Muscular System
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
Primary Functions of the Muscular System
Includes movement, posture, and heat production.
Secondary Functions of the Muscular System
Includes joint stability, circulation, and respiration.
Epimysium
The outermost connective tissue layer encasing the entire muscle.
Perimysium
The intermediate connective tissue layer that surrounds a fascicle.
Endomysium
The innermost connective tissue layer surrounding the plasma membrane of a muscle cell.
Sarcoplasm
The inner contents of muscle cells, equivalent to cytoplasm.
Sarcolemma
The plasma membrane of muscle cells.
Myofibrils
Structures within muscle fibers containing repeating units called sarcomeres.
Sarcomere
The functional, contractile unit of the muscle fiber composed of actin and myosin.
Actin
A thin filament involved in muscle contraction, providing a binding site for myosin.
Myosin
A thick filament that interacts with actin to produce muscle contraction.
Z disc
Anchoring protein for thin filaments; delineates the boundaries of a sarcomere.
A Bands
Dark bands containing thick myosin filaments overlapping with thin actin filaments.
I Bands
Light bands composed solely of thin actin filaments.
H zone
A light band at the center of an A band, lacking thin filaments.
M line
A dark band at the center of the H zone, composed of anchoring proteins.
Titin
An elastic protein that connects the thick filaments of neighboring sarcomeres.
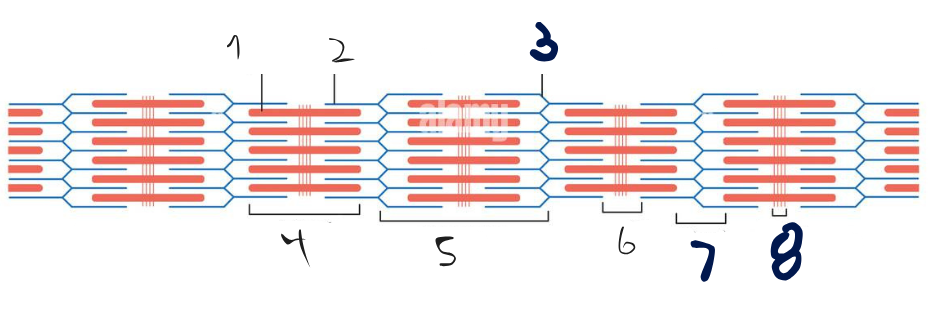
Label the following Sarcomere:
Myosin, 2. Actin, 3. Z-line, 4. A-band, 5. Sacromere 6. H-zone, 7. I-band, 8. M-line
T-Tubules
Extensions of the plasma membrane that help transmit the action potential into the cell.