(CIE A2 biology) Inheritance - key definitions
1/13
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
14 Terms
Gene
A length of DNA that helps code for a protein’s primary-structure polypeptide sequence.
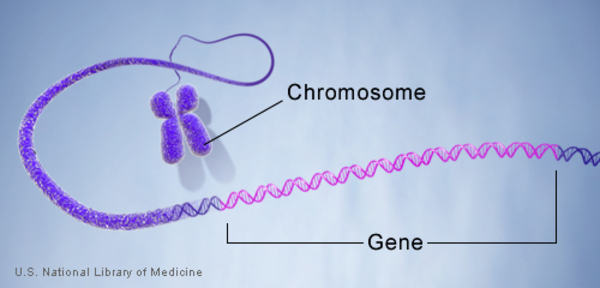
Locus
The chromosomal position where a particular gene can be found (always the same per gene).
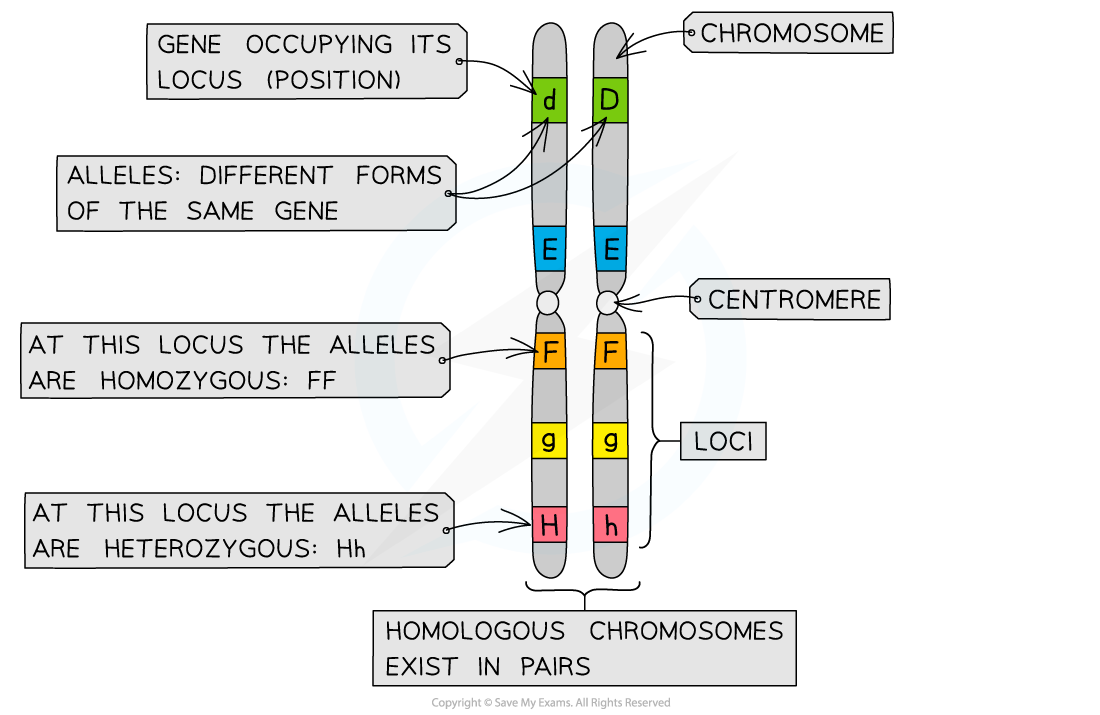
Allele
A particular variant of a specific gene that can be dominant, recessive, or co-dominant.
