Nematode Parasites of the Urinary Tract, Eyes, Integumentary, and central nervous systems
1/58
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
59 Terms
Which Capillaria sp is found in the urinary tract of dogs, foxes, wolves, coyotes, and cats?
Capillaria (Pearsonema) plica
Which Capillaria sp is found in the urinary bladder of only cats?
Capillaria (Pearsonema) feliscati
What are the clinical signs of Capillaria sp in the urinary tract in dogs and cats?
relatively harmless
occasional cystitis, difficulty with urination
How do we diagnose Capillaria sp in the urinary tract?
by observing eggs (65 × 35 micrometers) in clean urine catch
How do we treat Capillaria sp. in the urinary tract?
Ivermectin
How do we control Capillaria sp in the urinary tract?
environmental hygiene
Which parasite does this lifecycle match:
obligate indirect with earthworms as intermediate host
rodents/birds may serve as paratenic host (“bridge ecological gap”)
prepatent period 60 days
Capillaria sp
What size worms are Capillaria sp?
13-30mm for males
30-60mm for females
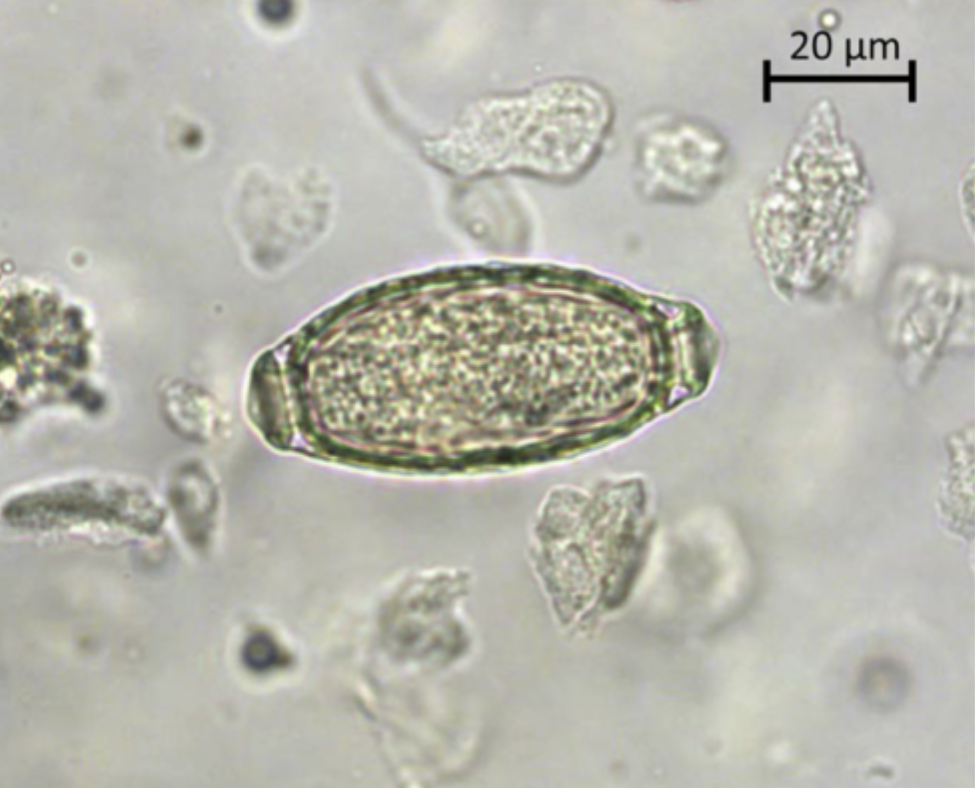
Which parasite egg is shown in the image?
Capillaria sp
What is the common name of Dioctophyma renale?
giant red kidney worm
What parasite is the largest of parasitic nematodes, with females being up to 100cm long and 1cm in diameter?
