Musculoskeletal System (copy)
1/119
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Nur152 PVCC Exam 4
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
120 Terms
Skeletal
Bones, cartilagage, ligaments, and tendons
Movement
___________ occurs when the muscles contract
GI tract, BV, Bladder
smooth muscle is found in the
body alignment, balance, coordination, joint mobility
the way people move involves
Factors affecting mobillity
developmental stage
nutrition
lifestyle
stress
external environment
culture
presence of disease
supporting structure of the musculoskeletal system
ligaments, tendons, cartilage
Joints
where 2 or more bones come together and allow specific movements in relation to one another
2 types: synovial and nonsynovial
hinge joint
allow for flexion and extension
ex. elbow joints, interphalangeal joins, knee joints
spheroidal ( ball and socket)
allow for flexion, extension, adduction, abduction, circumduction
ex. shooulder, hip
pivot (rotary)
rotation
ex. proximal radial joint
condyloid
allows for flexion, extension; abduction, adduction; circumduction
ex. wrist joints btwn radial and carpals shown
saddle
allows for flexion, extension, abduction, adduction; circumduction, thumb-finger opposition
gliding
allows one surface to move over another surface
tendons
_________ connects muscle to bone
ligaments
__________ connect bone to bone
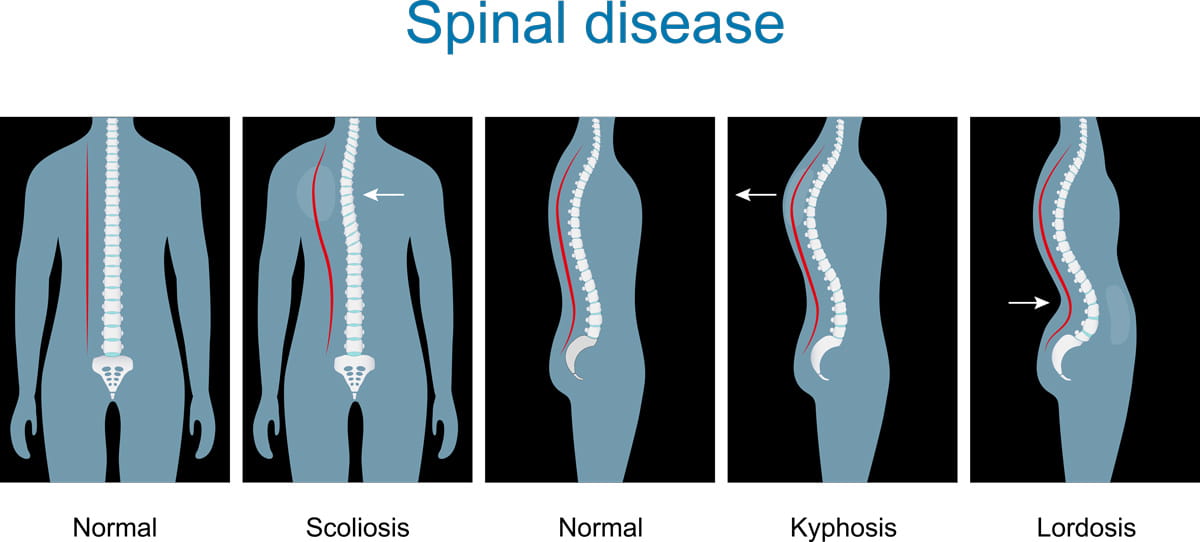
kyphotic
an abnormally rounded upper back
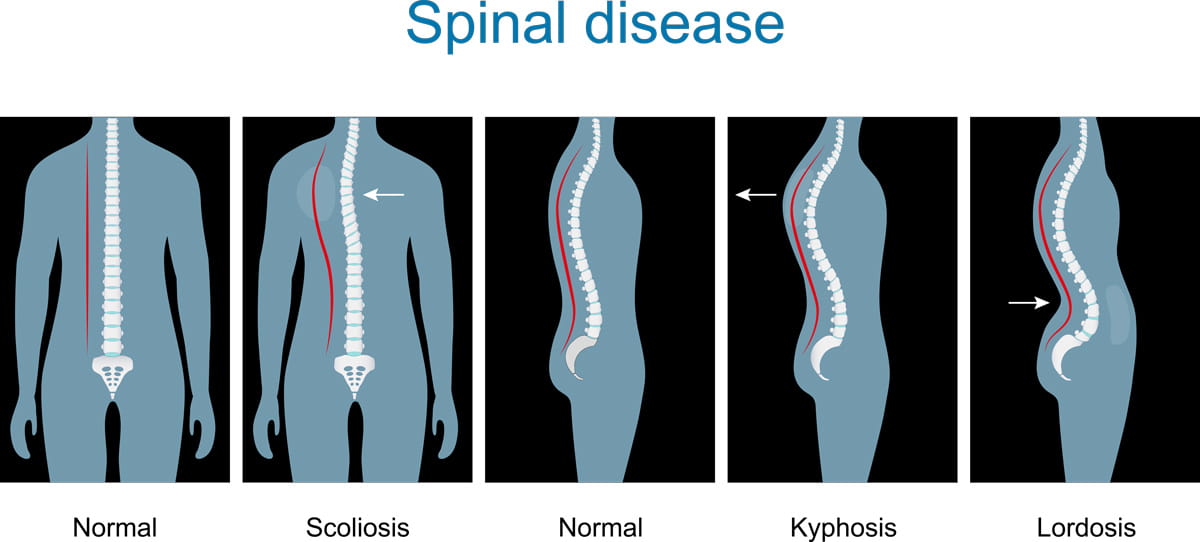
lordosis
an inward curvature of the lower back
musculoskeletal pain assessment
P = Provoking incident
Q = quality of pain
R = Region, radiation, and releif
S = Severity of pain
T = Time
serum calcium
9-11
serum phosphate
2.5 - 4.5
alkaline phosphatase
42-136
an enzyme produced in osteoblast
erythrocyte sedimentation rate
less than 30
serum muscle enzyme (creatine kinase)
_________ _________ ________ will be elevated in people with muscle damage it is also known as creatine kinase
osteoclast
bone destructor
osteoblast
bone reconstruction
rheumatoid factor
____________ _____________ assessed for the presence of autoimmune arthritis. It will be elevated in arthiritis
dexa
