Bio 305: Digestive System
gastrointestinal tract
mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, rectum, anus
Accessory organs
salivary glands, liver, gallbladder, pancreas
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
gastrointestinal tract
mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, rectum, anus
Accessory organs
salivary glands, liver, gallbladder, pancreas
role of stomach
-liquifies food through secretion of acid
-begins breakdown of proteins
Small intestine
-digestion (enzymes)
-absorption
3 parts of colon of the large intestine
ascending, transverse, descending
Partitioning
divide into parts
Large molecules we ingest
-carbohydrates
-proteins
-triglycerides
Monosaccharides of carbohydrates
glucose, fructose, galactose
Monosaccharides of Proteins
amino acids
Trigylcerides
free fatty acids
4 major processes of the GI tract
1. Secretion
2. Digestion
3. Absorption
4. Motility
Cirrhosis + jaundice
scarring of the liver
Peristalsis
the involuntary constriction and relaxation of the muscles of the intestine or another canal, creating wavelike movements that push the contents of the canal forward.
4 layers of tract wall
1. Lumen
2. Mucosa
3. Submucosa
4. Serosa
Salivary Anylase
an enzyme that breaks down starch into smaller particles and eventually into disaccharide maltose in the mouth
peritoneum
a multilayered membrane that protects and holds the organs in place within the abdominal cavity
enteric nervous system
the nervous system of the digestive tract (submucosal plexus + myenteric plexus)
components of the mouth
Hard pallet, Soft pallet, uvula, 3 salivary glands, teeth, tongue, and bolus
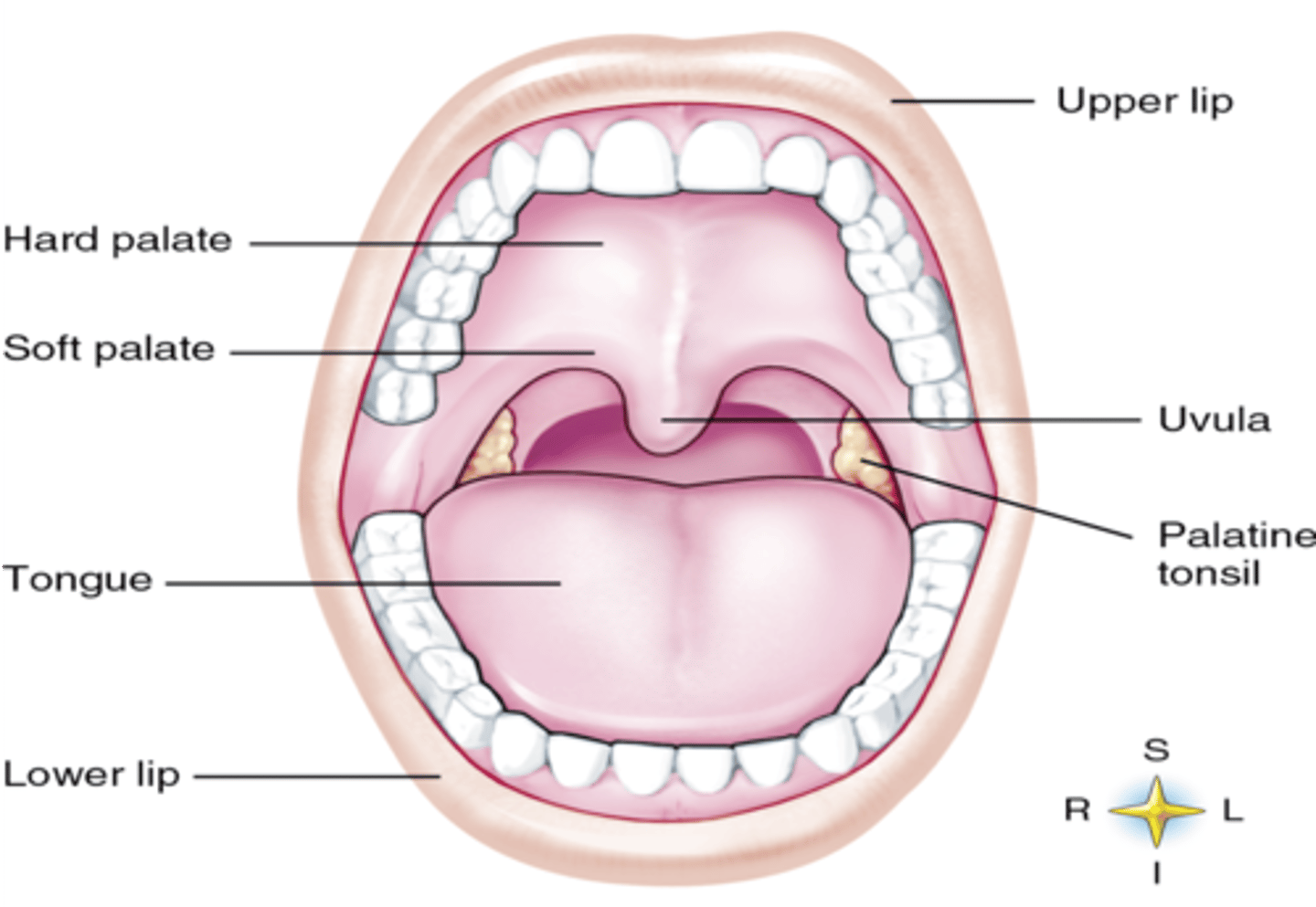
What prevents food from going down the windpipe
epiglottis + glottis (vocal cords)
gastric pits of mucosa in stomach
-have gastric glands
-secrete gastric juice (most is produced in the fundus and body of stomach)
Stomach takes about ___ - _____ hours to empty
2-6
paracrine factors
Local signaling molecules affecting nearby cells through interspatial fluid
celphalic phase
sight, smell, taste, thought of food; stimulates
gastric phase
phase of gastric secretion that begins when food enters the stomach
intestinal phase
Stage in which the duodenum responds to arriving chyme and moderates gastric activity through hormones and nervous reflexes
How stomach acid is made
-carbonic anhydrase
Regulation of stomach acid
-gastrin
-Histamine
- Ach
-Somatostatin (negative effect)