Blood Vessels & Cardiovascular Physiology
1/53
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
54 Terms
lumen, tunica intima, tunica media, tunica externa
structure of blood vessel - inner to outer
heart, elastic arteries, muscular arteries, arterioles, capillaries, venules, veins, heart
heart and blood vessel pathway
endothelium (simple squamous)
1
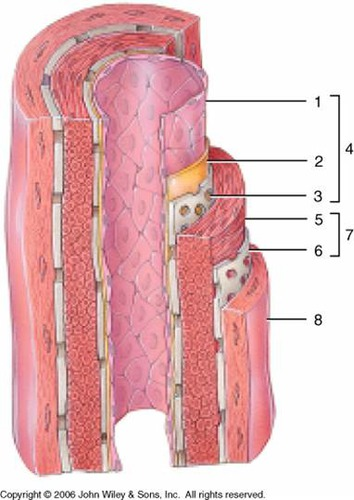
subendothelial layer (CT)
2
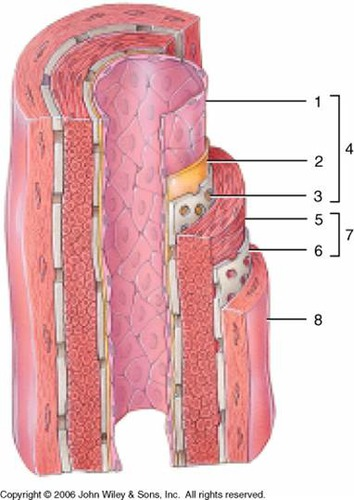