a ______ scan measures the bone mass and can be used to check for osteoporosis
arthroscopy
a fiber optic tube for direct visualization of knees, ankles, and shoulders can be used to take out bone fragments following a traumatic incident
osteoporosis
structural deterioration of bone tissue, increased bone fragility, low bone mass and porous bones are all characteristics of ____________
20
peak bone mass occurs before the age of __
true
(T OR F) The rate at which a person experiences bone loss after midlife can altered
osteopenia
low bone mass, the reversible form of osteoporosis
osteoporosis risk factors pneumonic
A - alcohol use
C - corticosteroid use
C - Calcium low
E - estrogen low
S - smoking
S - Sedentary lifestyle
first sign of osteoporosis
back pain, spontaneous fractures
bone vitamins
calcium, vitamin D
1000mg/day of vitamin D can help calcium absorb
osteoporosis drug therapy
calcium supplements, vitamin D, calcitonin, Hormone Replacement therapy, Biphosphonates
degenerative joint disease
aka osteoarthritis
most common type of arthritis
causes loss of cartilage in the joints, joint pain, loss of function
crepitus
creaking joints
osteoarthritis medication
tylenol
topical salicylates
NSAIDS
COX-2 Inhibitors
Arthroplasty
reconstruction or replacement of a joint
hemiarthroplasty
replacement of part of a joint
30-60
for osteoporosis to be visible via an x-ray __- __% of bone density must have been lost
total Hip Arthroplasty lateral Approach
slide 49
Bisphosphonates
_________________ will cause a rapid increase in bone marrow during yr1 of use but will be followed by a plateau in effectiveness after 2-3 years of use
evista
inhibits bone reabsorption
a Selective Estrogen Receptor modulator
bisphosphonates
Fosamax and Boniva
reverse bone loss and reduce fracture risk
Fosamax, Boniva SE
Esophageal irritation, N/V, bone pain
Fosamax, Boniva directions
take with full glass of water
remain sitting up for at least 30 minutes (to avoid irritating esophagus)
take 2 hours before breakfast
Fosamax, Boniva contraindications (do not use if)
allergic
esophageal dysfunction
inability to stand/sit upright for 30 min
hypocalcemia
evista (SERM)
Prevents osteoporosis by stimulating estrogen receptors in the bone, uterus and breast.