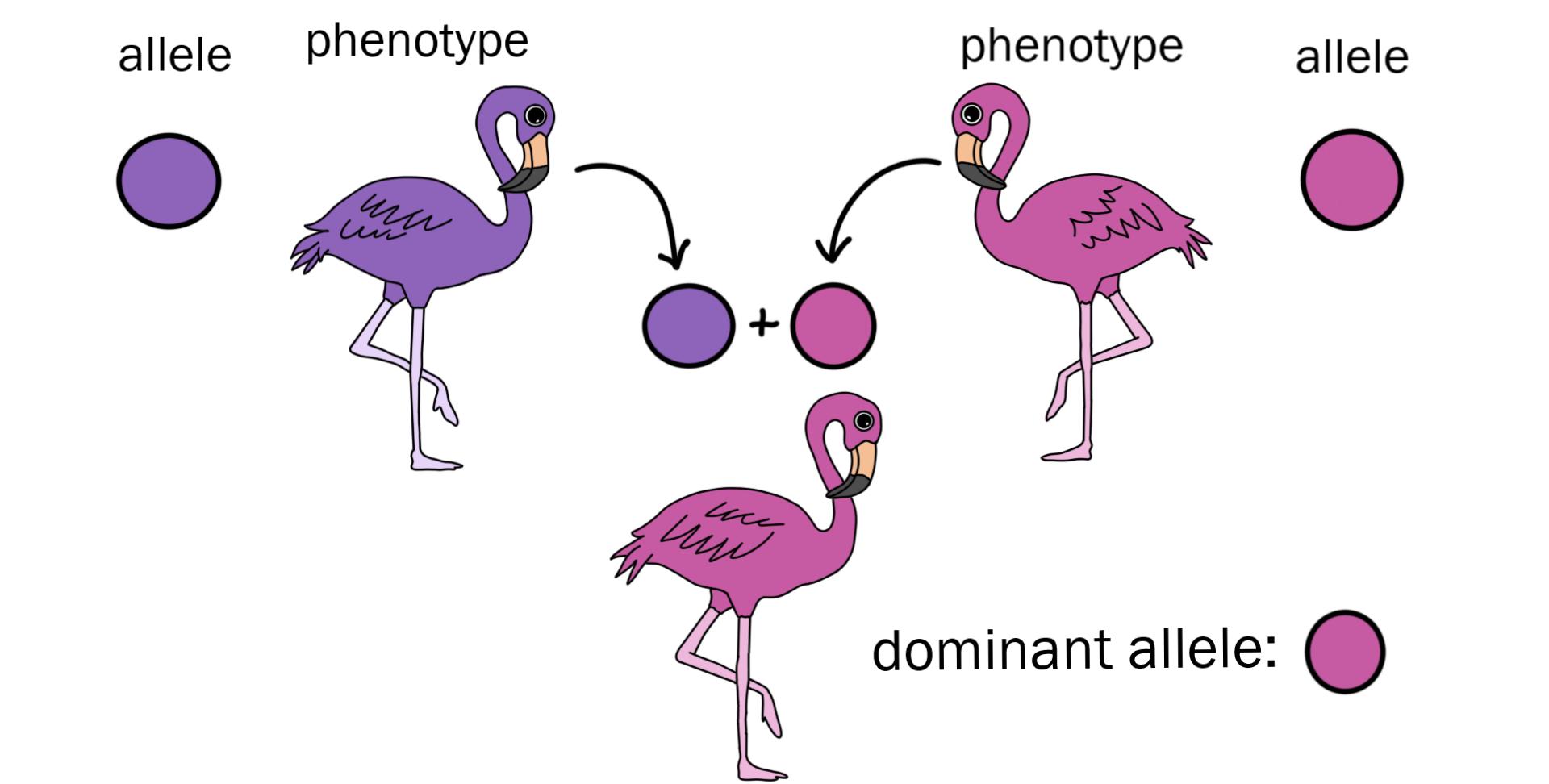
Dominant allele
An allele that affects heterozygous and homozygous phenotypes equally (only one copy is required in the genotype).
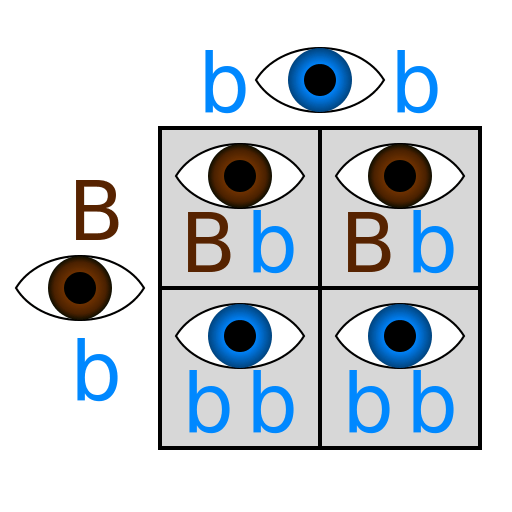
Recessive allele
An allele that only affects homozygous phenotypes without a dominant allele (two copies are required in the genotype).
