Radiographic Techniques and Patient Assessment
1/161
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
162 Terms
Settings for PA chest X-ray.
110 kVp @ 1.5 mAs
Settings for lateral chest X-ray.
110 kVp @ 4 mAs
Settings for pelvic X-ray.
80 kVp @ 12 mAs
Centering point for pelvic X-ray.
2" below ASIS, internally rotate 15-20 degrees putting greater trochanter in profile
Settings for KUB X-ray.
80 kVp @ 10 mAs
Upright KUB
CR centered 2" above iliac crest.
Supine KUB
CR centered at iliac crest level.
Settings for foot X-ray.
60 kVp @ 1.25 mAs
AP Axial Foot
CR 10 degrees towards heel, centered at base of 3rd metatarsal.
Obl Foot
Medial rotation of 30-40 degrees for imaging. CR perpendicular to IR
UGI
Upper Gastrointestinal series imaging.
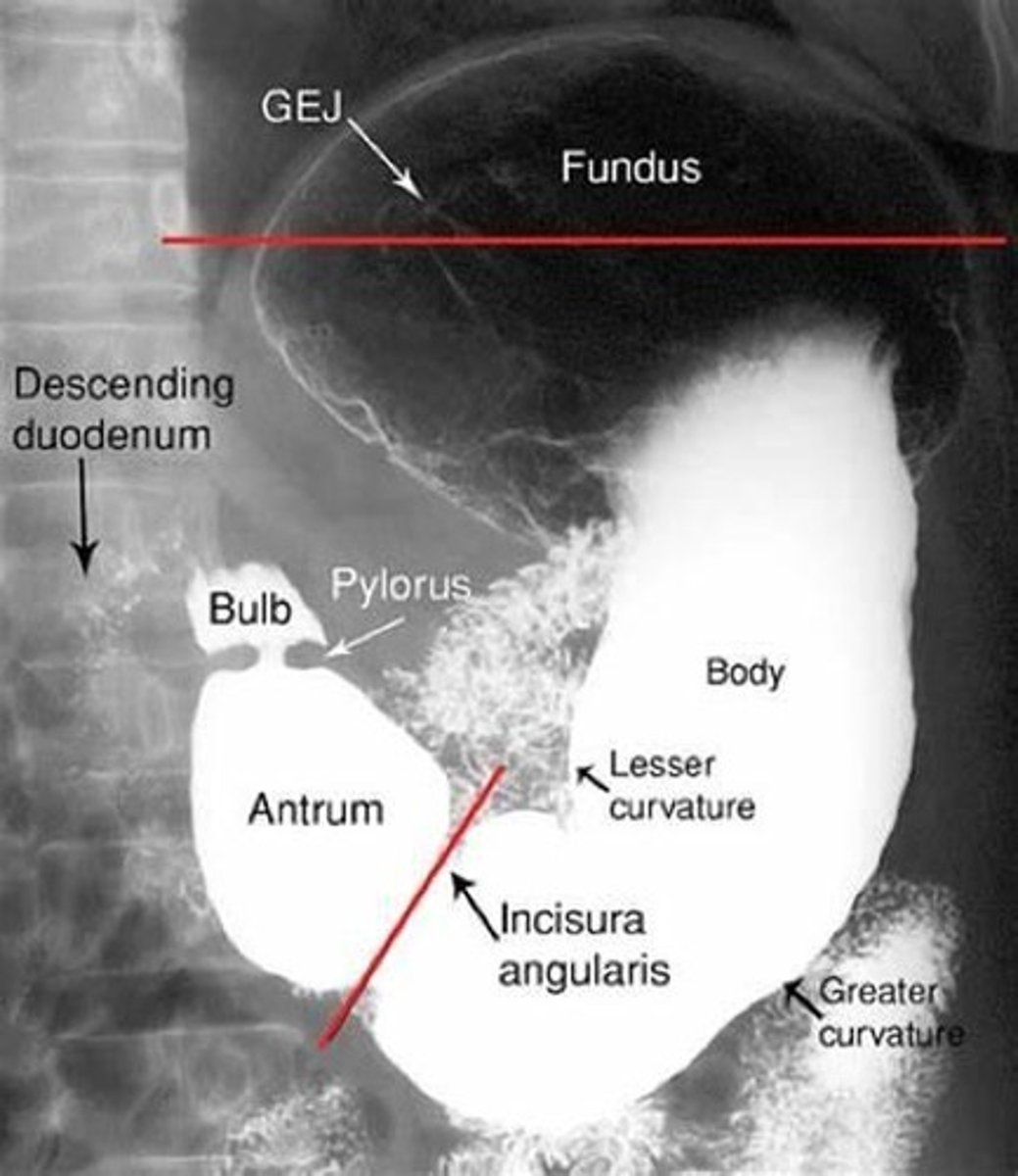
Settings for AP UGI X-ray
80 kVp @ 3.5 mAs
Centering point for AP UGI X-ray.