internal elastic membrane (muscular artery)
3
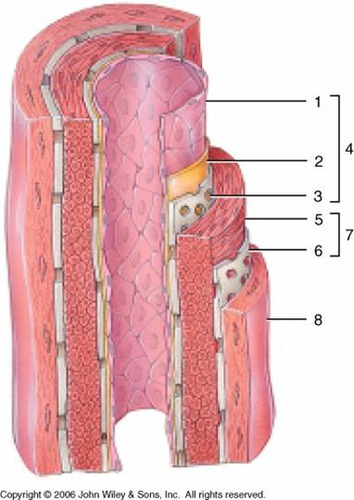
tunica intima
4
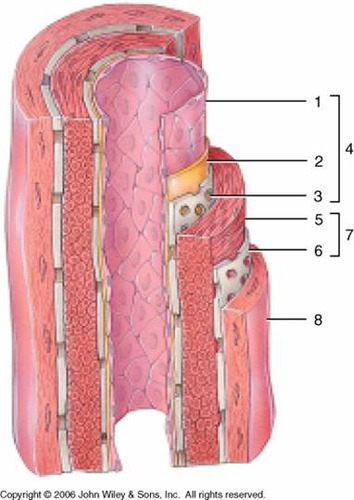
smooth muscle, elastic fibers
5
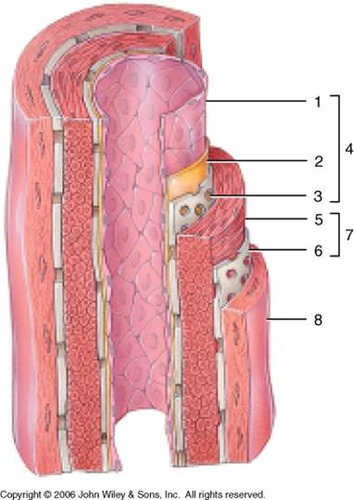
external elastic membrane (muscular artery)
6
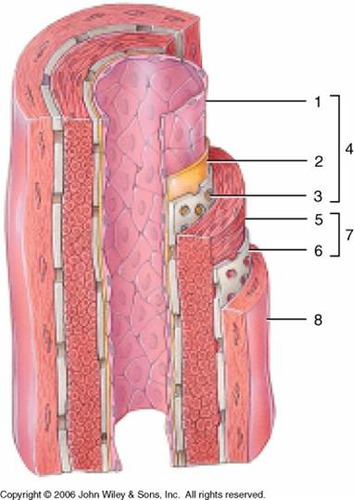
tunica media
7
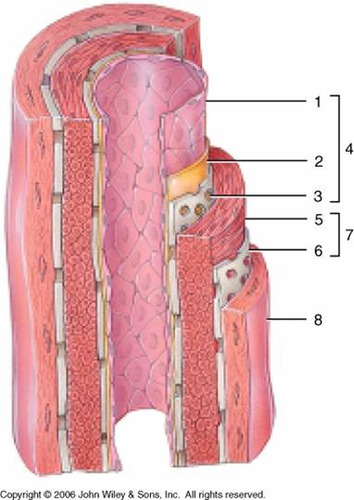
tunica externa (collagen fibers)
8
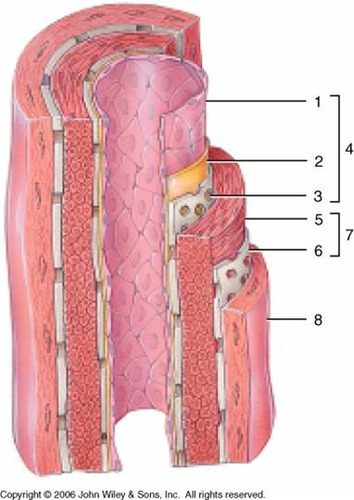
tunica media