Dioctophyma renale (giant red kidney worm)
Which parasite matches this lifecycle:
opportunistically infects pet dogs
important reservoid hosts include wild canidae, bear, mink, raccoon, otter
obligate indirect lifecycle
free living awuatic annelids are intermediate host
crayfish, frogs, fish are paratenic hosts
infective larvae 1) penetate bowel, 2) develop in peritoneum, 3) penetrate kidney, and 4) develop to adults and reproduce
prepatent period 138 days
Dioctophyma renale (giant red kidney worm)
How do we diagnose Dioctophyma renale?
by finding eggs (68 × 44 micrometers) in urine sediments
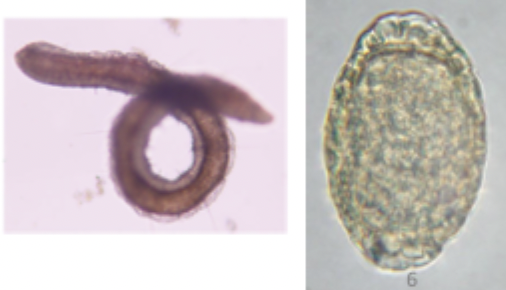
Which parasite is depicted in the image?
Dioctophyma renale
Where do adult Dioctophyma renale often reside?
pelvis of the kidney
Disease of Dioctphyma renale is caused by the destruction of what?
the parenchyma of the kidney, and eventually only the capsule remains
What happens if worms of Dioctophyma renale extend down to the ureter?
blockage/tissue destruction results in inability to remove waste from the body (uremia)
The presence of free Dioctophyma renale worms in peritoneum stimulates what?
inflammation, adhesions, and peritonitis
Severe infections of Dioctophyma renale ultimately results in what?
kidney failure and death
Sometimes infections of Dioctophyma renale occur without symptoms of clinical disease. Why?
worms show a tendency to parasitize only the right kidney
renal function is impaired, but functional with only one kidney
What are the common names of Dracunculus sp?
guinea worm
fiery serpent
Which parasite species is on the brink of eradication by international public health programs?
Dracunculus sp
Adult worms of Dracunculus sp are parasitic where?
in subcutaneous tissues of North American carnivorous mammals, usually seen on a limb
Which parasite does this lifecycle match:
opportunatically infects pet dogs and cats
important reservoir hosts are wild canidae, raccoon, otter, muskrats
carnivores frequenting aquatic habitats most susceptible
obligate indirect lifecyle
free living aquatic copepods are intermediate host
frogs may be an important paratenic host
1) accidental ingestion of IH containing infective larvae OR predatory ingestion of PH containing infective larvae, 2) infective larvae migrate through intestinal wall, reach SC tissues within 3 weeks, sexual maturity and reproduction reached 6-7 weeks PI, 3) host rx results in blister/ulcer at end of migration tunnel, 4) female workers protrudes uterus when stimulated by contact with water and discharges larvae
Dracunculus insignis
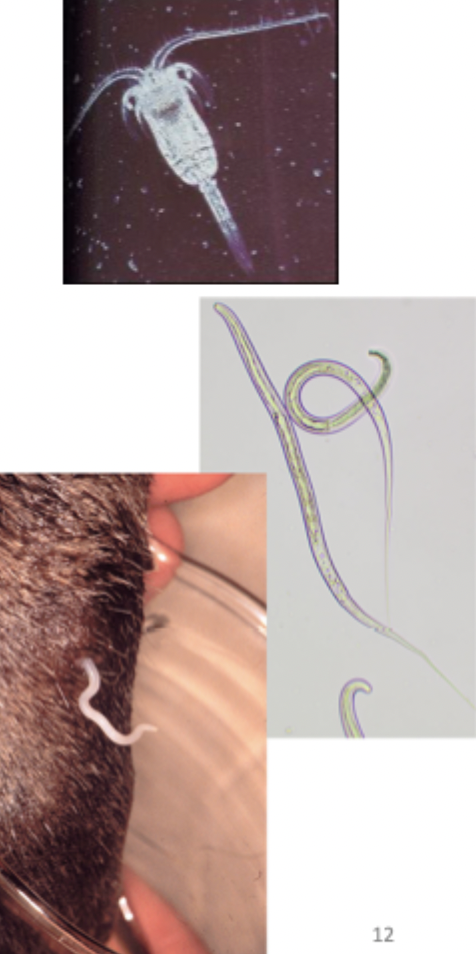
This image depicts what parasite?
Dracunculus insignis
What is the parasitic species of Dracunculus that affects humans residing in Africa?
Dracunculus medinensis
Is there an effective treatment for Dracnculus medinensis?
No
What happens if a Dracunculus medinensis breaks during extraction?
significant host reaction, inflammation, anaphylaxis, and possible death
Thelazia species are parasitic where?
in conjunctival and lacrimal sac
Which Thelazia species affect dogs, cats, people, sheep, and deer?
