Paper 2 Case Study Statistics
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
20 Terms
Opportunities of rapid Economic Growth in an NEE
International airport which brings 80% of all flights into West Africa
EKO ATLANTIC (new city being built) to provide accommodation for 250,000 people and PME provide 150,000 further jobs.
Urban trends in different parts of the world (HIC’s)
HIC’s
Slow rate of urbanization (avg 1%)bc Cities grew during Industrial Rev(late 1800s)
1950’s 79% of UK’s pop lived in towns or cities
2013 83% of pop lived in towns or cities
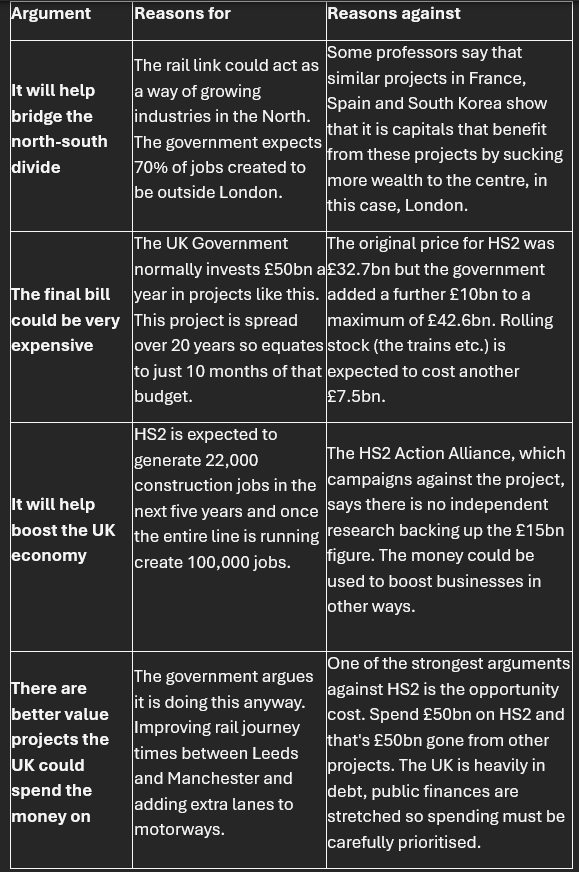
overpopulation in urbanized areas can lead to people moving back to rural areas .. need to improve transportation infrastructure to allow ppl to commute from far e.g Hs2 project
Pros and Cons of the Hs2 project
Urban trends around the world (LICS)
High rates of urbanisation (avg 6%)
only around 30% of pop live in urban areas, most live rural
e.g Ethiopia and Afghanistan
Urban trends around the world (NEEs)
Rapid Urbanisation
e.g 1978 18% China =Urban but 2018 59%
leads to formation of Megacities 2/3rds of megacities are LIC/NEE e.g Mumbai
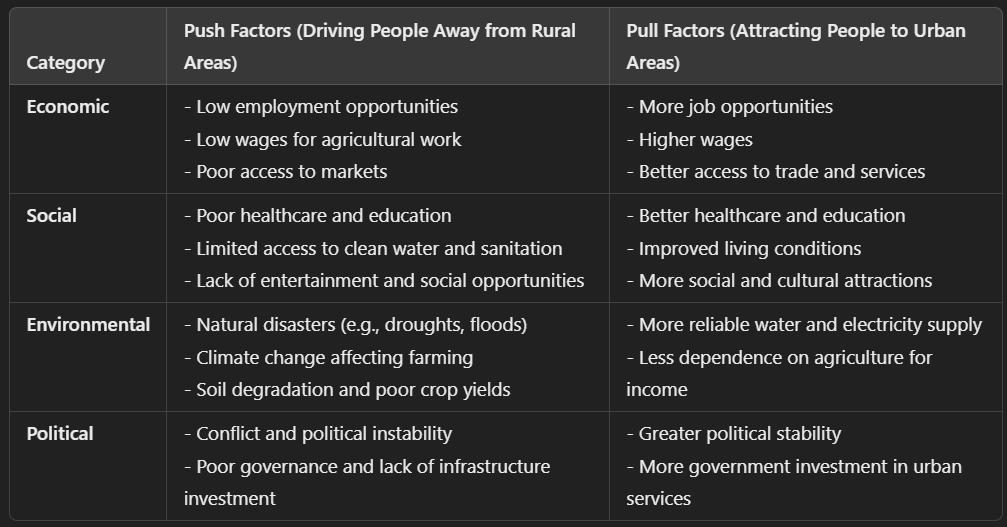
Factors affecting the rate of urbanisation
Limitations of Economic and Social measures
GNI per head- as it is an average it doesn’t account for the variations in a country e.g Qatar has GNI per head as high as HIC’s but has a lot of poor ppl.