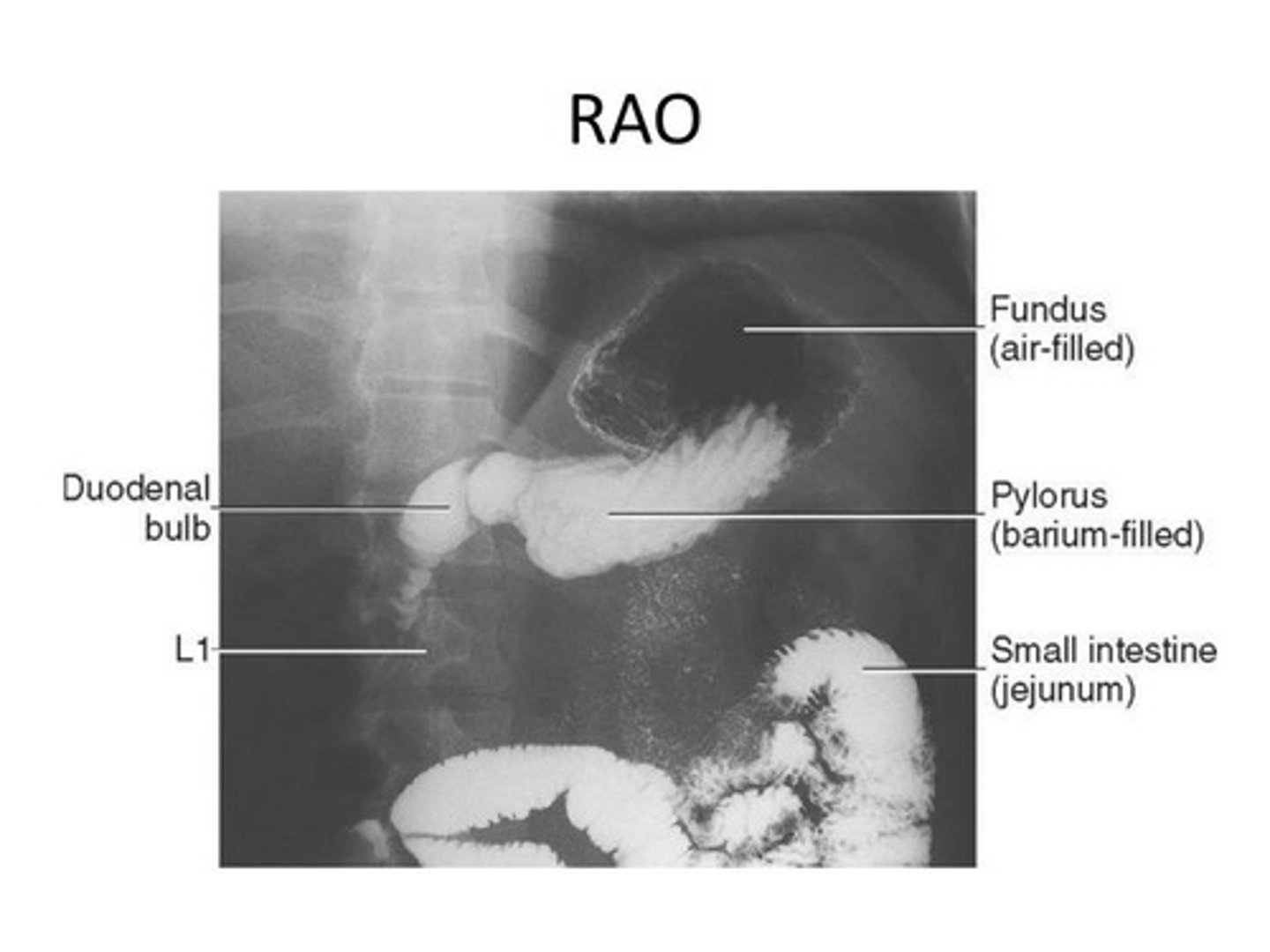
Between the vertebral border and lateral border and 1-2” above lower rib margin (L1-2). Barium filled fundus and doudenal bulb
Settings for lower leg (tib-fib) X-ray.