thickest layer in arteries
tunica externa
thickest layer of veins
one, endothelium, basement membrane
capillaries - __ cell layer, made of __ and ___
continuous capillaries, tight junctions
A
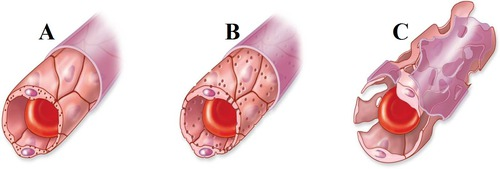
fenestrated capillaries
B
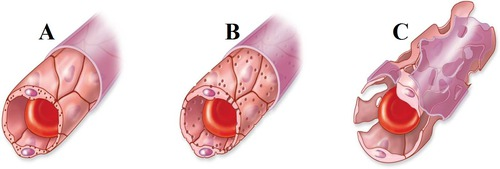
sinusoidal capillaries
C
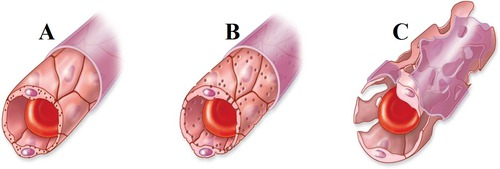
least permeable, nervous tissue, muscle, skin
continuous capillaries
semi permeable, filtration and absorption, intestines, kidneys
fenestrated capillaries
most permeable, liver, bone marrow, spleen, lymph nodes
sinusoidal capillaries
thick tunica media
arteries maintain shape bec
thin walls
veins collapsed bec
artery, very round
A
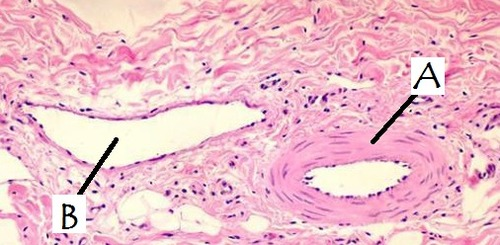
vein, big lumen
B
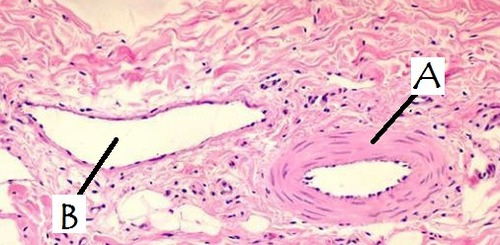
highest pressure (elastic), carries blood away from heart
artery
lowest pressure, carries blood toward heart