T. californiensis
Which Thelazia species affect horses?
T. lacryrmalis
Which Thelazia species affect cattle?
T. glucosa
Which Thelazia species affects people, dogs, and cats only?
T. callipaeda
Whcih parasite does this lifecycle match:
obligate indirect lifecycle is characteristic of the family
Flies are intermediate host
Feed on lachrymal secretions, ingest eggs, and develop into 3rd larvae within the fly
transmission back to DI when they return to feed
Thelazia species, Spiruidae family
How do we treat for Thelazia sp. infections?
macrocyclic lactones - 200 micrograms/kg ivermectin SID or 1-2 drops 1% Moxidectin OU or Tpical moxidectin + Imidacloprid (advantage multi)
What is the pathogenic effects of infection with Thelazia sp.?
irritation and conjunctivitis
increased tearing attracts flies which leads to increased transmission
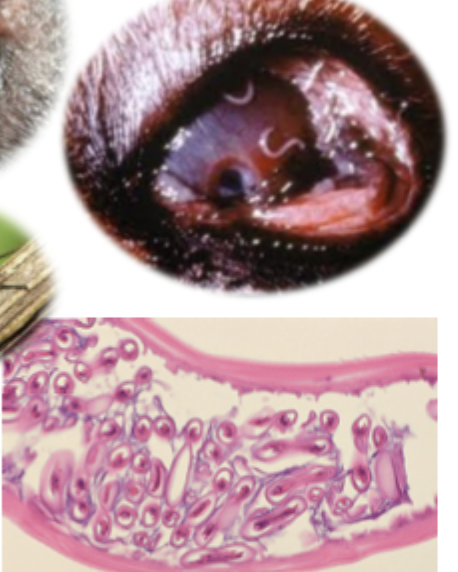
This image matches what parasite species?
Thelazia sp
How can you differentiate Thelazia sp from Onchocerca lupi in the dog eye?
Thelazia sp is a smal hookworm like body
Onchocerca lupi is a long filametous worm
What may help with prevention/transmission of Canine Ocular Onchocerciasis?
Canine Heartworm prophylaxis
Does Onchocerca lupi show zoonosis?
Yes
How is Onchocerca lupi transmitted?
Bite of black fly
Where can adult worms of Onchocerca lupi be found in the dog?
ocular nodules and granulomatous masses around eyeball/conjunctiva
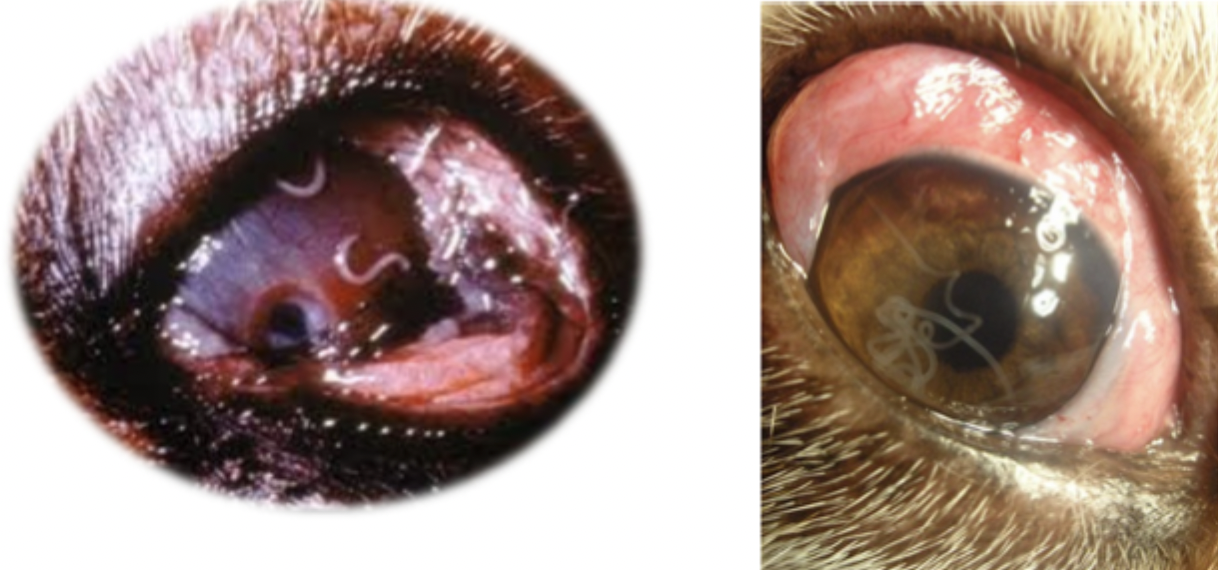
Which parasite is seen in the image on the left?
