Nucleic Acids-RNA-DNA
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
45 Terms
3 parts of nucleic acids
sugar
phosphate
base
Which sugar does RNA use?
beta-D-ribose
Which sugar does DNA use?
beta-D-deoxyribose
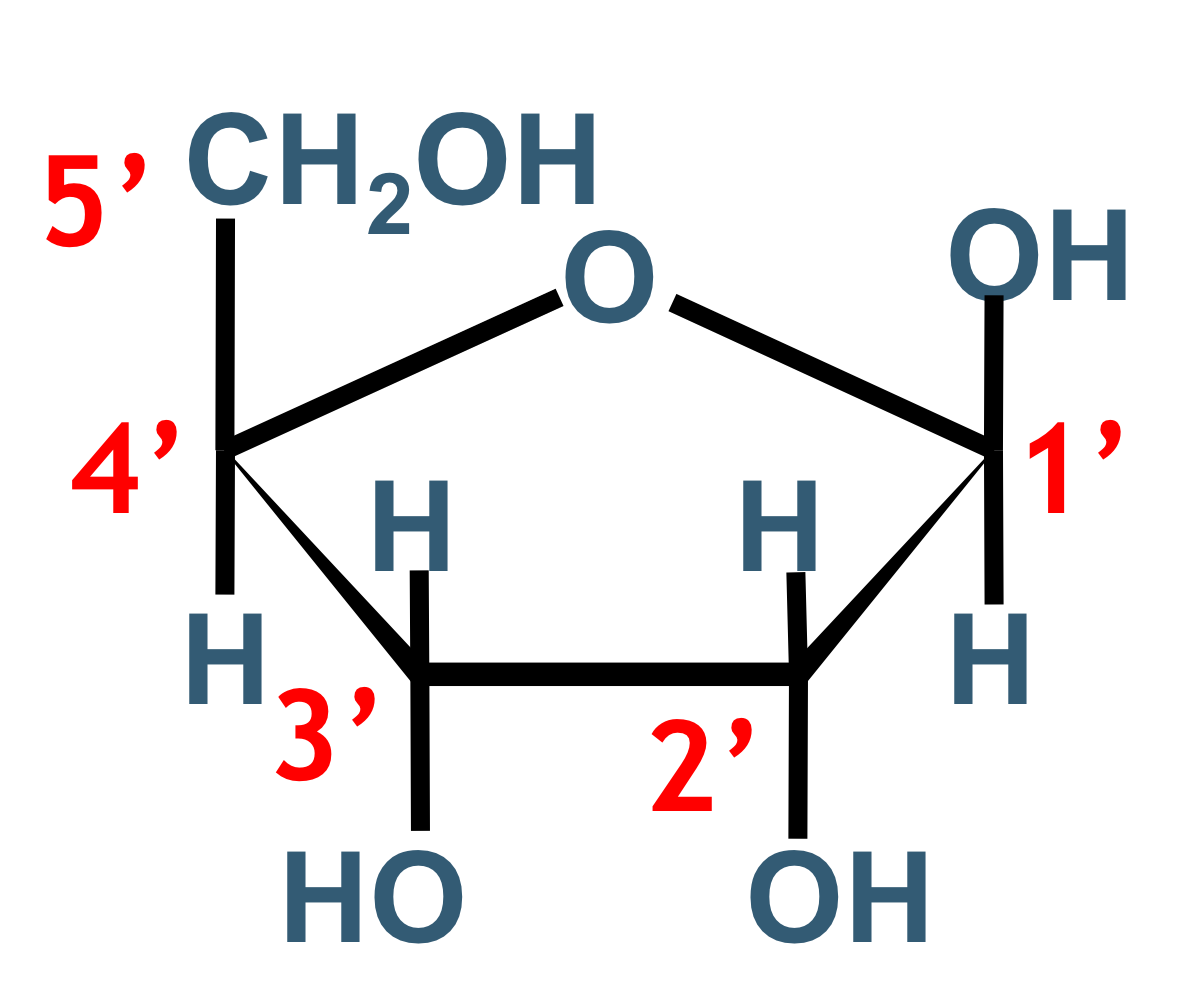
which sugar is this & in which structure we can find it
beta-D-ribose
RNA
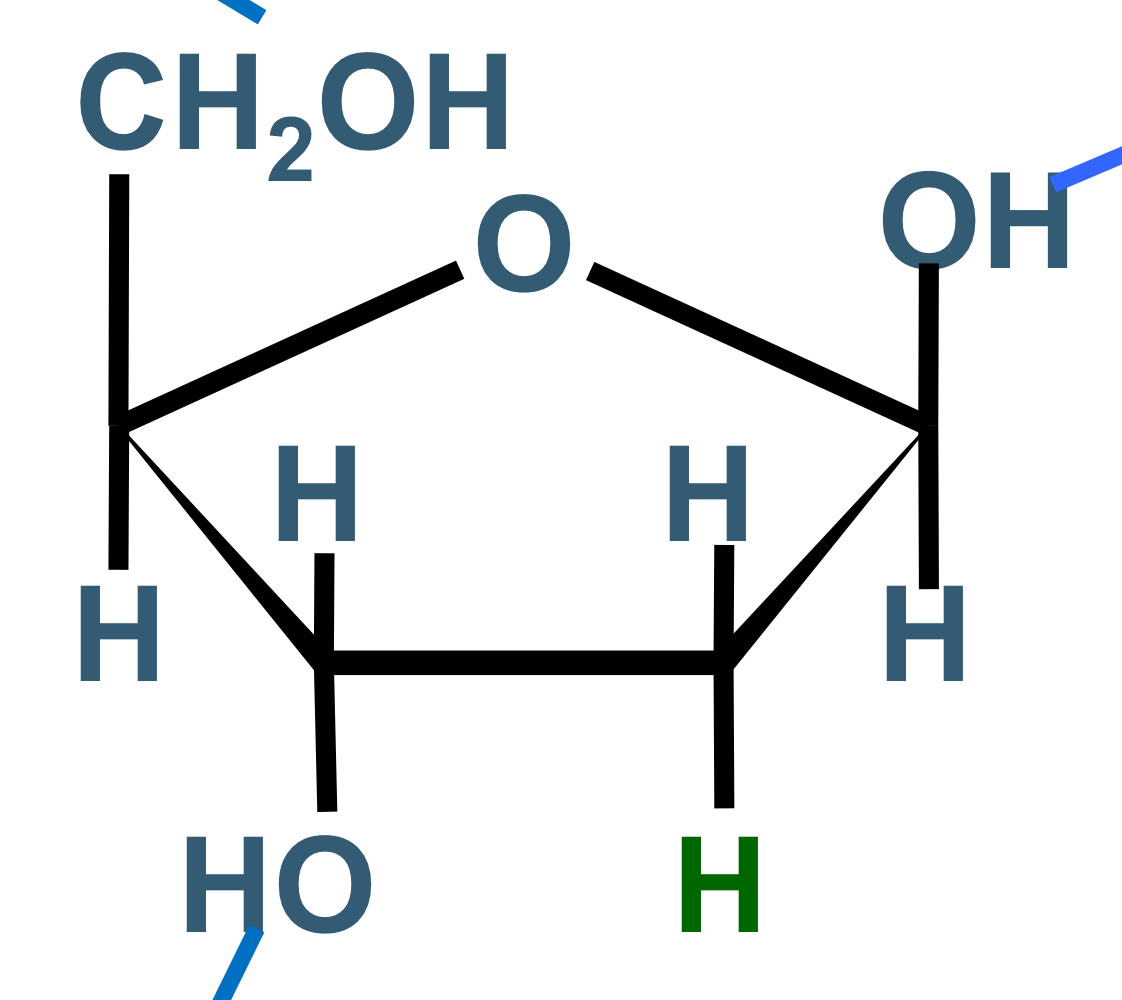
which sugar is this & in which structure we can find it
beta-D-deoxyribose
DNA
base + sugar
nucleoside
base + sugar + phosphate
nucleotide
Which strand carries genetic info?
sense (coding) strand
Which strand is used as a template for RNA?
antisense (non-coding) (complementary) strand
What is the name of the bond between sugar and base?
Glycosidic Bond
sugar conformation preferred by DNA?
C2’-endo
sugar conformation preferred by RNA?
C3’-endo
What causes unusual DNA helices in purines?
favourable interaction between N2 and 5’-PO42- that stabilizes the syn conformation
isomers that differ in the location of protons (and consequently double bonds)
tautomers
How do polynucleotides form if unfavourable?
Coupling with favourable reactions
Does RNA takes on more varied shaped and folding patterns than DNA?
Yes
2 reasons why non-coding RNA structure is less constrained than DNA structure
More no=umbers of building blocks (modified bases and sugars)
Non standard base pairing
a non-standard base pair that differs in geometry relative to the standard, Watson-Crick-Rosalind pairing
wobble
common non-standard base pair type
G-U
alternative H-bonding pattern that uses different faces of the base
Hoogsteen base pairing
Which configuration is favoured for base pairs along the Hoogsteen edge?
trans
Which configuration is favoured for base pairs along the Watson-Crick-Rosalind edge?
cis
How RNA stabilizes its secondary structure?