the stimulation/boost of estrogen leads to an increase in bone density
evista (SERM) SE
Hot flashes, Leg cramps, weight gain
increased thromboembolism risk
increased risk of death after a stroke (in women)
Miacalcin (calcitonin)
directly stops osteoclastic bone resorption by counteracting parathyroid hormone
promotes the excretion of calcium
salmon
miacalcin shouldn’t be given to anyone allergic to
miacalcin SE
face flushed
nausea
diarrhea
reduced appetite
irritated nasal mucosa
calcium, calcitonin. Calcitonin promotes renal excretion of calcium
_________ and ___________ should be taken together, why?
hypocalcemic tetany
A patient on calcitonin should be monitored for _____________ _________
signs of this include;
Nervousness/irritability
muscle twitching
paresthesia (burning or prickling sensation)
numbness/tingling around mouth
estrogen, calcium
Hormone replacement therapy in the form of __________ is most effective when ___________ is given in tandem
types of calcium supplements
tums, Os-cal
D
homebound older adults usually struggle to get enough vitamin __. This can negatively affect their bone density
ETOH, Opioids, other CNS depressants
muscle relaxants shouldn’t be used with
Flexeril, lioresal, zanaflex
_____________, ___________, ____________ are central acting skeletal muscle relaxants. The are CNS depressants
dantrium
__________ is a direct acting skeletal muscle relaxants
muscle relaxants SE
Drowsiness
dry mouth
dizziness
light headedness
bradycardia
hypotension
gastric lavage
the only reversal for a muscle relaxant OD is _______ _________
BP, RR, Neuro, muscle strength
pts on muscle relaxants should have ___, ___, _______, _________ _______ routinely assessed
Somatic, voluntary
The _________ nervous system controls ________ muscles
alignment
Places spine in neutral or resting position, posture
Balance
Achieved when the body is alignment
Coordination
Nervous system working together with musculoskeletal system to produce movement
Joint mobility
Allows us to sit stand walk and bend
Protein
_________ is important in muscle retention
GU effects on immobility
More prone to infection because supine position isn't good for drainage, immobility could also lead to calcium in urine
Metabolism effects on immobility
Glucose intolerance, increased fat stores
Psychology effects of immobility
Depression,mood Changes, sleep disturbances
4-6
To test for ROM move all joints _-_x each
PT, OT, CPM (continuous passive motion)
Passive range of motion is done by ___/___ or a _____ machine
Phosphorus
Bones store calcium and __________
Epiphysis
Blood cell production occurs in the ___________ of the bone
Metaphysis
Growth plate
Yellow bone marrow, diaphysis
Cartilage, fat, and bone
Irregular bones
Face bones, spinal cord, sacrum
Complex in their shape
Flat bones
Rib bones, sternum, skull, scapulae
Protection of internal organs
Long bone
Bones of the extremities also includes the metacarpals, metatarsals, and phalanges
Support weight and facilitate movement
Short bones
Cube shaped
Carpals and tarsals
Osteocytes
Mature bone cells
Parathyroid hormone
_____________ brings calcium out of bone and into the bloodstream
Synovial fluid
Acts as a shock absorber
Nonsynovial, skull
_________ joints are nonmovable and usually found in the _______
Nursing measured to promote mobility
Accepting current activity level
Proper alignment/positioning
ROM exercises
Positioning devices
Assist pts out of bed
Assist ambulation
Encourage exercise
Bones
Provide a framework for weight bearing
Support surrounding tissues/muscles
Assist in movement
Protect organs and tissues
Manufacture blood cells
Store minerals
Circulation, motion, sensation
A neurovascular assessment assess for _________, __________, _________ (C.M.S)
Musculoskeletal pain assessment
P = provoking incident
Q = quality of pain
R = region, radiation, relief
S = severity of pain
T = time
Inverse
Serum calcium found in blood has an ________ relationship to serum phosphate
statin
Drugs that end in ________ can cause muscle pain
Forward
Kyphosis brings ones center of gravity ________
Lordosis, pregnancy
___________ posture (inward curvature of the lower back) can be caused by _________
Arthroscopy
Following a traumatic incident where bone has been fragmented a ___________ can be conducted to remove the bone fragments
Senile
_________ osteoporosis refers to someone who develops osteoporosis after the age of 70
True
T or F: long term sedatives, anti seizure and steroid use can cause osteoporosis
Noncemented procedure
For younger/more active people, a porous mesh will be used so the bone can grow into/around the prosthetic making it more mobile/weight bearing