Thelazia sp
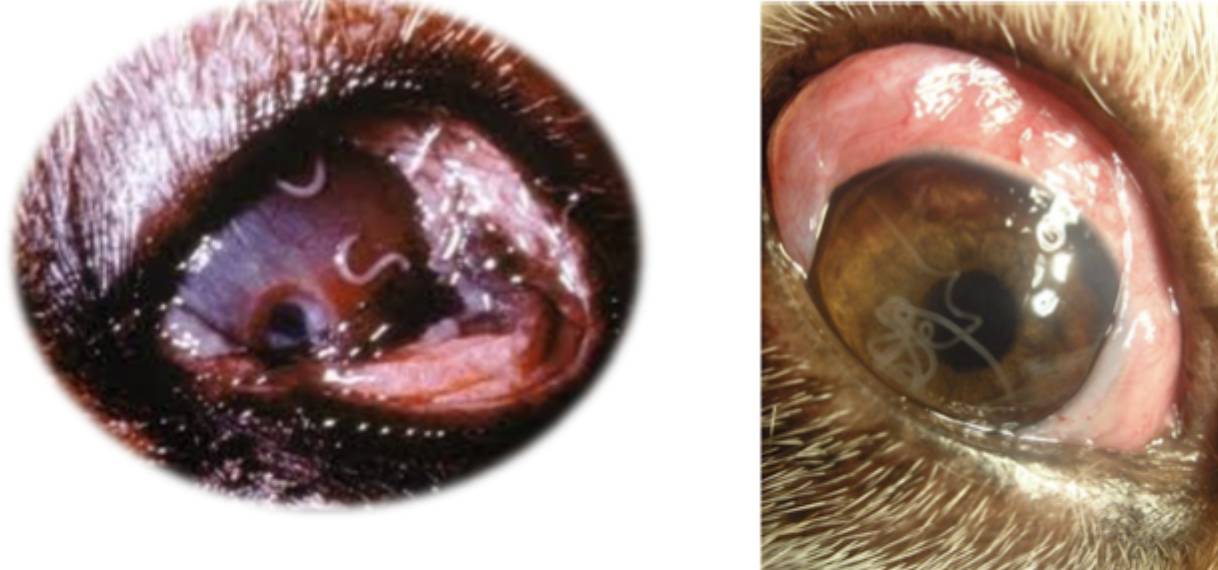
Which parasite is seen in the image on the right?
Onchocerca lupi
What is the common name of Paraelaphostrongylus tenuis?
Meningeal worm
Paraelaphostrongylus tenuis is a naturally occuring parasite of which animal?
White tail deer
Which parasite is a metastrongyloid parasite with an obligate indirect life cycle and shows significant morbidity and mortality in moose and elk?
Paraelaphostrongylus tenuis
Describe the seasonal epidemiology of Paraelaphostrongylus tenuis .
infective larvae acquired in summer
clinical signs appear during fall-early winter
consistent with deer activity on pastures
What are the first clinical signs of animals affected by Paraelaphostrongylus tenuis?
lateral recumbency, dysorexia, not doing right
ataxia, head tilt, circling
paraparesis with advanced disease
How do we diagnose infection of Paraelaphostrongylus tenuis?
antemortem diagnosis by exclusion
clinical signs can be suggestive
use complete database: signalment, history, CBC/Chem, CSF analysis, diagnostic imaging (CT)
definitive diagnosis by necropsy
How do we treat infections of Paraelaphostrongylus tenuis?