The negative backbone forces the bases to interact (pair&stack)
What prevents the formation of B-type dsRNA helices?
C3’ -endo conformation of RNA ribose
the intersection of 3 or more ssRNA, sometimes resulting in separation of the helices by unpaired residues
junctions
most common junction seen in RNA
three-stem
secondary structure of RNA composed of unpaired nucleotides within 1 strand of a base-paired region of RNA, and can be as short as a single base
bulge
Which secondary structure is associated with metal binding or cationic ligand binding?
bulge
This secondary structure occurs when there are unpaired nucleotides on both sides of dsRNA.
These can be symmetric or asymmetric.
internal loop
Which secondary structure of RNA result in sharp turns and kinks due to induced unwinding & critical for tertiary structures?
internal loop
This secondary structure is formed when the RNA folds sharply back onto itself, with the loops ranging in size from 2-14 residues.
hairpin loop
How hairpin loop stabilize the structure?
With its base-pairing and pi-pi stacking
What is GNRA tetraloops?
loops composed of the 4 bases:
G: guanosine
N: any base
R: purine
A: adenosine
What type of secondary structure are GNRA tetraloops?
type of hairpin loop
In this type of interactions, when 2 regular helical elements (A-type) stack end-t-end, they form a coaxial stack.
dsRNA - dsRNA interactions
How dsRNA-dsRNA interactions stabilize the tertiary structrure?
The base pair at the end of one helix can undergo pi-pi stacking interactions with the opposite base pair of the next helix.
Which type of interactions form pseudoknots?
ssRNA-ssRNA interactions
These are coaxial helical stacks of 2 helices that are discontinuous to each other
pseudoknots
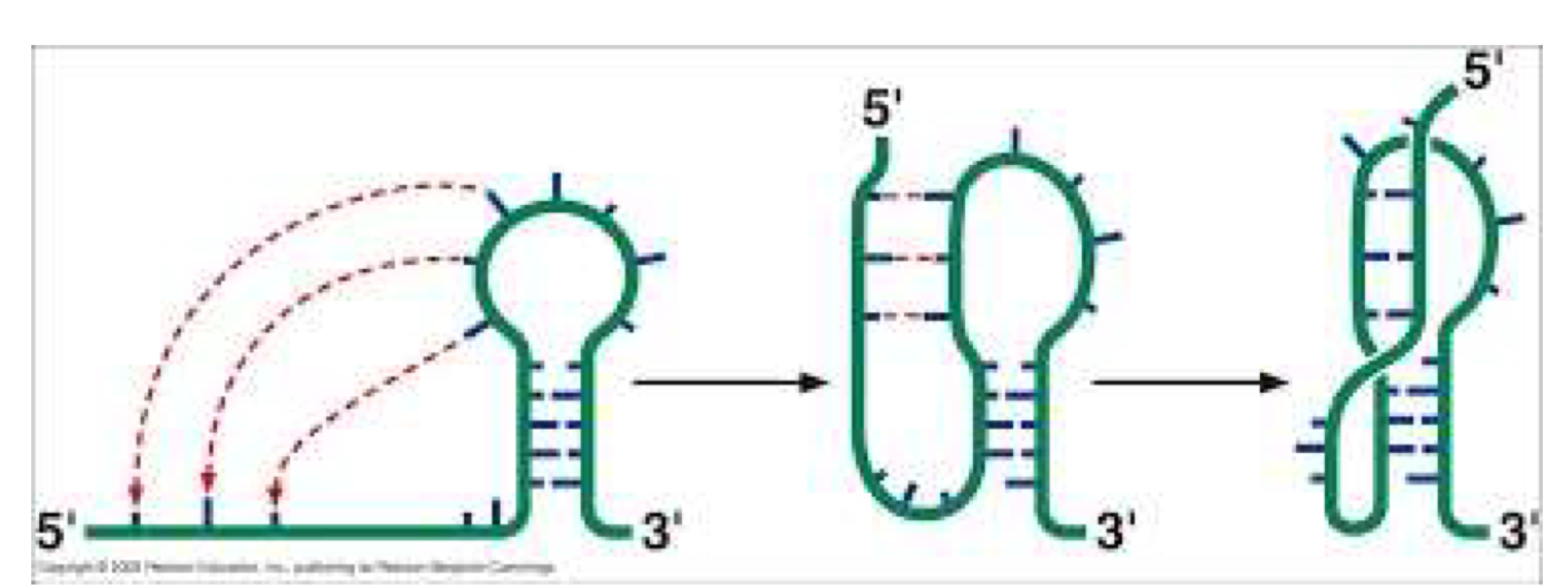
How do pseudoknots form?