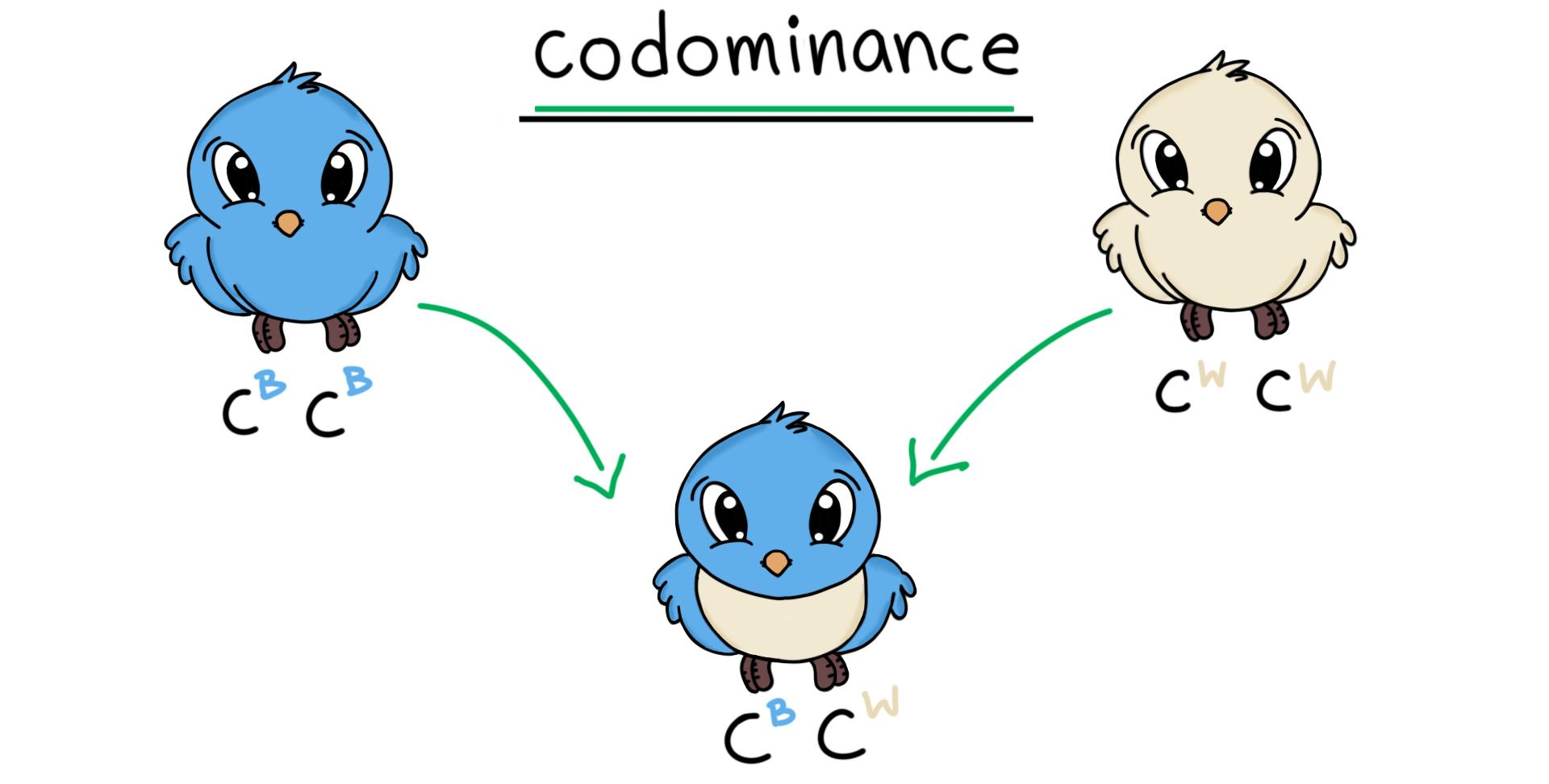
Co-dominant alleles
Alleles that both affect heterozygous phenotypes equally.