75 kVp @ 2.5 mAs
Settings for pediatric chest X-ray.
80 kVp @ 0.5 mAs
PA CALDWELL Sinuses
80 kVp @ 8 mAs
CR perpendicular to IR
CR exits at nasion. GAL parallel to IR
Petrous ridges lower 1/3 of orbits, OML 15 degrees from horizontal
Frontal and anterior ethmoid sinus view
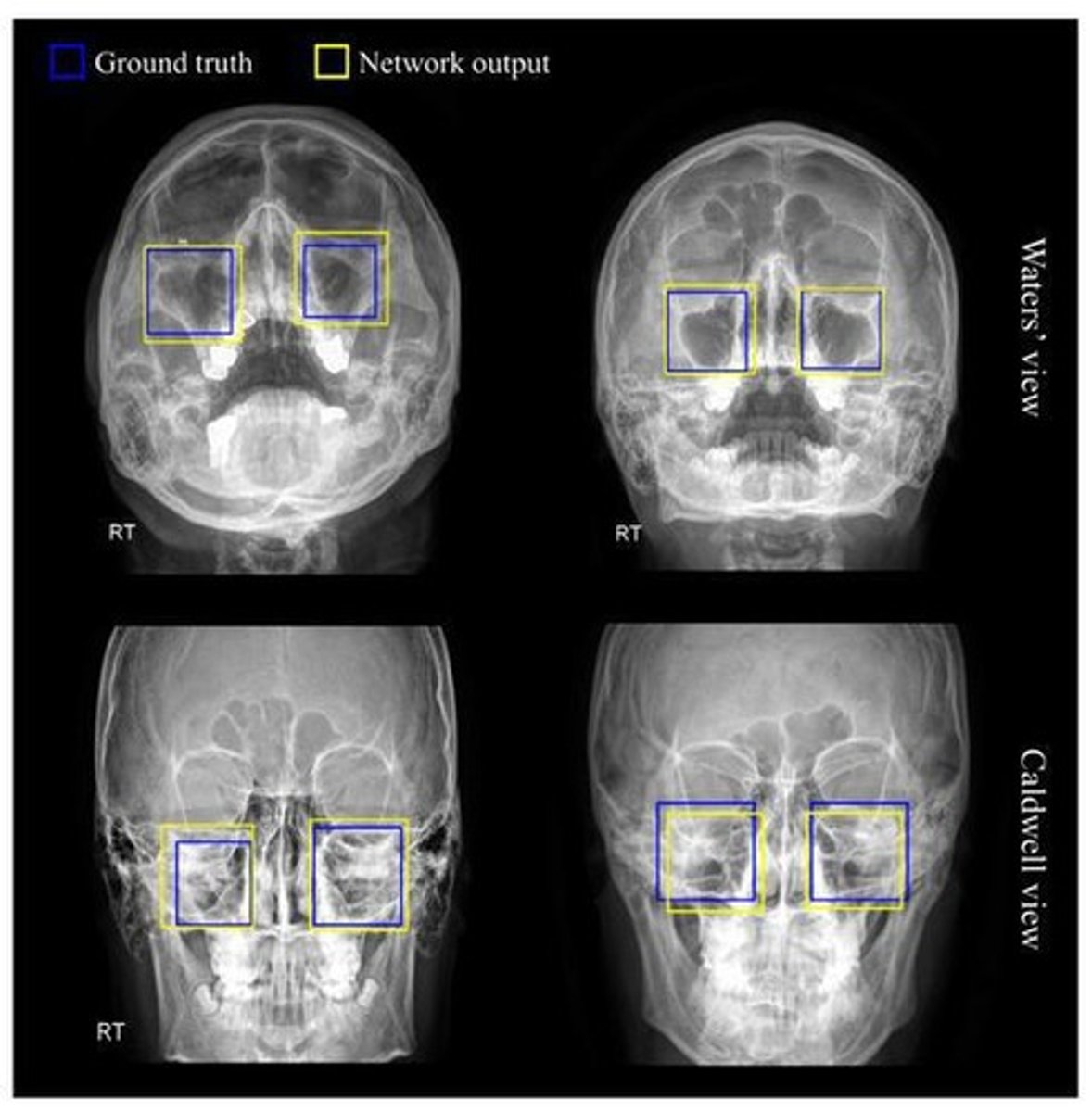
Parietoacanthial WATERS Sinuses
80 kVp @ 8 mAs
CR perpendicular to IR
CR exits at acanthion. MML parallel to IR
Petrous ridges below maxillary sinuses, OML 37 degrees from IR
Maxillary sinus view
Submentovertex (SMV) sinuses X-ray.
80 kVp @ 12 mAs
CR perpendicular to IR
CR entering between gonions, IOML parallel to IR
GAL perpendicular to IR
Ethmoid and sphenoid in view
Peds KUB
75 kVp @ 2 mAs
LATERAL sinuses X-ray
80 kVp @ 3 mAs
CR perpendicular to IR
CR centered between EAM and outer canthus, IOML parallel to floor
IPL perpendicular to IR
Demonstrated all 4 sinuses
Knee PA Axial Weight Bearing (Rosenberg Method)
Uses 40" SID with 10° caudad CR. Knees flexed 45°; patella on bucky