Birth rate- can be due to religious/cultural reasons, or political legislation e.g China’s one child rule can distort trends so doesnt reflect development.
Death rate- higher death rates may indicate an aging population rather than poor healthcare.
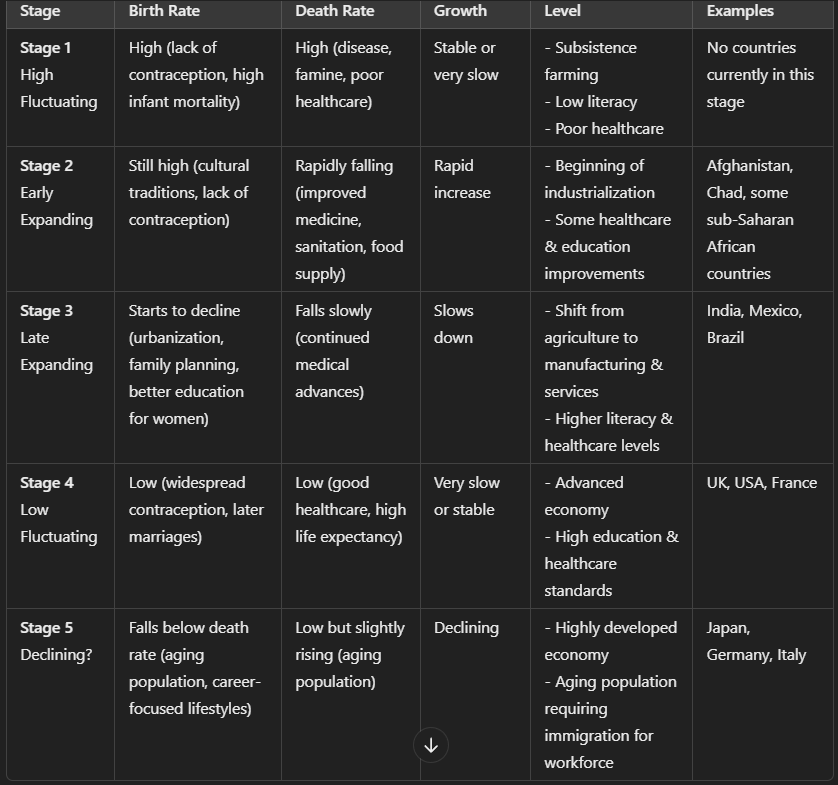
Links between the stages of DTM and the level of development
Causes of uneven development (physical, economic, historical)
Physical :
Poor Climate- low crop yield due to unsuitable environment, means not much food produced =malnutrition= low quality of life + low life expectancy. Fewer crops to sell therefore less is sold and bought so less money to spend of development
Few Raw Materials- fewer products to export= less money made, triggers the cycle of poverty
Natural Disaster- money spent on rebuilding therefore less money to spend on development, death rates increase + low quality of life + low HPI
Economic :
Poor trade links- limit a country’s ability to integrate into the global economy, restricting access to markets, technology, and investment, all of which are essential for development.
Debt- money needs to be payed back w interest from international loans taken (could be due to aid w natural disaster) therefore less money for development
Primary products- countries that mainly export raw materials are less developed as they are sold for less profit than manufactured goods. Price of product may fall below cost of production.
Historic :
Colonisation- Former colonies were exploited for resources, leaving weak economies (e.g India, Nigeria) profits went to colonisers instead of colonies, further increasing inequality.
War- money spent on arms and soldier training instead of development. Infrastructure rebuilding. Education and healthcare disrupted. Increase in infant mortality rates, decline in literacy rates. (e.g Syria 2008 has HDI of 0.65, dropped to 0.54 in 2016 after 5 years of war.
Strategies used to reduce development gap
Investment- FDI involves multinational companies investing in a country's businesses, infrastructure, or resources. This can boost the local economy, create jobs, improve skills, and transfer technology. It's one of the most effective ways to spur long-term economic growth and reduce the development gap.