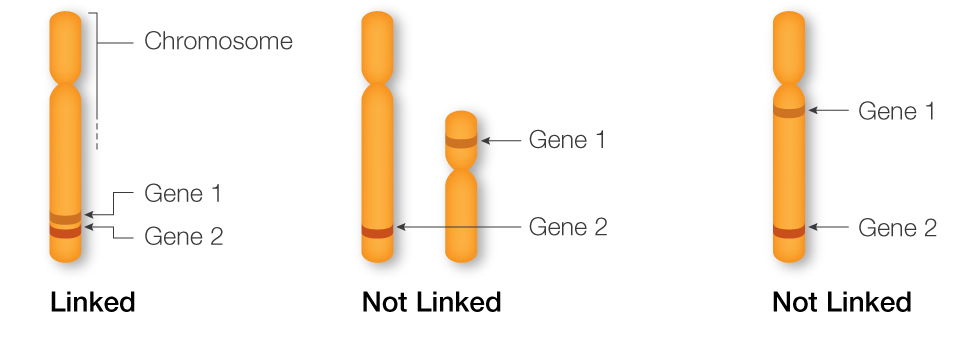
Linkage
When two genes are on the same chromosome so they can be inherited together instead of being independently assorted.
Test crosses
Genetic crosses where organisms with dominant allele-produced phenotypes are crossed with homozygous recessive-phenotype ones to determine the genotype of the dominant phenotype organism.
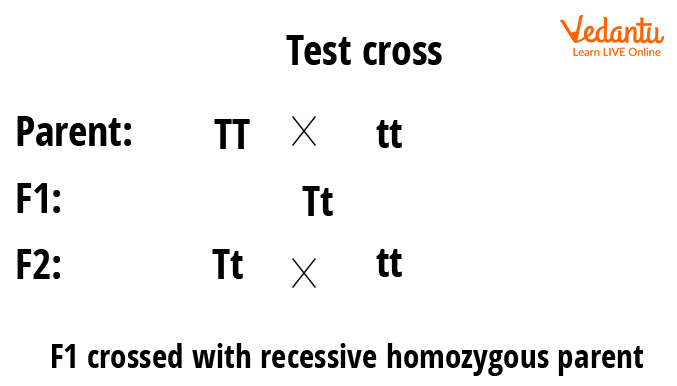
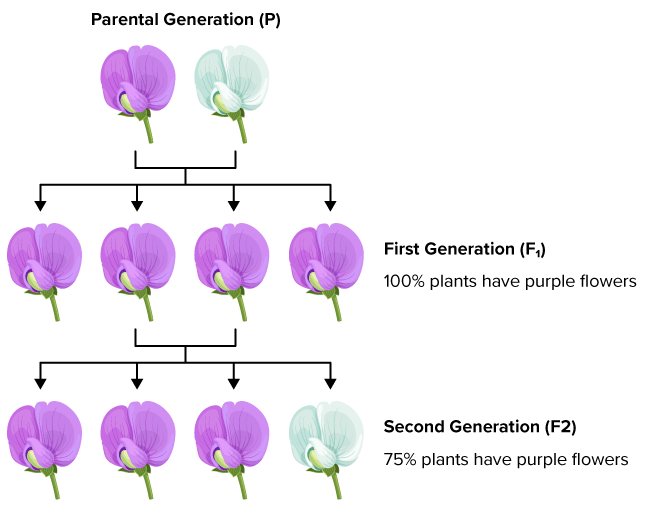
F1
The resultant offspring of a cross between a homozygous dominant-phenotype organism and a homozygous recessive-phenotype one.
