D,E,K)
Sneak into micelles
Absorbed along with fatty acids