vein
nutrient exchange, smallest blood vessel
capillary
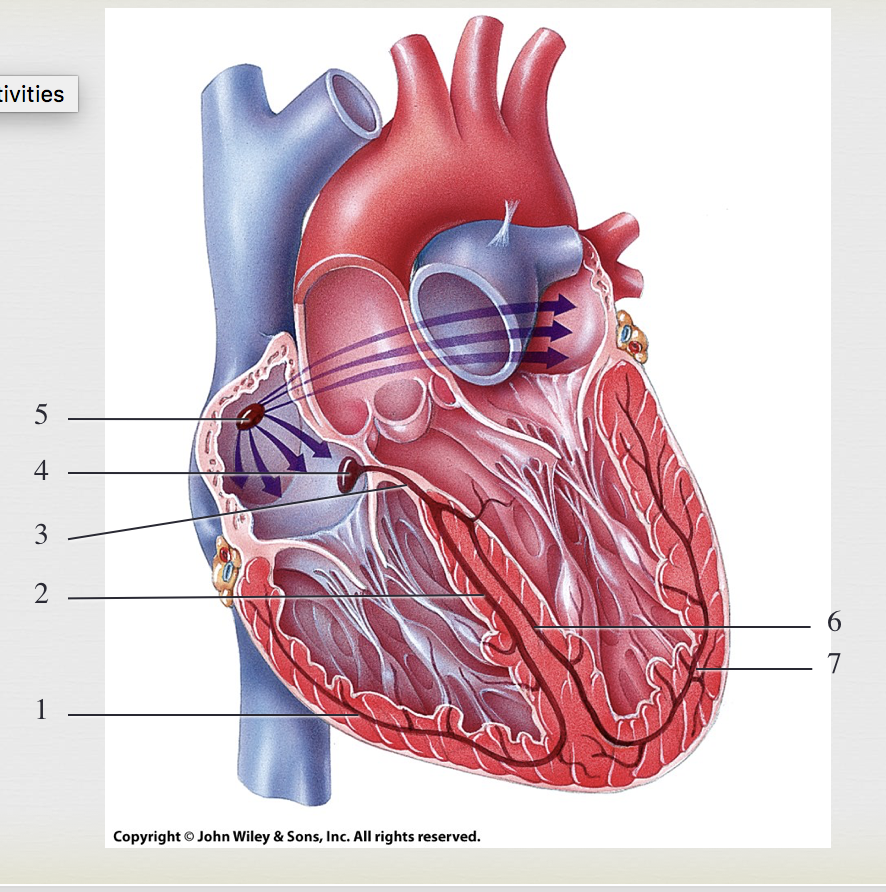
SA node, generate impulses
5
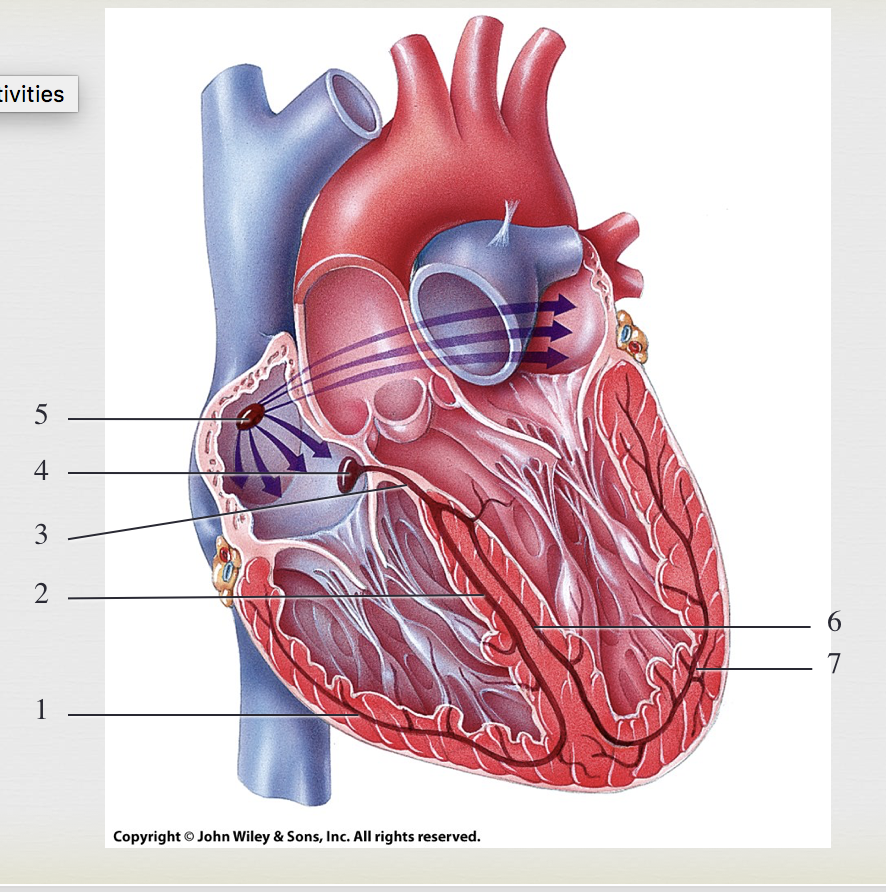
AV node, where impulses pause
4
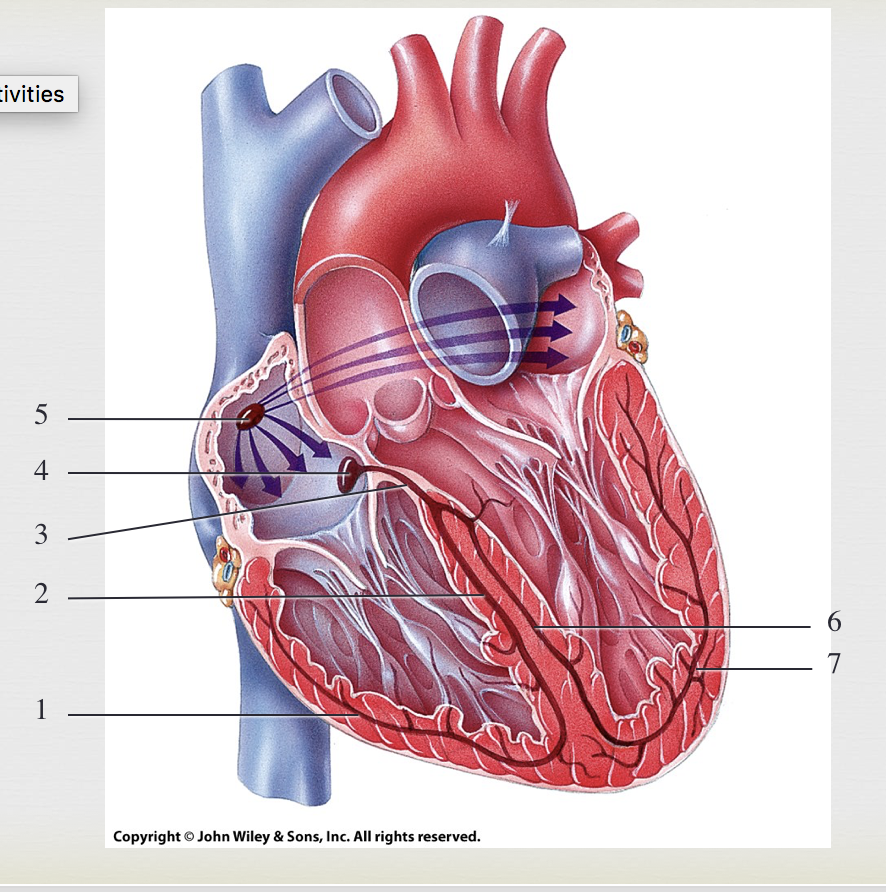
bundle of HIS, transmits impulse from atria to ventricle
3
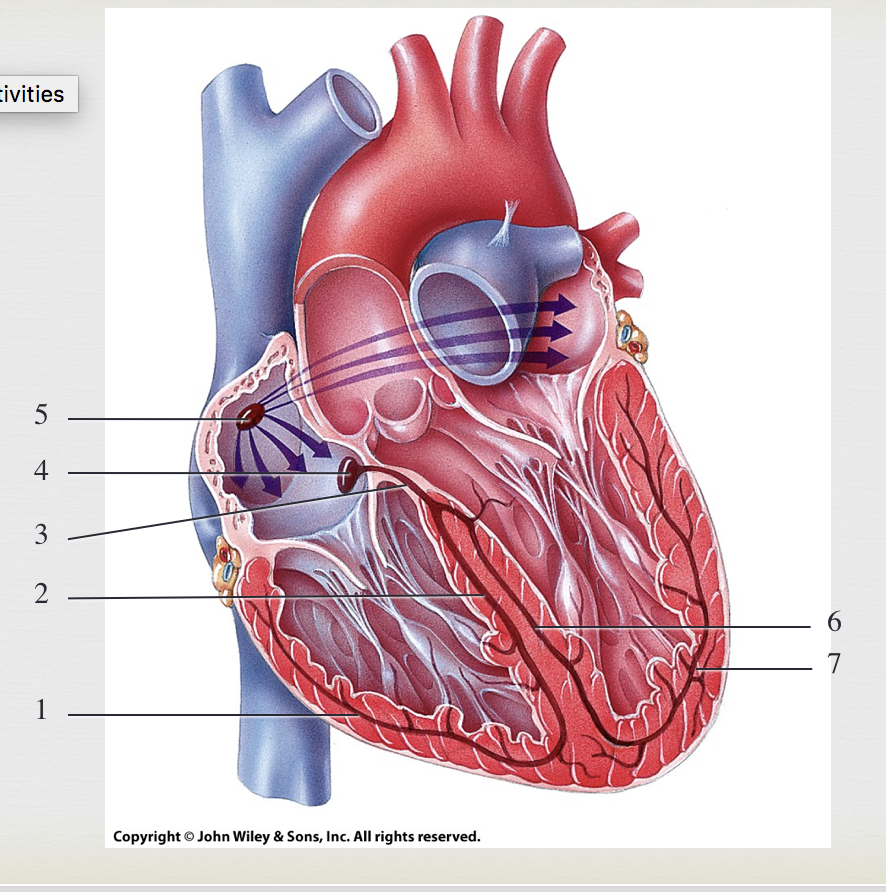
R/L bundle branches, conduct impulses through interventricular septum
2&6
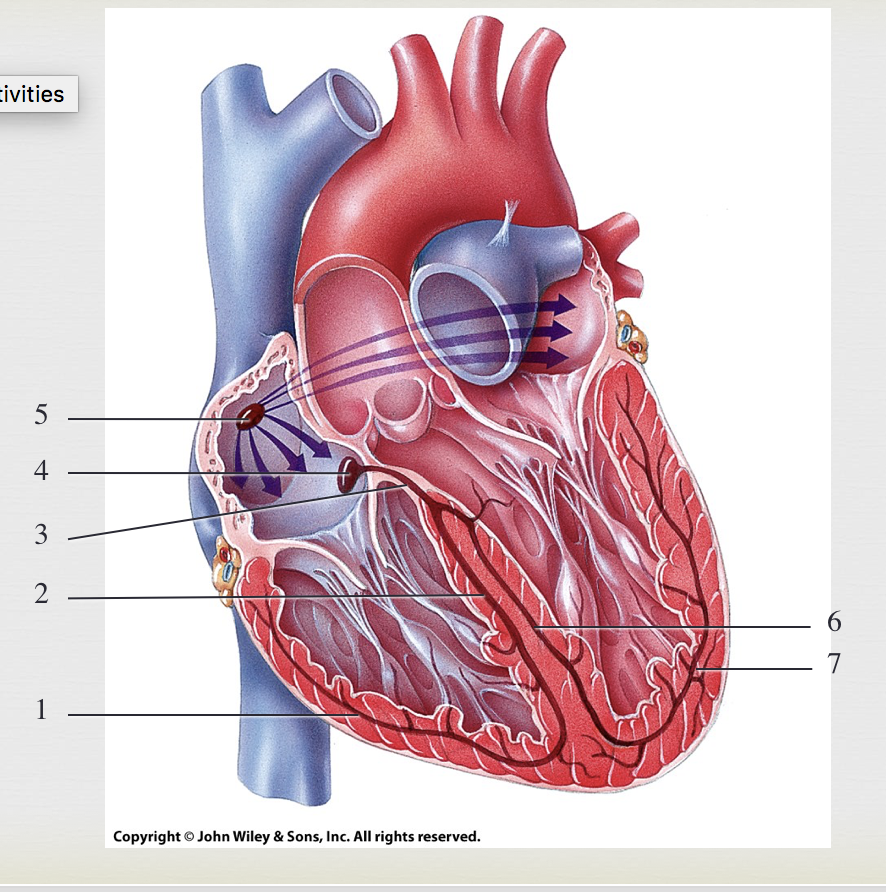