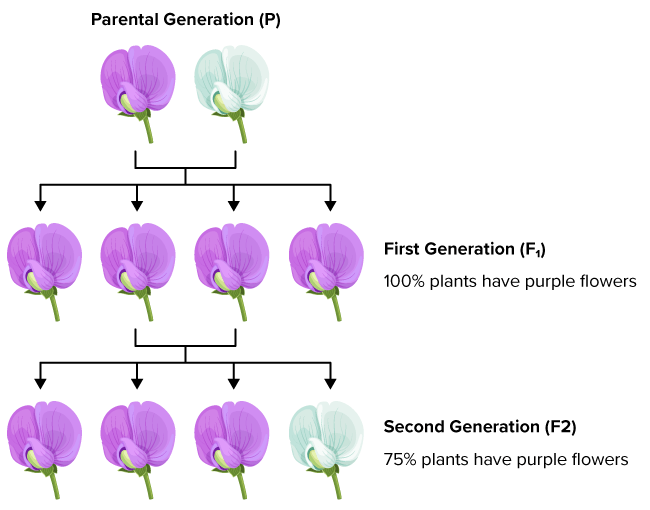
F2
The resultant offspring of a cross between two heterozygous F1 organisms.
Phenotype
A set of organismal characteristics often caused by genotype-environment interactions.
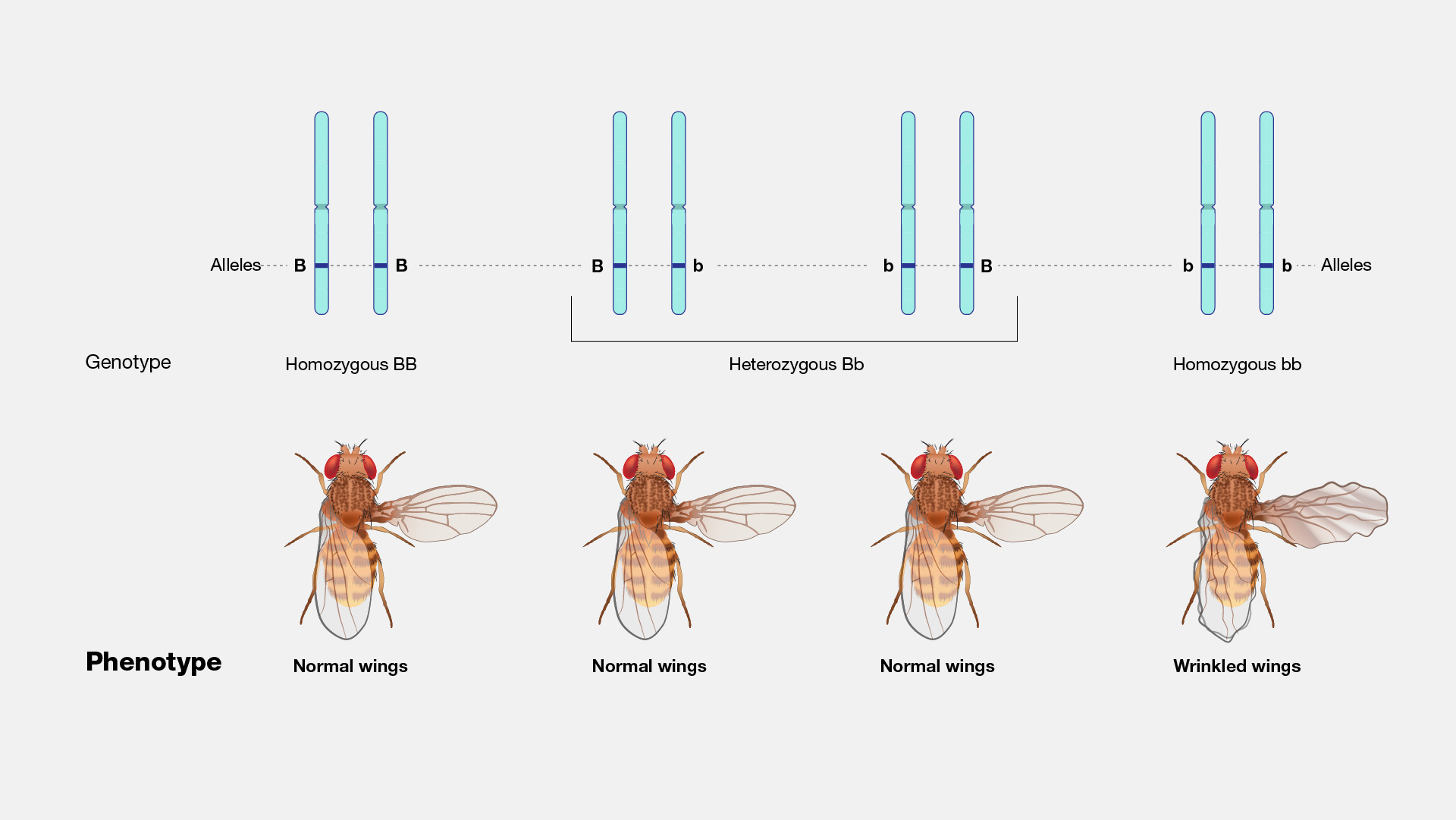
Genotype
A set of alleles possessed by an organism.