They form where unpaired nucleotides in the loop of a hairpin form base pairs with a distal complementary stretch of ssRNA.
clusters of 3 RNA nucleobases interacting along their edges via H bonds
base triples
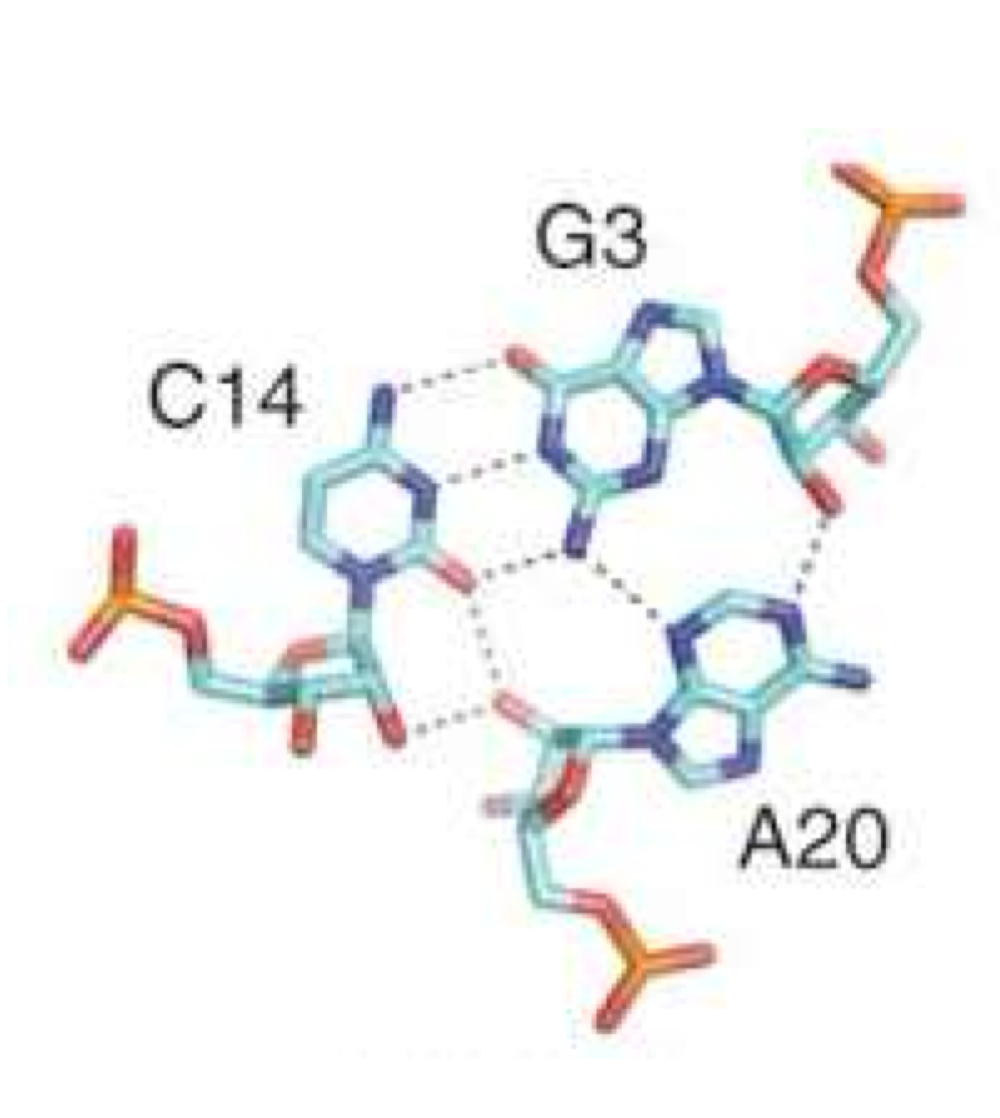
What type of interactions occur most often in the form of base triples?
dsRNA-ssRNA interactions
What type of pairing is a form of base triple?
Hoogsteen pairing
What is A-minor motif?
the interactions of the minor groove edges of adenine with the minor groove of neighbouring helices
minor groove edge = sugar edge
A minor motifs involve _______ interacting with the minor groove of ______, resulting in H-bonding & stacking of the ______
A-minor motifs involve polyA ssRNA interacting with the minor groove of dsRNA, resulting in H- bonding & stacking of the polyA