Aid- provide immediate relief for poorer countries. It can fund projects in education, healthcare, and infrastructure, contributing to long-term development. Loans help finance large-scale projects but can create debt burdens.
Fair Trade- better access to international markets allows poorer countries to sell their goods at higher prices. This can boost exports, stimulate economic growth, and reduce poverty. However only a small proportion of profit may reach producers, while the rest boosts retailers profits.
Using intermediate technology- tools, equipment, and processes that are simpler, cheaper, and more accessible to developing countries than advanced technologies. e.g solar-powered LED bulbs used in Nepal where only other lighting options are polluting and dangerous, allows people to study and work, therefore PME literacy rates increase, GNI increase etc
Microfinance Loans- Providing small loans to entrepreneurs in LICs can create financial independence and make small businesses to grow, create jobs, and reduce poverty. Smale scale and effective but not as effective as FDI
Industrial Development- industrialising countries that are very agriculturally dependent by building infrastructure… is crucial for facilitating trade, attracting investment, and improving the quality of life. Efficient infrastructure supports all aspects of development, from education to healthcare
Debt Relief- reduces the burden of repayment for countries, freeing up funds for development projects instead. While it can alleviate short-term financial strain, it does not directly stimulate economic growth or development without accompanying reforms or investments in key sectors.
Types of Aid
Bilateral Aid- aid from one country to another, conditions may be attached e.g aid money must be spent on goods from doner countries
Multilateral aid- countries donate money through organisation e.g UN, World Bank
Voluntary aid- given by individuals or companies and is distributed through charities or NGOs e.g Muslim AID or OxFam
Location and importance of Nigeria regionally and globally
Location: West Africa, Bordered by Chad, Niger, Benin & Cameroon.
Regional Importance:
Highest GDP in Africa
Largest farm output in Africa
Largest pop in Africa (200 mil)
Global importance:
worlds 21st largest economy
Nollywood 2nd largest film industry in the world (2500 movies in 2021)
12th largest producer of oil (countries who supply oil have a large political influence over those who don’t)
5th largest contributor to UN peacekeeping forces
Environmental impacts of economic development in Nigeria
Industrial Growth:
10,000 illegal industries illegally dump toxic waste into rivers —> decrease water quality, decrease quality of life, harm biodiversity, eutrophication
Breathing and lung problems caused by toxic fumes —> decrease air quality, health problems, Nigeria already has low life expectancy (56years)
Urban growth:
Waste in slums, dumped on streets
Traffic congestion —>increase in air pollution
70-80% of forests removed through urban sprawl and logging
Oil extraction:
Oil spills damage freshwater and marine ecosystems
Oil spills release CO2 —> acid rain
600,000 barrels of oil leaked in 2008 Bodo oil spill.
Oil theft costs Shell and the N-Government billions of dollars per year
Oil flares send toxic fumes into the air
Effects of economic development in an NEE and its affects on quality of life (TNC’s affects)
Nigeria highest rates globally of HDI improvements over the last 30yrs. (HDI 2005= 0.466 in 2013= -0.504)
Oil is the biggest export (98% of all export earnings)
Shell:
Direct employment 65,000
Indirect employment 250,000 (growth of small local businesses)
91% of Shell contracts are given to Nigerian companies
major contribution to Nigerian taxes
Locals develop new skills (training provided by Shell)
all ts triggers PME… therefore…
Improvements to infrastructure e.g roads
Better access to safe water and sanitation
More doctors + better equipped hospitals
Higher disposable income to buy food
Almeria challenges
illegal immigrants
low wages and poor conditions
aquifiers drying up
33,500 tonnes of plastic waste
greenhouses reflect sunlight
almeria advantages
3,000 hours of sunlight anually
$1.5 Billion annual income to area
hydroponics and drip irrigation (less water used)
warm temps avg 20= low energy costs
Rural urban fringe growth Cambridgeshire
15,000 in south cambridgeshire
150,000 180,000 by 2030
unis
Jamalpur rice fish farming
triples income for workers
10% increase in rice yeild
farming is 50% of their income
Kenya tourism
1.1 millions jobs
15% of exports is tourism
8% of GNI
Outer hebridies rural decline
1901 45,000 to 26,000 2020
50% decrease
limited transport