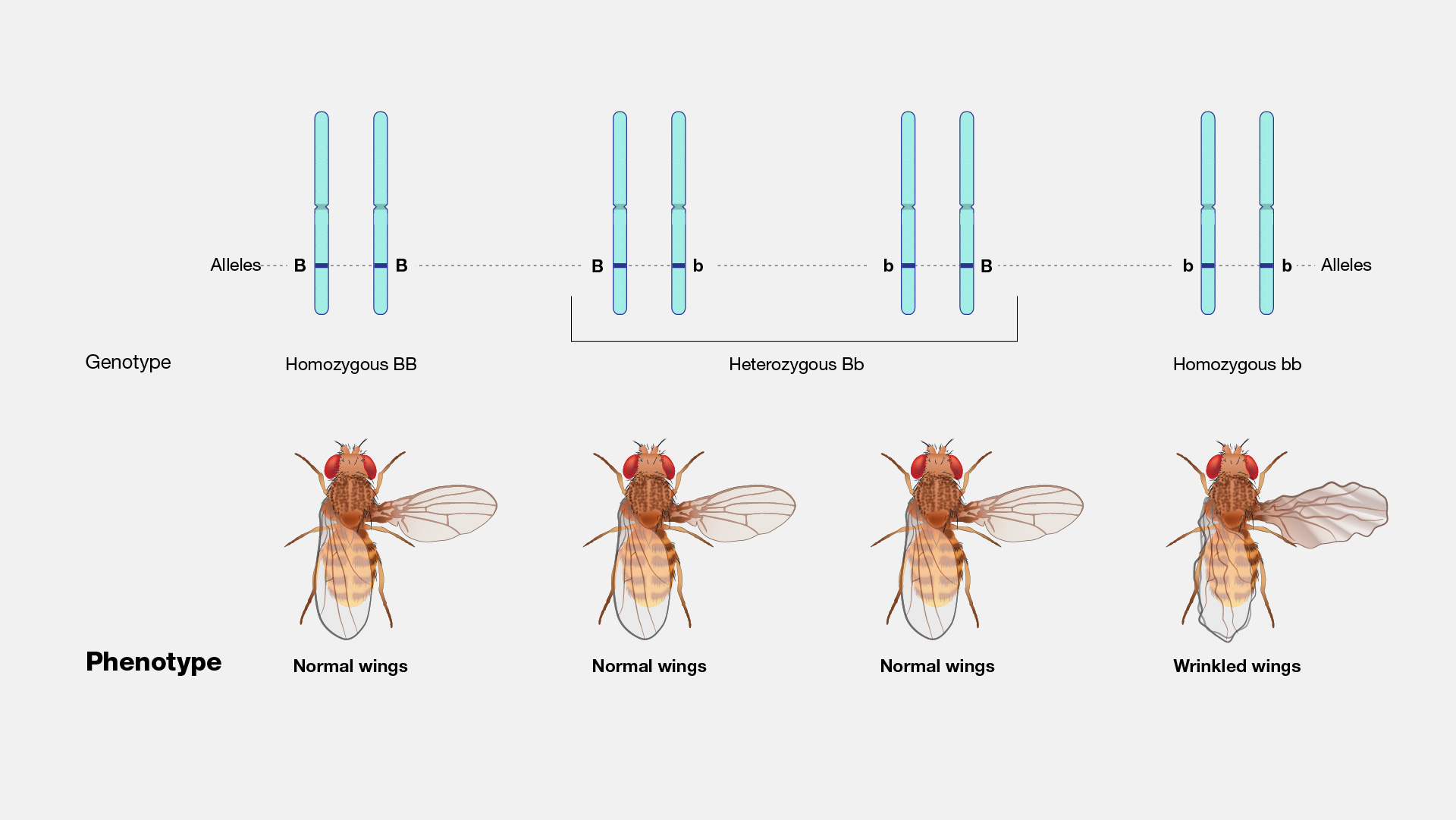
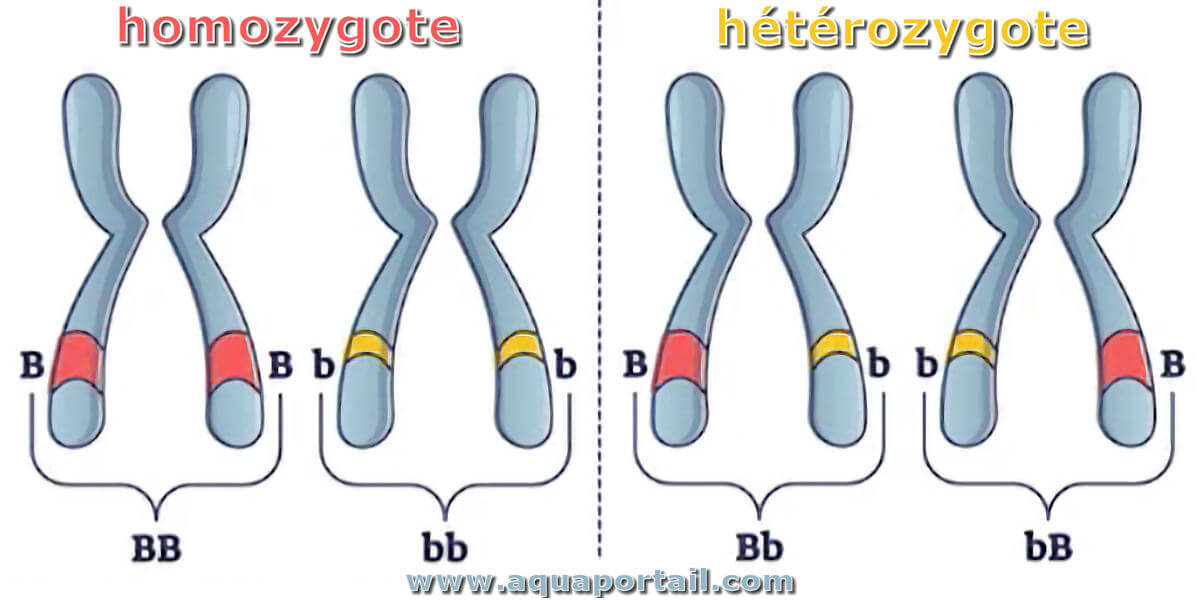
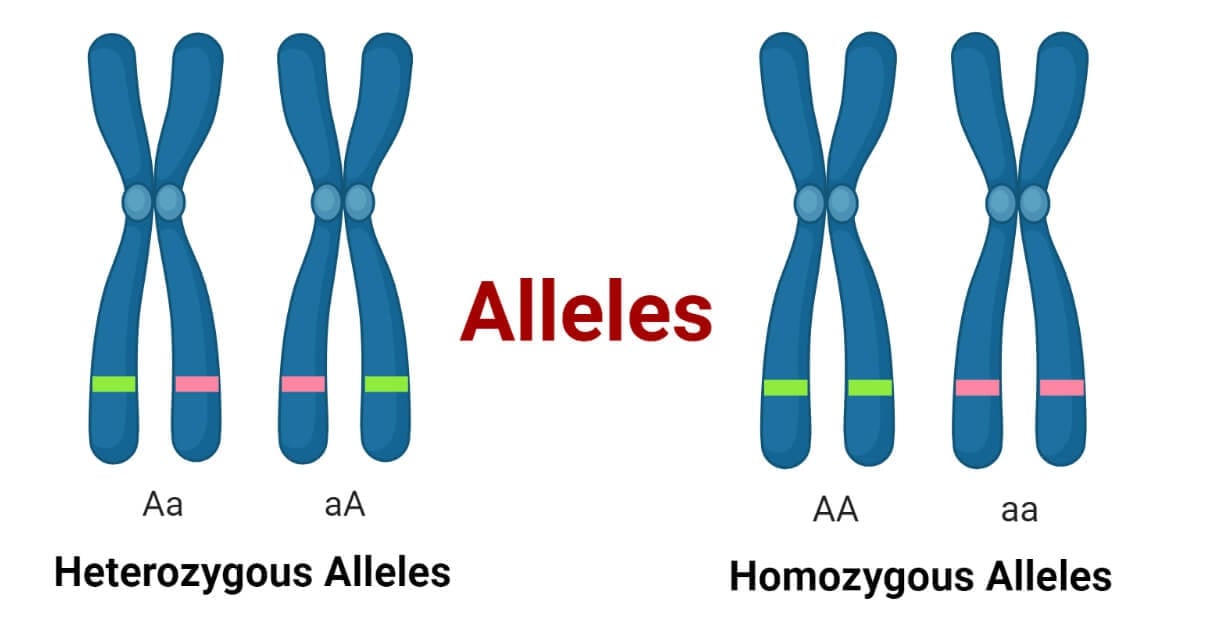