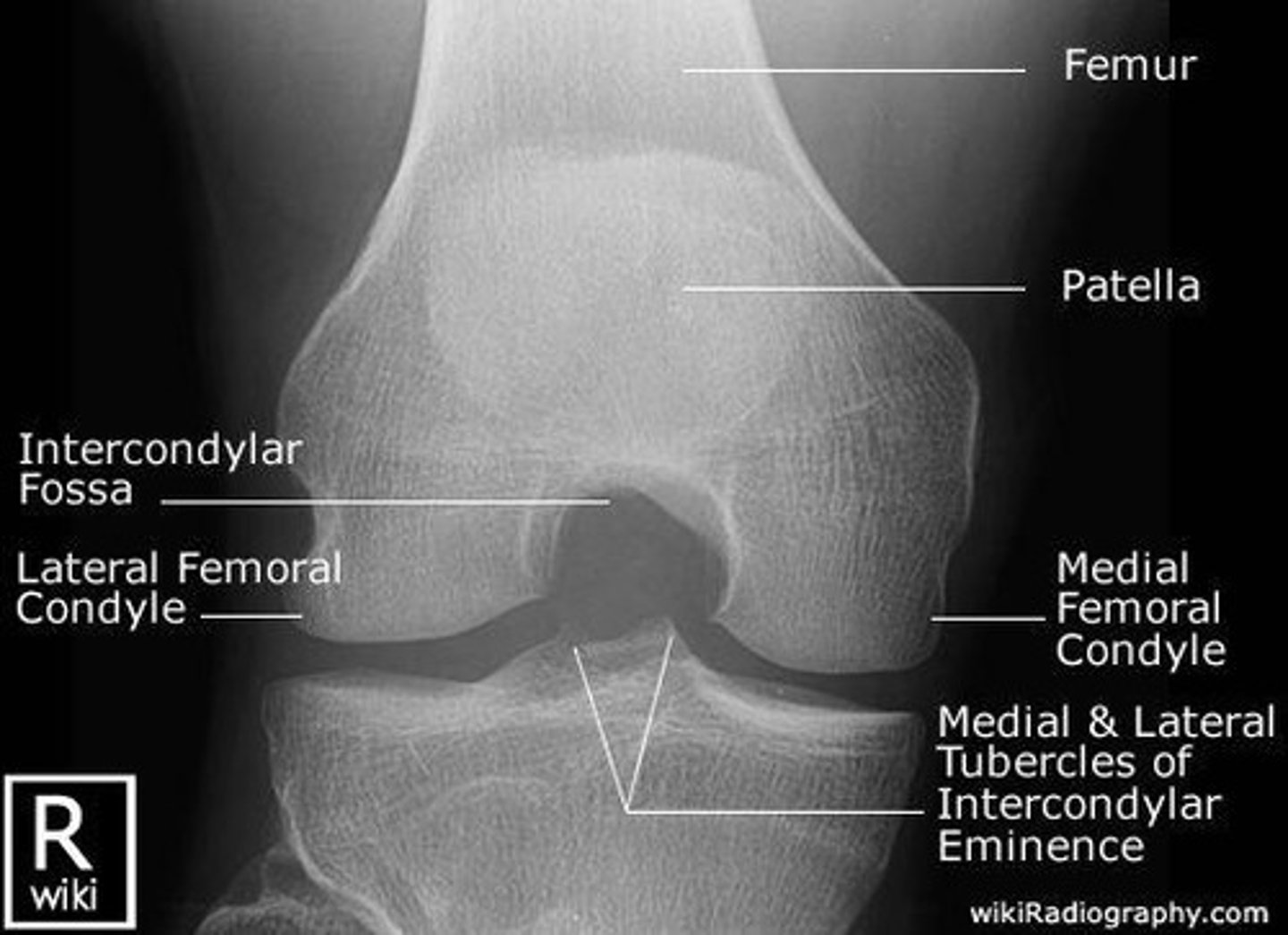
Knee Intercondylar Fossa Tunnel
rosenberg, beclere, holmblad, camp coventry
Camp Coventry Method
Prone position, 40-50° flexion, 40-50° caudad CR. (PA Axial)
Holmblad Method
Kneeling position, 60-70° flexion, perpendicular CR. (PA)
Beclere Method
Supine, 40-45° flexion, 40-45° cephalic CR. (AP Axial)
UGI RAO Projection
Prone, 40-70° rotation, CR above lower rib margin.
Barium filled body and pylorus
Gastric Peristalsis
More active in RAO position.
LPO Projection
30-60° posterior oblique, CR above lower rib margin.
Barium
Right Lateral UGI
Recumbent, CR at L1-2 level.
Right retrogastric space
LGI PA Axial Projection
Prone, 30-40° caudad CR enters at crest level and exits at ASIS.
Rectosigmoid with less superimposition than PA
LGI PA Oblique RAO
35-45° oblique, CR lateral to midline at crest level.
Visualized in LGI PA Oblique RAO projection.
Opened Right “Hepatic” Colic Flexure
LGI PA Oblique LAO
35-45° oblique, CR lateral to midline.
Visualized in LGI PA Oblique LAO projection.
Opened Left “Splenic” Colic Flexure
AP Axial LGI
Supine, 30-40° cephalad CR enters below ASIS.
Rectosigmoid with less superimposition than PA
Decubitus Position
Horizontal beam for air fluid levels.
Upside of both ascending and descending colon
Body Habitus Types
Sthenic, Hypersthenic, Asthenic, Hyposthenic classifications.
Sthenic Habitus
Average body type, 50% of population.
Hypersthenic Habitus
Overweight, stomach high and horizontal. 5%
Asthenic Habitus
Very thin, stomach low and vertical. 10%
Hyposthenic Habitus
Thin, stomach 'J' shaped, lower placement. (35%)
Grid Usage
Used for parts 10cm (4”) thick, 70+ kVp.
Patient Immobilization Devices
Cervical collar, backboard, air splint, traction splints.
Shock Pants
Used to slow hemorrhage in trauma patients.
Contrast Media for UGI
Barium sulfate
Water soluble iodinated contrast for perforation.
Water soluble
Contrast medium requiring 80-90 kVp for imaging.