purkinje fibers, depolarize both ventricles
1&7
64 to 72 bpm, 72 to 80 bpm
normal ECG for men and women
less than 60 bpm
Bradycardia
more than 100 bpm
Tachycardia
artery, contraction, relaxation, left ventricle
pulse/ heart rate is alternating surges of pressure in an ___ that occur with each ___ and ___ of _____
systolic minus diastolic
Pulse pressure equals
diastolic plus 1/3 pulse pressure
mean arterial pressure MAP equals
resumption, blood flow, occlusion
sound of korotkoff = characteristic sound indicating ___ of __ ___ into forearm after ____
carotid
pulse the strongest
dorsalis pedis
pulse the weakest
pushes water out of capillary via filtration
hydrostatic pressure
draws water into capillary via osmosis
osmotic pressure
begins at right ventricle, ends at left atrium
pulmonary circuit
systole, contraction
depolarization followed by
diastole, relaxation
repolarization followed by
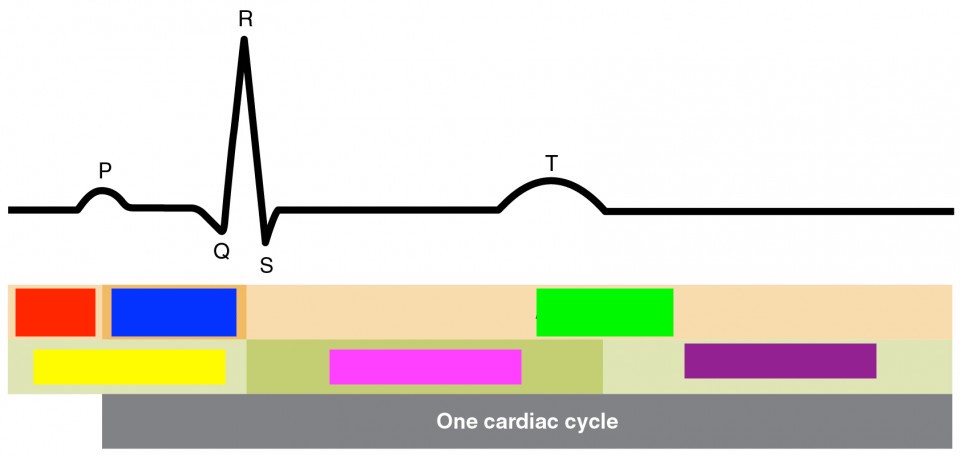
p
atrial depolarization
qrs
ventricular depolarization
t
ventricular repolarization
atrial diastole
red
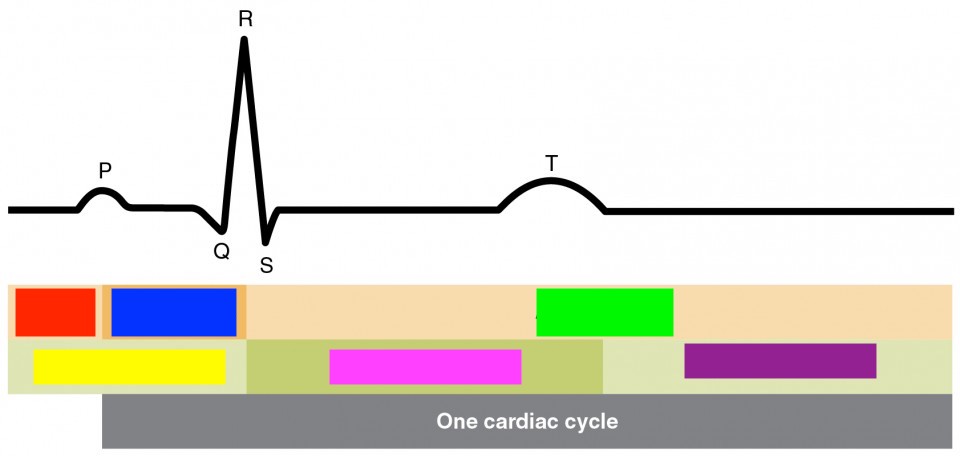
atrial systol
blue
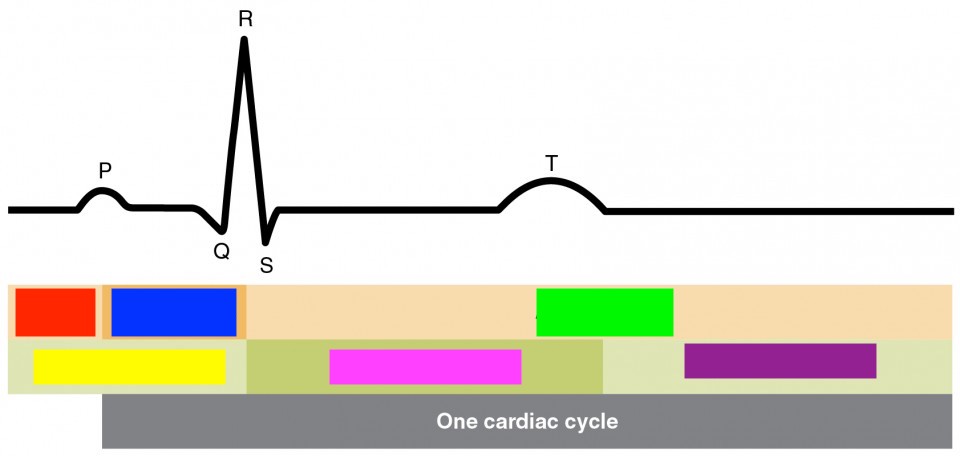
atrial diastole
green
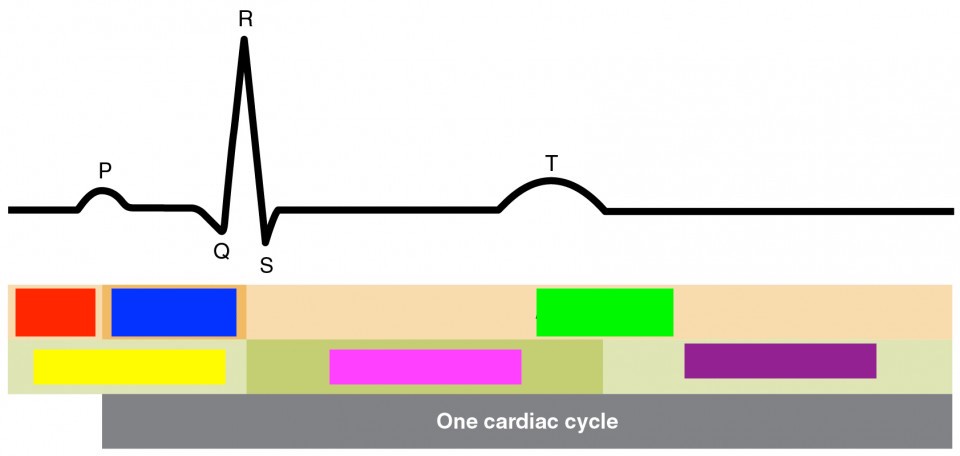
ventricular diastole
yellow
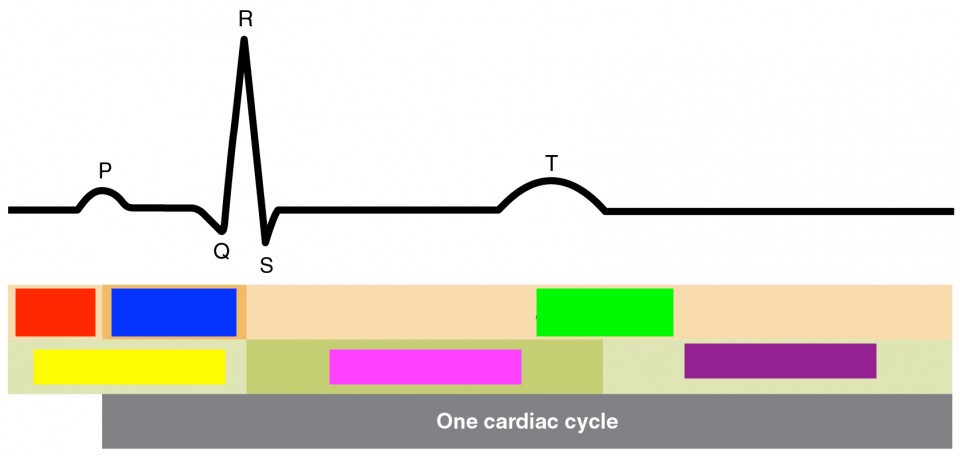
ventricular systol
pink
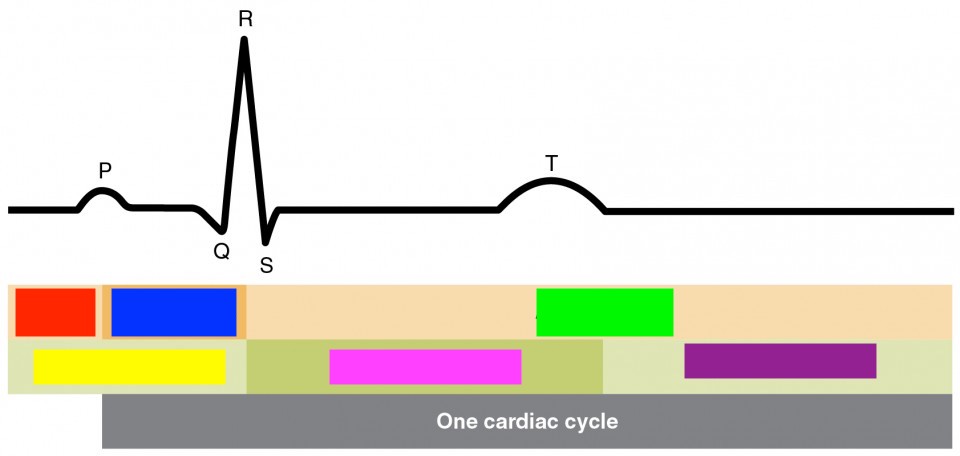
ventricular diastole
purple