Homozygosity
When two identical alleles of a gene are present in an organism.
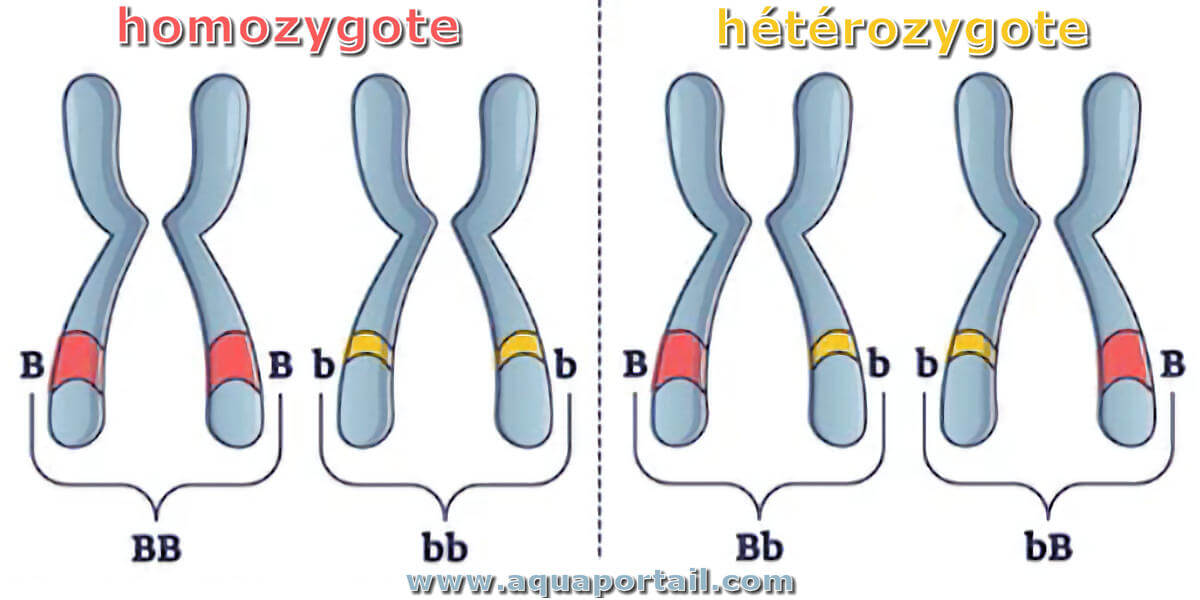
Heterozygosity
When two different alleles of a gene are present in an organism.