Barium
Contrast medium requiring 110-125 kVp for imaging.
CR for Sthenic UGI RAO
Center CR to duodenal bulb at L1 level. 45-55 degree
CR for Asthenic UGI RAO
Center CR 2 inches below L1, 40-degree oblique.
CR for Hypersthenic UGI RAO
Center CR 2 inches above L1, 70-degree oblique.
Evaluation criteria for UGI RAO
Duodenal bulb in profile, stomach and duodenum visible.
Barium filled body and pylorus
Respiration during exposure UGI RAO
Suspend respiration and expose on expiration.
Indications for UGI RAO
Used for diagnosing polyps and ulcers.
PA Projection UGI RAO
Patient prone with arms beside head, MSP aligned.
CR for PA Sthenic
Center CR at pylorus, 1 inch left of vertebral column.
CR for PA Asthenic
Center CR 2 inches below L1.
CR for PA Hypersthenic
Center CR 2 inches above L1, nearer midline.
Evaluation criteria for PA
Entire stomach and duodenum in profile.
Indications for PA
Used for polyps, diverticula, gastritis, bezoars.
Right Lateral Position
Patient recumbent, shoulders and hips in true lateral.
CR for Right Lateral Sthenic
Center at duodenal bulb, 1-1.5 inches anterior to MCP.
CR for Right Lateral Hypersthenic
Center about 2 inches above L1.
CR for Right Lateral Asthenic
Center 2 inches below L1.
Evaluation criteria for Right Lateral
Retrogastric space demonstrated, pylorus well visualized.
LPO position
Patient rotated 30-60 degrees from supine position.
CR for LPO Sthenic
Center CR at level of L1, 45-degree oblique.
Indications for LPO
Used for gastritis and ulcers.
AP Projection
Patient supine, MSP aligned to midline of table.
CR for AP Sthenic
Center at L1, midway between xiphoid and ribs.
Indications for AP
Demonstrates hiatal hernia, diaphragm, and lung fields.
Additive diseases
Increase tissue thickness, atomic number, or density.
Destructive diseases
Decrease tissue thickness, atomic number, or density.
kVp Increase
Required increase of 5-15% for certain diseases.
Empyema
Pus in thoracic cavity increases tissue density.
Pleural Effusions
Fluid in pleural cavity displaces lung tissue density.
Pneumoconiosis
Dust inhalation causes fibrotic lung tissue changes.
Pneumonectomy
Lung removal increases density on affected side.
Pneumonia
Lung inflammation fills alveoli with denser fluid.
Pulmonary Edema
Fluid in lungs increases density, common in heart failure.
Tuberculosis
Mycobacterial infection increases lung fluid density.
Aortic Aneurysm
Dilation of aorta increases affected area's thickness.
Ascites
Fluid in peritoneal cavity increases abdominal tissue thickness.
Calcified Stones
Calcium deposits in organs increase tissue atomic number.
Cirrhosis
Liver fibrosis leads to enlargement and ascites.
Osteoblastic Metastases
Cancer spread to bone causes new bone growth.
Osteochondroma
Tumor in bone/cartilage increases bone thickness.
Paget's Disease
Increased bone cell activity leads to thickened bones.
Sclerosis
Chronic inflammation hardens bone, increasing density.
Destructive Diseases
Conditions that decrease tissue thickness and density.
Emphysema
Lung over-distention decreases tissue density.
Pneumothorax
Free air in pleura decreases lung tissue density.
Aerophagia
Abnormal air swallowing dilates stomach, reducing density.
Bowel Obstruction
Air/fluid accumulation decreases bowel tissue density.
Osteolytic Metastases
Malignancies destroy bone, reducing density.
Osteomalacia
Bone mineralization defect decreases bone density.
Osteoporosis
Failure of osteoblasts reduces bone matrix density.
Multiple Myeloma
Plasma cell tumor causes osteolytic bone areas.
Patient Assessment
Evaluate patient status before starting exams.
Radiation Protection
Minimize radiation exposure to patients and staff.
ALARA Principle
Keep radiation exposure As Low As Reasonably Achievable.