FBZ at 20-50 mg/kg SID x5 days as parasiticide
Flunixin meglumine 1mg/kg BID x5 days for analgesia/pain
DMSO/prednisolone as steroidal tx to cross the BBB
How do we prevent infections of Paraelaphostrongylus tenuis?
limit contact with white tail deer
gravel/limestone barriers to snail-slug migration around fence lines
improve drainage
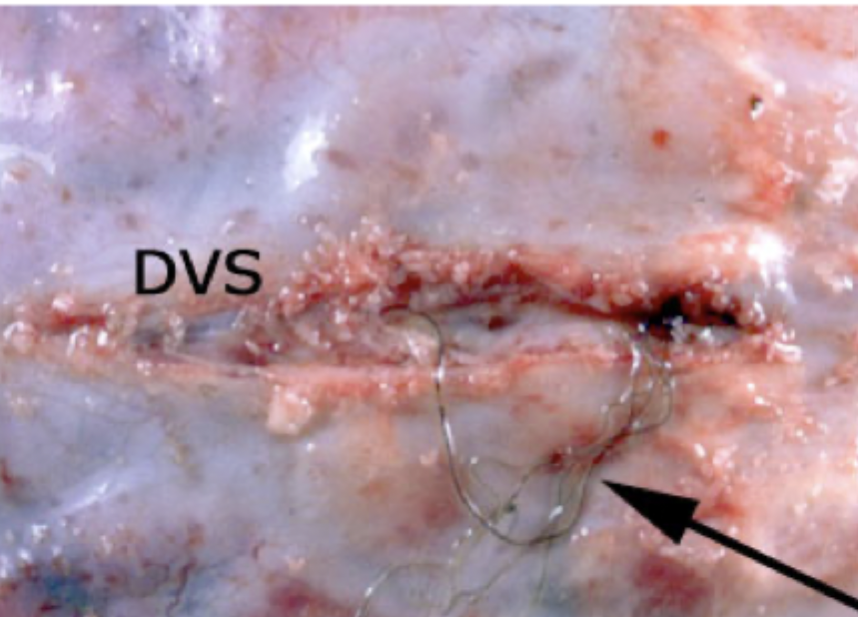
Which parasite is seen in this image (arrow pointing at worm)? DVS = dorsal venous sinus.
Paraelaphostrongylus tenuis
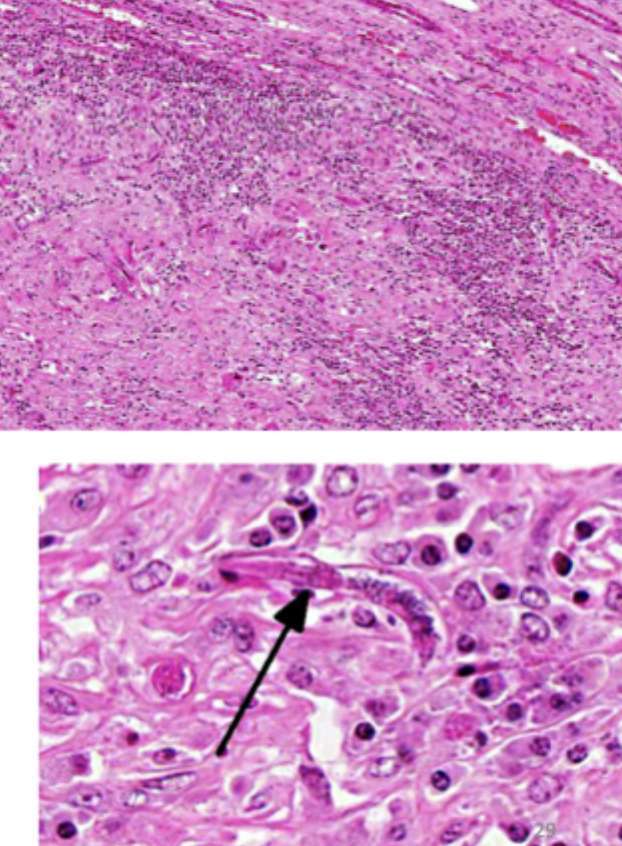
Which parasite is seen in this image?
Halicephalobus gingivalis
Which parasite may be a facilitating factor for drug resistance in Haemonchus?
Paraelaphostrongylus tenuis
Which parasite is a naturally occurring free living nematode and opportunstically infects horses with fatal consequences?
Halicephalobus gingivalis
How do we definitively diagnose Halicephalobus gingivalis?
at necropsy, clinical presentation is generalized not doing right, respiratory, renal effects, etc
Does Halicephalobus gingivalis portray zoonosis?
Yes
Is there an effective treatment for Halicephalobus gingivalis?
No